Screening of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors from Seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint. by Ligand Fishing and Their Neuroprotective Activity
Abstract
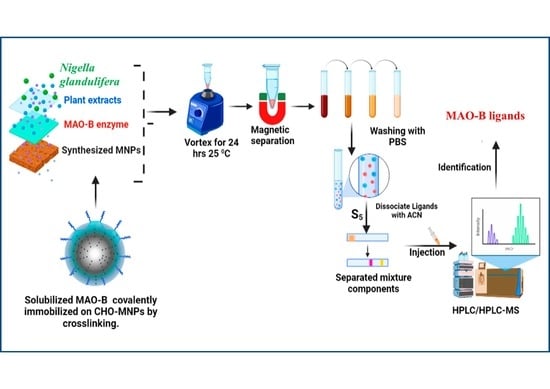
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Immobilized MAO-B
2.2. Identification of the Ligands of MAO-B
2.3. MAO-B Ligands from N. glandulifera
2.4. Enzymatic Kinetic Study
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.6. Neuroprotective Effect of the Inhibitors on 6-OHDA-Induced PC-12 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials, Reagents, and Instruments
3.2. Extraction of Seeds of N. glandulifera
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of MAO-B Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.4. Ligand Fishing of N. glandulifera
3.5. Isolation of the Target Ligands
3.6. Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibition Assay
3.7. Enzymatic Kinetic Study
3.8. Molecular Docking
3.9. Protective Effect of the Ligands on 6-OHDA-Induced PC-12
3.10. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, S.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Peng, L.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H. Statin use and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: An updated meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.K.; Farrer, M.J. Genetics and genomics of Parkinson’s disease. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ball, N.; Teo, W.P.; Chandra, S.; Chapman, J. Parkinson’s disease and the environment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Sherer, T.; Okun, M.S.; Bloem, B.R. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, S.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Qu, M.; Kan, G.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dong, Z.; et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s Disease: A Community-Based Study in China. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, D.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zengin, G.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S.; Bumbu, A.G. Role of Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Insight into the Therapeutic Potential of Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 2007, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Chen, L. Economic Burden Analysis of Parkinson’s disease patients in China. Park. Dis. 2017, 2017, e8762939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Ramakrishna, R.; Bhateria, M.; Bhatta, R.S. In Vitro Evaluation of Bacopa monniera Extract and Individual Constituents on Human Recombinant Monoamine Oxidase Enzymes. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Binda, C. Monoamine Oxidases. In Membrane Protein Complexes: Structure and Function; Harris, J., Boekema, E., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Jaka, O.; Iturria, I.; van der Toorn, M.; Hurtado de Mendoza, J.; Latino, D.A.R.S.; Alzualde, A.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J.; Koshibu, K. Effects of natural monoamine oxidase inhibitors on anxiety-like behavior in Zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 669370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoli, M.; Chinta, S.J.; Andersen, J.K. An inducible MAO-B mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: A tool towards better understanding basic disease mechanisms and developing novel therapeutics. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroni, E.; Bohrmann, B.; Grueninger, F.; Prinssen, E.; Nave, S.; Loetscher, H.; Chinta, S.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Rane, A.; Siddiqui, A.; et al. Sembragiline: A Novel, Selective Monoamine Oxidase Type B Inhibitor for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Diseases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 362, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herraiz, T.; Andrea, F.; Lidia, F. Analysis of monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymatic activity by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection combined with an assay of oxidation with a peroxidase and its application to MAO inhibitors from foods and plants. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1073, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Wilson, D.R.; Fugmann, S.D.; Moaddel, R. Synthesis and characterization of SIRT6 protein-coated magnetic beads: Identification of a novel inhibitor of SIRT6 deacetylase from medicinal plant extracts. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7400–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.L.; Peng, S.L.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.T.; Qing, L.S.; Liao, X. Selective extraction of berberine from Cortex phellodendri using polydopamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, J.; Li, Y. Preparation of carbon-functionalized magnetic graphene/mesoporous silica composites for selective extraction of miglitol and voglibose in rat plasma. Talanta 2018, 182, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Dong, C. Recent advances in nano-carrier immobilized enzymes and their applications. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Zhao, Y.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Magnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers for enzyme immobilization: A review. Int. J. Bio. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2530–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.M.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.P. Advances on methods and easy separated support materials for enzyme immobilization. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Ren, X.Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.M.; Liang, J.; Liao, X. Fast identification of lipase inhibitors in oolong tea by using lipase functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles coupled with UPLC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Hu, Y.; Chun, Z.; Liao, X. Monoamine oxidase B immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles for screening of the enzyme’s inhibitors from herbal extracts. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.F.; Jiang, X.L.; Gong, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.D.; Bai, X.L.; Liao, X. Ligand fishing of anti-neurodegenerative components from Lonicera japonica using magnetic nanoparticles immobilized with monoamine oxidase B. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Liu, Q.H.; Chen, B.Q. A new flavonol glycoside from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.H.; Lu, S.R.; Chen, B.Q. Dolabellane-type diterpene alkaloids from Nigella glandulifera. Biochem. Sys. Ecol. 2013, 49, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L.; Luan, M.; Zhu, W.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Q.L.; Xu, C.J.; Lu, X.H.; Xu, X.D.; Tian, J.K.; Zhang, L. Study on antitubercular constituents from the Seeds of Nigella glandulifera. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2015 ed; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, F.; Liu, R. Total Saponins from Nigella glandulifera Seeds Ameliorate Adjuvant-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis in Rats by Inhibition of an Inflammatory Response and Bone Erosion. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6613527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.L.; Asia, H.A.; Wang, H.Q. Flavonoids and phenolic compounds from seeds of the Chinese plant Nigella glandulifera. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008, 44, 368–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubertakh, B.; Liu, X.G.; Cheng, X.L.; Li, P. A spotlight on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint seeds. J. Chem. 2013, 820183. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, Q.; Liu, Q.; He, C.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; Talbi, A.; Zhou, J. UPLCQ-TOF/MS characterization, HPLC fingerprint analysis and species differentiation for quality control of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et. Sint. seeds and Nigella sativa L. seeds. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 4845–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Huang, H.; Gu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, W.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, C. Antitumor and antioxidant potential of total saponins from Nigella glandulifera seeds. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 827230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Shi, Y.Z.; Xu, F. Evaluation on arthritis of total saponins from Nigella glandulifera seeds. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2014, 30, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.B.; Xina, X.L.; Aisa, H.A. Pyrrolo-isoquinoline and glycosylated pyrrolidine alkaloids from Nigella glandulifera and their anti-PTP1B activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 19, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, B.Q.; Liu, Q.H. New phenolic compounds from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera and their inhibitory activities against human cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3864–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhu, L.L.; Pu, D.B.; Li, X.L.; Li, H.L.; Xu, M.; Xiao, W.L. In vitro human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitory, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities of alkaloids from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, F.; Zeng, L.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, R. Saponins from Nigella glandulifera seeds attenuate collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats via the OPG/RANKL/NF-κB and Ang/ Tie-2 pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Bilige, W.; Ganbold, T.; Ehexige, E.; He, M.; Temuqile, T.; Baigude, H. Neuroprotective and antioxidant activity of Nigella glandulifera Freyn & Sint seeds. Acad. J. Med. Plants 2018, 6, 412–420. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.H.; Jiang, X.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Hu, J.J.; Liang, J.; Liao, X. Screening of lipase inhibitors from Scutellaria baicalensis extract using lipase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles and study on the inhibitory mechanism. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.K.; Liu, Y.M.; Bai, X.L.; Chao, M.; Liao, X. Screening of Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors from Fragaria nubicola by Ligand Fishing and Their Neuroprotective Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Hu, Y.K.; Fan, W.Q.; Ayeni, E.A.; Liao, X. Ligand Fishing of Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors from Platycodon grandiflorum Roots by the Enzyme Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 34, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Han, C.; Guo, W.H.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, H.B.; Yao, H.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; et al. Nigegladines A-C, Three thymoquinone dimers from Nigella glandulifera. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6348–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, E.A.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Fan, W.Q.; Liao, X. Chemical components and monoamine oxidase B inhibition activities from the tubers of Sauromatum giganteum (Engl.) Cusimano & Hett. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Marzo, C.M.; Gambini, S.; Poletti, S.; Munari, F.; Assfalg, M.; Guzzo, F. Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidases A and B by Specialized Metabolites Present in Fresh Common Fruits and Vegetables. Plants 2022, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.C.; Lin, R.D.; Chen, C.T.; Lee, M.H. Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibition by active principles from Uncaria rhynchophylla. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Pan, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yao, X.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yao, X. Target discovery of chlorogenic acid derivatives from the flower buds of Lonicera macranthoides and their MAO B inhibitory mechanism. Fitoterapia 2019, 134, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patadiya, N.; Panchal, N.; Vaghela, V. A review on enzyme inhibitors. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2021, 12, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalingam, K.B.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Haleagrahara, N. Protective effects of flavonol isoquercitrin, against 6-hydroxy dopamine (6-OHDA)-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Gan, L.; Jia, L.Y.; Zhou, D.C.; Bi, S.; Meng, Z.Q.; Guan, G.J.; Huang, M.M.; He, X.; Zhang, C.F.; et al. Screen of anti-migraine active compounds from ‘Duijinsan’ by spectrum-effect relationship analysis and molecular docking. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.J.; Tan, E.-K.; Chao, Y.-X. Historical Perspective: Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Compound | Inhibitory MAO-B (100 µM) % | IC50 Inhibitory Concentration µM | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-BuOH fraction | 54.80 | - | - |
| 1 | 55.80 | 35.85 ± 0.03 | 0.98 |
| 2 | 65.70 | 25.54 ± 0.05 | 0.99 |
| Positive control (Safinamide) | 98.50 | 0.19 ± 0.09 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayeni, E.A.; Ma, C.; Hu, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, X. Screening of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors from Seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint. by Ligand Fishing and Their Neuroprotective Activity. Plants 2023, 12, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040882
Ayeni EA, Ma C, Hu Y, Bai X, Zhang Y, Liao X. Screening of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors from Seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint. by Ligand Fishing and Their Neuroprotective Activity. Plants. 2023; 12(4):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040882
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyeni, Emmanuel Ayodeji, Chao Ma, Yikao Hu, Xiaolin Bai, Yongmei Zhang, and Xun Liao. 2023. "Screening of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors from Seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint. by Ligand Fishing and Their Neuroprotective Activity" Plants 12, no. 4: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040882
APA StyleAyeni, E. A., Ma, C., Hu, Y., Bai, X., Zhang, Y., & Liao, X. (2023). Screening of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors from Seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint. by Ligand Fishing and Their Neuroprotective Activity. Plants, 12(4), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040882