Effects of Light and Oxygen on Chlorophyll d Biosynthesis in a Marine Cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Heterotrophic Growth with Carbon Sources
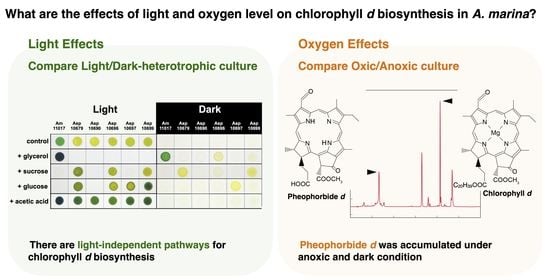
2.2. Biosynthesis of Chl in Dark Heterotrophic Growth
2.3. Biosynthesis of Chl d under Anoxic Conditions
2.4. Accumulation of Pheophorbide d
3. Discussion
3.1. Differences in Carbon Requirement for Heterotrophic Growth
3.2. Light and Oxygen Requirement on Chl d Biosynthesis
3.3. Accumulation of Pheide d and Degradation of Chl d
3.4. Increase in Chl a Content in the Dark-Heterotrophic Condition
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acaryochloris Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Pigment Extraction and HPLC Analysis
4.3. Synthesis of Pheophorbide d
4.4. LC-MS Measurement
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M. Chlorophyll modifications and their spectral extension in oxygenic photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Chlorophyll cycle regulates the construction and destruction of the light-harvesting complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1807, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Büchel, C. Light harvesting complexes in chlorophyll c-containing algae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, H.; Ikemoto, H.; Kurano, N.; Adachi, K.; Chihara, M.; Miyachi, S. Chlorophyll d as a major pigment. Nature 1996, 383, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Schliep, M.; Willows, R.D.; Cai, Z.-L.; Neilan, B.A.; Scheer, H. A Red-Shifted Chlorophyll. Science 2010, 329, 1318–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Gan, F.; Shen, G.; Bryant, D.A. RfpA, RfpB, and RfpC are the Master Control Elements of Far-Red Light Photoacclimation (FaRLiP). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Miyashita, H.; Iwasaki, I.; Kurano, N.; Miyachi, S.; Iwaki, M.; Itoh, S. A photosystem I reaction center driven by chlorophyll d in oxygenic photosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13319–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomo, T.; Okubo, T.; Akimoto, S.; Yokono, M.; Miyashita, H.; Tsuchiya, T.; Noguchi, T.; Mimuro, M. Identification of the special pair of photosystem II in a chlorophyll d-dominated cyanobacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7283–7288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.Y.; Shen, G.; Canniffe, D.P.; Zhao, C.; Bryant, D.A. Light-dependent chlorophyll f synthase is a highly divergent paralog of PsbA of photosystem II. Science 2016, 353, 6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trinugroho, J.P.; Bečková, M.; Shao, S.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Murray, J.W.; Sobotka, R.; Komenda, J.; Nixon, P.J. Chlorophyll f synthesis by a super-rogue photosystem II complex. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliep, M.; Crossett, B.; Willows, R.D.; Chen, M. 18O labeling of chlorophyll d in Acaryochloris marina reveals that chlorophyll a and molecular oxygen are precursors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28450–28456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kahlon, S.; Beeri, K.; Ohkawa, H.; Hihara, Y.; Murik, O.; Suzuki, I.; Ogawa, T.; Kaplan, A. A putative sensor kinase, Hik31, is involved in the response of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 to the presence of glucose. Microbiology 2006, 152, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J. FesM, a membrane iron-sulfur protein, is required for cyclic electron flow around photosystem I and photoheterotrophic growth of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matson, M.M.; Atsumi, S. Photomixotrophic chemical production in cyanobacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 50, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Nomata, J.; Fujita, Y. Differential operation of dual protochlorophyllide reductases for chlorophyll biosynthesis in response to environmental oxygen levels in the cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya boryana. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunsperger, H.M.; Randhawa, T.; Cattolico, R.A. Extensive horizontal gene transfer, duplication, and loss of chlorophyll synthesis genes in the algae. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyes, D.J.; Zhang, S.; Taylor, A.; Johannissen, L.O.; Hardman, S.J.O.; Hay, S.; Scrutton, N.S. Photocatalysis as the ‘master switch’ of photomorphogenesis in early plant development. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troup, B.; Jahn, M.; Hungerer, C.; Jahn, D. Isolation of the hemF operon containing the gene for the Escherichia coli aerobic coproporphyrinogen III oxidase by in vivo complementation of a yeast HEM13 mutant. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troup, B.; Hungerer, C.; Jahn, D. Cloning and characterization of the Escherichia coli hemN gene encoding the oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen III oxidase. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 3326–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goto, T.; Aoki, R.; Minamizaki, K.; Fujita, Y. Functional differentiation of two analogous coproporphyrinogen III oxidases for heme and chlorophyll biosynthesis pathways in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bollivar, D.W.; Suzuki, J.Y.; Beatty, J.T.; Dobrowolski, J.M.; Bauer, C.E. Directed Mutational Analysis of Bacteriochlorophyll a Biosynthesis in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 237, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinta, V.; Picaud, M.; Reiss-Husson, F.; Astier, C. Rubrivivax gelatinosus acsF (previously orf358) codes for a conserved, putative binuclear-iron-cluster-containing protein involved in aerobic oxidative cyclization of Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethylester. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamanashi, K.; Minamizaki, K.; Fujita, Y. Identification of the chlE gene encoding oxygen-independent Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester cyclase in cyanobacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamizaki, K.; Mizoguchi, T.; Goto, T.; Tamiaki, H.; Fujita, Y. Identification of two homologous genes, chlAI and chlAII, that are differentially involved in isocyclic ring formation of chlorophyll a in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hörtensteiner, S.; Kräutler, B. Chlorophyll breakdown in higher plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1807, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, H.; Tanaka, A.; Tanaka, R.; Ito, H. In Vitro Enzymatic Activity Assays Implicate the Existence of the Chlorophyll Cycle in Chlorophyll b-Containing Cyanobacteria. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2672–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Charng, Y.Y. Chlorophyll dephytylation in chlorophyll metabolism: A simple reaction catalyzed by various enzymes. Plant Sci. 2021, 302, 110682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodoni, S.; Muhlecker, W.; Anderl, M.; Krautler, B.; Moser, D.; Thomas, H.; Matile, P.; Hortensteiner, S. Chlorophyll Breakdown in Senescent Chloroplasts (Cleavage of Pheophorbide a in Two Enzymic Steps). Plant Physiol. 1997, 115, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Quinnell, R.G.; Larkum, A.W. The major light-harvesting pigment protein of Acaryochloris marina. FEBS Lett. 2002, 514, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.K.; Yin, Y.C.; Zhang, L.D.; Zhang, Z.C.; Dai, G.Z.; Chen, M.; Qiu, B.S. The identification of IsiA proteins binding chlorophyll d in the cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina. Photosynth. Res. 2018, 135, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Qing, Y.; Min, C. Incorporation of the chlorophyll d-binding light-harvesting protein from Acaryochloris marina and its localization within the photosynthetic apparatus of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1797, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirashima, M.; Satoh, S.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Pigment shuffling in antenna systems achieved by expressing prokaryotic chlorophyllide a oxygenase in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15385–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Kawakami, K.; Shinzawa-Itoh, K.; Inoue-Kashino, N.; Itoh, S.; Ifuku, K.; Yamashita, E.; Maeda, K.; Yonekura, K.; Kashino, Y. Structure of the far-red light utilizing photosystem I of Acaryochloris marina. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Akimoto, S.; Mizoguchi, T.; Watabe, K.; Kindo, H.; Tomo, T.; Tamiaki, H.; Mimuro, M. Artificially produced [7-formyl]-chlorophyll d functions as an antenna pigment in the photosystem II isolated from the chlorophyllide a oxygenase-expressing Acaryochloris marina. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1817, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapata, M.; Rodríguez, F.; Garrido, J.L. Separation of chlorophylls and carotenoids from marine phytoplankton: A new HPLC method using a reversed phase C8 column and pyridine-containing mobile phases. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 195, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hörtensteiner, S.; Vicentini, F.; Matile, P. Chlorophyll breakdown in senescent cotyledons of rape, Brassica napus L.: Enzymatic cleavage of phaeophorbide a in vitro. New Phytol. 1995, 129, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukatani, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Harada, J.; Yoshitomi, T.; Nomata, J.; Kasahara, M.; Mizoguchi, T.; Fujita, Y.; Tamiaki, H. An unexpectedly branched biosynthetic pathway for bacteriochlorophyll b capable of absorbing near-infrared light. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuzuki, Y.; Tsukatani, Y.; Yamakawa, H.; Itoh, S.; Fujita, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Effects of Light and Oxygen on Chlorophyll d Biosynthesis in a Marine Cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina. Plants 2022, 11, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070915
Tsuzuki Y, Tsukatani Y, Yamakawa H, Itoh S, Fujita Y, Yamamoto H. Effects of Light and Oxygen on Chlorophyll d Biosynthesis in a Marine Cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina. Plants. 2022; 11(7):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070915
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuzuki, Yuki, Yusuke Tsukatani, Hisanori Yamakawa, Shigeru Itoh, Yuichi Fujita, and Haruki Yamamoto. 2022. "Effects of Light and Oxygen on Chlorophyll d Biosynthesis in a Marine Cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina" Plants 11, no. 7: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070915
APA StyleTsuzuki, Y., Tsukatani, Y., Yamakawa, H., Itoh, S., Fujita, Y., & Yamamoto, H. (2022). Effects of Light and Oxygen on Chlorophyll d Biosynthesis in a Marine Cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina. Plants, 11(7), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070915