Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Larvicidal Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Plumbago auriculata Lam
Abstract
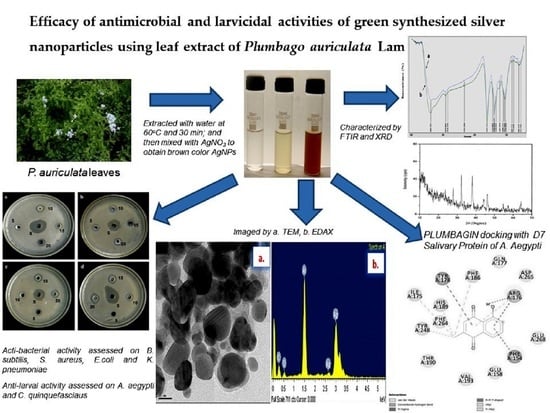
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of AgNPs Synthesized Using Plumbago auriculata Lam
2.2. Antibacterial Activity
2.3. Larvicidal Activity of Synthesis AgNPs
2.4. Molecular Docking-Mosquito Salivary Proteins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Plumbago auriculata Lam. Aqueous Extract
3.3. Synthesis of AgNPs Aqueous Extract Using P. auriculata
3.4. Characterization of AgNPs
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
3.6. Collection of Mosquitos’ Larvae
3.7. Bioassay for Larvicidal Activity
3.8. In Silico Docking Study
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.U.; Anjum, S.I.; Ansari, M.J.; Khan, M.H.U.; Kamal, S.; Rahman, K.; Shoaib, M.; Man, S.; Khan, A.J.; Khan, S.U.; et al. Antimicrobial potentials of medicinal plant’s extract and their derived silver nanoparticles: A focus on honey bee pathogen. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lediga, M.E.; Malatjie, T.S.; Olivier, D.K.; Ndinteh, D.T.; van Vuuren, S.F. Biosynthesis and characterisation of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles from a selection of fever-reducing medicinal plants of South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2018, 119, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, A.; Nayak, B.K.; Moorthy, K. Antimicrobial properties of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized from phylloplane fungus, Aspergillus tamarii. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Massarani, S.; El-Shaibany, A.; Tabanca, N.; Ali, A.; Estep, A.S.; Becnel, J.J.; Goger, F.; Demirci, B.; El-Gamal, A.; Husnu Can Baser, K. Assessment of selected Saudi and Yemeni plants for mosquitocidal activities against the yellow fever mosquito Aedesaegypti. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Hyder, M.Z.; Liaqat, I.; Scholz, M. Climatic Conditions: Conventional and Nanotechnology-Based Methods for the Control of Mosquito Vectors Causing Human Health Issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.I.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Venkatesalu, V. Chicory (Cichoriumintybus) and wormwood (Artemisia absinthium) extracts exhibit strong larvicidal activity against mosquito vectors of malaria, dengue fever, and filariasis. Parasit Int. 2018, 67, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, S.Z.A.; Ahmed, S.S.Z.; Sathyan, J.; Mahboob, M.R.; Venkatesh, K.P.; Ramesh, K. A comparative study on larvicidal potential of selected medicinal plants over green synthesized silver nano particles. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminade, C.; Marie McIntyre, K.; Jones, A.E. Impact of recent and future climate change on vector-borne diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1436, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowndarya, P.; Ramkumar, G.; Shivakumar, M.S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles conjugated Clausenadentata plant leaf extract and their insecticidal potential against mosquito vectors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavela, R.; Maggi, F.; Lannarelli, R.; Benelli, G. Plant extracts for developing mosquito larvicides: From laboratory to field, with insights on the modes of action. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 236–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, U.; Murugan, K.; Panneerselvam, C.; Rajaganesh, R.; Roni, M.; Aziz, A.T.; Al-Aoh, H.A.N.; Trivedi, S.; Rehman, H.; Kumar, S.; et al. Suaedamaritima-based herbal coils and green nanoparticles as potential biopesticides against the dengue vector Aedesaegypti and the tobacco cutworm Spodopteralitura. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 101, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneetha Pandiyan, G.; Mathew, N.; Munusamy, S. Larvicidal activity of selected essential oil in synergized combinations against Aedesaegypti. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarzebski, M.; Siejak, P.; Smułek, W.; Fathordoobady, F.; Guo, Y.; Pawlicz, J.; Trzeciak, T.; Kowalczewski, P.L.; Kitts, D.D.; Singh, A.; et al. Plant Extracts Containing Saponins Affects the Stability and Biological Activity of Hempseed Oil Emulsion System. Molecules 2020, 25, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, G.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Murugesan, K. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fruit extract of Cleome viscosa L. against antibacterial and anticancer activity. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Med. 2018, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kitts, D.D.; Singh, A.; Fathordoobady, F.; Doi, B.; Pratap-Singh, A. Plant Extracts Inhibit the Formation of Hydroperoxides and Help Maintain Vitamin E Levels and Omega-3 Fatty Acids During High Temperature Processing and Storage of Hempseed and Soybean oils. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathordoobady, F.; Singh, A.; Kitts, D.D.; Pratap-Singh, A. Hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) Extract: Anti-Microbial Properties, Methods of Extraction, and Potential Oral Delivery. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Jha, S.; Ramteke, S.; Jain, N.K. Pharmaceutical aspects of silver nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, s115–s126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. Green’ synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marslin, G.; Siram, K.; Maqbool, Q.; Selvakesavan, R.K.; Kruszka, D.; Kachlicki, P.; Franklin, G. Secondary Metabolites in the Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles. Materials 2018, 11, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Rifaqat, A.H.; Rao, A.K. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumitha, G.; Rajakumar, G.; Mohana Roopan, S.; Abdul Rahuman, A.; Mohana Priya, K.; Mary Saral, A.; Nawaz Khan, F.; Gopiesh Khanna, V.; Velayutham, K.; Jayaseelan, C.; et al. Acaricidal, insecticidal, and larvicidal efficacy of fruit peel aqueous extract of Annona squamosa and its compounds against blood-feeding parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohana Roopan, S.; Elango, G. Exploitation of Cocos nucifera a non-food toward the biological and nanobiotechnology field. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Fu, B.; Jiang, L.; Sun, T. Biosynthesis, characterization, and anticancer effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Coptischinensis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burlacu, E.; Tanase, C.; Coman, N.; Berta, L. A Review of Bark-Extract-Mediated Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruddarajua, L.K.; Pammi, S.V.N.; Guntukuc, G.S.; Padavalaa, V.S.; Kolapalli, V.R.M. A review on anti-bacterials to combat resistance: From ancient era of plants and metals to present and future perspectives of green nano technological combinations. Asian J. Pharm. 2020, 15, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, A.; Mousakhani-Ganjeh, A.; Amiri, Z.; Guo, Y.; Pratap-Singh, A.; Kenari, R.E. Fabrication of cumin loaded-chitosan particles: Characterized by molecular, morphological, thermal, antioxidant and anticancer properties as well as its utilization in food system. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Chávez, P.; Perez-Gonzalez, J.; Salgadogarciglia, R.; Ramírez-Chávez, E.; Molina-Torres, J.; Martinez-Trujillo, M.; Carreon-Abud, Y. Antibacterial and cytotoxicity activities and phytochemical analysis of three ornamental plants grown in Mexico. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91, e20180468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaryal, N.; Kaur, H.J. Plumbago auriculata leaf extract-mediated AgNPs and its activities as antioxidant, anti-TB and dye degrading agents. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniafu, B.M.; Wilber, L.; Ndiege, I.O.; Wanjala, C.C.; Akenga, T.A. Larvicidal activity of extracts from three Plumbagospp against Anopheles gambiae. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradeepa, V.; Narayanan, S.S.; Kirubakaran, S.A.; Nathan, S.S. Antimalarial efficacy of dynamic compound of plumbagin chemical constituent from Plumbagozeylanica Linn (Plumbaginaceae) against the malarial vector Anopheles stephensi Liston (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3105–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Gholamhoseinpoor, F. A study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moteriya, P.; Chanda, S. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Caesalpinia pulcherrima flower extract and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and genotoxic activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Zhan, G.; Zheng, B.; Sun, D.; Lu, F.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles by Cacumen Platyclade Extract: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism, and Antibacterial Activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9095–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, R.; Dhanasingh, S.; Kalimuthu, B.; Uthirappan, M.; Rose, C.; Mandal, A.B. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cocciniagrandis leaf extract and its application in the photocatalytic degradation. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 94, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Panghal, M.; Kadyan, S.; Chaudhary, U.; Yadav, J.P. Green silver nanoparticles of Phyllanthus amarus: As an antibacterial agent against multi drug resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alomar, T.S.; AlMasoud, N.; Awad, M.A.; El-Tohamy, M.F.; Soliman, D.A. An eco-friendly plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 249, 123007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Wang, M. Biocompatible fungal chitosan encapsulated phytogenic silver nanoparticles enhanced antidiabetic, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzębski, M.; Fathordoobady, F.; Guo, Y.; Xu, M.; Singh, A.; Kitts, D.D.; Kowalczewski, P.L.; Jeżowski, P.; Pratap-Singh, A. Pea Protein for Hempseed Oil Nanoemulsion Stabilization. Molecules 2019, 24, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arakha, M.; Saleem, M.; Mallick, B.C.; Jha, S. The effects of interfacial potential on antimicrobial propensity of ZnO nanoparticle. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.D.L.; Fernandes, D.A.; Nunes, F.C.; Teles, Y.C.F.; Rolim, Y.M.; da Silva, C.M.; de Albuquerque, J.B.L.; de Fatima Agra, M.; de Souza, M.D.F.V. Phytochemical study of Waltheria viscosissima and evaluation of its larvicidal activity against Aedesaegypti. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, J.; Labade, D.; Shankar, K.; Kata, N.; Chaudhari, M.; Wani, M.; Khetmalas, M. In vitro callus induction and estimation of plumbagin content from Plumbago auriculata Lam. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 52, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiktor, A.; Mandal, R.; Singh, A.; Pratap-Singh, A. Pulsed Light treatment below a Critical Fluence (3.82 J/cm2) minimizes photo-degradation and browning of a model Phenolic (Gallic Acid) Solution. Foods 2019, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Shajahan, A.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Kaviyarasan, V. Fungal chitosan-based nanocomposites sponges—An alternative medicine for wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Ruth, H.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDock Tools 4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuttelkopf, A.W.; Van Aalten, D.M.F. PRODRG: A tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein ligand complexes. Acta Crystallogr. D 2004, 60, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Bacillus subtilis | Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | Klebsiella pneumoniae | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA-AgNPs (μg/mL) | Zone of inhibition (mm) | |||
| 5 | 8 ± 0.5 | 10 ± 1.5 | 10 ± 0.8 | 11 ± 0.5 |
| 10 | 10 ± 1.7 | 10 ± 0.8 | 10 ± 0.6 | 11 ± 0.8 |
| 15 | 8 ± 0.9 | 8 ± 0.7 | 12 ± 1.0 | 12 ± 1.0 |
| 20 | 8 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 1.5 | 12 ± 2.5 | 14 ± 1.7 |
| Streptomycin (20) | 18 ± 2.0 | 15 ± 2.8 | 15 ± 3.7 | 18 ± 1.5 |
| Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) | ||||
| PA-AgNPs (μg/mL) | 10 ± 0.5 | 6 ± 0.5 | 8 ± 0.5 | 10 ± 0.8 |
| Species | Concentration (µg/mL) | Mortality (24 h) | LC50 (µg/mL) | LUL-UCL (µg/mL) | r2 | Regression Equation |
| Aedes aegypti | 100 | 95.0 | 45.1 | 37.4 −54.3 | 0.986 | Y = 0.787X + 15.9 |
| 80 | 80.7 | |||||
| 60 | 61.0 | |||||
| 40 | 44.0 | |||||
| 20 | 34.7 | |||||
| Species | Concentration (µg/mL) | Mortality (24 h) | LC50 (µg/mL) | LUL-UCL (µg/mL) | r2 | Regression Equation |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | 100 | 91.0 | 41.1 | 34.6–48.9 | 0.997 | Y = 0.785X + 15.8 |
| 80 | 83.5 | |||||
| 60 | 65.0 | |||||
| 40 | 41.5 | |||||
| 20 | 33.5 |
| Sl. No | Compound | Dock Score (kcal/mol) | Inhibitory Constant | H Bond Interactions (H-D…A) | Distance (Å) |
| Plumbagin with 3DXL (Aedes aegypti) | |||||
| 1 | Co-Crystal (Epinephrine) | −5.80 | 55.64 uM | O-H…O Ile 175 Tyr 178 O-H…N His 189 N(E2)-H…O | 3.1 2.9 3.4 |
| 2 | Plumbagin | −6.71 | 12.1 uM | O-H…O Arg 176 His 189 N(E2)-H…O | 2.7 3.1 |
| Plumbagin with 3OGN (Culex quinquefasciatus) | |||||
| 3 | Co-Crystal (Hexadecanolide) | −7.82 | 1.84 uM | -- | -- |
| 4 | Plumbagin | −7.48 | 3.31 uM | PHE 123 N-H…O O-H…O PHE 123 | 2.7 2.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Govindan, L.; Anbazhagan, S.; Altemimi, A.B.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Kuppan, S.; Pratap-Singh, A.; Kandasamy, M. Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Larvicidal Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Plumbago auriculata Lam. Plants 2020, 9, 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111577
Govindan L, Anbazhagan S, Altemimi AB, Lakshminarayanan K, Kuppan S, Pratap-Singh A, Kandasamy M. Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Larvicidal Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Plumbago auriculata Lam. Plants. 2020; 9(11):1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111577
Chicago/Turabian StyleGovindan, Lakshmanan, Sathiyaseelan Anbazhagan, Ammar B. Altemimi, Karthik Lakshminarayanan, Sivaranjan Kuppan, Anubhav Pratap-Singh, and Murugesan Kandasamy. 2020. "Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Larvicidal Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Plumbago auriculata Lam" Plants 9, no. 11: 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111577
APA StyleGovindan, L., Anbazhagan, S., Altemimi, A. B., Lakshminarayanan, K., Kuppan, S., Pratap-Singh, A., & Kandasamy, M. (2020). Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Larvicidal Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Plumbago auriculata Lam. Plants, 9(11), 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111577