Simple and Fast Two-Step Fully Automated Methodology for the Online Speciation of Inorganic Antimony Coupled to ICP-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
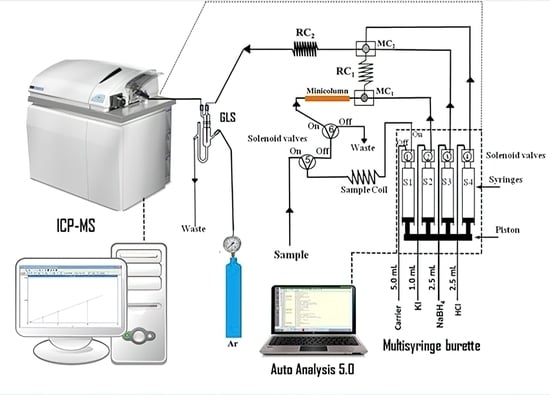
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the MSFIA-HG-ICP-MS Method for Antimony Determination
3.2. Validation Studies
3.3. Application to Natural Waters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, M.; Wang, N.; Long, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Pervaiz, A.; Shan, J. Antimony speciation in the environment: Recent advances in understanding the biogeochemical processes and ecological effects. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 14–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters II. Relevant solution Chemistry. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2002, 59, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Jiang, X.; Che, F.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L. Antimony speciation and potential ecological risk of metal(loid)s in plain wetlands in the lower Yangtze River valley, China. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Zhao, S.; Shi, T.; Zhang, F.; Pei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y. Accumulation, regional distribution, and environmental effects of Sb in the largest Hg–Sb mine area in Qinling Orogen, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Karmakar, D.; Begum, S.N.; Ali, S.Y.; Patra, P.K. Recent trends in the analysis of trace elements in the field of environmental research: A review. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Emons, H. Potential of high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to flow injection hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry for the speciation of inorganic and organic antimony compounds. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2000, 15, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portugal, L.A.; Ferrer, L.; Serra, A.M.; da Silva, D.G.; Ferreira, S.L.C.; Cerdà, V. A non-chromatographic automated system for antimony speciation in natural water exploiting multisyringe flow injection analysis coupled with online hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; dos Anjos, J.P.; Felix, C.S.A.; da Silva Junior, M.M.; Palacio, E.; Cerda, V. Speciation analysis of antimony in environmental samples employing atomic fluorescence spectrometry–Review. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornieles, A.C.; de Torres, A.G.; Alonso, E.V.; Cordero, M.T.S.; Pavón, J.M.C. Speciation of antimony(III) and antimony(V) in seawater by flow injection solid phase extraction coupled with online hydride generation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, C.; Deng, P.; Hou, X. Recent Advance of Hydride Generation–Analytical Atomic Spectrometry: Part I—Technique Development. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2012, 47, 382–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; dos Santos, W.N.; dos Santos, I.F.; Junior, M.M.; Silva, L.; Barbosa, U.A.; de Santana, F.A.; Queiroz, A.F.D.S. Strategies of sample preparation for speciation analysis of inorganic antimony using hydride generation atomic spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2014, 114, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Cao, J.; Qiu, B.; Yang, Z. Simultaneous Separation of Sb(III) and Sb(V) by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) with Application to Plants, Soils, and Sediments. Anal. Lett. 2021, 54, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Wang, C.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Online simultaneous speciation of ultra-trace inorganic antimony and tellurium in environmental water by polymer monolithic capillary microextraction combined with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectroscopy 2020, 168, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, X.; Guo, W.; Jin, L.; Hu, S. Field-based Speciation of Inorganic Sb Using Ion-exchange Resin Cartridge and ICP-MS Detection. At. Spectrosc. 2020, 41, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amereih, S.; Meisel, T.; Kahr, E.; Wegscheider, W. Speciation analysis of inorganic antimony in soil using HPLC-ID-ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Czapla, M.; Grygoyć, K. Spatial and temporal variability of metal(loid)s concentration as well as simultaneous determination of five arsenic and antimony species using HPLC-ICP-MS technique in the study of water and bottom sediments of the shallow, lowland, dam reservoir in Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12358–12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, F.; Ji, W.; Liu, H.; Huo, Z.; Liu, H. Determination of trace inorganic antimony in PET-bottled soy sauce by ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2019, 151, 104257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-Y.; Fei, J.-J.; Lian, H.-Z.; Mao, L.; Cui, X.-B. Simultaneous speciation analysis of chromium and antimony by novel carboxyl-functionalized hybrid monolithic column solid phase microextraction coupled with ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Schmidt, B.; Larsen, E.H.; Gammelgaard, B.; Stürup, S.; Hansen, H.R. Quantitative HPLC-ICP-MS analysis of antimony redox speciation in complex sample matrices: New insights into the Sb-chemistry causing poor chromatographic recoveries. Analyst 2011, 136, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcinkowska, M.; Barałkiewicz, D. Multielemental speciation analysis by advanced hyphenated technique–HPLC/ICP-MS: A review. Talanta 2016, 161, 177–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miravet, R.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Rubio, R.; Smichowski, P.; Polla, G. Speciation analysis of antimony in extracts of size-classified volcanic ash by HPLC-ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Cai, Q.; Guo, Z.-X.; Yang, Z.; Khoo, S.B. Antimony speciation by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry using solid phase extraction cartridges. Analyst 2002, 127, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerdà, V.; Ferrer, L.; Portugal, L.A.; de Souza, C.T.; Ferreira, S.L. Multisyringe flow injection analysis in spectroanalytical techniques-A review. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, M.M.S.; Portugal, L.A.; Serra, A.M.; Ferrer, L.; Cerdà, V.; Ferreira, S.L. On line automated system for the determination of Sb(V), Sb(III), thrimethyl antimony(v) and total antimony in soil employing multisyringe flow injection analysis coupled to HG-AFS. Talanta 2017, 165, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, L. Application of chemical vapor generation in ICP-MS: A review. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bruns, R.E.; Ferreira, H.S.; Matos, G.D.; David, J.M.; Brandão, G.C.; da Silva, E.G.P.; Portugal, L.A.; dos Reis, P.S.; Souza, A.S.; et al. Box-Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Ferreira, S.L.C.; Novaes, C.G.; dos Santos, A.M.P.; Valasques, G.S.; Cerqueira, U.M.F.D.M.; Alves, J.P.D.S. Simultaneous optimization of multiple responses and its application in Analytical Chemistry—A review. Talanta 2019, 194, 941–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.-L.; Chen, Y.-W.; Belzile, N. Antimony speciation at ultra trace levels using hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry and 8-hydroxyquinoline as an efficient masking agente. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 432, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, C. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: Recent trends and developments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, L.A. Detection and quantification limits: Origins and historical overview. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 391, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, N.; Leal, L.O.; Forteza, R.; Cerdà, V. Antimony determination and speciation by multisyringe flow injection analysis with hydride generation-atomic fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 530, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Ellison, S.L.R.; Wood, R. Harmonized guidelines for single-laboratory validation of methods of analysis (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 835–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Morita, Y.; Sakuragawa, A.; Isozaki, A. Inorganic speciation of As(III, V), Se(IV, VI) and Sb(III, V) in natural water with GF-AAS using solid phase extraction technology. Talanta 2007, 72, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Radiofrequency power | Forward | 1100 W |
| Gas flow | Plasma | 15 L min−1 |
| Auxiliary | 1.2 L min−1 | |
| Nebulizer | 0.7 L min−1 | |
| Acquisition parameters | Dwell time | 0.05 s |
| (All analysis) | Scan mode | Peak-hop transient |
| Sweeps per reading | 5 | |
| MCA channel per spectral peak | 1 | |
| Resolution/amu 10% peak maximum | 0.7 | |
| Signal processing | Spectral peaks integrated; sum | |
| Integration time | 30 s | |
| Smoothing signal profile | 15 | |
| Reading per replicate | 114 | |
| Replicates | 3 | |
| Isotope measured | 121Sb |
| Exp. | NaBH4 (%, w/v) | HCl (mol L−1) | KI (%, w/v) | Sb(III) | SbTotal | MR(Sb(III) + Sbtotal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 (0.1) | −1 (1.0) | 0 (12.5) | 35,566 | 35,345 | 1.157 |
| 2 | +1 (0.5) | −1 (1.0) | 0 (12.5) | 30,885 | 30,591 | 1.003 |
| 3 | −1 (0.1) | +1 (5.0) | 0 (12.5) | 19,116 | 19,494 | 0.630 |
| 4 | +1 (0.5) | +1 (5.0) | 0 (12.5) | 20,459 | 20,234 | 0.664 |
| 5 | −1 (0.1) | 0 (3.0) | −1 (10.0) | 51,664 | 51,484 | 1.683 |
| 6 | +1 (0.5) | 0 (3.0) | −1 (10.0) | 52,427 | 52,027 | 1.705 |
| 7 | −1 (0.1) | 0 (3.0) | +1 (15.0) | 37,983 | 38,783 | 1.253 |
| 8 | +1 (0.5) | 0 (3.0) | +1 (15.0) | 36,988 | 37,188 | 1.211 |
| 9 | 0 (0.3) | −1 (1.0) | −1 (10.0) | 27,434 | 26,930 | 0.887 |
| 10 | 0 (0.3) | +1 (5.0) | −1 (10.0) | 40,081 | 39,092 | 1.292 |
| 11 | 0 (0.3) | −1 (1.0) | +1 (15.0) | 38,276 | 38,741 | 1.257 |
| 12 | 0 (0.3) | +1 (5.0) | +1 (15.0) | 48,972 | 48,832 | 1.596 |
| 13 | 0 (0.3) | 0 (3.0) | 0 (12.5) | 60,804 | 61,003 | 1.988 |
| 14 | 0 (0.3) | 0 (3.0) | 0 (12.5) | 60,982 | 60,889 | 1.989 |
| 15 | 0 (0.3) | 0 (3.0) | 0 (12.5) | 60,864 | 61,563 | 1.998 |
| Experimental Factor | Critical Values for Sb(III) | Critical Values for SbTotal | Critical Values Using Multiple Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaBH4 (% w/v) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| HCl (mol L−1) | 2.98 | 2.98 | 2.98 |
| KI (% w/v) | 11.75 | 12.06 | 11.92 |
| Analytical Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| LOD, µg L−1 Sb(III) | 0.016 |
| LOQ, µg L−1 Sb(III) | 0.053 |
| Linear working range, µg L−1 Sb(III) | 0.053–5 |
| Precision, % RSD, n = 10 | 1.4 |
| Sample volume * (mL) | 4 |
| Reagent volume * (mL) | 4.4 |
| Waste volume * (mL) | 8.4 |
| Analysis frequency (h−1) | 30 |
| Sample | Sb(III) (n = 3) | Sb(V) (n = 3) | Sb Total (µg L−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addition (µg L−1) | Found (µg L−1) | Recovery (%) | Found (µg L−1) | Recovery (%) | ||
| RW 1 | - | 0.14 ± 0.03 | - | 0.28 ± 0.06 | - | 0.42 |
| 0.25 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 96 | 0.50 ± 0.04 | 90 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.64 ± 0.01 | 101 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 101 | ||
| CSW 2 | - | 0.11 ± 0.01 | - | 0.20 ± 0.02 | - | 0.31 |
| 0.25 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 104 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 109 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 111 | 0.73 ± 0.01 | 104 | ||
| DTW 3 | - | 0.10 ± 0.01 | - | 0.17 ± 0.01 | - | 0.27 |
| 0.25 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 107 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 92 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 93 | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 104 | ||
| DTW 3 | - | 0.11 ± 0.01 | - | 0.18 ± 0.01 | - | 0.28 |
| 0.25 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 99 | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 105 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.55 ± 0.02 | 90 | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 101 | ||
| GW 4 | - | 0.12 ± 0.01 | - | 0.12 ± 0.01 | - | 0.24 |
| 0.25 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 96 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 97 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 102 | 0.63 ± 0.03 | 102 | ||
| GW 4 | - | 0.11 ± 0.01 | - | 0.13 ± 0.02 | - | 0.24 |
| 0.25 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 105 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 97 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 98 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | 94 | ||
| CSW 5 | - | 0.11 ± 0.01 | - | 0.12 ± 0.01 | - | 0.22 |
| 0.25 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 103 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 98 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 93 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 101 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Portugal, L.A.; Palacio, E.; Cerdà, V.; Santos-Neto, J.H.; Ferrer, L.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Simple and Fast Two-Step Fully Automated Methodology for the Online Speciation of Inorganic Antimony Coupled to ICP-MS. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10040139
Portugal LA, Palacio E, Cerdà V, Santos-Neto JH, Ferrer L, Ferreira SLC. Simple and Fast Two-Step Fully Automated Methodology for the Online Speciation of Inorganic Antimony Coupled to ICP-MS. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(4):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10040139
Chicago/Turabian StylePortugal, Lindomar A., Edwin Palacio, Víctor Cerdà, Joao H. Santos-Neto, Laura Ferrer, and Sergio L. C. Ferreira. 2022. "Simple and Fast Two-Step Fully Automated Methodology for the Online Speciation of Inorganic Antimony Coupled to ICP-MS" Chemosensors 10, no. 4: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10040139
APA StylePortugal, L. A., Palacio, E., Cerdà, V., Santos-Neto, J. H., Ferrer, L., & Ferreira, S. L. C. (2022). Simple and Fast Two-Step Fully Automated Methodology for the Online Speciation of Inorganic Antimony Coupled to ICP-MS. Chemosensors, 10(4), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10040139