Physiological Adaptation to Water Salinity in Six Wild Halophytes Suitable for Mediterranean Agriculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set Up
2.2. Physiological Parameters Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
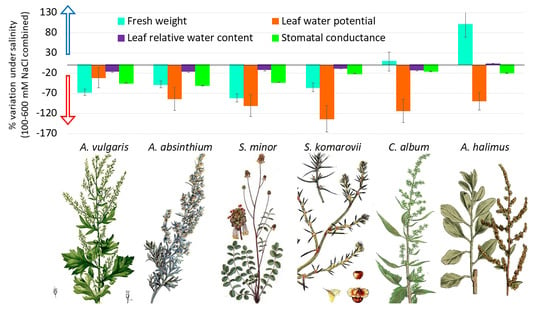
3. Results
3.1. Control versus Saline Water Treatments
3.2. Normalized Water Saline Treatments
3.3. Results of the Multivariate Analysis
3.4. Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN. World Population Prospects. 2019. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- McLeod, A.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. World Livestock 2011, Livestock in Food Security World; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011; ISBN 9789251070130. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Achlatis, M. Impacts of 1.5 °C global warming on natural and human systems. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 175–311. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Global Soil Status, Processes and Trends; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; ISBN 9789251090046. [Google Scholar]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z. Environmental Salinization Processes: Detection, Implications & Solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S.; Hussain, N.; Hanjra, M.A.; Akbar, S. Characterizing soil salinity in irrigated agriculture using a remote sensing approach. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 55–57, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.V. Crop salt tolerance. In Agricultural Salinity as-Sessment and Management; Tanji, K.K., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 262–304. ISBN 978-0-7844-7648-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tıpırdamaz, R.; Karakas, S.; Dikilitas, M. Halophytes and the Future of Agriculture. In Handbook of Halophytes; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–15. ISBN 9783030178543. [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli, A.; Fry, C.; Smith, R.J.; Simmonds, M.S.J.; Kersey, P.J.; Pritchard, H.W.; Abbo, M.S.; Acedo, C.; Adams, J.; Ainsworth, A.M.; et al. State of the World’s Plants and Fungi 2020; Royal Botanic Gardens: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Riadh, K.; Wided, M.; Hans-Werner, K.; Chedly, A. Responses of Halophytes to Environmental Stresses with Special Emphasis to Salinity. Adv. Bot. Res. 2010, 53, 117–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, Y.; Eshel, A.; Pasternak, D.; Sagi, M. The development of halophyte-based agriculture: Past and present. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bora, K.S.; Sharma, A. The genus Artemisia: A comprehensive review. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigam, M.; Atanassova, M.; Mishra, A.P.; Pezzani, R.; Devkota, H.P.; Plygun, S.; Salehi, B.; Setzer, W.N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Bioactive compounds and health benefits of Artemisia species. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brisibe, E.A.; Umoren, U.E.; Brisibe, F.; Magalhäes, P.M.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Luthria, D.; Wu, X.; Prior, R.L. Nutritional characterisation and antioxidant capacity of different tissues of Artemisia annua L. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, M.J.; Bedoya, L.M.; Apaza, L.; Bermejo, P. The Artemisia L. genus: A review of bioactive essential oils. Molecules 2012, 17, 2542–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasilyeva, T.N.; Galaktionova, L.V.; Lebedev, S.V. Assessment of remediation potential of flora of the Southern Urals. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 341, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branković, S.; Glišić, R.; Simić, Z.; Đekić, V.; Jovanović, M.; Topuzović, M. Bioaccumulation, translocation and phytoremediation by endemic serpentinophyte Artemisia alba Turra. Kragujev. J. Sci. 2019, 41, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebhi, A.E.M.; Lounici, H.; Lahrech, M.B.; Morel, J.L. Response of Artemisia herba alba to hexavalent chromium pollution under arid and semi-arid conditions. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 21, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trofimova, T.A.; Hossain, A.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A. The Ability of Medical Halophytes to Phytoremediate Soil Contaminated by Salt and Heavy Metals in Lower Volga, Russia. Asian Australas. J. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 6, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Rozentsvet, O.A.; Nesterov, V.N.; Bogdanova, E.S.; Tabalenkova, G.N.; Zakhozhiy, I.G.; Popov, A.V. Effect of Saline Soils on the Functional State of Species of the Genus Artemisia. Biol. Bull. 2019, 46, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeraj, C.; Kirti, S.; Prabhu, S.B.P.; Amritpal, S.; Udai, C.A.; Ashish, S. Phytochemistry and Pharmacological exploration of Chenopodium album: Current and future perspectives. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 3933–3940. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, S.; Saini, K.K. Chenopodium album Linn: An outlook on weed cum nutritional vegetable along with medicinal properties. emergent Life Sci. Res. 2020, 06, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Lan, H.; Zhang, F. Variation of seed heteromorphism in Chenopodium album and the effect of salinity stress on the descendants. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Chen, S.; Xu, D.; Lan, H. Plant growth and responses of antioxidants of Chenopodium album to long-term NaCl and KCl stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 60, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Shah, A.N. An insight into salt stress tolerance mechanisms of Chenopodium album. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16531–16535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tite, M.S.; Shortland, A.; Maniatis, Y.; Kavoussanaki, D.; Harris, S.A. The composition of the soda-rich and mixed alkali plant ashes used in the production of glass. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2006, 33, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centofanti, T.; Banuelos, G. Practical uses of halophytic plants as sources of food and fodder. In Halophytes and Climate Change: Adaptive Mechanisms and Potential Uses; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2019; pp. 324–342. ISBN 9781786394330. [Google Scholar]
- Saddhe, A.A.; Manuka, R.; Nikalje, G.C.; Penna, S. Halophytes as a Potential Resource for Phytodesalination. In Handbook of Halophytes; Grigore, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Karakas, S.; Dikilitas, M.; Tıpırdamaz, R. Phytoremediation of Salt-Affected Soils Using Halophytes. In Handbook of Halophytes; Grigore, M.N., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Centofanti, T.; Bañuelos, G. Evaluation of the halophyte Salsola soda as an alternative crop for saline soils high in selenium and boron. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Fallovo, C.; Cardarelli, M.; Graifenberg, A. Use of Salsola soda as a companion plant to improve greenhouse pepper (Capsicum annuum) performance under saline conditions. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2006, 34, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, C.R.; Franco, J.G.; King, S.R.; Volder, A. Intercropping halophytes to mitigate salinity stress in watermelon. Sustainability 2018, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graifenberg, A.; Botrini, L.; Giustiniani, L.; Filippi, F.; Curadi, M. Tomato growing in saline conditions with biodesalinating plants: Salsola soda L., and Portulaca oleracea L. Acta Hortic. 2003, 609, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Statti, G.A.; Passalacqua, N.G.; Peruzzi, L.; Menichini, F. In vitro angiotensin converting enzyme inhibiting activity of Salsola oppositifolia Desf., Salsola soda L. and Salsola tragus L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 846–851. [Google Scholar]
- Tundis, R.; Loizzo, M.R.; Statti, G.A.; Menichini, F. Inhibitory effects on the digestive enzyme α-amylase of three Salsola species (Chenopodiaceae) in vitro. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 473–475. [Google Scholar]
- Tundis, R.; Menichini, F.; Conforti, F.; Loizzo, M.R.; Bonesi, M.; Statti, G.; Menichini, F. A potential role of alkaloid extracts from Salsola species (Chenopodiaceae) in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iannuzzi, A.M.; Moschini, R.; De Leo, M.; Pineschi, C.; Balestri, F.; Cappiello, M.; Braca, A.; Del-Corso, A. Chemical profile and nutraceutical features of Salsola soda (agretti): Anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic potential of its flavonoids. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.J.; Lutts, S. The tolerance of Atriplex halimus L. to environmental stresses. Emirates J. Food Agric. 2014, 26, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orrego, F.; Ortíz-Calderón, C.; Lutts, S.; Ginocchio, R. Effect of single and combined Cu, NaCl and water stresses on three Atriplex species with phytostabilization potential. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 131, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Romero, J.A.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; López-Jurado, J.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Torres-Ruiz, J.M. Importance of physiological traits vulnerability in determine halophytes tolerance to salinity excess: A comparative assessment in Atrplex halimus. Plants 2020, 9, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabier, J.; Laffont-Schwob, I.; Pricop, A.; Ellili, A.; D’Enjoy-Weinkammerer, G.; Salducci, M.D.; Prudent, P.; Lotmani, B.; Tonetto, A.; Masotti, V. Heavy metal and arsenic resistance of the halophyte Atriplex halimus L. along a gradient of contamination in a French Mediterranean spray zone. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acuña, E.; Castillo, B.; Queupuan, M.; Casanova, M.; Tapia, Y. Assisted phytoremediation of lead contaminated soil using Atriplex halimus and its effect on some soil physical properties. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaoui, A.; Barhoumi, Z.; Rabhi, M.; Abdelly, C. Localization of potential ion transport pathways in vesicular trichome cells of Atriplex halimus L. Protoplasma 2011, 248, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaire, R.; Durickovic, I.; Framont-Terrasse, L.; Leblain, J.Y.; De Rouck, A.C.; Simonnot, M.O. Phytoextraction of Na+ and Cl- by Atriplex halimus L. and Atriplex hortensis L.: A promising solution for remediation of road runoff contaminated with deicing salts. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, A.; Ghanmi, E.; Ayeb, N.; Louhaichi, M.; Neffati, M.; Tarhouni, M. Revegetation of marginal saline rangelands of southern Tunisia using pastoral halophytes. African J. Range Forage Sci. 2020, 37, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.J.; Lutts, S.; Sánchez-García, M.; Correal, E. Atriplex halimus L.: Its biology and uses. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 100–101, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.J. Alternative plant species for revegetation and soil conservation in the tussock grasslands of New Zealand. In Review 42: Journal of the Tussock Grasslands & Mountain Lands Institute; Robertson, E.B.T., Ed.; TGMLI: Canterbury, New Zealand, 1984; pp. 3–124. [Google Scholar]
- Buckland, A.S.M.; Grime, J.P.; Hodgson, J.G.; Thompson, K. A Comparison of Plant Responses to the Extreme Drought of 1995 in Northern England. J. Ecol. 1997, 85, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duf, J.F. Plant Fact Sheet: Small Burnet Scop, Sanguisorba Minor; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccanti, C.; Landi, M.; Incrocci, L.; Pardossi, A.; Venturi, F.; Taglieri, I.; Ferroni, G.; Guidi, L. Comparison of three domestications and wild-harvested plants for nutraceutical properties and sensory profiles in five wild edible herbs: Is domestication possible? Foods 2020, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkanis, A.C.; Fernandes, Â.; Vaz, J.; Petropoulos, S.; Georgiou, E.; Ciric, A.; Sokovic, M.; Oludemi, T.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical composition and bioactive properties of: Sanguisorba minor Scop. under Mediterranean growing conditions. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finimundy, T.C.; Karkanis, A.; Fernandes, Â.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Calhelha, R.; Petrović, J.; Soković, M.; Rosa, E.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Bioactive properties of Sanguisorba minor L. cultivated in central Greece under different fertilization regimes. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaji, A.; Roosta, H.R.; Rezaei, S.A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Niknam, F. Morphological, physiological and phytochemical response of different Satureja hortensis L. accessions to salinity in a greenhouse experiment. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 10, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, Y.; Wuddineh, W.A.; Myrzabayeva, M.; Alikulov, Z.; Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Shpigel, M.; Samocha, T.M.; Sagi, M. Effect of seawater concentration on the productivity and nutritional value of annual Salicornia and perennial Sarcocornia halophytes as leafy vegetable crops. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 128, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, H.; Jeon, J.; Bae, S. Effects of irrigation with saline water on crop growth and yield in greenhouse cultivation. Water 2016, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, K.; Bose, J.; Shabala, L.; Eyles, A.; Shabala, S. Evaluating relative contribution of osmotolerance and tissue tolerance mechanisms toward salinity stress tolerance in three Brassica species. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 158, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.M.; Al-Mas’oudi, R.S.M.; Al-Said, F.; Khan, I. Salinity Effects on Growth, Electrolyte Leakage, Chlorophyll Content and Lipid Peroxidation in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Food and Agricultural Sciences, Melaka, Malaysia, 7–8 October 2013; IACSIT Press: Singapore, 2013; Volume 55. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, R.E.; Bingham, G.E. Rapid Estimates of Relative Water Content. Plant Physiol. 1974, 53, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R.V.; Buerkner, P.; Herve, M.; Love, J.; Riebl, H.; Singmann, H. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka LeastSquares Means. R Pack. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/index.html (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/reference/ (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Glenn, E.P.; Brown, J.J.; Blumwald, E. Salt Tolerance and Crop Potential of Halophytes. CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, A.J.; Griffiths, M. The New Royal Horticultural Society Dictionary of Gardening; MacMillan Press: Basingstoke, UK, 1992; ISBN 0-333-47494-5. [Google Scholar]
- Belkheiri, O.; Mulas, M. The effects of salt stress on growth, water relations and ion accumulation in two halophyte Atriplex species. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 86, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat Alla, M.M.; Khedr, A.H.A.; Serag, M.M.; Abu-Alnaga, A.Z.; Nada, R.M. Physiological aspects of tolerance in Atriplex halimus L to NaCl and drought. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, F.; Kiani-Pouya, A.; Tahir, A.; Shabala, L.; Chen, Z.; Shabala, S. A comparative analysis of stomatal traits and photosynthetic responses in closely related halophytic and glycophytic species under saline conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 181, 104300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, T.V.; Maiorova, O.V.; Orlova, Y.V.; Kuznetsova, E.I.; Khalilova, L.A.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Balnokin, Y.V.; Tsydendambaev, V.D. Cell ultrastructure and fatty acid composition of lipids in vegetative organs of Chenopodium album L. under salt stress conditions. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 63, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Very, A.A.; Robinson, M.F.; Mansfield, T.A.; Sanders, D. Guard cell cation channels are involved in Na+-induced stomatal closure in a halophyte. Plant J. 1998, 14, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, T.; Khan, M.M.A.; Idrees, M.; Nadeem, M.N.; Moinuddin, H. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth, Membrane Damage, Antioxidant Metabolism and Artemisinin Accumulation in Artemisia annua L. Plant Stress 2010, 4, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Paulino, M.K.S.S.; de Souza, E.R.; Lins, C.M.T.; Dourado, P.R.M.; de Carvalho Leal, L.Y.; Monteiro, D.R.; Junior, F.E.; de Carvalho Silva, C.U. Influence of vesicular trichomes of Atriplex nummularia on photosynthesis, osmotic adjustment, cell wall elasticity and enzymatic activity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araújo, S.A.M.; Silveira, J.A.G.; Almeida, T.D.; Rocha, I.M.A.; Morais, D.L.; Viégas, R.A. Salinity tolerance of halophyte Atriplex nummularia L. grown under increasing NaCl levels. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. e Ambient. 2006, 10, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lü, X.-Y.; You, T.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, S.-S.; Lan, H. Morphology and physiological responses of Chenopodium album L. under salt stress. Zhiwu Shengli Xuebao/Plant Physiol. J. 2012, 48, 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- Shariat, A.; H, H. Study of Salinity Tolerance in Salad Burnet (Poterium sanguisorba) Through Physiological Characteristics. J. Plant Prod. Agronomy, Breed. Hortic. 2012, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifivash, R.; Shokrpour, M. Physico-Chemical Evaluation of Some Wormwood (Artemisia absinthium L.) Ecotypes Under Salt Stress Condition. J. Plant Physiol. Breed. 2017, 7, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Amor, N.; Jiménez, A.; Boudabbous, M.; Sevilla, F.; Abdelly, C. Chloroplast Implication in the Tolerance to Salinity of the Halophyte Cakile maritima. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 67, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S. Learning from halophytes: Physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludlow, M.M. Contribution of Osmotic Adjustment to the Maintenance of Photosynthesis during Water Stress. In Progress in Photosynthesis Research; Biggins, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ogburn, R.M.; Edwards, E.J. The Ecological Water-Use Strategies of Succulent Plants, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 55, ISBN 9780123808684. [Google Scholar]



| Source | dF | n-FW | n-GS | n-RWC | n-WP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS | 5 | 21.74 ** | 15.67 ** | 7.36 ** | 2.18 (+) |
| WS | 4 | 7.56 ** | 61.88 ** | 9.99 ** | 21.07 ** |
| HS × WS | 20 | 3.91 ** | 3.18 ** | 1.67 (+) | 1.91 * |
| Halophyte Species | dF | n-FW | n-GS | n-RWC | n-WP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. absinthium | 4 | 24.05 ** | 6.14 ** | 3.60 * | 6.28 ** |
| A. vulgaris | 4 | 90.46 ** | 15.60 ** | 2.93 (+) | 1.41 ns |
| A. halimus | 4 | 2.02 ns | 38.19 ** | 0.17 ns | 1.26 ns |
| C. album | 4 | 3.76 (+) | 27.62 ** | 3.10 ns | 3.48 (+) |
| S. komarovii | 4 | 46.41 ** | 14.60 ** | 4.64 * | 19.40 ** |
| S. minor | 4 | 29.28 ** | 22.15 ** | 8.11 ** | 24.73 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calone, R.; Bregaglio, S.; Sanoubar, R.; Noli, E.; Lambertini, C.; Barbanti, L. Physiological Adaptation to Water Salinity in Six Wild Halophytes Suitable for Mediterranean Agriculture. Plants 2021, 10, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020309
Calone R, Bregaglio S, Sanoubar R, Noli E, Lambertini C, Barbanti L. Physiological Adaptation to Water Salinity in Six Wild Halophytes Suitable for Mediterranean Agriculture. Plants. 2021; 10(2):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020309
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalone, Roberta, Simone Bregaglio, Rabab Sanoubar, Enrico Noli, Carla Lambertini, and Lorenzo Barbanti. 2021. "Physiological Adaptation to Water Salinity in Six Wild Halophytes Suitable for Mediterranean Agriculture" Plants 10, no. 2: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020309
APA StyleCalone, R., Bregaglio, S., Sanoubar, R., Noli, E., Lambertini, C., & Barbanti, L. (2021). Physiological Adaptation to Water Salinity in Six Wild Halophytes Suitable for Mediterranean Agriculture. Plants, 10(2), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020309