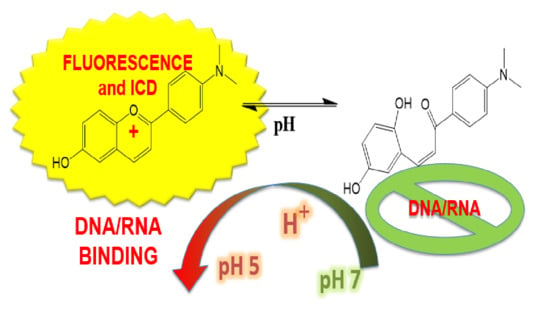
Flavylium Dye as pH-Tunable Fluorescent and CD Probe for Double-Stranded DNA and RNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Aqueous Solutions of Studied Compound F1
3.2. Study of Interactions of F1 with ds-DNA and ds-RNA in Aqueous Media
3.2.1. UV/Vis Titrations
3.2.2. Fluorimetric Titrations
3.2.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Titrations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melo, M.J. Missal Blue: Anthocyanins in Nature and Art. In Dyes in History and Archaeology; Kirby, J., Ed.; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2008; Volume 21, pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, F. Chemical applications of anthocyanins and related compounds A source of bio-inspiration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6885–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, F.; Parola, A.J.; Melo, M.J.; Lima, J.C.; De Freitas, V. Chemistry of Anthocyanins. In Anthocyanins from Natural Sources: Exploiting Targeted Delivery for Improved Health; Brook, M.S.-L., Celli, G.B., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 12, Chapter 2; pp. 34–76. [Google Scholar]
- Cheynier, V.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Yoshida, K. Polyphenols, From Plants to a Variety of Food and Nonfood Uses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7589–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangles, O.; Fenger, J.-A. The Chemical Reactivity of Anthocyanins and Its Consequences in Food Science and Nutrition. Molecules 2018, 23, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basílio, N.; Pina, F. Chemistry and Photochemistry of Anthocyanins and Related Compounds: A Thermodynamic and Kinetic Approach. Molecules 2016, 21, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, F.; Melo, M.J.; Parola, A.J.; Maestri, M.; Balzani, V. pH-Controlled Photochromism of Hydroxyflavylium ions. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, M.C.; Parola, A.J.; Lodeiro, C.; Pina, F.; Maestri, M.; Balzani, V. Multistate/Multifunctional Behaviour of 6-nitro-4’-hydroxyflavylium A Write-lock/Read/Unlock/Enable-erase/Erase Cycle Driven by Light and pH Stimulation. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, F.; Petrov, V.; Laia, C.A.T. Photochromism of flavylium systems: An overview of a versatile multistate system. Dyes Pigment. 2012, 92, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giestas, L.; Folgosa, F.; Lima, J.C.; Parola, A.J.; Pina, F. Bio-Inspired Multistate Networks Responsive to Light, pH and Thermal Inputs: An Example of a Multistate System Operating Through Different Algorithms. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 4187–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, A.; Pinheiro, C.; Parola, A.J.; Maestri, M.; Pina, F. The Chemistry of 6-Hydroxyflavylium, Zwitterionic base, and p-Quinoidal Chalcones A Multiswitchable System Operated by Proton, Electron and Photon Inputs. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, F.; Melo, M.J.; Laia, C.A.T.; Parola, A.J.; Lima, J.C. Chemistry and Applications of Flavylium Compounds, a Handful of Colours. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 869–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Mori, M.; Kondo, T. Blue flower color development by anthocyanins, from chemical structure to cell physiology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 884–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.; Parola, A.J.; Bastkowski, F.; Polkowska, J.; Klärner, F.-G. Host-guest interactions between molecular clips and multistate systems based on flavylium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8922–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basílio, N.; Pina, F. Flavylium network of chemical reactions in confined media, modulation of 3′,4′,7-trihydroxyflavilium reactions by host-guest interactions with cucurbit[7]uril. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubillaga, A.; Ferreira, P.; Parola, A.J.; Gago, S.; Basílio, N. pH-Gated Photoresponsive Shuttling in a Water-Soluble Pseudorotaxane. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2743–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seco, A.; Diniz, A.M.; Sarrato, J.; Mourão, H.; Cruz, H.; Parola, A.J.; Basílio, N. A pseudorotaxane formed from a cucurbit[7]uril wheel and a bioinspired molecular axle with pH, light and redox-responsive properties. Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 92, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, T.V.; Cai, Y.; Lilley, T.H.; Haslam, E. Polyphenol interactions. Part 5. Anthocyanin co-pigmentation. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1991, 8, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.D.; Sharma, R. Anthocyanin-DNA copigmentation complex: Mutual protection against oxidative damage. Phytochemistry 1999, 52, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, T.; Susperregui, J.; Berke, B.; Chèze, C.; Moreau, S.; Nuhrich, A.; Vercauteren, J. DNA triplex stabilization prop-erty of natural anthocyanins. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermeyer, M.; Fritz, J.; Barthelmes, H.U.; Christensen, M.O.; Larsen, M.K.; Boege, F.; Marko, D. Anthocyanidins modulate the activity of human DNA topoisomerases I and II and affect cellular DNA integrity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.R.; Min, K.; Ebeler, S.E. Anthocyanin interactions with DNA: Intercalation, topoisomerase I inhibition and oxidative reactions. J. Food Biochem. 2008, 32, 576–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Czerney, P.; Levell, J.R.; Du, W. Molecular Engineering of Benzo[b]pyrylium Salts by Indirect Electrophilic Substitution. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haucke, G.; Czerney, P.; Steen, D.; Rettig, W.; Hartmann, H. Radiationless Transitions in Substituted Benzopyrylium Dyes, Competing Adiabatic Photoreactions Towards Nonradiative Funnels. Ber Bunsenges Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laia, C.A.T.; Parola, A.J.; Folgosa, F.; Pina, F. Multistate reaction kinetics of 6-hydroxy-4’-dimethylaminoflavylium driven by pH A stopped-flow study. Org Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumir, L.M.; Piantanida, I.; Cindric, I.J.; Hrenar, T.; Meic, Z.; Zinic, M. New permanently charged phenanthridinium-nucleobase conjugates. Interactions with nucleotides and polynucleotides and recognition of ds-polyAH(+). J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2003, 16, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Schuck, P. Global Multi-Method Analysis of Affinities and Cooperativity in Complex Systems of Macromolecular Interactions. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9513–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Piszczek, G.; Schuck, P. SEDPHAT—A platform for global ITC analysis and global multi-method analysis of molecular interactions. Methods 2015, 76, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scatchard, G. The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhee, J.D.; von Hippel, P.H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions, Co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J. Mol. Biol. 1976, 103, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenken, S.; Jovanovic, S.V. How Easily Oxidizable Is DNA? One-Electron Reduction Potentials of Adenosine and Guanosine Radicals in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 617–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.F.; Lima, J.C.; Quina, F.H.; Maçanita, A.L. Excited-State Electron Transfer in Anthocyanins and Related Flavylium Salts. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 10133–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantanida, I.; Mašić, L.; Rusak, G. Structure-spectrophotometric selectivity relationship in interactions of quercetin related flavonoids with double stranded and single stranded RNA. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 924, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinić, M.; Piantanida, I.; Rusak, G.; Žinić, M. Interactions of quercetin and its lanthane complex with double stranded DNA/RNA and single stranded RNA, Spectrophotometric sensing of poly G. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeunynck, M.; Bailly, C.; Wilson, W.D. Small Molecule DNA and RNA Binders: From Synthesis to Nucleic Acid Complexes; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.C.; Barton, J.K. On demonstrating DNA intercalation. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmidlehner, T.; Piantanida, I.; Pescitelli, G. Polarization spectroscopy methods in the determination of interactions of small molecules with nucleic acids-tutorial. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, M.; Nordén, B. Drug–Nucleic Acid Interactions. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 340, pp. 68–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Folgado, L.; Schmuck, C.; Tomić, S.; Piantanida, I. A novel pyrene-guanidiniocarbonyl-pyrrole cation efficiently differentiates between ds-DNA and ds-RNA by two independent, sensitive spectroscopic methods. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, B.A. DNA Binders and Related Subjects: Cyanine dye-DNA interactions: Intercalation, groove binding, and aggregation. Top. Curr. Chem. 2005, 253, 55–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mergny, J.L.; Lacroix, L. Analysis of thermal melting curves. Oligonucleotides 2003, 13, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantanida, I.; Palm, B.S.; Žinić, M.; Schneider, H.J. A new 4,9-diazapyrenium intercalator for single- and double-stranded nucleic acids: Distinct differences from related diazapyrenium compounds and ethidium bromide. Perkin Trans. 2001, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; Lee, C.; Tannock, I.F. Reduction of intracellular pH as a strategy to enhance the pH-dependent cytotoxic effects of melphalan for human breast cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3553–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillies, R.J.; Robey, I.; Gatenby, R.A. Causes and consequences of increased glucose metabolism of cancers. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 24s–42s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghunand, N.; Gillies, R.J. pH and drug resistance in tumors. Drug Resist. Update 2000, 3, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Sample | τ/ps |
|---|---|
| F1 | 47 ± 7 |
| F1 + pApU | 284 ± 10 |
| F1 + pdAdT | 232 ± 6 |
| F1 + p(dAdT)2 | 220 ± 12 |
| F1 + p(dGdC)2 | 117 ± 8 |
| F1 + pdGdC | 118 ± 16 |
| Polynucleotides | logKs | n | a Δλ/nm | b ΔIcalc | c Stokes Shift/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ctDNA | 5.2 | 0.12 | +12 | 227 | 88 |
| poly A–poly U | 4.8 | 0.18 | +17 | 375 | 88 |
| poly dA–poly dT | 6.1 | 0.05 | +10 | 419 | 90 |
| poly dG–poly dC | 5.5 | 0.07 | +18 | 122 | 97 |
| poly (dA–dT)2 | 5.2 | 0.14 | +11 | 296 | 90 |
| poly (dG–dC)2 | 4.9 | 0.23 | +15 | 89 | 92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crnolatac, I.; Giestas, L.; Horvat, G.; Parola, A.J.; Piantanida, I. Flavylium Dye as pH-Tunable Fluorescent and CD Probe for Double-Stranded DNA and RNA. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040129
Crnolatac I, Giestas L, Horvat G, Parola AJ, Piantanida I. Flavylium Dye as pH-Tunable Fluorescent and CD Probe for Double-Stranded DNA and RNA. Chemosensors. 2020; 8(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrnolatac, Ivo, Letícia Giestas, Gordan Horvat, António Jorge Parola, and Ivo Piantanida. 2020. "Flavylium Dye as pH-Tunable Fluorescent and CD Probe for Double-Stranded DNA and RNA" Chemosensors 8, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040129
APA StyleCrnolatac, I., Giestas, L., Horvat, G., Parola, A. J., & Piantanida, I. (2020). Flavylium Dye as pH-Tunable Fluorescent and CD Probe for Double-Stranded DNA and RNA. Chemosensors, 8(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040129