A Global ETCCDI-Based Precipitation Climatology from Satellite and Rain Gauge Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Rain Gauge Measurements
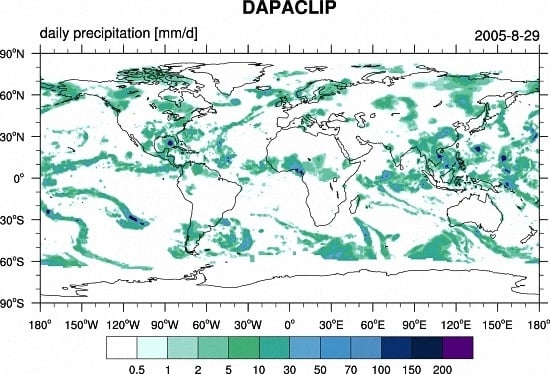
2.2. Satellite Remote Sensing
2.3. Data Merging
2.4. ETCCDI
3. Results
3.1. Global Climatology
3.2. Europe
3.3. Monsoon Asia
4. Summary and Discussion
5. Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marotzke, J.; Müller, W.A.; Vamborg, F.S.E.; Becker, P.; Cubasch, U.; Feldmann, H.; Kaspar, F.; Kottmeier, C.; Marini, C.; Polkova, I.; et al. MiKlip—A national research project on decadal climate prediction. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.-P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Morrissey, M.M.; Bolvin, D.T.; Curtis, S.; Joyce, R.; McGavock, B.; Susskind, J. Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G. Improving the global precipitation record: GPCP Version 2.1. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V. Global observed long-term changes in temperature and precipitation extremes: A review of progress and limitations in IPCC assessments and beyond. Weather Clim. Extremes 2016, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillmann, J.; Kharin, V.V.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Bronaugh, D. Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: Part 1. Model evaluation in the present climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1716–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillmann, J.; Kharin, V.V.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Bronaugh, D. Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: Part 2. Future climate projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2473–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Kunkel, K.E.; Wehner, M.F.; Sun, L. Detection and attribution of climate extremes in the observed record. Weather Clim. Extremes 2016, 11, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raykova, K. Trendanalysen Von Niederschlagsextremen Und Untersuchung Der Extremwertverteilung Basierend Auf Täglichen Stationsmessungen von 1988 bis 2013. Master Thesis, Goethe University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vose, S.V.; Peterson, T.C.; Schmoyer, R.L.; Eischeid, J.K. The global historical climatology network: A preview of version 2.75. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Meteorological Society, Diamond Anniversary, United States of America, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–20 January 1995.
- Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Wijngard, J.B.; Können, G.P.; Böhm, R.; Demaree, G.; Gocheva, A.; Mileta, M.; Pashiardis, S.; Hejkrlik, L.; Kern-Hansen, C.; et al. Daily dataset of 20th-century surface air temperature and precipitation series for the European Climate Assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schamm, K.; Ziese, M.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Schneider, U.; Schröder, M.; Stender, P. Global gridded precipitation over land: A description of the new GPCC First Guess Daily product. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2014, 6, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.; Rowe, C.; Philpot, W. A sensitivity analysis of some common assumptions associated with grid-point interpolation and contouring. Am. Cartogr. 1985, 12, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krige, D. Lognormal-de Wijsian Geostatistics for Ore Evolution; South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1981; pp. 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shepard, D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM National Conference, New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 517–524. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Ziese, M.; Rudolf, B. GPCC’s new land surface precipitation climatology based on quality-controlled in-situ data and its role in quantifying the global water cycle. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rudolf, B.; Ziese, M. GPCC Full Data Reanalysis Version 7.0 at 1.0°: Monthly land-surface precipitation from rain-gauges built on GTS-based and historic data. Deutsch. Wetterd. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, J. An alternative measure of the reliability of ordinary kriging estimates. Math. Geol. 2000, 32, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring. Available online: http://cmsaf.eu (accessed on 21 November 2016).
- Hamburg Ocean Atmosphere Parameters and Fluxes from Satellite Data. Available online: http://hoaps.org (accessed on 21 November 2016).
- Andersson, A.; Fennig, K.; Klepp, C.; Bakan, S.; Grassl, H.; Schulz, J. The Hamburg Ocean atmosphere parameters and fluxes from satellite data—HOAPS-3. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2010, 2, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennig, K.; Andersson, A.; Bakan, S.; Klepp, C.; Schröder, M. Hamburg Ocean atmosphere parameters and fluxes from satellite data — HOAPS-3.2 — monthly means/6-hourly composites. Satell. Appl. Facil. Clim. Monit. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Fennig, K.; Schröder, M. Algorithm theoretical basis document HOAPS release 3.2. Satell. Appl. Facil. Clim. Monit. 2011, 1, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, A.; Ziese, M.; Dietzsch, F.; Schröder, M.; Becker, A.; Schamm, K. HOAPS/GPCC European Daily Precipitation Data Record With Uncertainty Estimates Using Satellite and Gauge Based Observations at 0.5°; Deutscher Wetterdienst: Offenbach, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Ziese, M.; Dietzsch, F.; Schröder, M.; Becker, A.; Schamm, K. HOAPS/GPCC Global Daily Precipitation Data Record With Uncertainty Estimates Using Satellite and Gauge Based Observations at 1.0°; Deutscher Wetterdienst: Offenbach, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Ziese, M.; Dietzsch, F.; Schröder, M.; Becker, A.; Schamm, K. HOAPS/GPCC Global Daily Precipitation Data Record With Uncertainty Estimates Using Satellite and Gauge Based Observations at 2.5°; Deutscher Wetterdienst: Offenbach, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HOAPS/GPCC global daily precipitation data record with uncertainty estimates using satellite and gauge based observations Version 1. Available online: ftp://ftp.dwd.de/pub/data/gpcc/html/HOGP_V001.html (accessed on 19 October 2016).
- CLIMDEX. Datesets for Indices of Climate Extremes. Available online: http://climdex.org (accessed on 26 September 2016).
- Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X. Guidelines on Analysis of Extremes in a Changing Climate in Support of Informed Decisions for Adaptation; World Meteorological Organisation (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.C. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, B.; Rapp, J. Das Jahrhunderthochwasser der Elbe: Synoptische Entwicklung und klimatologische Aspekte. In Klimastatusbericht 2002; Deutscher Wetterdienst: Offenbach(Main), Germany, 2002; pp. 172–187. [Google Scholar]
- Hazeleger, W.; Wang, X.; Severijns, C.; Ştefănescu, S.; Bintanja, R.; Sterl, A.; Wyser, K.; Semmler, T.; Yang, S.; van den Hurk, B.; et al. EC-Earth V2.2: description and validation of a new seamless earth system prediction model. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 2611–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.-P.; Misra, V.; Chassignet, E.P. The El Niño and Southern Oscillation in the historical centennial integrations of the new generation of climate models. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Index | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| cdd | Maximum number of Consecutive Dry Days | days |
| cwd | Maximum number of Consecutive Wet Days | days |
| r10 | Number of days with more than 10 mm of precipitation | days |
| r20 | Number of days with more than 20 mm of precipitation | days |
| r95p | 95th percentile of the daily precipitation amount | mm·day−1 |
| r99p | 99th percentile of the daily precipitation amount | mm·day−1 |
| rx1 | Maximum precipitation sum of one day | mm |
| rx5 | Maximum precipitation sum of five consecutive days | mm |
| sdii | Simple Daily Intensity Index | mm·day−1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dietzsch, F.; Andersson, A.; Ziese, M.; Schröder, M.; Raykova, K.; Schamm, K.; Becker, A. A Global ETCCDI-Based Precipitation Climatology from Satellite and Rain Gauge Measurements. Climate 2017, 5, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5010009
Dietzsch F, Andersson A, Ziese M, Schröder M, Raykova K, Schamm K, Becker A. A Global ETCCDI-Based Precipitation Climatology from Satellite and Rain Gauge Measurements. Climate. 2017; 5(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleDietzsch, Felix, Axel Andersson, Markus Ziese, Marc Schröder, Kristin Raykova, Kirstin Schamm, and Andreas Becker. 2017. "A Global ETCCDI-Based Precipitation Climatology from Satellite and Rain Gauge Measurements" Climate 5, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5010009
APA StyleDietzsch, F., Andersson, A., Ziese, M., Schröder, M., Raykova, K., Schamm, K., & Becker, A. (2017). A Global ETCCDI-Based Precipitation Climatology from Satellite and Rain Gauge Measurements. Climate, 5(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5010009