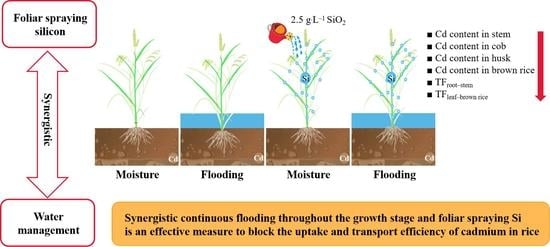
Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on Cd Content in Rice Organs and Yield
2.2. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Cd Translocation Factor of Rice Organs
2.3. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on SPAD Values of Rice Leaves
2.4. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on Rice Photosynthesis
2.5. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on MDA, SOD and POD Content in Rice Leaves
3. Discussion
3.1. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on Cd Content in Rice Organs and on Rice Yield
3.2. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Cd Translocation Factor of Rice Organs
3.3. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on SPAD Values of Rice Leaves
3.4. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on Photosynthesis in Rice
3.5. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on MDA, SOD and POD Content in Rice Leaves
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Test Station and Materials
4.2. Experimental Design and Treatment
4.3. Measurement Methods
4.3.1. Determination of Cd Content
4.3.2. Determination of Relative Chlorophyll Content
4.3.3. Determination of Photosynthetic Parameters
4.3.4. Determination of MDA, SOD and POD Contents
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, J.P.; Han, J.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, M.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Fu, R.F.; Luo, Z.J.; Hu, J.P.; Liang, W.Q.; et al. Two rice receptor-like kinases maintain male fertility under changing temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12327–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.F.; Xin, J.L.; Dai, H.W.; Zhou, W.J. Effects of interaction between cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) on grain yield and Cd and Se accumulation in a hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9537–9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Rinklebe, J.; Tack, F.M.G.; Ok, Y.S. A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Zia, U.R.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Tsang, D.; Bashir, A.; Maqbool, A.; Tack, F.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium phytoremediation potential of Brassica crop species: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Sun, H.B.; Kinney, P.L.; Pitiranggon, M.; Chillrud, S.; Ma, L.Q.; et al. An interventional study of rice for reducing cadmium exposure in a Chinese industrial town. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.Z.; Xiao, H.J.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J. Uptake, transportation, and accumulation of C60 fullerene and heavy metal ions (Cd, Cu, and Pb) in rice plants grown in an agricultural soil. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.L.; Wei, X.D.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sun, Y.B.; Luo, X.W.; Bao, Z.A.; Zheng, W.T.; Wang, J.; et al. Thallium contamination in farmlands and common vegetables in a pyrite mining city and potential health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.J.; Wang, S.L.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Huang, F.; Shan, S.P.; Guo, Z.H.; Yi, H.W.; Sun, Z.G.; et al. Combined amendment reduces soil Cd availability and rice Cd accumulation in three consecutive rice planting seasons. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanglard, L.M.; Martins, S.C.; Detmann, K.C.; Silva, P.E.; Lavinsky, A.O.; Silva, M.M.; Detmann, E.; Araujo, W.L.; DaMatta, F.M. Si nutrition alleviates the negative impacts of arsenic on the photosynthetic apparatus of rice leaves: An analysis of the key limitations of photosynthesis. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.R.; Xu, Y.M. Use of clay to remediate cadmium contaminated soil under different water management regimes. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Geng, L.P.; Fan, L.M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Q.L.; Xue, P.Y.; Liu, W.J. Spraying Si to decrease inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grain from arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsue, Y.; Takasaki, K.; Abe, J. Water management for improvement of rice yield, appearance quality and palatability with high temperature during ripening period. Rice Sci. 2021, 28, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.N.; Huang, Q.Q.; Camara, A.Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.F. Water management impacts on the solubility of Cd, Pb, As, and Cr and their uptake by rice in two contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.F.; Huang, D.Y.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhu, Q.H. Water managements limit heavy metal accumulation in rice: Dual effects of iron-plaque formation and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, A.; Pedersen, O.; Ella, E.; Ismail, A.M.; Colmer, T.D. Gas film retention and underwater photosynthesis during field submergence of four contrasting rice genotypes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3225–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.Y.; Ding, X.D.; Li, F.B.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, S.R.; Yi, J.C.; Liu, C.P.; Xu, X.H.; Wang, Q. The availabilities of arsenic and cadmium in rice paddy fields from a mining area: The role of soil extractable and plant Si. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.H.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.J.; Li, H. Protective Effect of foliar application of sulfur on photosynthesis and antioxidative defense system of rice under the stress of Cd. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Sun, W.C.; Zhu, Y.G.; Christie, P. Mechanisms of Si-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumdar, A.; Upadhyay, M.K.; Kumar, J.S.; Sheena; Barla, A.; Srivastava, S.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Bose, S. Ultra-structure alteration via enhanced Si uptake in arsenic stressed rice cultivars under intermittent irrigation practices in Bengal delta basin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh Memari-Tabrizi, E.; Yousefpour-Dokhanieh, A.; Babashpour-Asl, M. Foliar-applied Si nanoparticles mitigate cadmium stress through physio-chemical changes to improve growth, antioxidant capacity, and essential oil profile of summer savory (Satureja hortensis L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 165, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Feng, A.X.; Liu, N.; Jiang, Z.M.; Wei, S.Q. Si application improved the yield and nutritional quality while reduced cadmium concentration in rice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20370–20379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.Y.; Qin, X.; Zhao, L.J.; Liang, X.F.; Xu, Y.M. Selenite mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative stress and affects Cd uptake in rice seedlings under different water management systems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.R.; Xu, Y.M. Immobilization remediation of Cd-polluted soil with different water condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.M.; Wei, X.D. Effects of soil pH on soil cadmium formations and its accumulation in rice. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. 2018, 44, 176–182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.Q.; Huang, S.Y.; Kong, L.X.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.F.; Wan, Y.N. The risks of sulfur addition on cadmium accumulation in paddy rice under different water-management conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 118, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Zheng, M.M.; Liu, H.Y.; Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.J.; Cui, K.H.; Nie, L.X. Water management practices affect arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice grains. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 596438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.T.; Zhu, Z.K.; Zhu, H.H.; Tang, Z.Z.; Pang, J.; Li, B.Z.; Su, Y.R.; Ge, T.D.; Wu, J.S. Input and distribution of photosynthesized carbon in soil-rice system affected by water management and nitrogen fertilization. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 1227–1234. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.Y.; Qin, J.H.; Li, H.S. Effect of different water management modes on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth and heavy metal transport characteristics. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 2177–2184. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Müller, T.; Mirzaeitalarposhti, R. Si application affects cadmium translocation and physiological traits of Lallemantia royleana under cadmium stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 43, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.P.; Li, F.B.; Luo, C.L.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, S.H.; Liu, T.X.; Li, X.D. Foliar application of two silica sols reduced cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, S.; Suzui, N.; Ishioka, N.S.; Kawachi, N.; Ito, S.; Chino, M.; Nakamura, S. Tracing cadmium from culture to spikelet: Noninvasive imaging and quantitative characterization of absorption, transport, and accumulation of cadmium in an intact rice plant. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaji, N.; Mitatni, N.; Ma, J.F. A transporter regulating silicon distribution in rice shoots. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greger, M.; Kabir, A.H.; Landberg, T.; Maity, P.J.; Lindberg, S. Silicate reduces cadmium uptake into cells of wheat. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.N.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qiao, Y.H.; Li, H.F. Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: Influence of different forms of selenium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppe, D.; Sommer, M. Experiments, uptake mechanisms, and functioning of silicon foliar fertilizationda review focusing on maize, rice, and wheat. Adv. Agron. 2018, 152, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.M.; Wang, X.M.; Beesley, L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhi, S.L.; Ding, Y.Z. Cadmium uptake reduction in paddy rice with a combination of water management, soil application of calcium magnesium phosphate and foliar spraying of Si/Se. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 50378–50387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Wei, B.Y.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.F.; Liao, B.H. Co-application of water management and foliar spraying silicon to reduce cadmium and arsenic uptake in rice: A two-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 818, 151801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.J.; Ouyang, Y.N.; Wu, L.H.; Shen, L.B.; Luo, Y.M.; Christie, P. Effects of water management on arsenic and cadmium speciation and accumulation in an upland rice cultivar. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 27, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Hou, S.Z.; Muhammad, A.K.; Chao, Y.; Xiao, L.L.; Ruan, Z.B.; Hong, L.; Chen, Z.H.; Ceng, S.W.; Ye, Z.Q.; et al. Effect of water and fertilization management on Cd immobilization and bioavailability in Cd-polluted paddy soil. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, W.T.; Hu, Y.M.; Liang, J.N.; Zhou, J. Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, N.; Ma, J.F.; Iwashita, T. Identification of the silicon form in xylem sap of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N. Silicon uptake and accumulation in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dian, Y.; Le, Y.; Fang, S.; Xu, Y.; Yao, C.; Liu, G. Influence of spectral bandwidth and position on chlorophyll content retrieval at leaf and canopy levels. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouni, Y.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Abdelly, C.; Lakhdar, A. Interactive effect of salinity and zinc stress on growth and photosynthetic responses of the perennial grass, Polypogon monspeliensis. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, T.; Ghnaya, T.; Abdelly, C. Nickel, cadmium and lead phytotoxicity and potential of halophytic plants in heavy metal extraction. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 111, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, H.; Parsa, M.; Bayat, H.; Aminifard, M.H. The behavior of heavy metals in relation to their influence on the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) symbiosis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 193, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, J.B.; Chang, H.B.; Yu, X.B.; Xu, H.S. Effects of silicon on rice leaf photosynthesis and ultrastructure. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2011, 33, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Cang, Z.M.; Jiao, F.; Bai, X.J.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, R.C. Influence of drought stress on photosynthetic characteristics and protective enzymes of potato at seedling stage. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2017, 16, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, F.B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; He, X.Y.; Zhang, G.P.; Wu, F.B. Differences in photosynthesis, yield and grain cadmium accumulation as affected by exogenous cadmium and glutathione in the two rice genotypes. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 75, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Harris, P. Photosynthesis under stressful environments: An overview. Photosynthetica 2013, 51, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezara, W.; Marín, O.; Rengifo, E.; Martínez, D.; Herrera, A. Photosynthesis and photoinhibition in two xerophytic shrubs during drought. Photosynthetica 2005, 43, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwugo, C.C.; Huerta, A.J. Effects of Si nutrition on cadmium uptake, growth and photosynthesis of rice plants exposed to low-level cadmium. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.L.; Li, P.; Li, Z.J.; Fan, F.L.; Nikolic, M.; Liang, Y.C. The alleviation of zinc toxicity by Si is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant Soil 2011, 344, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Wang, F.Y.; Gao, S.C. Foliar application with nano-Si alleviates Cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Ashraf, M.A.; Rasheed, R.; Asghar, A.; Sajid, M.A.; Iqbal, M. Exogenous application of Si at the boot stage decreases accumulation of cadmium in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. Braz. J. Bot. 2015, 38, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Farid, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Irshad, M.K. Mechanisms of Si-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 119, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.F.; Yang, X.E.; Islam, E.; Liu, D.; Mahmood, Q. Effects of cadmium on ultrastructure and antioxidative defense system in hyperaccumulator and non-hyperaccumulator ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ahammed, G.J.; Yin, L.; Shi, K.; Xia, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, J. Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Chai, T.Y. Si attenuates cadmium toxicity in Solanum nigrum L. by reducing cadmium uptake and oxidative stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwaar, S.A.; Ali, S.; Ali, S.; Ishaque, W.; Farid, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Najeeb, U.; Abbas, F.; Sharif, M. Si (Si) alleviates cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) from zinc (Zn) toxicity stress by limiting Zn uptake and oxidative damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.F.; Xiao, X.M.; Dong, Z.X.; Chen, Y. Si effects on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of peanut under aluminum stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 3063–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Pandey, P.; Rajpoot, R.; Rani, A.; Gautam, A.; Dubey, R.S. Exogenous application of calcium and silica alleviates cadmium toxicity by suppressing oxidative damage in rice seedlings. Protoplasma 2015, 252, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, Y.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Ma, C.Y.; Yin, M.Q.; Wen, Y.Y.; Song, X.E.; Dong, S.Q.; Yang, X.F.; Yuan, X.Y. Physiological response of millet callus with different herbicide-resistance to sethoxydim stress. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 917–928. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Luo, Y.F.; Liao, B.; Xie, L.J.; Chen, L.; Xiao, S.; Li, J.T.; Hu, S.N.; Shu, W.S. Comparative transcriptome analysis of transporters, phytohormone and lipid metabolism pathways in response to arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). New Phytol. 2012, 195, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmardi, Z.K.; Abdolzadeh, A.; Sadeghipour, H.R. Si nutrition potentiates the antioxidant metabolism of rice plants under iron toxicity. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.R.; Cai, Q.S.; Liu, C.F.; Wu, L. Si alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 61, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez–Rubio, D.; Grindlay, G.; Llaver, M.; Wuilloud, R.G.; Mora, J. Development of preconcentration strategies for the simultaneous ultratrace determination of As, Cd and Pb in foods by ICP-OES: Knotted-reactorvs. dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; El–Shehawi, A.M.; Elseehy, M.M.; Naheen, N.N.; Rahman, M.M.; Kabir, A.H. Molecular characterization and bioinformatics analysis of transporter genes associated with Cd-induced phytotoxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, L.; Sherstneva, O.; Sukhova, E.; Grinberg, M.; Mysyagin, S.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Inactivation of H+-ATPase Participates in the Influence of Variation Potential on Photosynthesis and Respiration in Peas. Plants 2020, 9, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Liu, S.T.; Zhou, J.P.; Luo, T.X. Measuration of catalase vigor in plants with spectrophotometry. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2007, 72, 72–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.F.; Jia, R.Y.; Li, H.C.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zeng, M.; Liao, B.H. Cadmium accumulation and bioavailability in paddy soil under different water regimes for different growth stages of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 2019, 440, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cd | Treatment | Cd Content in Various Parts of Rice (mg·kg−1) | Yield (kg·ha−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Stem | Leaf | Cob | Husk | Brown Rice | |||
| A | CK | 0.431 ± 0.039 d | 0.063 ± 0.009 a | 0.020 ± 0.002 c | 0.027 ± 0.004 b | 0.024 ± 0.003 ab | 0.044 ± 0.010 a | 4369.4 ± 157.6 ab |
| W | 0.591 ± 0.078 c | 0.033 ± 0.005 b | 0.030 ± 0.001 b | 0.021 ± 0.003 b | 0.028 ± 0.004 a | 0.014 ± 0.002 b | 3987.3 ± 151.6 c | |
| Si | 0.918 ± 0.058 a | 0.074 ± 0.004 a | 0.026 ± 0.005 b | 0.041 ± 0.005 a | 0.017 ± 0.001 b | 0.026 ± 0.011 b | 4552.1 ± 116.9 a | |
| WSi | 0.726 ± 0.084 b | 0.035 ± 0.010 b | 0.037 ± 0.002 a | 0.023 ± 0.002 b | 0.026 ± 0.006 a | 0.014 ± 0.002 b | 4115.5 ± 149.2 bc | |
| B | CK | 1.137 ± 0.153 b | 0.071 ± 0.002 b | 0.053 ± 0.003 ab | 0.044 ± 0.005 b | 0.048 ± 0.004 c | 0.109 ± 0.019 a | 4144.6 ± 76.6 a |
| W | 1.295 ± 0.202 b | 0.078 ± 0.006 b | 0.045 ± 0.002 b | 0.049 ± 0.005 b | 0.031 ± 0.009 a | 0.099 ± 0.013 ab | 3370.9 ± 152.7 b | |
| Si | 1.259 ± 0.114 b | 0.174 ± 0.022 a | 0.057 ± 0.007 a | 0.071 ± 0.004 a | 0.028 ± 0.005 b | 0.103 ± 0.011 ab | 4242.5 ± 207.2 a | |
| WSi | 1.844 ± 0.112 a | 0.156 ± 0.018 a | 0.049 ± 0.003 ab | 0.070 ± 0.007 a | 0.029 ± 0.007 b | 0.079 ± 0.008 c | 3615.6 ± 151.1 b | |
| C | CK | 2.639 ± 0.409 a | 0.601 ± 0.040 a | 0.102 ± 0.006 b | 0.164 ± 0.013 b | 0.118 ± 0.010 a | 0.167 ± 0.011 a | 3654.9 ± 234.2 ab |
| W | 1.874 ± 0.444 b | 0.178 ± 0.016 c | 0.082 ± 0.002 c | 0.131 ± 0.005 c | 0.054 ± 0.010 c | 0.117 ± 0.004 c | 3152.2 ± 156.6 c | |
| Si | 2.931 ± 0.081 a | 0.611 ± 0.026 a | 0.129 ± 0.004 a | 0.267 ± 0.018 a | 0.078 ± 0.008 b | 0.146 ± 0.008 b | 3879.3 ± 229.5 a | |
| WSi | 2.339 ± 0.224 ab | 0.231 ± 0.005 b | 0.100 ± 0.004 b | 0.169 ± 0.008 b | 0.052 ± 0.008 c | 0.096 ± 0.015 d | 3359.2 ± 182.1 bc | |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Soil type | Yellow soil |
| pH | 6.58 |
| Organic matter content (g∙kg−1) | 115.01 |
| Alkali hydrolysable N (mg∙kg−1) | 49.25 |
| Rapidly available P (mg∙kg−1) | 5.96 |
| Rapidly available K (mg∙kg−1) | 153.90 |
| Total Cd (mg∙kg−1) | 0.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Fan, C.; Xie, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Qin, S.; Fu, T.; He, T.; Gao, Z. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2023, 12, 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061414
Huang X, Fan C, Xie D, Chen H, Zhang S, Chen H, Qin S, Fu T, He T, Gao Z. Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants. 2023; 12(6):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061414
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaoyun, Chengwu Fan, Dongyi Xie, Hongxing Chen, Song Zhang, Hui Chen, Song Qin, Tianling Fu, Tengbing He, and Zhenran Gao. 2023. "Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)" Plants 12, no. 6: 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061414
APA StyleHuang, X., Fan, C., Xie, D., Chen, H., Zhang, S., Chen, H., Qin, S., Fu, T., He, T., & Gao, Z. (2023). Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants, 12(6), 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061414