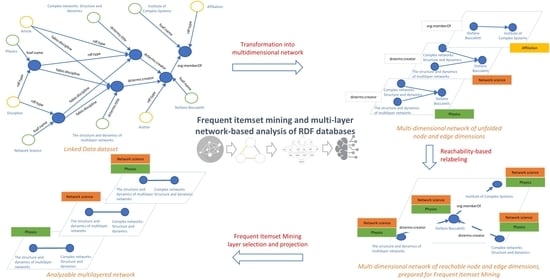
Frequent Itemset Mining and Multi-Layer Network-Based Analysis of RDF Databases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The RDF databases are represented as multidimensional networks in Section 2.
- We propose a frequent itemset mining-based method to extract information from the multidimensional network in Section 3.
- The resultant frequent itemsets of multidimensional networks can be represented as a multi-layer network that can be analysed by metrics presented in Section 4.
- We present the methodology through an example in which we uncover the scientific realms of climate change and sustainability, including an alternative co-author, co-organisational network ranking used to measure the impact of authors in multiple disciplines in Section 5.
2. Multidimensional Network-Based Representation of RDF Databases
3. Frequent Itemset Mining in Multidimensional Networks
4. Analysis of the Resulted Multilayer Network
5. Results
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Musto, C.; Narducci, F.; Lops, P.; de Gemmis, M.; Semeraro, G. Linked open data-based explanations for transparent recommender systems. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2019, 121, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayo, J.E.L.; Jeuring, J.; Rodríguez, J.M.Á. Inductive representations of RDF graphs. Sci. Comput. Program. 2014, 95, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzein, N.M.; Majid, M.A.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Yaqoob, I.; Alaba, F.A.; Imran, M. Managing big RDF data in clouds: Challenges, opportunities, and solutions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyne, G.; Carroll, J.J.; McBride, B. RDF 1.1 Concepts and Abstract Syntax. 2014. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/rdf11-concepts (accessed on 25 February 2014).
- Hayes, J.; Patel-Schneider, P.F. RDF 1.1 Semantics. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/rdf11-mt (accessed on 25 February 2014).
- Papadaki, M.E.; Spyratos, N.; Tzitzikas, Y. Towards Interactive Analytics over RDF Graphs. Algorithms 2021, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.; Gutierrez, C. Bipartite graphs as intermediate model for RDF. In Proceedings of the International Semantic Web Conference, Hiroshima, Japan, 7–11 November 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Shadbolt, N.; Berners Lee, T.; Hall, W. The semantic web revisited. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2006, 21, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decker, S.; Melnik, S.; Van Harmelen, F.; Fensel, D.; Klein, M.; Broekstra, J.; Erdmann, M.; Horrocks, I. The semantic web: The roles of XML and RDF. IEEE Internet Comput. 2000, 4, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalampokis, E.; Zeginis, D.; Tarabanis, K. On modeling linked open statistical data. J. Web Semant. 2019, 55, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadbolt, N.; O’Hara, K. Linked data in government. IEEE Internet Comput. 2013, 17, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callahan, A.; Cruz-Toledo, J.; Ansell, P.; Dumontier, M. Bio2RDF release 2: Improved coverage, interoperability and provenance of life science linked data. In Proceedings of the Extended Semantic Web Conference, Montpellier, France, 26–30 May 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Jentzsch, A.; Zhao, J.; Hassanzadeh, O.; Cheung, K.H.; Samwald, M.; Andersson, B. Linking Open Drug Data. In Proceedings of the I-Semantics, the 5th International Conference on Semantic Systems, Graz, Austria, 2–4 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cimiano, P.; Chiarcos, C.; McCrae, J.P.; Gracia, J. Representing Annotated Texts as RDF. In Linguistic Linked Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 61–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ermilov, I.; Martin, M.; Lehmann, J.; Auer, S. Linked open data statistics: Collection and exploitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and the Semantic Web, St. Petersburg, Russia, 7–9 October 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Marie, N.; Gandon, F. Survey of linked data based exploration systems. In Proceedings of the IESD 2014—Intelligent Exploitation of Semantic Data, Riva del Garda, Italy, 20 October 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fensel, D.; Van Harmelen, F.; Horrocks, I.; McGuinness, D.L.; Patel-Schneider, P.F. OIL: An ontology infrastructure for the semantic web. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2001, 16, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabasi, A.l.; Frangos, J. Linked: The New Science of Networks; American Association of Physics Teachers: College Park, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Özsu, M.T. Graph-based RDF data management. Data Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil, R.; García, R.; Delgado, J. Measuring the semantic web. AIS SIGSEMIS Bull. 2004, 1, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bellomi, F.; Bonato, R. Network analysis for Wikipedia. In Proceedings of the Wikimania, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 4–8 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mika, P. Flink: Semantic web technology for the extraction and analysis of social networks. Web Semant. Sci. Serv. Agents World Wide Web 2005, 3, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano-Morales, E.P.; Ah-Pine, J.; Loudcher, S. Hypergraph Modelization of a Syntactically Annotated English Wikipedia Dump. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2016), Portoroz, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Palla, G.; Farkas, I.J.; Pollner, P.; Derényi, I.; Vicsek, T. Fundamental statistical features and self-similar properties of tagged networks. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 123026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollner, P.; Palla, G.; Vicsek, T. Clustering of tag-induced subgraphs in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2010, 389, 5887–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palla, G.; Tibély, G.; Mones, E.; Pollner, P.; Vicsek, T. Hierarchical networks of scientific journals. Palgrave Commun. 2015, 1, 15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passant, A. Measuring Semantic Distance on Linking Data and Using it for Resources Recommendations. In Proceedings of the AAAI spring symposium: Linked Data Meets Artificial Intelligence, Stanford, CA, USA, 22–24 March 2010; Volume 77, p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivam, G.S.; Saranya, K.; Karrthik, K. Hypergraph-based Wikipedia search with semantics. Int. J. Web Sci. 2013, 2, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirizzi, R.; Ragone, A.; Di Noia, T.; Di Sciascio, E. Ranking the Linked Data: The Case of DBpedia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Engineering, Vienna, Austria, 5–9 July 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 337–354. [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia, V.; Latora, V. Measuring and modeling correlations in multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 032805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boccaletti, S.; Bianconi, G.; Criado, R.; Del Genio, C.I.; Gómez-Gardenes, J.; Romance, M.; Sendina-Nadal, I.; Wang, Z.; Zanin, M. The structure and dynamics of multilayer networks. Phys. Rep. 2014, 544, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yu, T.; Sheng, H.; Luo, Z.; Mao, Y. Semantic text mining with linked data. In Proceedings of the 2009 Fifth International Joint Conference on INC, IMS and IDC, Seoul, Korea, 25–27 August 2009; pp. 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, Q.; Saleem, M.; Sahay, R.; Ngomo, A.C.N.; D’Aquin, M. QPPDs: Querying Property Paths Over Distributed RDF Datasets. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 101031–101045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosup, A.; Hegeman, T.; Ngai, W.L.; Heldens, S.; Prat-Pérez, A.; Manhardto, T.; Chafio, H.; Capotă, M.; Sundaram, N.; Anderson, M.; et al. LDBC Graphalytics: A benchmark for large-scale graph analysis on parallel and distributed platforms. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2016, 9, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadaki, M.E.; Tzitzikas, Y.; Spyratos, N. Analytics over RDF Graphs. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1197, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, L.; Li, D. Research on partitioning algorithm based on RDF graph. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2019, 5600–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailis, T.; Kotidis, Y.; Nikolopoulos, V.; Kharlamov, E.; Horrocks, I.; Ioannidis, Y. An efficient index for RDF query containment. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Management of Data, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 30 June–5 July 2019; pp. 1499–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Morzy, M.; Ławrynowicz, A.; Zozuliński, M. Using substitutive itemset mining framework for finding synonymous properties in linked data. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 9202, pp. 422–430. [Google Scholar]
- Boytcheva, S.; Angelova, G.; Angelov, Z.; Tcharaktchiev, D.; Vodenicharov, V. Enrichment of EHR with linked open data for risk factors identification. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies (CompSysTech’19), Ruse, Bulgaria, 21–22 June 2019; pp. 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Harth, A.; Hose, K.; Karnstedt, M.; Polleres, A.; Sattler, K.U.; Umbrich, J. Data Summaries for On-Demand Queries over Linked Data. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, Raleigh, NC, USA, 26–30 April 2010; pp. 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- WSW Group. SPARQL 1.1 Overview. 2013. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/sparql11-overview (accessed on 21 March 2013).
- Hertig, H.P. Universities, Rankings and the Dynamics of Global Higher Education. Perspectives from Asia, Europe and North America; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkkila, T.; Piironen, O. Rankings and Global Knowledge Governance: Higher Education, Innovation and Competitiveness; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aleman-Meza, B.; Halaschek-Weiner, C.; Arpinar, I.B.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Sheth, A.P. Ranking complex relationships on the semantic web. IEEE Internet Comput. 2005, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Barabási, A.L. Distribution of node characteristics in complex networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17916–17920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Färber, M. The Microsoft Academic Knowledge Graph: A Linked Data Source with 8 Billion Triples of Scholarly Data. In Proceedings of the International Semantic Web Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 26–30 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, A.; Genta, L.; Montanelli, S.; Castano, S. Dimensional clustering of linked data: Techniques and applications. In Transactions on Large-Scale Data-and Knowledge-Centered Systems XIX; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 55–86. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.; Srikant, R. Fast Algorithms for Mining Association Rules. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference Very Large Data Bases (VLDB), Santiago de Chile, Chile, 12–15 September 1994; Volume 1215, pp. 487–499. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, M.J.; Hsiao, C.J. CHARM: An Efficient Algorithm for Closed Itemset Mining. In Proceedings of the 2002 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SIAM), Arlington, VA, USA, 11–13 April 2002; pp. 457–473. [Google Scholar]
- Grahne, G.; Zhu, J. Fast algorithms for frequent itemset mining using FP-Trees. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Yin, Y.; Mao, R. Mining Frequent Patterns without Candidate Generation: A Frequent-Pattern Tree Approach. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2004, 8, 53–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, C.H.; Jaafar, J.; Aziz, I.A.; Hasan, M.H.; Yeoh, W. Algorithms for frequent itemset mining: A literature review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2603–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menichetti, G.; Remondini, D.; Panzarasa, P.; Mondragón, R.J.; Bianconi, G. Weighted multiplex networks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Bakos, J. Gpapriori: Gpu-accelerated frequent itemset mining. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing, Austin, TX, USA, 26–30 September 2011; pp. 590–594. [Google Scholar]
- Xun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Zhao, X. FiDoop-DP: Data Partitioning in Frequent Itemset Mining on Hadoop Clusters. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2017, 28, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, R.; Sherly, K.K. Parallel frequent itemset mining with spark RDD framework for disease prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Circuit, Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT), Nagercoil, India, 18–19 March 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Frequent Itemset Mining | Multi-Dimensional Network | |
|---|---|---|
| Items | The products, in traditional FIM | The labels of the RDF |
| Transactions | Set of items | A node with extended reachable tags |
| Database | all transactions | The enriched dataset |
| Support | Number of itemset occurrences | |
| Frequent itemset | if |
| Network_Layer_Resolver | No.Nodes | No.Edges | Density | No.Clusters | Modularity | Avg.Clustering_Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agroforestry | 208 | 251 | 0.0117 | 174 | 0.9592 | 0.0011 |
| Agronomy | 89 | 120 | 0.0306 | 70 | 0.9278 | 0.0029 |
| Algorithm | 50 | 118 | 0.0963 | 33 | 0.7231 | 0.0582 |
| Artificial intelligence | 55 | 58 | 0.0391 | 53 | 0.9738 | 0.0063 |
| Atmospheric sciences | 1285 | 14,217 | 0.0172 | 360 | 0.2958 | 0.0011 |
| Atmospheric sciences|Geophysics | 168 | 213 | 0.0152 | 130 | 0.9431 | 0.0016 |
| Atmospheric sciences|Meteorology | 638 | 2332 | 0.0115 | 248 | 0.6023 | 0.0034 |
| Atmospheric sciences|Oceanography | 45 | 48 | 0.0485 | 42 | 0.9679 | 0.0000 |
| Atmospheric sciences|Remote sensing | 44 | 56 | 0.0592 | 35 | 0.8616 | 0.0056 |
| Botany | 67 | 72 | 0.0326 | 63 | 0.9780 | 0.0029 |
| Cartography | 47 | 52 | 0.0481 | 42 | 0.9608 | 0.0000 |
| Ecology | 999 | 4370 | 0.0088 | 436 | 0.5001 | 0.0020 |
| Ecology|Fishery | 58 | 61 | 0.0369 | 55 | 0.9766 | 0.0000 |
| Ecology|Geomorphology | 66 | 72 | 0.0336 | 60 | 0.9776 | 0.0000 |
| Ecology|Oceanography | 239 | 401 | 0.0141 | 140 | 0.8644 | 0.0064 |
| Econometrics | 126 | 141 | 0.0179 | 112 | 0.9850 | 0.0032 |
| Environmental chemistry | 78 | 92 | 0.0306 | 66 | 0.9698 | 0.0077 |
| Environmental engineering | 208 | 231 | 0.0107 | 186 | 0.9884 | 0.0005 |
| Environmental planning | 184 | 200 | 0.0119 | 169 | 0.9893 | 0.0011 |
| Environmental protection | 86 | 123 | 0.0337 | 77 | 0.8606 | 0.0308 |
| Environmental resource management | 201 | 260 | 0.0129 | 167 | 0.9291 | 0.0047 |
| Fishery | 248 | 385 | 0.0126 | 171 | 0.9085 | 0.0061 |
| Fishery|Oceanography | 71 | 96 | 0.0386 | 56 | 0.9015 | 0.0132 |
| Forestry | 99 | 107 | 0.0221 | 91 | 0.9823 | 0.0000 |
| Genetics | 97 | 117 | 0.0251 | 82 | 0.9654 | 0.0110 |
| Geodesy | 71 | 80 | 0.0322 | 62 | 0.9753 | 0.0000 |
| Geomorphology | 1148 | 5850 | 0.0089 | 368 | 0.4877 | 0.0010 |
| Geomorphology|Geophysics | 55 | 63 | 0.0424 | 47 | 0.9499 | 0.0000 |
| Geomorphology|Hydrology | 254 | 363 | 0.0113 | 186 | 0.9375 | 0.0020 |
| Geomorphology|Oceanography | 291 | 511 | 0.0121 | 160 | 0.8614 | 0.0080 |
| Geomorphology|Paleontology | 78 | 101 | 0.0336 | 60 | 0.9556 | 0.0256 |
| Geophysics | 503 | 1013 | 0.0080 | 286 | 0.7733 | 0.0030 |
| Geophysics|Oceanography | 42 | 46 | 0.0534 | 38 | 0.9631 | 0.0000 |
| Hydrology | 1128 | 2893 | 0.0046 | 537 | 0.7027 | 0.0008 |
| Hydrology|Meteorology | 309 | 411 | 0.0086 | 232 | 0.9548 | 0.0023 |
| Mathematical optimisation | 60 | 62 | 0.0350 | 58 | 0.9807 | 0.0000 |
| Meteorology | 1904 | 9299 | 0.0051 | 788 | 0.5096 | 0.0005 |
| Meteorology|Oceanography | 221 | 320 | 0.0132 | 168 | 0.8769 | 0.0017 |
| Meteorology|Remote sensing | 75 | 84 | 0.0303 | 66 | 0.9691 | 0.0000 |
| Oceanography | 1164 | 7617 | 0.0113 | 370 | 0.3972 | 0.0022 |
| Palaeontology | 145 | 179 | 0.0171 | 119 | 0.9627 | 0.0075 |
| Remote sensing | 448 | 739 | 0.0074 | 304 | 0.8733 | 0.0015 |
| Seismology | 89 | 101 | 0.0258 | 78 | 0.9756 | 0.0023 |
| Soil science | 128 | 217 | 0.0267 | 100 | 0.8141 | 0.0074 |
| Statistics | 275 | 314 | 0.0083 | 246 | 0.9813 | 0.0013 |
| Water resource management | 66 | 99 | 0.0462 | 56 | 0.8316 | 0.0210 |
| Organisation Leaderboard | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Most Important in Layer | Agg. Eigen. Centr. |
| 1 | The United States of America (USA) | Artificial intelligence|Pattern recognition | 56.0279 |
| 2 | China (CHN) | Agroforestry|Hydrology | 35.6429 |
| 3 | Australia (AUS) | Economy | 33.0746 |
| 4 | Canada (CAN) | Thermodynamics | 24.4631 |
| 5 | United Kingdom of Great Britain (GBR) | Environmental protection | 23.2615 |
| Organisation Leaderboard | |||
| Rank | Name | Most Important in Layer | Agg. Eigen. Centr. |
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | Geodesy | 24.1449 |
| 2 | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration | Meteorology|Remote sensing | 5.0147 |
| 3 | National Center for Atmospheric Research | Econometrics | 3.3779 |
| 4 | French National Centre for Scientific Research | Ecology|Oceanography | 2.9609 |
| 5 | Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research | Geomorphology|Oceanography | 2.0770 |
| Individual Leaderboard | |||
| Rank | Name | Most Important in Layer | Agg. Eigen. Centr. |
| 1 | Vijay P. Singh | Hydrology | 1.4517 |
| 2 | Hai Cheng | Geomorphology | 1.2189 |
| 3 | R. Lawrence Edwards | Geomorphology | 1.0049 |
| 4 | Colin Schultz | Meteorology|Oceanography | 1.0005 |
| 5 | Qiang Zhang | Geomorphology|Hydrology | 0.8854 |
| Publication Count Based Ranks | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization | Multi-Objective Rank | Global Rank | Hydrology | Ecology | Paleontology | Geophysics |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration | 2 | 76 | 75 | 51 | 573 | 39 |
| National Center for Atmospheric Research | 3 | 177 | 133 | 840 | 2558 | 28 |
| French National Centre for Scientific Research | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research | 5 | 197 | 291 | 87 | 166 | 135 |
| Russian Academy of Sciences | 6 | 9 | 42 | 6 | 4 | 4 |
| Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research | 7 | 1323 | 407 | 1061 | 3521 | 921 |
| California Institute of Technology | 8 | 37 | 71 | 571 | 307 | 3 |
| Goddard Space Flight Center | 9 | 71 | 1478 | 2765 | 2637 | 551 |
| Wageningen University and Research Centre | 10 | 44 | 16 | 24 | 560 | 835 |
| Beijing Normal University | 11 | 227 | 18 | 241 | 1083 | 684 |
| Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory | 12 | 409 | 396 | 667 | 310 | 35 |
| Ocean University of China | 13 | 380 | 345 | 399 | 617 | 326 |
| United States Forest Service | 14 | 111 | 33 | 10 | 718 | 1084 |
| International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis | 15 | 939 | 537 | 847 | 3240 | 3085 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honti, G.; Abonyi, J. Frequent Itemset Mining and Multi-Layer Network-Based Analysis of RDF Databases. Mathematics 2021, 9, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040450
Honti G, Abonyi J. Frequent Itemset Mining and Multi-Layer Network-Based Analysis of RDF Databases. Mathematics. 2021; 9(4):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040450
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonti, Gergely, and János Abonyi. 2021. "Frequent Itemset Mining and Multi-Layer Network-Based Analysis of RDF Databases" Mathematics 9, no. 4: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040450
APA StyleHonti, G., & Abonyi, J. (2021). Frequent Itemset Mining and Multi-Layer Network-Based Analysis of RDF Databases. Mathematics, 9(4), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040450