Low-Cost, High-Sensitivity Paper-Based Bacteria Impedance Sensor Based on Vertical Flow Assay
Abstract
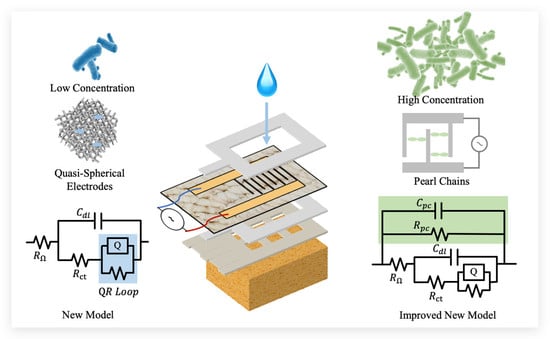
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Design
2.2. Sensor Fabrication
2.3. Impedance Measurement
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Concentration Derivation
3.2. Low-Concentration Circuit Modeling for a Paper-Based Impedance Sensor
3.3. High-Concentration Circuit Modeling for a Paper-Based Impedance Sensor
3.4. Paper-Based Impedance Sensor Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altekruse, S.; Cohen, M.; Swerdlow, D. Emerging foodborne diseases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, L.H.; Mody, R.K.; Ong, K.L. Increased recognition of non-O157 Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli infections in the United States during 2000–2010: Epidemiologic features and comparison with E. coli O157 infections. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, J.R.; Goggins, J.A.; McLachlan, J.B. Salmonella infection: Interplay between the bacteria and host immune system. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 190, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y. New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors 2012, 12, 3449–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, M.; Chikindas, M.L. Listeria: A foodborne pathogen that knows how to survive. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.; Carroll, C.; Jordan, K. Environmental survival mechanisms of the foodborne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Salazar, J.K. Culture-independent rapid detection methods for bacterial pathogens and toxins in food matrices. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.E.; Daugherity, E.K.; Altier, C.; Maurer, K.J. Efficacy and limitations of an ATP-based monitoring system. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2010, 49, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, W.E.; Jansson, J.K.; Chelm, B.K.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA probe method for the detection of specific microorganisms in the soil bacterial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: An emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarridge, J.E., III. Impact of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for identification of bacteria on clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 840–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Saona, L.; Khambaty, F.; Fry, F.; Calvey, E. Rapid detection and identification of bacterial strains by Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayan, H.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Recent development in rapid detection techniques for microorganism activities in food matrices using bio-recognition: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, D.-W.; Wei, Q.; Pu, H. Quantification and visualization of α-tocopherol in oil-in-water emulsion based delivery systems by Raman microspectroscopy. Lwt 2018, 96, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Whole-bacterium SELEX of DNA aptamers for rapid detection of E. coli O157: H7 using a QCM sensor. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 266, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Q.; Weng, X. Microfluidic thread-based electrochemical aptasensor for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Tang, W.; Qi, W.; Guo, X.; Lin, J. An ultrasensitive biosensor for fast detection of Salmonella using 3D magnetic grid separation and urease catalysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 157, 112160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriacò, M.S.; Parlangeli, I.; Sirsi, F.; Poltronieri, P.; Primiceri, E. Impedance sensing platform for detection of the food pathogen listeria monocytogenes. Electronics 2018, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felice, C.; Valentinuzzi, M. Medium and interface components in impedance microbiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 46, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, M.; Lazzarini, R.; Lanzoni, M.; Pompei, A.; Matteuzzi, D.; Riccò, B. A portable sensor with disposable electrodes for water bacterial quality assessment. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, S.M.; Alocilja, E.C. Design and fabrication of a micro impedance biosensor for bacterial detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, M.; Li, Y. Interdigitated array microelectrodes based impedance biosensors for detection of bacterial cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Erf, G.F. Interdigitated array microelectrode-based electrochemical impedance immunosensor for detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehret, R.; Baumann, W.; Brischwein, M.; Schwinde, A.; Stegbauer, K.; Wolf, B. Monitoring of cellular behaviour by impedance measurements on interdigitated electrode structures. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1997, 12, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Tiwari, B.S.; Pandya, A. Field deployable vertical flow based immunodevice for detection of Potato virus Y in potato leaves. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Määttänen, A.; Vanamo, U.; Ihalainen, P.; Pulkkinen, P.; Tenhu, H.; Bobacka, J.; Peltonen, J. A low-cost paper-based inkjet-printed platform for electrochemical analyses. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2013, 177, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Kumachev, A.; Martinez, A.W.; Narovlyansky, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab A Chip 2010, 10, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, N.V.; Tiwari, B.S.; Pandya, A. Paper disc interfaced Prussian blue nanocube modified immunodevice for electrochemical detection of diverse biomarker at point of care. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 150, 108346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Ryu, J.; Seol, I.-H.; Jeong, K.-B.; You, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-R. based radial chromatographic immunoassay for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in milk. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46472–46478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choopara, I.; Suea-Ngam, A.; Teethaisong, Y.; Howes, P.D.; Schmelcher, M.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Thunyaharn, S.; Wongsawaeng, D.; DeMello, A.J.; Dean, D.; et al. Fluorometric Paper-Based, Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Devices for Quantitative Point-of-Care Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Chao, R.; Ren, Y.; Hu, C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.L. Smartphone based portable bacteria pre-concentrating microfluidic sensor and impedance sensing system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based portable biosensing system using impedance measurement with printed electrodes for 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, Q. Protein detecting with smartphone-controlled electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for point-of-care applications. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2016, 222, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güder, F.; Ainla, A.; Redston, J.; Mosadegh, B.; Glavan, A.; Martin, T.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based electrical respiration sensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5727–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Bashir, R. Electrical/electrochemical impedance for rapid detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-free impedance biosensors: Opportunities and challenges. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisdat, F.; Schäfer, D. The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochowski, S.; Nitsch, K. Description of the frequency behaviour of metal–SiO2–GaAs structure characteristics by electrical equivalent circuit with constant phase element. Thin Solid Film. 2002, 415, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Semiconductors and Mott-Schottky Plots. In Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Suehiro, J.; Yatsunami, R.; Hamada, R.; Hara, M. Quantitative estimation of biological cell concentration suspended in aqueous medium by using dielectrophoretic impedance measurement method. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, Y.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, G.L. Low-Cost, High-Sensitivity Paper-Based Bacteria Impedance Sensor Based on Vertical Flow Assay. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040238
Long Y, Ai Z, Zhang L, Zhang H, Jiang J, Liu GL. Low-Cost, High-Sensitivity Paper-Based Bacteria Impedance Sensor Based on Vertical Flow Assay. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(4):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040238
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Yifan, Zhehong Ai, Longhan Zhang, Han Zhang, Jing Jiang, and Gang Logan Liu. 2023. "Low-Cost, High-Sensitivity Paper-Based Bacteria Impedance Sensor Based on Vertical Flow Assay" Chemosensors 11, no. 4: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040238
APA StyleLong, Y., Ai, Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, H., Jiang, J., & Liu, G. L. (2023). Low-Cost, High-Sensitivity Paper-Based Bacteria Impedance Sensor Based on Vertical Flow Assay. Chemosensors, 11(4), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040238