Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Using Nanoparticle-Modified Voltammetric Sensors and Electronic Tongue Principles
Abstract
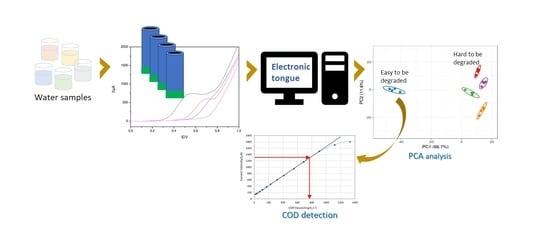
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Electrodes Fabrication
2.3.1. Fabrication of Electrode E1
2.3.2. Fabrication of Electrodes E2, E3, and E4
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
2.4.1. Cyclic Voltammetric Response
2.4.2. Reproducibility Study
2.5. Measurements of Real Water Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Voltammetric Array Response
3.2. Calibration Curves
3.3. Reproducibility Study
3.4. Real Samples Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez-Capitán, M.; Baldi, A.; Gómez, R.; García, V.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C.; Fernández-Sánchez, C. Electrochemical nanocomposite-derived sensor for the análisis of chemical oxygen demand in urban wastewaters. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2152–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.A.; Olean-Oliveira, A.; Cardoso, C.X.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Photochemiresistor sensor development based on a bismuth vanadate type semiconductor for determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18723–18729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Wu, H. A rapid determination method of chemical oxygen demand in printing and dyeing wastewater using ultraviolet spectroscopy. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wu, B.; Qu, H.; Cheng, Y. A high throughput chemiluminescence method for determination of chemical oxygen demand in waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 633, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, H. A surface-fluorinated-TiO2–KMnO4 photocatalytic system for determination of chemical oxygen demand. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 571, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, G. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and detection of chemical oxygen demand by fluorescence methods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Hao, N.; Xiong, M.; Han, X.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, K. Portable photoelectrochromic visualization sensor for detection of Chemical Oxygen Demand. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13604–13609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ma, C.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, H. Flow injection analysis of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) by using a boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, X.; Chen, A. Determination of chemical oxygen demand based on photoelectrocatalysis of nanoporous TiO2 electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, L.; Xian, Y.; Jin, L. Rh2O3/Ti electrode preparation using laser anneal and its application to the determination of chemical oxygen demand. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C. Effect of calcination temperature on electrocatalytic activities of Ti/IrO2 electrodes in methanol aqueous solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 6258–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Wu, C.; Wu, K.B.; Cheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.K. Electrochemical sensing chemical oxygen demand based on the catalytic activity of cobalt oxide film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 736, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, K. Electrochemical tuning the activity of nickel nanoparticle and application in sensitive detection of Chemical Oxygen Demand. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 22845–22850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jing, T.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, S. A sensitive and environmentally friendly method for determination of chemical oxygen demand using NiCu alloy electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 74, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.R.; Conceição, C.D.C.; Bonifácio, V.G.; Fatibelho Filho, O.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Using a Copper Electrode: A Clean Alternative Method. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carchi, T.; Lapo, B.; Alvarado, J.; Montero, P.J.E.; Llorca, J.; Fernández, L. A Nafion film cover to enhance the analytical performance of the CuO/Cu electrochemical sensor for determination of chemical oxygen demand. Sensors 2019, 19, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, H.H.; Badr, I.H.A.; Abdel-Fatah, H.T.M.; Elfeky, E.M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, A.M. Low cost chemical oxygen demand sensor based on electrodeposited nano-copper film. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badr, I.H.A.; Hassan, H.H.; Hamed, E.; Abdel-Aziz, A.M. Sensitive and green method for determination of chemical oxygen demand using a nano-copper based electrochemical sensor. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winquist, F.; Olsson, J.; Eriksson, M. Multicomponent analysis of drinking water by a voltammetric electronic tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 683, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Sun, Q.; Su, K.; Wan, H.; Li, H.; Xu, N.; Sun, F.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. Recent achievements in electronic tongue and bioelectronic tongue as taste sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Aguayo, D.; Bonet-San-Emeterio, M.; del Valle, M. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of acetaminophen, ascorbic acid and uric acid by use of integrated array of screen-printed electrodes and chemometric tools. Sensors 2019, 19, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Chacón, A.; Torabi, F.; Faridbod, F.; Ghasemi, J.B.; González-Calabuig, A.; del Valle, M. Voltammetric electronic tongue for the simultaneous determination of three benzodiazepines. Sensors 2019, 19, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarma, M.; del Valle, M. Improved Sensing of Capsaicin with TiO2 Nanoparticles Modified Epoxy Graphite Electrode. Electroanalysis 2019, 32, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetó, X.; Apetrei, C.; del Valle, M.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L. Evaluation of Red Wines Antioxidant Capacity by Means of a Voltammetric E-Tongue with an Optimized Sensor Array. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 120, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-San-Emeterio, M.; González-Calabuig, A.; del Valle, M. Artificial Neural Networks for the Resolution of Dopamine and Serotonin Complex Mixtures Using a Graphene-Modified Carbon Electrode. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, K.; Brycht, M.; Leniart, A.; Domagała, S.; Kaczmarek, K.; Kalcher, K.; Skrzypek, S. A Sensitive Sensor Based on Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes: Its Preparation, Characterization and Application in the Electrochemical Determination of Drug Clorsulon in Milk Samples. Electroanalysis 2019, 32, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Tan, F.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Quan, X. Sensitive Amperometric Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand Using Ti/Sb-SnO2/PbO2 Composite Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, S. A Nano-Nickel Electrochemical Sensor for Sensitive Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, L.; Xian, Y.; Ai, S.; Jin, L. Amperometric determination of chemical oxygen demand with flow injection analysis using F-PbO2 modified electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 548, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | y = 1.5281x +112.75, R2 = 0.9999 | y = 0.2044x + 14.23, R2 = 0.9934 | y = 0.1504x + 10.21, R2 = 0.9946 | y = 0.1908x + 59.18, R2 = 0.9720 |
| Glycine | y = 1.8878x + 121.02, R2 = 0.9941 | y = 0.1067x + 10.49, R2 = 0.9925 | -- | -- |
| Ethylene Glycol | y = 2.6844x + 122.71, R2 = 0.9945 | -- | -- | -- |
| KHP | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Sensor | Electrode Modifier | Standard Substance | LOD (mg O2·L−1) | Linear Range (mg O2·L−1) | Reproducibility (RSD%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO/AgO sensor [1] | CuO/AgO nanoparticle | Glucose | 28 | 106–1292 | Not mentioned |
| Boron Doped Diamond [8] | - | KHP, phenol | 7.5 | 20–9000 | 1.9 |
| Cobalt oxide/GCE [12] | Cobalt oxide film | Glycine | 1.1 | 5.7–155.8 | 5.7 |
| Ni Cu alloy/GCE [14] | Ni Cu alloy film | Glucose | 1.0 | 10–1533 | 1.0 |
| CuO/Cu electrode [15] | CuO nanoparticle | Glucose | 20.3 | 53.0–28014 | Not mentioned |
| Ti/Sb-SnO2/PbO2 [27] | Sb-SnO2/PbO2 | Glucose | 0.3 | 0.5–200 | <5% |
| Nano-Ni/GCE [28] | Nano-Ni | Glucose | 1.1 | 10–1533 | 4.7 |
| F-PbO2 sensor [29] | Pb (II) particles | Glucose | 15.5 | 100–1200 | Not mentioned |
| This work, electrode E1 | Cu/CuO-Nf | Glucose | 12.3 | 19.2–905.5 | 2.48% |
| RSD | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank 1 | 4.04% | 3.07% | 3.90% | 3.44% |
| Glucose 2 | 2.48% | 3.57% | 3.87% | 4.14% |
| Real Samples | COD Values (mg O2·L−1) | Real Sample Found (mg O2·L−1) | COD Measuring Vessel (mg O2·L−1) | Added Glucose (mg O2·L−1) | Spiked Sample Found (mg O2·L−1) | Recovery Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 1312 | <LOD | 6.6 * | 38.32 | 27.11 | 109.5% |
| Sample 2 | 2088 | <LOD | 10.4 * | 38.32 | 27.67 | 108.6% |
| Sample 1nd | 1312 | 33.76 | 656 * | 95.52 | 112.11 | 82.02% |
| Sample 2nd | 2088 | 17.10 | 1044 * | 95.52 | 101.64 | 88.51% |
| Sample 3nd | Not detected | 18.56 | - | 95.52 | 97.37 | 82.50% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; del Valle, M. Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Using Nanoparticle-Modified Voltammetric Sensors and Electronic Tongue Principles. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9030046
Wang Q, del Valle M. Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Using Nanoparticle-Modified Voltammetric Sensors and Electronic Tongue Principles. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qing, and Manel del Valle. 2021. "Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Using Nanoparticle-Modified Voltammetric Sensors and Electronic Tongue Principles" Chemosensors 9, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9030046
APA StyleWang, Q., & del Valle, M. (2021). Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Using Nanoparticle-Modified Voltammetric Sensors and Electronic Tongue Principles. Chemosensors, 9(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9030046