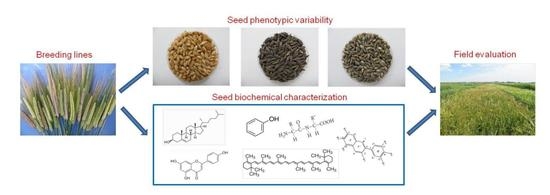
Genetic Diversity for Agronomic Traits and Phytochemical Compounds in Coloured Naked Barley Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Field Trials
4.3. Agronomic Traits
4.4. Biochemical Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newton, A.C.; Flavell, A.J.; George, T.S.; Leat, P.; Mullholland, B.; Ramsay, L.; Revoredo-Giha, C.; Russell, J.; Steffenson, B.J.; Swanston, J.S.; et al. Crops that feed the world 4. Barley: A resilient crop? Strengths and weaknesses in the context of food security. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 141–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Gautam, S.; Palikhey, E.; Joshi, B.K.; Ghimire, K.H.; Gurung, R.; Adhikari, A.R.; Pudasaini, N.; Dhakal, R. Agro-morphological diversity of Nepalese naked barley landraces. Agric. Food Secur. 2018, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.; Arendt, E.; Gallagher, E. The increasing use of barley and barley by-products in the production of healthier baked goods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Shang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, Q.; Li, C.; Yang, J. A study of genetic diversity of colored barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) using SSR markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2014, 62, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehen, E.; Tang, Y.; Sang, S. Bioactive phytochemicals in barley. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Anjum, F.M.; Zahoor, T.; Nawaz, H.; Dilshad, S.M.R. Beta glucan: A valuable functional ingredient in foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarasi, A.L.; Kun, S.; Tankó, G.; Stefanovits-Bányai, É.; Hegyesné-Vecseri, B. A comparative assessment of antioxidant properties; total phenolic content of einkorn; wheat; barley and their malts. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahouar, L.; El Arem, A.; Ghrairi, F.; Chahdoura, H.; Ben Salem, H.; El Felah, M.; Achour, L. Phytochemical content and antioxidant properties of diverse varieties of whole barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) grown in Tunisia. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeeva, E.I.; Glagoleva, A.Y.; Kukoeva, T.V.; Khlestkina, E.K.; Shoeva, O.Y. Purple-grained barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): Marker-assisted development of NILs for investigating peculiarities of the anthocyanin biosynthesis regulatory network. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meints, B.; Hayes, P.M. Breeding naked barley for food; feed; and malt. Plant Breed. Rev. 2019, 43, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Ali, M.; Jiang, C.; Shen, Z.; Cai, Y.; Yang, P.; Feng, Z. Marker-assisted selection in a global barley (Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare) collection revealed a unique genetic determinant of the naked barley controlled by the nud locus. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudar, G.; Sharma, P.; Janghu, S.; Longvah, T. Effect of processing on barley β-glucan content; its molecular weight and extractability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickin, E.; Steele, K.; Edwards-Jones, G.; Wright, D. Agronomic diversity of naked barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): A potential resource for breeding new food barley for Europe. Euphytica 2012, 184, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.; Meints, B.; Hayes, P. Introgression breeding in barley: Perspectives and case studies. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Cuesta-Marcos, A.; Hayes, P.M.; Muehlbauer, G.J. Barley genetic variation: Implications for crop improvement. Brief Funct. Genom. 2014, 13, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suriano, S.; Iannucci, A.; Codianni, P.; Fares, C.; Russo, M.; Pecchioni, N.; Marciello, U.; Savino, M. Phenolic acids profile; nutritional and phytochemical compounds; antioxidant properties in colored barley grown in southern Italy. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, R.W. Principles of Plant Breeding; John Willey and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghamitra, P.; Sah, R.P.; Bagchi, T.B.; Sharma, S.G.; Kumar, A.; Munda, S.; Sahu, R.K. Evaluation of variability and environmental stability of grain quality and agronomic parameters of pigmented rice (O. sativa L.). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasuonno, P.; Marcotuli, I.; Blanco, A.; Maccaferri, M.; Condorelli, G.E.; Tuberosa, R.; Parada, R.; de Camargo, A.C.; Schwember, A.R.; Gadaleta, A. Carotenoid pigment content in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var durum): An overview of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Pandey, P.; Singh, S. Genetic variability and direct selection criterion for seed yield in segregating generations of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falconer, D.S.; Mackay, T.F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 5th ed.; Longman Harlow: Essex, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Martinia, D.; Taddei, F.; Ciccoritti, R.; Pasquini, M.; Nicoletti, I.; Corradini, D.; D’Egidio, M.G. Variation of total antioxidant activity and of phenolic acid; total phenolics and yellow coloured pigments in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum) as a function of genotype; crop year and growing area. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleggia, R.; Ficco, D.B.M.; Nigro, F.M.; Giovanniello, V.; Colecchia, S.A.; Pecorella, I.; De Vita, P. Effect of sowing date on bioactive compounds and grain morphology of three pigmented cereal species. Agronomy 2021, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Shi, B.; Chai, Y.; Han, N.; Zhu, M.; Bian, H. Overexpression of HvHGGT enhances tocotrienol levels and antioxidant activity in barley. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5181–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamel, T.H.; Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M. Phenolic acids and antioxidant properties of barley wholegrain and pearling fractions. Agric. Food Sci. 2012, 21, 118131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Silvestro, R.; Di Loreto, A.; Bosi, S.; Bregola, V.; Marotti, I.; Benedettelli, S.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Dinelli, G. Environment and genotype effects on antioxidant properties of organically grown wheat varieties: A 3-year study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loskutov, I.G.; Khlestkina, E.K. Wheat, barley, and oat breeding for health benefit components in grain. Plants 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Beta, T. Comparison of antioxidant activities of different colored wheat grains and analysis of phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9235–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimić, G.; Horvat, D.; Lalić, A.; Koceva Komlenić, D.; Abičić, I.; Zdunić, Z. Distribution of β-Glucan; phenolic acids; and proteins as functional phytonutrients of hull-less barley grain. Foods 2019, 8, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, H.W.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Estimates of genetic and environmental variability in soybeans. Agron. J. 1955, 47, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, C.N.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, P.C.; Bhardwaj, D.N.; Singh, H.L. Genetic variability in barley. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2007, 3, 220–221. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.W.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Genotypic and phenotypic correlations in soybeans and their implications in selection. Agron. J. 1955, 47, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Jia, Q.; Zhu, J.; Shang, Y.; Hua, W.; Zhou, M. A New QTL for plant height in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) showing no negative effects on grain yield. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Guo, H.; Bu Gong, J.D.; Lu, M.; Lu, M.-Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.-T.; Qin, W. Phenolic profiles, β-glucan contents, and antioxidant capacities of colored Qingke (Tibetan hulless barley) cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Orozco, R.; Li, L.; Harflett, C.; Shewry, P.R.; Ward, J.L. Effects of environment and genotype on phenolic acids in wheat in the HEALTHGRAIN diversity screen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9341–9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mérida-García, R.; Liu, G.; He, S.; GonzalezDugo, V.; Dorado, G.; Gálvez, S.; Solís, I.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Reif, J.C.; Hernandez, P. Genetic dissection of agronomic and quality traits based association mapping and genomic selection approaches in durum wheat grown in Southern Spain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Choo, T.-M.; Dhillon, S.; Rabalski, I. Free and bound phenolic acids and total phenolics in black; blue; and yellow barley and their contribution to free radical scavenging capacity. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, S.; Savino, M.; Codianni, P.; Iannucci, A.; Caternolo, G.; Russo, M.; Pecchioni, N.; Troccoli, A. Anthocyanin profile and antioxidant capacity in coloured barley. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2478–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficco, D.B.M.; De Simone, V.; Colecchia, S.A.; Pecorella, I.; Platani, C.; Nigro, F.; Finocchiaro, F.; Papa, R.; De Vita, P. Genetic variability in anthocyanin composition and nutritional properties of blue; purple; and red bread (Triticum aestivum L.) and durum (Triticum turgidum L. ssp. turgidum convar. durum) wheats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8686–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleggia, R.; Platani, C.; Nigro, F.; Cattivelli, L. A micromethod for the determination of yellow pigment content in durum wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, S.; Oomah, B.D.; Mazza, G. Wheat quality: Antioxidant activity of wheat millstreams. In Wheat Quality Elucidation; Ng, P., Wrigley, C.W., Eds.; American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC) International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2002; p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.S.; Ricardo Da Silva, J.M.; Spranger, I. Critical factors of vanillin assay for catechins and proanthocyanidins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoids contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 22, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, C.; Platani, C.; Baiano, A.; Menga, V. Effect of processing and cooking on phenolic acid profile and antioxidant capacity of durum wheat pasta enriched with debranning fractions of wheat. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespel, L.; Le Bras, C.; Relion, D.; Morel, P. Genotype × year interaction and broad-sense heritability of architectural characteristics in rose bush. Plant Breed. 2014, 133, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Month | Maximum Temperature (°C) | Minimum Temperature (°C) | Rainfall (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 15-Year Average | 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 15-Year Average | 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 15-Year Average | |
| November | 20.8 | 22.8 | 22.6 | 18.0 | 11.8 | 9.7 | 13.5 | 7.6 | 41.0 | 15.8 | 101.2 | 58.6 |
| December | 17.1 | 16.2 | 16.8 | 13.7 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 8.7 | 4.0 | 38.4 | 69.1 | 78.6 | 72.2 |
| January | 13.1 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 13.1 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 21.5 | 39.1 | 61.2 |
| February | 8.3 | 13.9 | 9.7 | 13.8 | 1.1 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 81.8 | 31.9 | 60.2 | 44.7 |
| March | 14.8 | 10.3 | 13.6 | 16.9 | 5.3 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 4.7 | 23.2 | 52.9 | 29.1 | 55.2 |
| April | 17.6 | 15.1 | 17.6 | 20.8 | 5.2 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 7.5 | 8.2 | 54.3 | 23.2 | 52.9 |
| May | 18.9 | 22.6 | 20.4 | 25.8 | 5.5 | 8.3 | 8.0 | 11.4 | 23.5 | 6.7 | 35.4 | 37.2 |
| June | 25.0 | 25.3 | 20.2 | 31.1 | 10.5 | 12.9 | 9.7 | 15.5 | 80.0 | 97.9 | 90.7 | 45.7 |
| Mean | 17.0 | 17.3 | 16.7 | 19.1 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 7.1 | ||||
| Total | 299.2 | 350.1 | 457.5 | 427.6 | ||||||||
| Trait | Whole Collection | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | CV (%) | σ2g | σ2p | GCV (%) | PCV (%) | h2b (%) | ΔG (%) | |
| HT | 12.2 | 10.0–15.0 | 11.6 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 10.5 | 11.4 | 83.6 | 19.7 |
| PH | 96.8 | 88.9–107.2 | 5.8 | 25.0 | 30.7 | 5.2 | 5.7 | 81.6 | 9.6 |
| SY | 4.6 | 3.4–5.4 | 9.7 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 9.0 | 22.8 | 15.6 | 7.3 |
| SW | 79.9 | 68.0–82.1 | 3.7 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 93.5 | 7.1 |
| TSW | 38.2 | 34.8–45.5 | 6.3 | 4.6 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 82.1 | 10.5 |
| TPro | 12.8 | 10.8–14.4 | 8.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 99.8 | 16.4 |
| TCarot | 2.3 | 1.7–4.6 | 28.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 27.9 | 29.3 | 90.2 | 54.5 |
| β-glu | 4.1 | 2.5–4.6 | 12.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 11.9 | 12.6 | 90.6 | 23.4 |
| TPh | 2374.8 | 1929.0–2917.0 | 11.5 | 74,143.0 | 77,141.0 | 11.5 | 11.7 | 96.1 | 23.2 |
| TPAnt | 1336.7 | 1037.0–1630.0 | 11.5 | 22,753.7 | 25,021.7 | 11.3 | 11.8 | 90.9 | 22.2 |
| TAnt | 81.9 | 1.0–132.3 | 44.1 | 1217.7 | 1230.8 | 42.6 | 42.8 | 98.9 | 87.3 |
| TFlav | 1041.3 | 657.0–1421.7 | 17.5 | 28,736.6 | 42,500.8 | 16.3 | 19.8 | 67.6 | 27.6 |
| DPPH | 10.5 | 8.2–13.4 | 16.1 | 2.3 | 4.0 | 14.4 | 19.1 | 56.7 | 22.3 |
| TEAC | 13.0 | 10.5–15.6 | 12.1 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 12.0 | 12.2 | 97.2 | 24.4 |
| Trait | HT | PH | SY | SW | TSW | TPro | TCarot | β-glu | TPh | TPAnt | TAnt | TFlav | DPPH | TEAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT | 0.34 | 0.04 | −0.44 * | 0.13 | −0.10 | 0.39 | 0.38 | −0.21 | 0.63 ** | −0.63 ** | −0.27 | −0.16 | −0.10 | |
| PH | 0.42 | −0.59 ** | −0.10 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.17 | −0.31 | 0.15 | −0.28 | −0.30 | −0.22 | −0.25 | |
| SY | 0.03 | −0.77 ++ | −0.09 | 0.10 | −0.13 | −0.06 | 0.34 | 0.47 * | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.52 * | 0.46 * | |
| SW | −0.48 | −0.16 | −0.12 | 0.37 | 0.23 | −0.84 ** | −0.13 | −0.01 | −0.31 | 0.43 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| TSW | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.37 | −0.23 | −0.25 | 0.15 | −0.02 | 0.16 | −0.17 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.01 | |
| TPro | −0.11 | 0.05 | −0.13 | 0.23 | −0.26 | −0.12 | 0.39 | 0.22 | −0.33 | 0.20 | −0.20 | 0.19 | 0.40 | |
| TCarot | 0.45 | 0.24 | −0.08 | −0.91 ++ | −0.30 | −0.12 | 0.25 | −0.12 | 0.23 | −0.54 * | 0.01 | −0.17 | −0.19 | |
| β-glu | 0.42 | 0.19 | 0.38 | −0.14 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.27 | −0.22 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.31 | |
| TPh | −0.23 | −0.36 | 0.51 | −0.01 | −0.03 | 0.21 | −0.10 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.81 ** | 0.91 ** | |
| TPAnt | 0.71 + | 0.19 | 0.24 | −0.30 | 0.18 | −0.32 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.36 | −0.29 | −0.02 | 0.28 | 0.32 | |
| TAnt | −0.68 | −0.32 | 0.15 | 0.47 | −0.17 | 0.21 | −0.57 | −0.23 | 0.18 | −0.29 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.16 | |
| TFlav | −0.35 | −0.35 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.16 | −0.21 | −0.01 | 0.06 | 0.19 | −0.02 | 0.48 | 0.20 | 0.04 | |
| DPPH | −0.19 | −0.31 | 0.65 ++ | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.20 | −0.20 | 0.32 | 0.92 ++ | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.84 ** | |
| TEAC | −0.12 | −0.29 | 0.52 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.41 | −0.19 | 0.32 | 0.91 ++ | 0.33 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.95 |
| Principal Component Axis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Eigenvalues | 3.81 | 3.14 | 1.72 | 1.62 | 1.04 |
| PC variation (%) | 27.2 | 22.4 | 12.3 | 11.5 | 7.4 |
| Cumulative variation (%) | 27.2 | 49.6 | 61.9 | 73.5 | 80.9 |
| Trait | Eigenvectors | ||||
| HT | −0.230 | 0.402 | 0.111 | 0.163 | 0.032 |
| PH | −0.270 | 0.088 | 0.419 | 0.096 | 0.062 |
| SY | 0.307 | 0.208 | −0.318 | 0.059 | 0.130 |
| SW | 0.208 | −0.350 | 0.312 | 0.339 | 0.054 |
| TSW | 0.062 | 0.052 | 0.133 | 0.672 | 0.200 |
| TPro | 0.147 | 0.037 | 0.520 | −0.427 | 0.236 |
| TCarot | −0.252 | 0.336 | −0.203 | −0.298 | 0.196 |
| β-glu | 0.097 | 0.339 | 0.256 | −0.045 | 0.603 |
| TPh | 0.417 | 0.225 | 0.012 | −0.125 | −0.194 |
| TPAnt | 0.026 | 0.423 | −0.062 | 0.263 | −0.261 |
| TAnt | 0.277 | −0.331 | −0.090 | −0.097 | 0.127 |
| TFlav | 0.174 | 0.068 | −0.415 | 0.093 | 0.549 |
| DPPH | 0.425 | 0.199 | 0.081 | 0.071 | −0.080 |
| TEAC | 0.420 | 0.223 | 0.167 | −0.118 | −0.220 |
| Trait | No. of Genotypes | Mean | Superior Line for Multiple Traits | Parent Comparison | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1997 (I) | L3004 (II) | L3005 (I) | L3006 (I) | L3007 (II) | L3008 (II) | L3009 (I) | Mean (M) | Parent Mean (PM) | Difference (%) | |||
| HT | 11 | 11.1 | - | 11.6 | 10.4 | 11.8 | 11.6 | - | 11.0 | 11.3 | 13.6 | −16.9 |
| PH | 5 | 89.9 | - | - | 88.9 | 89.4 | 91.1 | - | 90.0 | 89.9 | 102.5 | −12.3 |
| SY | 4 | 5.2 | - | - | 5.4 | 5.3 | - | - | - | 5.4 | 4.5 | +20.0 |
| SW | 1 | 82.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 82.1 | 77.5 | +5.9 |
| TSW | 1 | 45.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 45.5 | 39.0 | +16.7 |
| TPro | 3 | 14.3 | - | - | - | - | 14.0 | 14.3 | - | 14.2 | 12.7 | +11.8 |
| TCarot | 2 | 3.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.9 | 3.1 | +25.8 |
| β-glu | 2 | 4.6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4.6 | 4.5 | +2.2 |
| TPh | 3 | 2780.7 | 2691.0 | - | - | - | - | 2734.0 | 2917.0 | 2780.7 | 2223.8 | +25.0 |
| TPAnt | 3 | 1594.3 | 1630.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1630.0 | 1407.3 | +15.8 |
| TAnt | 2 | 128.2 | 124.0 | - | - | - | - | - | 132.3 | 128.1 | 31.8 | +302.8 |
| TFlav | 3 | 1356.2 | 1421.7 | - | - | - | - | - | 1327.0 | 1374.4 | 979.7 | +40.3 |
| DPPH | 6 | 12.7 | 12.4 | 12.8 | 12.6 | - | 12.4 | - | 13.4 | 12.7 | 9.7 | +30.9 |
| TEAC | 4 | 15.2 | - | 14.8 | 14.7 | - | - | 15.6 | 15.6 | 15.2 | 12.2 | +24.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannucci, A.; Suriano, S.; Codianni, P. Genetic Diversity for Agronomic Traits and Phytochemical Compounds in Coloured Naked Barley Lines. Plants 2021, 10, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081575
Iannucci A, Suriano S, Codianni P. Genetic Diversity for Agronomic Traits and Phytochemical Compounds in Coloured Naked Barley Lines. Plants. 2021; 10(8):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081575
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannucci, Anna, Serafino Suriano, and Pasquale Codianni. 2021. "Genetic Diversity for Agronomic Traits and Phytochemical Compounds in Coloured Naked Barley Lines" Plants 10, no. 8: 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081575
APA StyleIannucci, A., Suriano, S., & Codianni, P. (2021). Genetic Diversity for Agronomic Traits and Phytochemical Compounds in Coloured Naked Barley Lines. Plants, 10(8), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081575