The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Function of In Vitro and In Vivo Assay Systems: A Comparative Analysis
Abstract
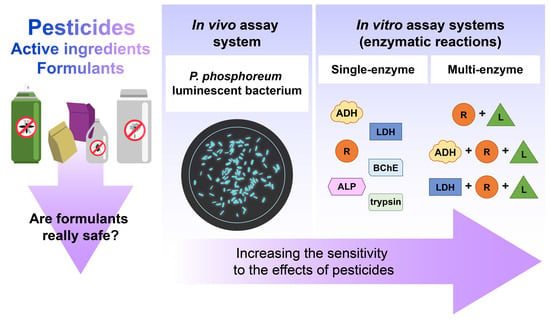
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Pesticides
2.2. Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Activities of Single-Enzyme Systems
2.3. The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Activity of Multi-Enzyme Systems
2.4. The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on Bioluminescence of the Assay System Based on P. Phosphoreum Luminescent Bacterium
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Commercial Pesticide Formulations
3.2. Estimating Sensitivity of Assay Systems to Commercial Pesticide Formulations
3.2.1. The Effect of Pesticide Formulations on the Activity of Single-Enzyme Assay Systems
3.2.2. The Effect of Pesticide Formulations on Multi-Enzyme Systems
3.3. Comparison of the Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on In Vivo and In Vitro Assay Systems
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, J.E.; Morris, A.D.; Hung, H.; Jantunen, L.; Vorkamp, K.; Rigét, F.; Evans, M.; Houde, M.; Muir, D.C. Levels and trends of current-use pesticides (CUPs) in the arctic: An updated review, 2010–2018. Emerg. Contam. 2019, 5, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyabina, V.P.; Esimbekova, E.N.; Kopylova, K.V.; Kratasyuk, V.A. Pesticides: Formulants, distribution pathways and effects on human health – a review. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.F.; Parrón, T.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Requena, M.; Alarcón, R.; López-Guarnido, O. Toxic effects of pesticide mixtures at a molecular level: Their relevance to human health. Toxicology 2013, 307, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution Biomarkers in Environmental and Human Biomonitoring. Open Biomarkers J. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semren, T.; Žunec, S.; Pizent, A. Oxidative stress in triazine pesticide toxicity: A review of the main biomarker findings. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2018, 69, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, F.S.; Neves, R.A.; Crapez, M.A.C.; Teixeira, V.L.; Krepsky, N. How does the brown mussel Perna perna respond to environmental pollution? A review on pollution biomarkers. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 111, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.M.; Rocha, C.P.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, F.J. Enzymes as useful biomarkers to assess the response of freshwater communities to pesticide exposure – A review. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 122, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandour, R. Environmental risks of insecticides cholinesterase inhibitors. Toxicol. Int. 2013, 20, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, S.; Sharma, A.; Serajuddin, M. Toxicity assessment of cypermethrin nanoparticles in Channa punctatus: Behavioural response, micronuclei induction and enzyme alteration. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 100, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, M.S.; de Melo, G.D.; Sandrini-Neto, L.; Di Domenico, M.; Prodocimo, M.M. A meta-analytic review of fish antioxidant defense and biotransformation systems following pesticide exposure. Chemosphere 2021, 291, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemec, A.; Drobne, D.; Tišler, T.; Sepčić, K. Biochemical Biomarkers in Environmental Studies–Lessons Learnt from Enzymes Catalase, Glutathione S-Transferase and Cholinesterase in Two Crustacean Species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2010, 17, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esimbekova, E.N.; Torgashina, I.G.; Kalyabina, V.P.; Kratasyuk, V.A. Enzymatic Biotesting: Scientific Basis and Application. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2021, 14, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajangam, B.; Daniel, D.K.; Krastanov, A.I. Progress in enzyme inhibition based detection of pesticides. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 18, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madasamy, T.; Pandiaraj, M.; Balamurugan, M.; Bhargava, K.; Sethy, N.K.; Karunakaran, C. Copper, zinc superoxide dismutase and nitrate reductase coimmobilized bienzymatic biosensor for the simultaneous determination of nitrite and nitrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artabe, A.E.; Cunha-Silva, H.; Barranco, A. Enzymatic assays for the assessment of toxic effects of halogenated organic contaminants in water and food. A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, R.; Chen, G.; Liu, G.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, M.; Xu, D.; et al. Enzyme inhibition methods based on Au nanomaterials for rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticides in agricultural and environmental samples: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 37, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wei, L. Color-coded detection of malathion based on enzyme inhibition with dark-field optical microscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 353, 131135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolosova, M.; Sutormin, S.; Esimbekova, N.; Lonshakova-Mukina, V.I.; Kratasyuk, V. Set of enzymatic bioassays for assessment of soil pollution. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2019, 489, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, B.; Munteanu, F.-D.; Marty, J.-L.; Vasilescu, A. Advances in Enzyme-Based Biosensors for Pesticide Detection. Biosensors 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amine, A.; Arduini, F.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Recent advances in biosensors based on enzyme inhibition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 76, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyabina, V.P.; Esimbekova, E.N.; Torgashina, I.G.; Kopylova, K.V.; Kratasyuk, V.A. Principles for Construction of Bioluminescent Enzyme Biotests for Analysis of Complex Media. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 485, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodicheva, E.K.; Vydryakova, G.A.; Medvedeva, S.E. The Ibso Catalogue of Luminous Bacteria Cultures. Available online: http://www.ibp.ru/collection/default.php (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Formulation Codes. Available online: https://www.cipac.org/index.php/methods-publications/further-information/formulation-codes (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilboudo, S.; Fouche, E.; Rizzati, V.; Toé, A.M.; Gamet-Payrastre, L.; Guissou, P.I. In vitro impact of five pesticides alone or in combination on human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch, R.; Singh, A.K.; Pathak, M.K.; Singh, A.; Kesavachandran, C.N.; Bihari, V.; Mudiam, M.K.R. Saliva and urine metabolic profiling reveals altered amino acid and energy metabolism in male farmers exposed to pesticides in Madhya Pradesh State, India. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, K.V.B.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Alves, O.L.; Barbieri, E. Co-exposure of carbon nanotubes with carbofuran pesticide affects metabolic rate in Palaemon pandaliformis (shrimp). Chemosphere 2021, 288, 132359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamat, H.; Sauvant-Rochat, M.-P.; Tauveron, I.; Bagheri, R.; Ugbolue, U.C.; Maqdasi, S.; Navel, V.; Dutheil, F. Metabolic syndrome and pesticides: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebbia, C. Biotransformation Enzymes as Determinants of Xenobiotic Toxicity in Domestic Animals. Veter-J. 2001, 161, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotthoff, L.; Keller, J.; Lörchner, D.; Mekonnen, T.F.; Koch, M. Transformation Products of Organic Contaminants and Residues—Overview of Current Simulation Methods. Molecules 2019, 24, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, F.; Zhongyuan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wong, C.-O.; Karagas, N.E.; Roessner, U.; Rupasinghe, T.; Venkatachalam, K.; Perry, T.; Bellen, H.J.; et al. Low doses of the neonicotinoid insecticide imidacloprid induce ROS triggering neurological and metabolic impairments in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 202011828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ares, I.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X.; Martínez, M.-A. Deltamethrin toxicity: A review of oxidative stress and metabolism. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 260–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Miao, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Xu, S. Exposure to imidacloprid induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and mitophagy via NF-kappaB/JNK pathway in grass carp hepatocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 120, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankley, G.T.; Edwards, S.W. The adverse outcome pathway: A multifaceted framework supporting 21st century toxicology. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Singh, S.; Pandey, R.S.; Sharma, B. Enzymes of Earthworm as Indicators of Pesticide Pollution in Soil. Adv. Enzym. Res. 2016, 04, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Basic Information about Pesticide Ingredients. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/basic-information-about-pesticide-ingredients (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Mesnage, R.; Antoniou, M.N. Ignoring Adjuvant Toxicity Falsifies the Safety Profile of Commercial Pesticides. Front. Public Health 2018, 5, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straw, E.A.; Thompson, L.J.; Leadbeater, E.; Brown, M.J.F. ‘Inert’ ingredients are understudied, potentially dangerous to bees and deserve more research attention. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2022, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, E.; Gerstle, V.; Schmitt, T.; Brühl, C.A. Co-formulants and adjuvants affect the acute aquatic and terrestrial toxicity of a cycloxydim herbicide formulation to European common frogs (Rana temporaria). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesticide Formulations. Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/formulations.html (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Stevanovic, M.; Gasic, S.; Pipal, M.; Blahova, L.; Brkic, D.; Neskovic, N.; Hilscherova, K. Toxicity of clomazone and its formulations to zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 188, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcocer-Cuarón, C.; Rivera, A.L.; Castaño, V.M. Hierarchical structure of biological systems. Bioengineered 2013, 5, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, S.; Da Silva, J.E. Quantitative analysis of organophosphorus pesticides in freshwater using an optimized firefly luciferase-based coupled bioluminescent assay. Luminescence 2013, 29, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.H.; Oh, S.E. Improved detection of toxic chemicals by Photobacterium phosphoreum using modified Boss medium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2010, 101, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qu, R.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z. Effect of water quality on mercury toxicity to Photobacterium phosphoreum: Model development and its application in natural waters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Adil, M.; Ehtisham-Ul-Haque, S.; Munir, B.; Yameen, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Shar, G.A.; Tahir, M.A.; Iqbal, M. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerald, T. (Ed.) Handbook of Cell Biosensors; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasova, A.; Kislan, S.; Fedorova, E.; Kuznetsov, A.; Mogilnaya, O.; Stom, D.; Kudryasheva, N. Bioluminescence as a tool for studying detoxification processes in metal salt solutions involving humic substances. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2012, 117, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchovská, E.; Morin, B.; López-Cabeza, R.; Barré, M.; Gouffier, C.; Bláhová, L.; Cachot, J.; Bláha, L.; Gonzalez, P. Comparison of imidacloprid, propiconazole, and nanopropiconazole effects on the development, behavior, and gene expression biomarkers of the Pacific oyster (Magallana gigas). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 764, 142921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annett, R.; Habibi, H.R.; Hontela, A. Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, D.M.; de Molina, M.C.R.; Juárez, B. Oxidative stress induced by a commercial glyphosate formulation in a tolerant strain of Chlorella kessleri. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 74, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Duan, C.; Michelle, W.H.G.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. Individual and combined toxic effects of cypermethrin and chlorpyrifos on earthworm. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, L.; Vidal, T.; Nogueira, A.J.A.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Pereira, J.L. Ecotoxicological assessment of the herbicide Winner Top and its active substances—Are the other formulants truly inert? Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinhold, B. Mystery in a Bottle: Will the EPA Require Public Disclosure of Inert Pesticide Ingredients? Environ. Health Persp. 2010, 118, A168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnage, R.; Benbrook, C.; Antoniou, M.N. Insight into the confusion over surfactant co-formulants in glyphosate-based herbicides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggel, S.; Werner, I.; Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.P. Sublethal toxicity of commercial insecticide formulations and their active ingredients to larval fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3169–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.I.L.; Ammendola, A.; Casini, S.; Amorim, M.J.B. Toxicity of Fungicides to Terrestrial Non-Target Fauna—Formulated Products versus Active Ingredients (Azoxystrobin, Cyproconazole, Prothioconazole, Tebuconazole)—A Case Study with Enchytraeus Crypticus (Oligochaeta). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takács, E.; Klátyik, S.; Mörtl, M.; Rácz, G.; Kovács, K.; Darvas, B.; Székács, A. Effects of neonicotinoid insecticide formulations and their components on Daphnia magna—The role of active ingredients and co-formulants. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Merwe, J.; Neale, P.; Melvin, S.D.; Leusch, F. In vitro bioassays reveal that additives are significant contributors to the toxicity of commercial household pesticides. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, M.; Brkić, D.; Tomić, T.; Mihajlović, V.; Đorđević, T.; Gašić, S. Effects of the technical ingredient clomazone and its two formulated products on aquatic macrophytes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossi, P.F.; Herbert, L.T.; Yusseppone, M.S.; Pérez, A.F.; Kristoff, G. Toxicity evaluation of the active ingredient acetamiprid and a commercial formulation (Assail® 70) on the non-target gastropod Biomphalaria straminea (Mollusca: Planorbidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.; DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Smith, B.H.; Johnson, M.; Kaftanoglu, O.; Cogley, T.; Fewell, J.H.; Harrison, J.F. Colony field test reveals dramatically higher toxicity of a widely-used mito-toxic fungicide on honey bees (Apis mellifera). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 269, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Pesticide Group | Active Ingredient | Commercial Pesticide Formulation | Form | Structural Formula | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrethroids | Fenvalerate | Sempay | EC * |  | JSC “Avgust”, Russia |
| Fenaksin | Dust | “Agrovit” LLC, Russia | |||
| Deltamethrin | Delcid | EC * |  | NVC “AgroVetZashita” LLC, Russia | |
| Cypermethrin | Inta-vir | ST ** |  | “Garden Retail Service” LLC, Russia | |
| Briz | EC * | “Spetsbioservice” LLC, Russia | |||
| Neonicotinoids | Imidacloprid | Biotlin | WSC *** |  | JSC “Avgust”, Russia |
| Corado | ZPF Agrorus-Ryazan LLC, Russia | ||||
| Confidor Extra | WG **** | Bayer Garden, Germany | |||
| OPs | Malathion | Aliot | EC * |  | JSC “Avgust”, Russia |
| Fufanon-Nova | Emulsion, oil in water | Firm “Gardener’s Green Pharmacy” LLC, Russia | |||
| Diazinon | Muravyed | EC * |  | JSC “Avgust”, Russia | |
| Pochin | Granule | Firm “Gardener’s Green Pharmacy” LLC, Russia | |||
| Muravin | Bait (ready for use) | CJSC «TPK Technoexport», Russia | |||
| Glyphosate | Liquidator | Water solution |  | CJSC «TPK Technoexport», Russia | |
| Tornado Extra | JSC “Avgust”, Russia |
| Commercial Pesticide Formulation | Active Ingredient | Distilled Water | Alcohol | Acetonitrile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sempay | Fenvalerate | − | + | + |
| Fenaksin | − | − | − | |
| Delcid | Deltamethrin | − | + | + |
| Inta-vir | Cypermethrin | − | − | − |
| Briz | − | + | + | |
| Biotlin | Imidacloprid | − | + | + |
| Corado | − | + | + | |
| Confidor Extra | + | − | − | |
| Aliot | Malathion | − | + | − |
| Fufanon-Nova | − | − | − | |
| Muravyed | Diazinon | − | + | + |
| Pochin | − | − | − | |
| Muravin | − | − | − | |
| Liquidator | Glyphosate | + | − | − |
| Tornado Extra | + | + | − |
| Active Ingredient | Commercial Pesticide Formulation | In Vitro Assay Systems | In Vivo Assay System | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Enzyme Assay Systems | Multi-Enzyme Assay Systems | P. Phos-phoreum | MRL RUS mg/kg | |||||||||
| Trypsin | ALP | BChE | LDH | ADH | Red | Red + Luc | ADH + Red + Luc | LDH + Red + Luc | ||||
| Fenvalerate | Sempay | * | * | – | 0.2 | * | * | 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 | * | 0.02–0.1 |
| Deltamethrin | Delcid | – | – | 0.76 | 6.2 | 16.7 | 146 | 39.5 | 12.7 | 11.5 | * | 0.01–0.3 |
| Cypermethrin | Briz | * | – | 30930 | 150 | 100 | 300 | 5 | 3 | 1 | * | 0.01–2.0 |
| Imidacloprid | Biotlin | * | * | 200 | – | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 2000 | 0.1–1.0 |
| Corado | * | * | – | 180 | 0.08 | – | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 500 | ||
| Confidor Extra | – | * | 80,000 | 1 | 49.9 | 14.9 | 34.4 | 47.8 | 1.9 | 110 | ||
| Malathion | Aliot | * | * | 4 | 30 | * | * | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.014 | * | 0.05–1.0 |
| Diazinon | Muravyed | * | * | 20 | 0.05 | 0.2 | * | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.005 | * | 0.1–0.5 |
| Glyphosate | Liquidator | 5400 | 600 | 1000 | 6000 | 1.5 | 9.0 | 1.11 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 400 | 0.1–5.0 |
| Tornado Extra | 2400 | 220 | 2.4 | 52 | 2.1 | 5.0 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 400 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esimbekova, E.N.; Kalyabina, V.P.; Kopylova, K.V.; Lonshakova-Mukina, V.I.; Antashkevich, A.A.; Torgashina, I.G.; Lukyanenko, K.A.; Kratasyuk, V.A. The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Function of In Vitro and In Vivo Assay Systems: A Comparative Analysis. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10080328
Esimbekova EN, Kalyabina VP, Kopylova KV, Lonshakova-Mukina VI, Antashkevich AA, Torgashina IG, Lukyanenko KA, Kratasyuk VA. The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Function of In Vitro and In Vivo Assay Systems: A Comparative Analysis. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(8):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10080328
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsimbekova, Elena N., Valeriya P. Kalyabina, Kseniya V. Kopylova, Victoria I. Lonshakova-Mukina, Anna A. Antashkevich, Irina G. Torgashina, Kirill A. Lukyanenko, and Valentina A. Kratasyuk. 2022. "The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Function of In Vitro and In Vivo Assay Systems: A Comparative Analysis" Chemosensors 10, no. 8: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10080328
APA StyleEsimbekova, E. N., Kalyabina, V. P., Kopylova, K. V., Lonshakova-Mukina, V. I., Antashkevich, A. A., Torgashina, I. G., Lukyanenko, K. A., & Kratasyuk, V. A. (2022). The Effects of Commercial Pesticide Formulations on the Function of In Vitro and In Vivo Assay Systems: A Comparative Analysis. Chemosensors, 10(8), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10080328