Tannic Acid-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Novel Nanozyme for Colorimetric Determination of Pb2+ Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of TA-Capped AuNPs
2.3. Comparison of Catalytic Activity of TA-Capped AuNPs in the Absence/Presence of Pb2+
2.4. Colorimetric Detection of Pb2+ in Aqueous Solutions
2.5. Specificity of the Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Real Water Samples
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of TA-Capped AuNPs
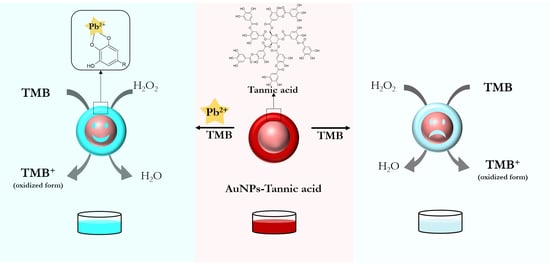
3.2. Principle of the Nanozyme-Based Colorimetric Pb2+ Detection
3.3. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions for Colorimetric Pb2+ Detection
3.4. Colorimetric Technique for Determining the Catalytic Activity of TA-Capped AuNPs
3.5. Quantitative Pb2+ Detection Using Colorimetric Sensor
3.6. Selectivity
3.7. Evaluation of Nanozyme-Based Colorimetric Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahamed, M.; Siddiqui, M. Low level lead exposure and oxidative stress: Current opinions. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 383, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Daşbaşı, T.; Saçmacı, Ş.; Ülgen, A.; Kartal, Ş. A solid phase extraction procedure for the determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in food and water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarudin, A.; Lenghor, N.; Liping, Y.; Furusho, Y.; Motomizu, S. Automated Online Preconcentration System for the Determination of Trace Amounts of Lead Using Pb-Selective Resin and Inductively Coupled Plasma–Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Spectrosc. Lett. 2006, 39, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamilari, E.; Farsalinos, K.; Poulas, K.; Kontoyannis, C.G.; Orkoula, M.G. Detection and quantitative determination of heavy metals in electronic cigarette refill liquids using Total Reflection X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 116, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Liu, X.-q.; Chen, B.; Luo, F.; Wu, X.; Jiang, D.; Luo, Z. Determination of heavy metals in soil by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with internal standard method. Electron Sci Technol Appl. 2017, 4, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Dai, H.; Jin, Y. Electrochemical sensing of lead(II) by differential pulse voltammetry using conductive polypyrrole nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 187, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Gaur, M.S.; Dzantiev, B.B. Rapid and selective electrochemical detection of pb2+ ions using aptamer-conjugated alloy nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Su, Z. Colorimetric Detection of Pb2+ Using Glutathione Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Shang, Y.; Wu, F. Colorimetric detection of lead (II) based on silver nanoparticles capped with iminodiacetic acid. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnarathorn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Dungchai, W. Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of lead using maleic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 132, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengan, M.; Kamlekar, R.K.; Veerappan, A. Highly selective rapid colorimetric sensing of Pb2+ ion in water samples and paint based on metal induced aggregation of N-decanoyltromethamine capped gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 239, 118485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Pridvorova, S.M.; Gaur, M.; Dzantiev, B.B. Rapid Visual Detection of Lead and Mercury via Enhanced Crosslinking Aggregation of Aptamer-Labeled Gold Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 5489–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y. A colorimetric method for the determination of lead(II) ions using gold nanoparticles and a guanine-rich oligonucleotide. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dai, J.; Shi, H.; Luo, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, C.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, D. A rapid and colorimetric biosensor based on GR-5 DNAzyme and self-replicating catalyzed hairpin assembly for lead detection. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chu, L.T.; Hartanto, H.; Utomo, W.B.; Pravasta, R.A.; Chen, T.-H. Microfluidic Particle Dam for Visual and Quantitative Detection of Lead Ions. ACS Sensors 2019, 5, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. Gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric and fluorescent detection of ions and small organic molecules. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komova, N.S.; Serebrennikova, K.V.; Berlina, A.N.; Pridvorova, S.M.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Mercaptosuccinic-Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Colorimetric Sensing of Fe(III) Ions. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Zherdev, A.V.; Gaur, M.S.; Dzantiev, B.B. Colorimetric Determination of Lead Using Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Lett. 2014, 48, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.L.S.; Vuong, K.Q.; Chow, E. Nanozymes for Environmental Pollutant Monitoring and Remediation. Sensors 2021, 21, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BineshUnnikrishnana, C.-W.; Chu, H.-W.; Huang, C.-C. A review on metal nanozyme-based sensing of heavy metal ions: Challenges and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hu, L.; Yao, W. Recent developments of nanoenzyme-based colorimetric sensors for heavy metal detection and the interaction mechanism. Analyst 2020, 145, 3173–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y. A facile colorimetric sensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of Lead(II) in environmental and biological samples based on intrinsic peroxidase-mimic activity of WS2 nanosheets. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1106, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.N.; Choi, J.-S.; Kwon, J. Gold nanozyme-based paper chip for colorimetric detection of mercury ions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.-F.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Jin, Z.-Y.; Shao, G. Colorimetric assay for the simultaneous detection of Hg2+ and Ag+ based on inhibiting the peroxidase-like activity of core–shell Au@Pt nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.-W.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Logic Control of Enzyme-Like Gold Nanoparticles for Selective Detection of Lead and Mercury Ions. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J. Surface modification of nanozymes. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1125–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.M.; Park, S.H.; Kim, G.; Kim, D.-H.; Ahn, D.; Kim, Y.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Kang, H.J.; Chung, S.J. Metal-induced redshift of optical spectra of gold nanoparticles: An instant, sensitive, and selective visual detection of lead ions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; He, L.; Pang, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles: Design principles and recent advances. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 122, 115754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onireti, O.O.; Lin, C.; Qin, J. Combined effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids on mobilization of arsenic and lead from multi-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-S.; Huang, F.-F.; Lin, Y.-W. Fluorescent Detection of Lead in Environmental Water and Urine Samples Using Enzyme Mimics of Catechin-Synthesized Au Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosaf, K.; Ipe, B.I.; Suresh, C.H.; Thomas, K.G. In Situ Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles and Selective Naked-Eye Detection of Lead Ions from Aqueous Media. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12839–12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, B.H.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Ariño, C.; Esteban, M. Heavy Metal Binding by Tannic Acid: A Voltammetric Study. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Bu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; et al. Tannic acid modified single nanopore with multivalent metal ions recognition and ultra-trace level detection. Nano Today 2020, 33, 100868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ma, M.; Wang, Y. Using gallic acid-modified gold nanoassemblies to detect the Pb2+ of tea. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 3570–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.J.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.J.; Tang, J.; Huang, C.Z. Visual observation of the mercury-stimulated peroxidase mimetic activity of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11939–11941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Kannan, P.; Lin, Z.; Qiu, B.; Guo, L. Gold Nanorods as Colorful Chromogenic Substrates for Semiquantitative Detection of Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Small Molecules with the Naked Eye. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, K.D.; Sylvester, F.C.; Hopcia, K.L.; Biaglow, J.E. Role of Fenton Chemistry in Thiol-Induced Toxicity and Apoptosis. Radiat. Res. 1996, 145, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ni, D.; Rosenkrans, Z.T.; Huang, P.; Yan, X.; Cai, W. Nanozyme: New horizons for responsive biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3683–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Duan, D.; Gao, L.; Zhou, M.; Fan, K.; Tang, Y.; Xi, J.; Bi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Gao, G.F.; et al. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Wang, H.; Xi, J.; Liu, Q.; Meng, X.; Duan, D.; Gao, L.; Yan, X. Optimization of Fe3O4 nanozyme activity via single amino acid modification mimicking an enzyme active site. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Josephy, P.D.; Eling, T.; Mason, R.P. The horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of 3,5,3′,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Free radical and charge-transfer complex intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 3669–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.-C.; Nam, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.-B. A colorimetric probe to determine Pb2+ using functionalized silver nanoparticles. Anal. 2015, 140, 8209–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Xiong, X.; Deng, S. Colorimetric Detection of Lead Ion Based on Gold Nanoparticles and Lead-Stabilized G-Quartet Formation. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2015, 08, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Priyadarshini, E.; Pradhan, N. Metal-induced aggregation of valine capped gold nanoparticles: An efficient and rapid approach for colorimetric detection of Pb2+ ions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.-J.; Shi, M.-R.; Wang, L.-Y.; Peng, C.-F.; Wei, X.-L. Colorimetric determination of Pb2+ ions based on surface leaching of Au@Pt nanoparticles as peroxidase mimic. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Leng, Y.; Miao, L.; Xin, J.; Wu, A. The colorimetric detection of Pb2+ by using sodium thiosulfate and hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide modified gold nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 5485–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, B.J.; Shilowa, P.M.; Anyanwu, G.O.; Modise, J.S. Removal of Pb2+ from Water by Synthesized Tannin Resins from Invasive South African Trees. Water 2018, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.; Shao, P.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; You, D.; Shi, H.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Lai, W.; Liang, D.; Luo, X. Tannic acid-based adsorbent with superior selectivity for lead(II) capture: Adsorption site and selective mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sensing probe | [E] (M) | Substrate | Km (mM) | ʋmax (M s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA-capped AuNPs | 11.8 × 10−10 | TMB | 0.2 | 6.7 × 10−8 |
| H2O2 | 190 | 3.8 × 10−8 | ||
| Pb2+-TA-capped AuNPs | 11.8 × 10−10 | TMB | 0.09 | 1.4 × 10−7 |
| H2O2 | 100 | 3.3 × 10−7 | ||
| HRP [43] | 6.2 × 10−11 | TMB | 0.43 | 10 × 10−8 |
| H2O2 | 3.7 | 8.7 × 10−8 |
| Sensing Material | Sensing Mechanism | LOD (ng×mL−1) | Linear Range (ng×mL−1) | Analysis Time (min) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid assays | |||||
| TA-capped AuNPs | Pb2+-promoted nanozyme activity of TA-capped AuNPs | 11.3 | 25–500 | 10 | This work |
| 1-(2-mercaptoethyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione functionalized silver nanoparticles (MTT-AgNPs) | aggregation of the MTT−AgNPs in the presence of Pb2+ ions | 19.8 | 103–600 | 3 | [44] |
| N-decanoyltromethamine(NDTM)-capped AuNPs | Pb2+-induced aggregation of NDTM-AuNPs | 72.4 | 0–6200 | <1 | [13] |
| Oligonucleotide functionalized AuNPs | Change in guanine-rich ssDNA conformation into a rigid G-quartet structure in the presence of Pb2+ and NaCl-induced aggregation of unmodified AuNPs | 1035 | 20.7–2070 | 5 | [45] |
| AuNPs | Aggregation of the as-synthesized AuNPs in the presence of Pb2+ | 3730 | 0–20.7 × 103 | <5 | [29] |
| Valine-capped AuNPs | Pb2+-induced aggregation of valine-capped AuNPs | 6300 | 0–289 × 103 | 5 | [46] |
| Time consuming assays | |||||
| Catechin synthesized AuNPs | Pb2+-promoted nanozyme activity of catechin modified AuNPs in the H2O2-mediated oxidation of Amplex UltraRed | 0.3 | 2–207 | 60 | [32] |
| Gold core-platinum shell nanohybrids (Au@PtNPs) | Pb2+-S2O32− ions-inhibited nanozyme activity of Au@PtNP | 0.6 | 4–166 | 40 | [47] |
| Sodium thiosulfate and hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) modified AuNPs | leaching of CTAB-capped Au NPs induced by Na2S2O3 and Pb2+ | 8.3 | 207–1200 | 30 | [48] |
| Sample | Added (ng×mL−1) | Found (ng×mL−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drinking water | 25 | 33.3 | 133.4 | 2.8 |
| 50 | 54.5 | 108.9 | 3.2 | |
| 100 | 128.2 | 128.2 | 5.6 | |
| Tap water | 25 | 27.7 | 110.9 | 2.9 |
| 50 | 56.5 | 112.9 | 7.7 | |
| 100 | 106.6 | 106.6 | 3.8 | |
| Spring water | 25 | 29.7 | 118.7 | 1.9 |
| 50 | 56.8 | 113.6 | 2.9 | |
| 100 | 106.8 | 106.8 | 6.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serebrennikova, K.V.; Komova, N.S.; Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Tannic Acid-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Novel Nanozyme for Colorimetric Determination of Pb2+ Ions. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120332
Serebrennikova KV, Komova NS, Berlina AN, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Tannic Acid-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Novel Nanozyme for Colorimetric Determination of Pb2+ Ions. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(12):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120332
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerebrennikova, Kseniya V., Nadezhda S. Komova, Anna N. Berlina, Anatoly V. Zherdev, and Boris B. Dzantiev. 2021. "Tannic Acid-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Novel Nanozyme for Colorimetric Determination of Pb2+ Ions" Chemosensors 9, no. 12: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120332
APA StyleSerebrennikova, K. V., Komova, N. S., Berlina, A. N., Zherdev, A. V., & Dzantiev, B. B. (2021). Tannic Acid-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Novel Nanozyme for Colorimetric Determination of Pb2+ Ions. Chemosensors, 9(12), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120332