Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation, Growth Characteristics, and Yield of Pisum sativum L. Grown in Agricultural Soil-Sewage Sludge Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Analyses of Sewage Sludge and Agricultural Soil
2.2. Plant Growth Measurements
2.3. Postharvest Chemical and Heavy Metal Analyses of Soil and Pea Portions
2.4. Bioaccumulation and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Pea
3. Materials and Methods
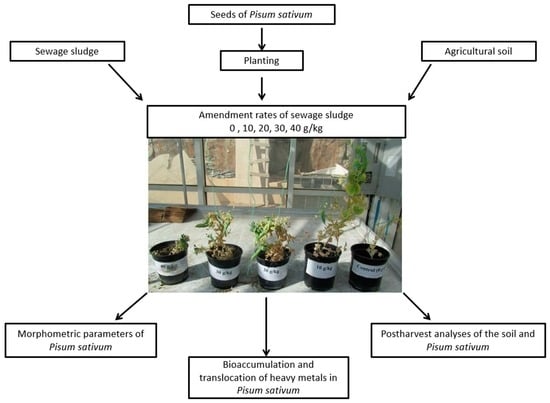
3.1. Plant Materials, Sewage Sludge Treatments, and Experimental Design
3.2. Plant Morphology and Biomass Measurements
3.3. Sample Analysis
3.4. Data Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomócsik, A.; Makádi, M.; Orosz, V.; Aranyos, T.; Demeter, I.; Mészáros, J.; Füleky, G. Effect of sewage sludge compost treatment on crop yield. AGROFOR Int. J. 2016, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otobbang, E.; Sadovnikova, L.; Lakimenko, O.; Nilsson, I.; Persson, J. Sewage sludge: Soil conditioner and nutrient source II. Availability of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd to barley in a pot experiment. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 1997, 47, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascó, G.; Lobo, M.C. Comparison of a Spanish sewage sludge and effects on treated soil and olive trees. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolín, M.C.; Muro, I.; Sánchez-Díaz, M. Application of sewage sludge improves growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant activities of nodulated alfalfa plants under drought conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Biochemical and physiological responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown on different sewage sludge amendments rates. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotto, D.; Batista, B.L.; Souza, J.M.O.; Carneiro, M.F.H.; dos Santos, D.; Melo, W.J.; Barbosa, F., Jr. Essential and nonessential element translocation in corn cultivated under sewage sludge application and associated health risk. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroubas, S.D.; Antoniadis, V.; Fotiadis, S.; Damalas, C.A. Growth, grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of Mediterranean wheat in soils amended with municipal sewage sludge. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 100, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsadilas, C.; Samaras, V.; Evangelou, E.; Shaheen, S.M. Influence of fly ash and sewage sludge application on wheat biomass production, nutrients availability, and soil properties. Int. J. Coal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, D.D.; Temizgül, A. Determination of heavy-metal concentration with chlorophyll contents of wheat (Triticum aestivum) exposed to municipal sewage sludge doses. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant 2014, 45, 2754–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Fawy, K.F.; Taher, M.A.; Hesham, A.; El-Shaboury, G.A.; Ahmed, M.T. Evaluation of the potential of sewage sludge as a valuable fertilizer for wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Gómez, I.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Jordán, M.M. The transfer of heavy metals to barley plants from soils amended with sewage sludge with different heavy metal burdens. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.M.; Plaza, C.; García-Gil, J.C.; Polo, A. Biochemical properties and barley yield in a semiarid Mediterranean soil amended with two kinds of sewage sludge. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Tsadilas, C.D.; Samaras, V. Trace element availability in a sewage sludge-amended cotton grown Mediterranean soil. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Fawy, K.F.; Taher, M.A.; Hesham, A.; El-Shaboury, G.A.; Ahmed, M.T. The evaluation of sewage sludge application as a fertilizer for broad bean (Faba sativa Bernh.) crops. Food Energy Secur. 2018, 7, e00142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Chopra, A.K. Accumulation and translocation of metals in soil and different parts of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) amended with sewage sludge. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 92, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Hesham, A.; Taher, M.A.; Fawy, K.F. The effects of different sewage sludge amendment rates on the heavy metal bioaccumulation, growth and biomass of cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16371–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waqas, M.; Khan, S.; Qing, H.; Reid, B.J.; Chao, C. The effects of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar on PAHs and potentially toxic element bioaccumulation in Cucumis sativa L. Chemosphere 2014, 105, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Strezov, V.; Chan, K.Y.; Nelson, P.F. Agronomic properties of wastewater sludge biochar and bioavailability of metals in production of cherry tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Vela, J.; Sellés, S.; Díaz-Crespo, C.; Navarro-Pedreňo, J.; Mataix-Beneyto, J.; Gómez, I. Effect of composted sewage sludge application to soil on sweet pepper crop (Capsicum annuum var. annuum) grown under two exploitation regimes. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonious, G.F.; Kochhar, T.S.; Coolong, T. Yield, quality, and concentration of seven heavy metals in cabbage and broccoli grown in sewage sludge and chicken manure amended soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2012, 47, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, Ö.; Sensoy, S.; Dursun, A.; Turan, M. Sewage sludge as a substitute for mineral fertilization of spinach (Spinacia oleraceae L.) at two growing periods. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2004, 54, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Chopra, A.K.; Srivastava, S. Assessment of heavy metals in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) grown in sewage sludge-amended soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Alrumman, S.A.; Hesham, A.; Taher, M.A.; Fawy, K.F. Effects of different sewage sludge applications on heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Int. J. Phytoremed. 2017, 19, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.L.; Dobermann, A.; Sander, D.H.; Cassman, K.G. Biosolids as nitrogen source for irrigated maize and rainfed sorghum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy metal tolerance in plants: Role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Husaini, Y.; Rai, L.C. Studies on nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism and the photosynthetic electron transport system of Nostoc linckia under cadmium stress. J. Plant Physiol. 1991, 138, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Laura, J.S. Effect of sewage irrigation on yield of pea and pigeon pea. J. Integr. Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, I.; Javaid, A.; Bajwa, R. Sewage farming and VA mycorrhiza III: Effect of sewage irrigation on growth, yield, nodulation and VA mycorrhizal colonization in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2000, 3, 967–968. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.N.; Paul, D. Impact of sewage water on seed germination and vigour index of Cicer arietinum L. and Pisum Sativum L. Int. J. Food Agric. Vet. Sci. 2013, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.A.; Lumsden, R.D.; Millner, P.D.; Keinath, A.P. Suppression of damping-off of peas and cotton in the field with composted sewage sludge. Crop Prot. 1992, 11, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, R.D.; Lewis, J.A.; Millner, P.D. Effect of sewage sludge on several soilborne pathogens and diseases. Phytopathology 1983, 73, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Stoffella, P.J. Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2005, 19, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.K. Germination and seedling growth of field pea Pisum sativum Malviya Matar-15(HUDP-15) and Pusa Prabhat (DDR-23) under varying level of copper and chromium. J. Am. Sci. 2008, 4, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.G.; Daniel, G.; Konjit, M.; Thomas, A.; Eyasu, S.S.; Awoke, G. Impact of textile waste water on seed germination and some physiological parameters in pea (Pisum sativum L.), lentil (Lens esculentum L.) and gram (Cicer arietinum L.). Asian J. Plant Sci. 2011, 10, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burzynski, M. The influence of lead and cadmium on the absorption and distribution of potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron in cucumber seedlings. Acta Physiol. Plant. 1987, 9, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, E.H.; Asp, H.; Bornman, J.F. Influence prior Cd+2 exposure on the uptake of Cd+2 and other elements in the phytochelatin-deficient mutant, cad1-3, of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Qamar, Z.; Waqas, M. The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13772–13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Yadav, S.; Mohan, D. Effect of distillery sludge on seed germination and growth parameters of green gram (Phaseolus mungo L.). J. Hazard Mater. 2008, 152, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides, 2nd ed.; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Adriano, D.C. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments. Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability and Risks of Metals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; Bell, M.J.; Wright, G.C.; Cozens, G.D. Uptake and partitioning of cadmium by cultivars of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Soil 2000, 222, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.; Pandey, V.; Shyam, R. Different antioxidative responses to cadmium in roots and leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Azad). J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme Codex Committee on Contaminants in Foods. In Proceedings of the FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme Fifth Session, Hague, The Netherlands, 21–25 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, S.; Chandraya, S.; Rai, V.; Bhattacharyya, A.K.; Ramanathan, A.L. Trannslocation of metals in pea plants grown on various amendment of electroplating industrial sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4467–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, E.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; Alamri, S.A.M.; Sewelam, N.A.; Galal, T.M.; Brima, E.I. Prediction models for evaluating heavy metal uptake by Pisum sativum L. in soil amended with sewage sludge. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2019, 55, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, P.J. Growth analysis formulae—Their use and abuse. Crop Sci. 1967, 7, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, B.M. Determination of chemical and physical soil properties. In Manual for Soil Analysis—Monitoring and Assessing Soil Bioremediation; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 47–95. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S. Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials; Blackwell Scientific Publications: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, M.; Singh, S.P. A review on phytoremediation of heavy metals and utilization of its byproducts. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2005, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, A.C.B.; Filho, H.G.; Lobo, T.F.; Lima, R.A.D.S. Composted sewage sludge in replacement of mineral fertilization on wheat production and development. J. Braz. Assoc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 36, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsoft. Statistica Version 7.1.; Statsoft Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]



| Properties | Sewage Sludge | Agricultural Soil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Values | Permissible Limits * | Measured Values | Average Normal Limits ** | |
| Salinity (mS/cm) | 1.39 ± 0.10 | NA | 0.07 ± 0.00 | NA |
| pH | 6.98 ± 0.02 | NA | 8.68 ± 0.02 | NA |
| Organic matter (%) | 65.0 ± 0.9 | NA | 0.9 ± 0.2 | NA |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 1.17 ± 0.08 | 20.0–40.0 | 2.91 ± 0.05 | 3.0 |
| Co (mg/kg) | 25.86 ± 1.31 | - | 35.49 ± 1.13 | 35.0 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 176.18 ± 1.94 | 900.0 | 134.34 ± 0.66 | 125.0 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 162.56 ± 2.32 | 1000.0–1750.0 | 15.01 ± 0.57 | 105.0 |
| Fe (mg/g) | 24.41 ± 0.52 | - | 42.37 ± 0.53 | 39.2 |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 560.70 ± 9.81 | - | 677.27 ± 3.23 | 775.0 |
| Mo (mg/kg) | 0.91 ± 0.04 | - | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 7.0 |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 138.73 ± 3.71 | 300.0–400.0 | 68.09 ± 3.70 | 40.0 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 671.11 ± 6.22 | 750.0–1200.0 | 3.51 ± 0.39 | 160.0 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 667.62 ± 13.44 | 2500.0–4000.0 | 77.18 ± 1.94 | 200.0 |
| Properties | Sewage Sludge Amendment Rate (g/kg) | F-value | Maximum Permissible Limits in Agricultural Soil † | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |||
| Salinity (mS/cm) | 0.35 ± 0.05 a | 0.47 ± 0.03 ab | 0.52 ± 0.02 ab | 0.55 ± 0.05 b | 0.58 ± 0.07 b | 4.0 * | NA |
| pH | 8.38 ± 0.07 e | 7.88 ± 0.03 d | 7.63 ± 0.03 c | 7.37 ± 0.03 b | 7.09 ± 0.01 a | 157.2 *** | NA |
| Organic matter (%) | 1.20 ± 0.15 a | 3.04 ± 0.11 b | 4.66 ± 0.18 c | 6.85 ± 0.26 d | 6.78 ± 0.06 d | 215.9 *** | NA |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 2.21 ± 0.17 a | 3.29 ± 0.23 b | 3.39 ± 0.09 b | 3.64 ± 0.03 b | 3.65 ± 0.09 b | 17.9 *** | 1.0–5.0 |
| Co (mg/kg) | 26.21 ± 0.27 a | 26.56 ± 0.10 a | 28.60 ± 1.88 ab | 28.70 ± 0.22 ab | 30.86 ± 0.31 b | 4.7 ** | 20.0–50.0 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 131.34 ± 3.72 a | 134.33 ± 4.23 ab | 139.82 ± 1.40 ab | 145.89 ± 1.13 b | 146.72 ± 4.41 b | 4.3 ** | 50.0–200.0 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 16.51 ± 0.64 a | 19.97 ± 1.30 a | 29.37 ± 0.78 b | 31.34 ± 3.03 b | 31.70 ± 0.09 b | 20.9 *** | 60.0–150.0 |
| Fe (mg/g) | 38.16 ± 0.39 a | 39.88 ± 0.34 a | 40.44 ± 0.82 a | 42.74 ± 1.68 a | 42.76 ± 6.05 a | 0.5 ns | 20.0–40.0 †† |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 587.5 ± 2.7 a | 607.6 ± 22.3 ab | 616.9 ± 7.2 ab | 621.6 ± 6.3 ab | 641.2 ± 2.0 b | 3.2 * | <450.0 ‡ |
| Mo (mg/kg) | 1.05 ± 0.12 a | 1.07 ± 0.10 a | 1.10 ± 0.01 a | 1.18 ± 0.02 a | 1.19 ± 0.06 a | 1.1 ns | 4.0–10.0 |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 31.30 ± 0.24 a | 32.11 ± 1.25 a | 32.71 ± 0.12 a | 34.88 ± 0.04 b | 35.02 ± 0.36 b | 7.8 *** | 20.0–60.0 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 3.27 ± 0.15 a | 3.43 ± 0.04 a | 3.85 ± 0.11 a | 3.97 ± 0.25 a | 4.73 ± 0.24 b | 10.5 *** | 20.0–30.0 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 71.18 ± 0.72 a | 72.42 ± 3.70 a | 100.70 ± 8.67 b | 102.08 ± 0.03 b | 108.52 ± 2.02 b | 16.9 *** | 100.0–300.0 |
| Metal | Tissue | Sewage Sludge Amendment Rate (g/kg) | F-Value | Safe Limit + | Phytotoxic Range ‡ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |||||
| Cd | Fruit | 0.21 ± 0.03 a | 0.24 ± 0.03 a | 0.24 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 a | 0.51 ± 0.00 b | 44.4 *** | 0.3 | 5–30 |
| Shoot | 0.24 ± 0.00 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 0.27 ± 0.02 a | 0.30 ± 0.02 a | 1.5 ns | |||
| Root | 0.42 ± 0.03 a | 0.53 ± 0.08 a | 0.68 ± 0.09 ab | 0.80 ± 0.01 b | 0.81 ± 0.09 b | 6.0 ** | |||
| Co | Fruit | 1.60 ± 0.01 a | 1.79 ± 0.13 ab | 1.93 ± 0.03 b | 3.17 ± 0.06 c | 4.60 ± 0.01 d | 399.6 *** | - | 30–40 |
| Shoot | 0.84 ± 0.10 a | 1.44 ± 0.07 b | 1.51 ± 0.03 b | 1.74 ± 0.12 bc | 2.03 ± 0.09 c | 25.6 *** | |||
| Root | 9.66 ± 0.24 a | 13.16 ± 1.69 b | 13.96 ± 0.59 b | 14.54 ± 0.12 b | 14.76 ± 0.30 b | 6.5 ** | |||
| Cr | Fruit | 1.44 ± 0.02 a | 2.52 ± 0.21 b | 4.09 ± 0.25 c | 4.84 ± 0.16 d | 5.33 ± 0.07 d | 94.9 *** | 5 | 10–100 |
| Shoot | 2.43 ± 0.06 a | 2.85 ± 0.13 ab | 3.63 ± 0.03 abc | 4.09 ± 0.74 bc | 5.14 ± 0.49 c | 7.0 ** | |||
| Root | 30.64 ± 4.64 a | 43.15 ± 7.29 a | 44.29 ± 3.38 a | 45.41 ± 3.58 a | 63.39 ± 2.32 b | 6.6 ** | |||
| Cu | Fruit | 4.97 ± 0.02 a | 6.08 ± 0.04 a | 6.94 ± 0.03 a | 9.35 ± 0.83 b | 11.83 ± 0.88 c | 26.1 *** | 40 | 20–100 |
| Shoot | 3.48 ± 0.48 a | 4.49 ± 0.27 a | 4.61 ± 0.04 a | 4.70 ± 0.01 a | 8.49 ± 0.52 b | 32.7 *** | |||
| Root | 4.48 ± 0.22 a | 14.66 ± 0.22 b | 16.00 ± 1.96 bc | 17.03 ± 1.03 bc | 18.77 ± 0.19 c | 31.4 *** | |||
| Fe | Fruit | 112.3 ± 4.2 a | 227.7 ± 39.9 b | 264.1 ± 45.3 bc | 281.9 ± 5.0 bc | 347.7 ± 11.9 c | 9.8 *** | 450 | >1000 |
| Shoot | 266.9 ± 28.7 a | 278.5 ± 43.9 a | 364.7 ± 33.2 a | 370.4 ± 76.9 a | 647.7 ± 53.7 b | 9.4 *** | |||
| Root | 8405.6 ± 1152.4 a | 12,189.6 ± 2123.5 a | 12,212.5 ± 890.9 a | 12,290.8 ± 910.3 a | 17,479.6 ± 251.6 b | 6.9 ** | |||
| Mn | Fruit | 43.2 ± 0.9 a | 85.3 ± 6.9 b | 93.5 ± 0.9 b | 167.0 ± 5.0 c | 218.2 ± 3.8 d | 274.8 *** | - | >400 |
| Shoot | 95.2 ± 10.5 a | 152.9 ± 3.5 b | 158.7 ± 2.5 b | 164.4 ± 0.6 b | 271.1 ± 1.2 c | 157.0 *** | |||
| Root | 366.7 ± 25.7 a | 380.1 ± 2.1 a | 391.3 ± 15.0 a | 416.1 ± 0.5 a | 454.1 ± 61.9 a | 1.3 ns | |||
| Mo | Fruit | 3.23 ± 0.12 a | 4.02 ± 0.01 b | 4.21 ± 0.07 b | 9.83 ± 0.13 c | 21.16 ± 0.21 d | 3632.6 *** | 10 | 135 |
| Shoot | 2.31 ± 0.11 a | 2.34 ± 0.12 a | 4.88 ± 0.59 b | 5.20 ± 0.65 b | 15.43 ± 0.84 c | 97.9 *** | |||
| Root | 1.87 ± 0.38 a | 3.16 ± 0.45 ab | 3.99 ± 0.89 ab | 4.88 ± 0.45 bc | 6.85 ± 1.14 c | 6.7 ** | |||
| Ni | Fruit | 5.17 ± 0.04 a | 5.20 ± 0.09 a | 5.88 ± 0.60 ab | 6.20 ± 0.07 ab | 6.57 ± 0.07 b | 4.9 ** | 20 | 40–246 |
| Shoot | 2.07 ± 0.31 a | 2.11 ± 0.08 a | 2.21 ± 0.01 a | 3.09 ± 0.13 b | 3.68 ± 0.36 b | 10.3 *** | |||
| Root | 21.07 ± 1.42 a | 22.72 ± 1.01 a | 23.36 ± 3.11 ab | 24.49 ± 0.59 ab | 29.30 ± 0.08 b | 3.7 * | |||
| Pb | Fruit | 0.39 ± 0.02 a | 0.41 ± 0.02 a | 0.44 ± 0.03 a | 0.49 ± 0.05 a | 1.02 ± 0.01 b | 77.4 *** | 5 | 30–300 |
| Shoot | 0.38 ± 0.05 a | 3.44 ± 0.21 b | 4.09 ± 0.31 b | 5.90 ± 0.44 c | 6.03 ± 0.32 c | 59.6 *** | |||
| Root | 5.05 ± 0.95 a | 6.36 ± 0.47 a | 6.55 ± 0.56 ab | 7.83 ± 1.02 ab | 9.31 ± 0.43 b | 4.9 ** | |||
| Zn | Fruit | 29.8 ± 0.3 a | 32.0 ± 0.5 b | 33.2 ± 0.3 c | 37.2 ± 0.2 d | 63.7 ± 0.2 e | 1925.9 *** | 60 | 100–500 |
| Shoot | 13.6 ± 1.4 a | 18.6 ± 1.0 ab | 19.3 ± 1.0 ab | 24.8 ± 0.1 b | 39.2 ± 3.5 c | 29.6 *** | |||
| Root | 51.3 ± 6.1 a | 62.9 ± 1.0 a | 69.7 ± 5.4 a | 69.8 ± 1.8 a | 148.2 ± 20.3 b | 15.5 *** | |||
| Y | A | SE | B | SE | R2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Fruit | 0.168 | 0.027 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.530 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 0.241 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.154 | 0.032 | |
| Root | 0.437 | 0.052 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.461 | 0.000 | |
| Co | Fruit | 1.142 | 0.152 | 0.074 | 0.006 | 0.833 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 0.978 | 0.073 | 0.027 | 0.003 | 0.743 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 10.899 | 0.666 | 0.116 | 0.027 | 0.393 | 0.000 | |
| Cr | Fruit | 1.624 | 0.153 | 0.101 | 0.006 | 0.904 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 2.299 | 0.297 | 0.066 | 0.012 | 0.518 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 31.819 | 3.617 | 0.678 | 0.148 | 0.429 | 0.000 | |
| Cu | Fruit | 4.434 | 0.433 | 0.170 | 0.018 | 0.767 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 3.103 | 0.395 | 0.102 | 0.016 | 0.591 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 7.998 | 1.098 | 0.310 | 0.045 | 0.630 | 0.000 | |
| Fe | Fruit | 141.751 | 21.614 | 5.250 | 0.882 | 0.558 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 214.941 | 42.742 | 8.536 | 1.745 | 0.461 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 8865.751 | 993.829 | 182.494 | 40.573 | 0.419 | 0.000 | |
| Mn | Fruit | 35.101 | 5.589 | 4.316 | 0.228 | 0.927 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 95.846 | 8.908 | 3.632 | 0.364 | 0.781 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 359.479 | 22.653 | 2.109 | 0.925 | 0.157 | 0.030 | |
| Mo | Fruit | 0.155 | 1.086 | 0.417 | 0.044 | 0.759 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 0.212 | 0.934 | 0.291 | 0.038 | 0.676 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 1.815 | 0.539 | 0.117 | 0.022 | 0.502 | 0.000 | |
| Ni | Fruit | 5.046 | 0.207 | 0.038 | 0.008 | 0.419 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 1.791 | 0.183 | 0.042 | 0.007 | 0.530 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 20.540 | 1.234 | 0.182 | 0.050 | 0.319 | 0.001 | |
| Pb | Fruit | 0.278 | 0.052 | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.595 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 1.218 | 0.308 | 0.138 | 0.013 | 0.810 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 5.020 | 0.540 | 0.100 | 0.022 | 0.421 | 0.000 | |
| Zn | Fruit | 24.582 | 2.313 | 0.731 | 0.094 | 0.681 | 0.000 |
| Shoot | 11.580 | 1.722 | 0.575 | 0.070 | 0.705 | 0.000 | |
| Root | 40.256 | 9.673 | 2.006 | 0.395 | 0.480 | 0.000 | |
| Metal | Factor | Sewage Sludge Amendment rate (g/kg) | F-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |||
| Cd | BF | 0.194 ± 0.008 ab | 0.156 ± 0.012 a | 0.196 ± 0.024 ac | 0.219 ± 0.005 bc | 0.219 ± 0.019 bc | 2.9 * |
| TFshoot | 0.582 ± 0.036 b | 0.566 ± 0.108 b | 0.426 ± 0.053 ab | 0.333 ± 0.028 a | 0.384 ± 0.013 ab | 3.7 * | |
| TFfruit | 0.501 ± 0.071 ab | 0.497 ± 0.083 ab | 0.404 ± 0.059 a | 0.308 ± 0.003 a | 0.675 ± 0.077 b | 4.3 ** | |
| Co | BF | 0.368 ± 0.005 a | 0.495 ± 0.063 a | 0.506 ± 0.054 a | 0.507 ± 0.001 a | 0.478 ± 0.007 a | 2.5 ns |
| TFshoot | 0.086 ± 0.009 a | 0.116 ± 0.010 ab | 0.108 ± 0.003 ab | 0.120 ± 0.009 b | 0.138 ± 0.009 b | 5.3 ** | |
| TFfruit | 0.166 ± 0.003 b | 0.141 ± 0.009 a | 0.139 ± 0.008 a | 0.218 ± 0.006 c | 0.312 ± 0.007 d | 113.6 *** | |
| Cr | BF | 0.239 ± 0.042 a | 0.331 ± 0.065 ab | 0.316 ± 0.021 ab | 0.312 ± 0.027 ab | 0.432 ± 0.009 b | 3.3 * |
| TFshoot | 0.091 ± 0.016 a | 0.074 ± 0.009 a | 0.084 ± 0.007 a | 0.086 ± 0.009 a | 0.080 ± 0.005 a | 0.4 ns | |
| TFfruit | 0.053 ± 0.008 a | 0.063 ± 0.006 ab | 0.093 ± 0.001 c | 0.112 ± 0.012 c | 0.085 ± 0.004 bc | 10.3 *** | |
| Cu | BF | 0.276 ± 0.024 a | 0.746 ± 0.038 b | 0.556 ± 0.082 b | 0.587 ± 0.089 b | 0.592 ± 0.006 b | 8.8 *** |
| TFshoot | 0.759 ± 0.071 c | 0.308 ± 0.023 ab | 0.309 ± 0.035 ab | 0.281 ± 0.017 a | 0.451 ± 0.023 b | 26.4 *** | |
| TFfruit | 1.122 ± 0.055 c | 0.415 ± 0.008 a | 0.468 ± 0.056 a | 0.545 ± 0.016 ab | 0.628 ± 0.040 b | 49.9 *** | |
| Fe | BF | 0.222 ± 0.032 a | 0.304 ± 0.051 ab | 0.305 ± 0.028 ab | 0.294 ± 0.033 ab | 0.452 ± 0.069 b | 3.5 * |
| TFshoot | 0.038 ± 0.009 a | 0.023 ± 0.001 a | 0.030 ± 0.001 a | 0.029 ± 0.004 a | 0.037 ± 0.003 a | 1.9 ns | |
| TFfruit | 0.014 ± 0.002 a | 0.019 ± 0.000 ab | 0.021 ± 0.002 b | 0.024 ± 0.002 b | 0.020 ± 0.001 ab | 4.7 ** | |
| Mn | BF | 0.625 ± 0.046 a | 0.629 ± 0.019 a | 0.639 ± 0.032 a | 0.669 ± 0.007 a | 0.709 ± 0.099 a | 0.5 ns |
| TFshoot | 0.256 ± 0.011 a | 0.403 ± 0.011 a | 0.407 ± 0.009 a | 0.395 ± 0.002 a | 0.656 ± 0.087 b | 13.3 *** | |
| TFfruit | 0.122 ± 0.011 a | 0.224 ± 0.017 a | 0.241 ± 0.012 a | 0.401 ± 0.012 b | 0.536 ± 0.081 b | 18.2 *** | |
| Mo | BF | 1.697 ± 0.174 a | 2.942 ± 0.420 ab | 3.591 ± 0.776 abc | 4.121 ± 0.346 bc | 5.609 ± 0.687 c | 7.5 *** |
| TFshoot | 1.642 ± 0.399 ab | 0.854 ± 0.159 a | 1.845 ± 0.559 ab | 1.176 ± 0.241 ab | 2.496 ± 0.292 b | 3.1 * | |
| TFfruit | 2.256 ± 0.531 ab | 1.420 ± 0.205 a | 1.425 ± 0.332 a | 2.089 ± 0.166 ab | 3.554 ± 0.560 b | 4.9 ** | |
| Ni | BF | 0.675 ± 0.051 a | 0.719 ± 0.059 a | 0.712 ± 0.093 a | 0.702 ± 0.017 a | 0.837 ± 0.010 a | 1.3 ns |
| TFshoot | 0.095 ± 0.008 a | 0.093 ± 0.001 a | 0.104 ± 0.014 ab | 0.126 ± 0.003 b | 0.125 ± 0.012 ab | 3.2 * | |
| TFfruit | 0.251 ± 0.015 a | 0.230 ± 0.006 a | 0.257 ± 0.009 a | 0.254 ± 0.009 a | 0.224 ± 0.003 a | 2.6 ns | |
| Pb | BF | 1.624 ± 0.360 a | 1.862 ± 0.154 a | 1.730 ± 0.195 a | 2.092 ± 0.382 a | 2.014 ± 0.183 a | 0.5 ns |
| TFshoot | 0.081 ± 0.007 a | 0.557 ± 0.059 b | 0.668 ± 0.109 b | 0.877 ± 0.209 b | 0.658 ± 0.054 b | 7.1 ** | |
| TFfruit | 0.095 ± 0.019 a | 0.067 ± 0.008 a | 0.071 ± 0.010 a | 0.075 ± 0.018 a | 0.111 ± 0.005 a | 1.9 ns | |
| Zn | BF | 0.726 ± 0.094 a | 0.884 ± 0.059 a | 0.743 ± 0.118 a | 0.683 ± 0.017 a | 1.386 ± 0.213 b | 5.9 ** |
| TFshoot | 0.267 ± 0.006 a | 0.296 ± 0.020 ab | 0.292 ± 0.037 ab | 0.357 ± 0.008 b | 0.274 ± 0.014 a | 3.1 * | |
| TFfruit | 0.629 ± 0.081 a | 0.508 ± 0.001 a | 0.493 ± 0.043 a | 0.535 ± 0.012 a | 0.474 ± 0.064 a | 1.5 ns | |
| F-valueBF | 17.7 *** | 33.4 *** | 15.6 *** | 53.2 *** | 46.0 *** | ||
| F-valueTFshoot | 15.1 *** | 17.3 *** | 8.7 *** | 13.4 *** | 54.3 *** | ||
| F-valueTFfruit | 16.4 *** | 34.5 *** | 14.0 *** | 126.4 *** | 32.7 *** | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eid, E.M.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Taher, M.A.; Alrumman, S.A.; Galal, T.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; Sewelam, N.A.; Ahmed, M.T. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation, Growth Characteristics, and Yield of Pisum sativum L. Grown in Agricultural Soil-Sewage Sludge Mixtures. Plants 2020, 9, 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101300
Eid EM, El-Bebany AF, Taher MA, Alrumman SA, Galal TM, Shaltout KH, Sewelam NA, Ahmed MT. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation, Growth Characteristics, and Yield of Pisum sativum L. Grown in Agricultural Soil-Sewage Sludge Mixtures. Plants. 2020; 9(10):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101300
Chicago/Turabian StyleEid, Ebrahem M., Ahmed F. El-Bebany, Mostafa A. Taher, Sulaiman A. Alrumman, Tarek M. Galal, Kamal H. Shaltout, Nasser A. Sewelam, and Mohamed T. Ahmed. 2020. "Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation, Growth Characteristics, and Yield of Pisum sativum L. Grown in Agricultural Soil-Sewage Sludge Mixtures" Plants 9, no. 10: 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101300
APA StyleEid, E. M., El-Bebany, A. F., Taher, M. A., Alrumman, S. A., Galal, T. M., Shaltout, K. H., Sewelam, N. A., & Ahmed, M. T. (2020). Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation, Growth Characteristics, and Yield of Pisum sativum L. Grown in Agricultural Soil-Sewage Sludge Mixtures. Plants, 9(10), 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101300