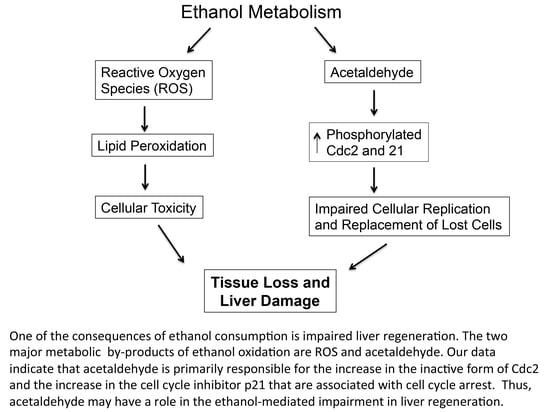
The Involvement of Acetaldehyde in Ethanol-Induced Cell Cycle Impairment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Immunoblotting
4.3. DNA Determination and Cell Cycle Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemens, D.L.; Calisto, L.E.; Sorrell, M.F.; Tuma, D.J. Ethanol metabolism results in a G2/M cell-cycle arrest in recombinant Hep G2 cells. Hepatology 2003, 38, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, D.L.; Forman, A.; Jerrells, T.R.; Sorrell, M.F.; Tuma, D.J. Relationship between acetaldehyde levels and cell survival in ethanol-metabolizing hepatoma cells. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Q.; Lin, H.Z.; Yin, M.; Albrecht, J.H.; Diehl, A.M. Effects of chronic ethanol consumption on cytokine regulation of liver regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G696–G704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koteish, A.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Diehl, A.M. Ethanol induces redox-sensitive cell-cycle inhibitors and inhibits liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, A.M. Recent events in alcoholic liver disease V. effects of ethanol on liver regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G1–G6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Jelnes, P.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Bisgaard, H.C. Progenitor cells in liver regeneration: Molecular responses controlling their activation and expansion. APMIS 2005, 113, 876–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S. Heterogeneity and plasticity of hepatocyte lineage cells. Hepatology 2001, 33, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlson, L.C.; Koroxenidou, L.; Hallstrom, I.P. Inhibition of in vivo rat liver regeneration by 2-acetylaminofluorene affects the regulation of cell cycle-related proteins. Hepatology 1998, 27, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskams, T.; Yang, S.Q.; Koteish, A.; Durnez, A.; DeVos, R.; Huang, X.; Achten, R.; Verslype, C.; Diehl, A.M. Oxidative stress and oval cell accumulation in mice and humans with alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Koteish, A.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Roskams, T.; Dawson, V.; Diehl, A.M. Oval cells compensate for damage and replicative senescence of mature hepatocytes in mice with fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2004, 39, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, R.; Kofman, A.V.; Landis, C.S.; Swenson, E.S.; Barendswaard, E.; Theise, N.D. The hepatic stem cell niche: Identification by label-retaining cell assay. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, M.B.; Mendenhall, C.L.; French, S.W.; Gartside, P.S. Bile duct changes in alcoholic liver disease. Liver 1993, 13, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulter, L.; Govaere, O.; Bird, T.G.; Radulescu, S.; Ramachandran, P.; Pellicoro, A.; Ridgway, R.A.; Seo, S.S.; Spee, B.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Macrophage-derived Wnt opposes Notch signaling to specify hepatic progenitor cell fate in chronic liver disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, T.M.; Osna, N.A.; Clemens, D.L. Recombinant Hep G2 cells that express alcohol dehydrogenase and cytochrome P450 2E1 as a model of ethanol-elicited cytotoxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, D.L.; Schneider, K.J.; Nuss, R.F. Ethanol metabolism activates cell cycle checkpoint kinase, Chk2. Alcohol 2011, 45, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurse, P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature 1990, 344, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: The yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell 1995, 80, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton-Fessler, S.; Parker, L.L.; Geahlen, R.L.; Piwnica-Worms, H. Mechanisms of p34cdc2 regulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, E.; Clot, P.; Morimoto, M.; Tomasi, A.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; French, S.W. Role of cytochrome P4502E1-dependent formation of hydroxyethyl free radical in the development of liver damage in rats intragastrically fed with ethanol. Hepatology 1996, 23, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwel, P.; Dominguez-Rosales, J.A.; Mavi, G.; Rivas-Estilla, A.M.; Rojkind, M. Hydrogen peroxide: A link between acetaldehyde-elicited a1(i) collagen gene up-regulation and oxidative stress in mouse hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2000, 31, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, J.B.; Pastorino, J.G. Ethanol, oxidative stress, and cytokine-induced liver cell injury. Alcohol 2002, 27, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomes, P.G.; Ehlers, R.A.; Trambly, C.S.; Clemens, D.L.; Fox, H.S.; Tuma, D.J.; Donohue, T.M. Multilevel regulation of autophagosome content by ethanol oxidation in HepG2 cells. Autophagy 2013, 9, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basuroy, S.; Sheth, P.; Mansbach, C.M.; Rao, R.K. Acetaldehyde disrupts tight junctions and adherens junctions in human colonic mucosa: Protection by EGF and l-glutamine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G367–G375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennett, R.B.; Sorrell, M.F.; Saffari-Fard, A.; Ockner, J.L.; Tuma, D.J. Preferential covalent binding of acetaldehyde to the α-chain of purified rat liver tubulin. Hepatology 1989, 9, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duguay, L.; Coutu, D.; Hetu, C.; Joly, J.G. Inhibition of liver regeneration by chronic alcohol administration. Gut 1982, 23, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, A.M.; Chacon, M.; Wagner, P. The effect of chronic ethanol feeding on ornithine decarboxylase activity and liver regeneration. Hepatology 1988, 8, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wands, J.R.; Carter, E.A.; Bucher, N.L.; Isselbacher, K.J. Inhibition of hepatic regeneration in rats by acute and chronic ethanol intoxication. Gastroenterology 1979, 77, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.J.; Scheer, M.; Suhr, M.; Clemens, D.L. Ethanol administration impairs pancreatic repair after injury. Pancreas 2012, 41, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deiry, W.S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V.E.; Levy, D.B.; Parsons, R.; Trent, J.M.; Lin, D.; Mercer, W.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993, 75, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.W.; Adami, G.R.; Wei, N.; Keyomarsi, K.; Elledge, S.J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 1993, 75, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.D.; Xuan, Y.; Broude, E.V.; Zhu, H.; Schott, B.; Fang, J.; Roninson, I.B. Role of p53 and p21waf1/cip1 in senescence-like terminal proliferation arrest induced in human tumor cells by chemotherapeutic drugs. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4808–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunz, F.; Dutriaux, A.; Lengauer, C.; Waldman, T.; Zhou, S.; Brown, J.P.; Sedivy, J.M.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 1998, 282, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setshedi, M.; Wands, J.R.; Monte, S.M. Acetaldehyde adducts in alcoholic liver disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2010, 3, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crary, G.S.; Albrecht, J.H. Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in human liver. Hepatology 1998, 28, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravinthan, A.; Pietrosi, G.; Hoare, M.; Jupp, J.; Marshall, A.; Verrill, C.; Davies, S.; Bateman, A.; Sheron, N.; Allison, M.; et al. Hepatocyte expression of the senescence marker p21 is linked to fibrosis and an adverse liver-related outcome in alcohol-related liver disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravinthan, A.; Scarpini, C.; Tachtatzis, P.; Verma, S.; Penrhyn-Lowe, S.; Harvey, R.; Davies, S.E.; Allison, M.; Coleman, N.; Alexander, G. Hepatocyte senescence predicts progression in non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.D.; Watanabe, K.; Broude, E.V.; Fang, J.; Poole, J.C.; Kalinichenko, T.V.; Roninson, I.B. Effects of p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 on cellular gene expression: Implications for carcinogenesis, senescence, and age-related diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarca, C.; Paigen, K. A simple, rapid and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 102, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Cells | Control | EtOH | EtOH and NAC | EtOH and Trolox |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VL-17A | 77.1 ± 4.8 a | 45.2 ± 3.4 a | 42.1 ± 4.9 a | 39.4 ± 4.1 a |
| VA-13 | 78.3 ± 3.4 a | 49.3 ± 4.8 a | 48.1 ± 5.1 a | 41.9 ± 4.2 a |
| Cells | Control | EtOH | NAC | NAC and EtOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VA-13 | 6.8 ± 0.5 a | 21.8 ± 0.15 a | 6.8 ± 0.3 a | 19.6 ± 0.52 a |
| VL-17A | 7.68 ± 0.22 a | 27.15 ± 0.57 a | 6.48 ± 0.56 a | 27.65 ± 1.19 a |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scheer, M.A.; Schneider, K.J.; Finnigan, R.L.; Maloney, E.P.; Wells, M.A.; Clemens, D.L. The Involvement of Acetaldehyde in Ethanol-Induced Cell Cycle Impairment. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6020017
Scheer MA, Schneider KJ, Finnigan RL, Maloney EP, Wells MA, Clemens DL. The Involvement of Acetaldehyde in Ethanol-Induced Cell Cycle Impairment. Biomolecules. 2016; 6(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleScheer, Marc A., Katrina J. Schneider, Rochelle L. Finnigan, Eamon P. Maloney, Mark A. Wells, and Dahn L. Clemens. 2016. "The Involvement of Acetaldehyde in Ethanol-Induced Cell Cycle Impairment" Biomolecules 6, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6020017
APA StyleScheer, M. A., Schneider, K. J., Finnigan, R. L., Maloney, E. P., Wells, M. A., & Clemens, D. L. (2016). The Involvement of Acetaldehyde in Ethanol-Induced Cell Cycle Impairment. Biomolecules, 6(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6020017