Application of PEDOT:PSS and Its Composites in Electrochemical and Electronic Chemosensors
Abstract
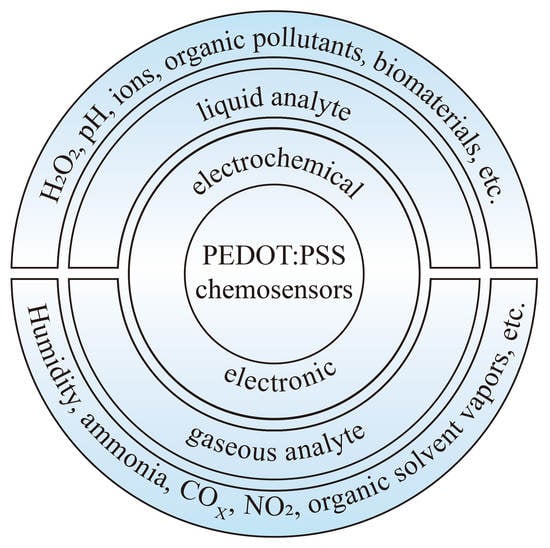
:1. Introduction
2. PEDOT:PSS-Based Electrochemical Chemosensors
2.1. H2O2 Detection
2.2. pH Detection
2.3. Ion Detection
2.4. Other Analyte Detection
| Working Electrode | Analyte | Model | LDL | Sensitivity | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS-PB-EG-DVS/SPGE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 219 nM | −0.95 A M−1 cm−2 | 0.1–25.6 μM | [19] |
| Nafion/HRP/PEDOT:PSS-CS micelle/GCE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 0.03 nM | - | 0.1 nM–10 nM | [33] |
| Nafion/HRP/PEDOT:PSS hydrogel/GCE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 0.94 μM | 155 μA mM−1 | 0.0088–0.15 mM | [34] |
| 0.045 mM | 3.5 μA mM−1 | 0.4–10 mM | ||||
| HRP-PEDOT:PSS-AuNPs/GCE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 0.1 μM | - | 0.2–380 μM | [35] |
| Nafion/HRP/AgNPs/PEDOT:PSS-Nafion/GCE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 0.02 μM | - | 0.05–20 μM | [36] |
| HRP/PEDOT:PSS-rGO-AuNPs/SPGE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 0.08 μM | 677 μA mM−1 cm−2 | 0.5–400 μM | [37] |
| PEDOT:PSS-MDB/GCE | H2O2 | Amperometry | 0.1 μM | 353.9 mA mM−1 cm−2 | 5–120 μM | [38] |
| PANI/PEDOT:PSS/G | pH | Potentiometry | - | 75.06 mV pH−1 | 4–7 | [39] |
| PANI/PEDOT:PSS-MWCNTs-cotton | pH | Potentiometry | - | −61 ± 2 mV pH−1 | 2–12 | [40] |
| PANI/PEDOT:PSS fiber | pH | Potentiometry | - | −56 ± 7 mV pH−1 | 3–7 | [43] |
| K+ ISM/PEDOT:PSS-acrylic textile | K+ | OECT | - | 3.49 M−1 | 0.01–1000 mM | [44] |
| NH4+ and Ca2+ ISM/PEDOT:PSS | NH4+ Ca2+ | OECT | - | - | 10–1000 μM | [45] |
| Cu2+-ISM/PEDOT:PSS/GCE | Cu2+ | Potentiometry | 0.5 nM | 28.1 ± 0.4 mV dec−1 | 1 nM–1 mM | [46] |
| ISMs/PEDOT:PSS/GCE | Na+ | Potentiometry | - | 56 ± 1 mV dec−1 | 0.1–100 μM | [47] |
| K+ | - | 58 ± 1 mV dec−1 | 0.01 mM–100 μM | |||
| Ca2+ | - | 29 ± 1 mV dec−1 | 0.01–100 μM | |||
| Mg2+ | - | 30 ± 1 mV dec−1 | 1–100 μM | |||
| Cl− | - | −54 ± 1 mV dec−1 | 0.1–100 μM | |||
| Pb2+-ISM/PEDOT:PSS/GCE | Pb2+ | Potentiometry | 0.1 μM | 27 mV dec−1 | 10−5–10−7 M | [49] |
| PEDOT:PSS/glassy-carbon disk | thiols | Amperometry | 0.005 mM | 0.43 A M−1 cm−2 | 0.005–0.1 mM | [50] |
| PEDOT:PSS/GCE | Tricresyl phosphate | Voltammetry | 70 ppb | - | 50–300 ppb | [51] |
| PEDOT:PSS-GO/PET | carbofuran | Voltammetry | 0.1 µM | - | 1 mM–90 mM | [52] |
| PEDOT:PSS-β-CD-SWCNT-COOH/GCE | shikonin | Voltammetry | 1.80 nM | - | 6.0–30,000 nM | [53] |
| PEDOT:PSS-rGO/GCE | nimesulide | Voltammetry | 2.4 nM | - | 80–1900 nM | [54] |
| piroxicam | 0.1 µM | 0.87–260 µM | ||||
| PEDOT:PSS-G/SPCE | 2,2-diphenyl1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) | Amperometry | 0.59 μM | - | 5–30 μM | [55] |
| PEDOT:PSS-MgO/GCE | bisphenol A | Voltammetry | 0.5 nM | - | 1.0 nM–0.4 μM and 0.4–10 μM | [56] |
| CuNPs/GO-CB-PEDOT:PSS/GCE | isoproterenol | Voltammetry | 1.9 μM | 0.062 μA μM−1 | 8–50 μM | [57] |
| acetaminophen | 0.23 μM | 0.29 μA μM−1 | 0.9–7 μM | |||
| folic acid | 1.0 μM | 0.098 μA μM−1 | 5–31 μM | |||
| propranolol | 0.18 μM | 0.92 μA μM−1 | 0.5–2.9 μM | |||
| caffeine | 3.4 μM | 0.028 μA μM−1 | 11–64 μM | |||
| PEDOT:PSS-ZnO/GCE | chlorogenic acid | Voltammetry | 0.02 μM | 26.38 μA mΜ−1 cm−2 | 0.03–476.2 μM | [58] |
| AgNPs/PEDOT:PSS-H2SO4/glass | nitrite | Amperometry | 0.34 μM | 0.03639 μA μM−1 cm−2 | 0.5–3400 μM | [59] |
| PEDOT:PSS-DMSO film | tert-butylhydroquinone | Voltammetry | 0.15 μM | - | 0.5–200 μM | [60] |
| PEDOT:PSS-CMC/GCE | tryptophan | Voltammetry | 0.02 μM | - | 0.05–100 mM | [61] |
| PEDOT:PSS-CMC-SWCNT/GCE | maleic hydrazide | Voltammetry | 0.1 µM | - | 0.8–51 µM | [62] |
3. PEDOT:PSS-Based Electronic Chemosensors
3.1. Humidity Detection
3.2. Ammonia Detection
3.3. CO and CO2 Detection
3.4. NO2 Detection
3.5. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Detection
| Sensing Material | Mechanism | Sensor Structure | Analyte | Sensitivity | Response/Recovery Time | Sensing Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS | Capacitance | IDT | Humidity | - | <30 s/<1 min | 52.0–93.4% RH | [63] |
| PEDOT:PSS/MoS2 | Impedance | Dual IDT’s in series Sensor array | Humidity | 50 kΩ/%RH, 850 Hz/%RH | 0.5 s/0.8 s | 0–80% RH | [64] |
| PEDOT:PSS | Resistance | Dielectric elastomer actuator | Humidity | - | - | 30–90%RH | [65] |
| PEDOT:PSS | Resistance | Nanowires | Humidity | 5.46% | 0.63 s/2.05 s | 0–60% RH | [67] |
| PEDOT:PSS-Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 | Resistance | electrodes on substrate | Humidity | 0.65%/ΔRH | >1 s/>1 s | 30–70%RH | [69] |
| PEDOT:PSS-Graphene | Resistance | paper substrate | Humidity | - | - | 20–90% RH | [70] |
| PEDOT:PSS | Resistance | micron line | Humidity | 0.19% (ΔR/R0)/%RH | 0.86 s/0.59 s | 11–69% RH | [71] |
| PEDOT:PSS)/polyacrylonitrile fabrics | Resistance | IDT | Humidity | 110% | 2 s/7 s | 0–100% RH | [72] |
| PEDOT:PSS-ZnSnO3 | Impedance | IDT with SAW effect | Humidity | - | 0.2 s/0.2 s | 0–90%RH | [75] |
| PEDOT:PSS–PVA | Impedance Capacitance | IDT with SAW effect | Humidity | 350 Ω/%RH 28 pF/%RH | 0.63 s/0.56 s | 0–80% RH | [76] |
| PEDOT:PSS/GO | Capacitance | Two interdigitally arranged IDT | Humidity | 1.22 nF/%RH | - | 25–85% RH | [77] |
| PEDOT:PSS-MoS2 | Impedance based | Glass substrates | Humidity | - | - | 50–75% RH | [79] |
| PEDOT:PSS-Graphene | Resistance | IDT | NH3 | 116.38% (1000 ppm) | 7.7 min/10 min | −1500 ppm | [12] |
| AgNWs/PEDOT:PSS | Resistance | PET substrate | NH3 | 5% (1 ppm) | - | 0.5–25 ppm | [20] |
| PEDOT:PSS nanowire | Resistance | Silicon substrate | NH3 | 0.8% (3.2 ppm) | 57 s/163 s | 3–60 ppm | [66] |
| Si/PEDOT:PSS | Current | OFET | NH3 | - | 13 s/8 s | - | [81] |
| ITO/PEDOT:PSS | NH3 | - | 29 s/22 s | ||||
| PEDOT:PSS-FeCl3 | Resistance | IDT | NH3 | 7.6% (0.5 ppm) | 20 s | 0.1–200 ppm | [82] |
| PEDOT:PSS-MWCNTs | Resistance | IDT | NH3 | 73.7% (1000 ppm) | - | 0–1000 ppm | [83] |
| PEDOT:PSS-graphene | Resistance | IDT | NH3 | 6.9% (1000 ppm) | 3 min/5 min | 25–1000 ppm | [84] |
| (CuTSPc@3D-(N)GF)/(PEDOT-PSS) | Resistance | IDT | NH3 | - | - | 1–1000 ppm | [85] |
| PEDOT-PSS rGO | Resistance | IDT | NH3 | - | 1.05 min/2.84 min | - | [86] |
| PEDOT:PSS-Co(salen) | Resistance | IDT | CO | 25.0 ± 0.05% | - | 0.5–10.0% CO (v/v) N2 | [88] |
| PEDOT:PSS-Fe(III)(salen) | Resistance | IDT | CO | 31.32 ± 0.88% | 38 s/5 s | - | [89] |
| PEDOT:PSS-B2HDDT | Resistance | PET substrate | CO | 55% (common gas) | - | 0–66 vol% | [90] |
| PEDOT:PSS-MWCNTs | Resistance | PDMS substrate | CO | 0.05 ± 0.004% (1000 ppm) | 10.6 ± 0.4 s/24.6 ± 1.2 s | 250–1000 ppm | [91] |
| Graphene/PEDOT:PSS | Resistance | PET substrate | CO2 | 4.7 µΩ/Ω/ppm (420 ppm) | - | 400–4200 ppm | [92] |
| PEDOT:PSS-PANI | Resistance | IDT | CO | 3.24% (1000 ppm) | - | 500–2000 ppm | [93] |
| PEDOT:PSS-WO3 | Resistance | IDT | NO2 | 2.31 (80 ppm) | - | 10–80 ppm | [94] |
| PEDOT:PSS-WO3 | Resistance | IDT | NO2 | - | 45.1 s/88.7 s | 50–220 ppb | [95] |
| PEDOT:PSS-TiO2 | Current | IDT | NO2 | - | - | 10–130 ppb | [96] |
| PEDOT:PSS-graphene | Resistance | IDT | Methanol | 13.5% (50 ppm) | 12 s/32 s | 1–1000 ppm | [97] |
| PEDOT:PSS-GO | Resistance | IDT | Methanol | 11% (35 ppm) | 3.2 s/16 s | 3–700 ppm | [98] |
| PEDOT:PSS thin film | Resistance | PDMS substrate | Methanol | ∼106 (300 ppm) | <5 s/<5 s | 6–300 ppm | [99] |
| PEDOT:PSS-Ti3C2Tx | Resistance | IDT | Methanol | 5.54 | - | - | [100] |
| PEDOT:PSS-cotton | Current | Cotton | Acetone | 53% | 1 min/2 min | 1–30% (acetone solvent) | [101] |
| PEDOT:PSS-MWCNTs | Resistance | IDT | Formaldehyde | 30.5% (10 ppm) | 45 s/<7 s | 10–200 ppm | [102] |
| PEDOT:PSS-graphite nanosheets | Resistance | Glass substrate | Nitroaromatics | - | 1.15 min/1.88 min | - | [103] |
4. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, H.; Kumari, N.; Sharma, R. Nanocomposites (conducting polymer and nanoparticles) based electrochemical biosensor for the detection of environment pollutant: Its issues and challenges. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 85, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezakati, T.; Seifalian, A.; Tan, A.; Seifalian, A.M. Conductive polymers: Opportunities and challenges in biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6766–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdzan, N.S.M.; Fen, Y.W.; Anas, N.A.A.; Omar, N.A.S.; Saleviter, S. Development of biopolymer and conducting polymer-based optical sensors for heavy metal ion detection. Molecules 2020, 25, 2548–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.P.; Xu, J.K. Scientific importance of water-processable PEDOT-PSS and preparation, challenge and new application in sensors of its film electrode: A review. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 1121–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, N.; Kushwaha, C.S.; Shukla, S.K. A review on electrically conducting polymer bionanocomposites for biomedical and other applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 69, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamiri, G.; Haseeb, A. Recent trends and developments in graphene/conducting polymer nanocomposites chemiresistive sensors. Materials 2020, 13, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Hwang, Y.; Park, S.-H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, A.; Park, S.; Kwon, O.S. An elaborate sensor system based on conducting polymer-oligosaccharides in hydrogel and the formation of inclusion complexes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 90, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, D.; Del Agua, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Mecerreyes, D. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) derivatives: Innovative conductive polymers for bioelectronics. Polymers 2017, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Yu, H.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, J. Facile synthesis of palladium-decorated three-dimensional conducting polymer nanofilm for highly sensitive H2 gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5156–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, R.M.; Klem, M.d.S.; Nogueira, G.L.; Gomes, T.C.; Alves, N. Low cost humidity sensor based on PANI/PEDOT:PSS printed on paper. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 2647–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Nejad, F.G.; Shoaie, I.S.; Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Asl, M.S.; Van Le, Q.; Zhang, K.; Jang, H.W.; Shokouhimehr, M. Recent developments in conducting polymers: Applications for electrochemistry. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37834–37856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.; Salehi, A.; Boroumand, F.A. Fabrication and characterization of an ammonia gas sensor based on PEDOT-PSS with n-doped graphene quantum dots dopant. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6149–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, Z.; Naghib, S.M.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. An overview on the synthesis and recent applications of conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) in industry and biomedicine. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 7575–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elschner, A.; Kirchmeyer, S.; Lövenich, W.; Merker, U.; Reuter, K. PEDOT-Principles and Applications of an Intrinsically Conductive Polymer; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zeng, H.N.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, J.W. Recent advances in conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate hybrids for thermoelectric applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 8858–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, S.P.; Li, P.C.; Xia, Y.J.; Zhang, X.; Du, D.H.; Isikgor, F.H.; Ouyang, J.Y. Review on application of PEDOTs and PEDOT:PSS in energy conversion and storage devices. J Mater. Sci. Mater Electron. 2015, 26, 4438–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.Y. Recent advances of intrinsically conductive polymers. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2018, 34, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, H. Review on nanomaterials/conducting polymer based nanocomposites for the development of biosensors and electrochemical sensors. Polym. Plast. Tech. Mat. 2020, 60, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; O’Hare, D. Exhaled breath condensate based breath analyser-a disposable hydrogen peroxide sensor and smart analyser. Analyst 2020, 145, 3549–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Zhuo, B.G.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, W.J.; Guo, X.J. Flexible ammonia sensor based on PEDOT:PSS/silver nanowire composite film for meat freshness monitoring. IEEE Electr. Device L. 2017, 38, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, L.V.; Lipomi, D.J. Stretchable Conductive polymers and composites based on PEDOT and PEDOT: PSS. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, J.R.; Tompson, B.C.; Skotheim, T.A. Conjugated Polymers: Properties, Processing, and Applications; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.J.; Si, H.W.; Zhang, X.D.; Lin, S.W. Functional sensing interfaces of PEDOT: PSS organic electrochemical transistors for chemical and biological sensors: A mini review. Sensors 2019, 19, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.J.; Wu, X.M.; Chen, Q.Z.; Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, H.P.; Guo, T.L. High-performance low-voltage flexible photodetector arrays based on all-solid-state organic electrochemical transistors for photosensing and imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 20214–20224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choosang, J.; Thavarungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Numnuam, A. AuNPs/PpPD/PEDOT: PSS-Fc modified screen-printed carbon electrode label-free immunosensor for sensitive and selective determination of human serum albumin. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104709–104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Wahab, F.; Abdul Guthoos, H.F.; Wan Salim, W.W.A. Solid-state rGO-PEDOT: PSS transducing material for cost-effective enzymatic sensing. Biosensors 2019, 9, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhasin, A.; Sanders, E.C.; Ziegler, J.M.; Briggs, J.S.; Drago, N.P.; Attar, A.M.; Santos, A.M.; True, M.Y.; Ogata, A.F.; Yoon, D.V.; et al. Virus bioresistor (VBR) for detection of bladder cancer marker DJ-1 in urine at 10 pM in one minute. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6654–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Said, W.A.; Abdelshakour, M.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, J.W. Application of conducting polymer nanostructures to electrochemical biosensors. Molecules 2020, 25, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirzadeh, Z.; Javadpour, S.; Shariat, M.H.; Knibbe, R. Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on copper oxide and multi-wall carbon nanotubes using PEDOT: PSS matrix. Synth. Met. 2018, 245, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, F.; Gualandi, I.; Tonelli, D.; Decataldo, F.; Possanzini, L.; Fraboni, B.; Scavetta, E. Design of an electrochemically gated organic semiconductor for pH sensing. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 116, 106763–106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodagholy, D.; Rivnay, J.; Sessolo, M.; Gurfinkel, M.; Leleux, P.; Jimison, L.H.; Stavrinidou, E.; Herve, T.; Sanaur, S.; Owens, R.M. High transconductance organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borras-Brull, M.; Blondeau, P.; Riu, J. The use of conducting polymers for enhanced electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Xu, X.F.; Fan, X.X.; Yang, R.C.; Wu, T.; Zhang, C.G. Application of conducting micelles self-assembled from commercial poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) and chitosan for electrochemical biosensor. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słoniewska, A.; Kasztelan, M.; Berbeć, S.; Pałys, B. Influence of buffer solution on structure and electrochemical properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(styrenesulfonate) hydrogels. Synth. Met. 2020, 263, 116363–116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Peng, R.; Ran, Q.; Xian, Y.Z.; Tian, Y.; Jin, L.T. A highly soluble poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrene sulfonic acid)/Au nanocomposite for horseradish peroxidase immobilization and biosensing. Talanta 2010, 82, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.Y.; Wen, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.K.; Wang, Z.F.; Duan, X.M. A stable sandwich-type hydrogen peroxide sensor based on immobilizing horseradish peroxidase to a silver nanoparticle monolayer supported by PEDOT: PSS-nafion composite electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 9348–9359. [Google Scholar]
- Mercante, L.A.; Facure, M.H.M.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. One-pot preparation of PEDOT: PSS-reduced graphene decorated with Au nanoparticles for enzymatic electrochemical sensing of H2O2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 407, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siao, H.-W.; Chen, S.-M.; Lin, K.-C. Electrochemical study of PEDOT-PSS-MDB-modified electrode and its electrocatalytic sensing of hydrogen peroxide. J. Solid State Electr. 2010, 15, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahed, M.A.; Barman, S.C.; Das, P.S.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Yoon, H.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, J.Y. Highly flexible and conductive poly (3, 4-ethylene dioxythiophene)-poly (styrene sulfonate) anchored 3-dimensional porous graphene network-based electrochemical biosensor for glucose and pH detection in human perspiration. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 160, 112220–112229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Totti, S.; Velliou, E.; Campagnolo, P.; Hingley-Wilson, S.M.; Ward, N.I.; Varcoe, J.R.; Crean, C. Development of a novel highly conductive and flexible cotton yarn for wearable pH sensor technology. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 287, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naficy, S.; Oveissi, F.; Patrick, B.; Schindeler, A.; Dehghani, F. Printed, flexible pH sensor hydrogels for wet environments. Adv. Mater. Technol. US 2018, 3, 1800137–1800146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, C.C.; Jiang, Q.L.; Xu, J.K. Effective approaches to improve the electrical conductivity of PEDOT:PSS: A review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500017–1500032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.O.; Smith, R.E.; Garcia-Torres, J.; Watts, J.F.; Crean, C. Solvent treatment of wet-spun PEDOT:PSS fibers for fiber-based wearable pH sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 4213–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppedè, N.; Giannetto, M.; Villani, M.; Lucchini, V.; Battista, E.; Careri, M.; Zappettini, A. Ion selective textile organic electrochemical transistor for wearable sweat monitoring. Org. Electron. 2020, 78, 105579–105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, S.T.; Fogarty, D.; Cooke, R.; Casadevall, C.D.; Salleo, A.; Parlak, O. Wearable organic electrochemical transistor patch for multiplexed sensing of calcium and ammonium ions from human perspiration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1901321–1901328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd, E.A.; Mohamed, A.-O.; Ayman, H.K.; Elsayed, A.E. Single-piece solid contact Cu(2+)-selective electrodes based on a synthesized macrocyclic calix[4]arene derivative as a neutral carrier ionophore. Molecules 2019, 24, 920–931. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowicz, M.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Jasiński, A.; Ekman, M.; Bocheńska, M.K. A miniaturized solid-contact potentiometric multisensor platform for determination of ionic profiles in human saliva. J. Solid State Electr. 2019, 23, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ocana, C.; Munoz-Correas, M.; Abramova, N.; Bratov, A. Comparison of different commercial conducting materials as ion-to-electron transducer layers in low-cost selective solid-contact electrodes. Sensors 2020, 20, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, M.; Lisak, G.; Ivaska, A.; Bobacka, J. Durable PEDOT: PSS films obtained from modified water-based inks for electrochemical sensors. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 181, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrina, A.A.; Nikiforova, T.G.; Poturai, D.O. Fabrication of electrodes modified with poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene-polystyrene sulfonate film and study of their applicability in thiol-sensitive sensors. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2015, 88, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kirsch, J.; Olsen, E.V.; Fergus, J.W.; Simonian, A.L. Anti-fouling PEDOT: PSS modification on glassy carbon electrodes for continuous monitoring of tricresyl phosphate. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 177, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekol, F.; Mehretie, S.; Hailu, F.A.; Tolcha, T.; Megersa, N.; Admassie, S. Roll-to-roll printed PEDOT/PSS/GO plastic film for electrochemical determination of carbofuran. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Y.P.; Zou, L.; Zhang, X.X.; Xin, X.; Zhou, M.H.; Xu, J.K.; Zhang, G. Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor based on PEDOT:PSS-β-CD-SWCNT-COOH modified glassy carbon electrode enables trace analysis shikonin. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B388–B394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Santos, A.M.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Determination of piroxicam and nimesulide using an electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and PEDOT: PSS. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 799, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirawattanakoson, R.; Rattanarat, P.; Ngamrojanavanich, N.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O. Free radical scavenger screening of total antioxidant capacity in herb and beverage using graphene/PEDOT:PSS-modified electrochemical sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 767, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L. An electrochemical sensor on the novel MgO-PEDOT: PSS platform for sensitive bisphenol a determination. Int. J. Electrochem. Sc. 2019, 14, 9030–9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Santos, A.M.; Silva, T.A.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Simultaneous determination of isoproterenol, acetaminophen, folic acid, propranolol and caffeine using a sensor platform based on carbon black, graphene oxide, copper nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS. Talanta 2018, 183, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, K.; Sivakumar, M.; Cheng, C.-C.; Lu, C.-H.; Chen, J.-K. An effective electrochemical detection of chlorogenic acid in real samples: Flower-like ZnO surface covered on PEDOT: PSS composites modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2019, 301, 127002–127009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Ma, C.; Chen, D.Z.; Shen, Y.L.; Zhu, W.Q.; Gao, J.J.; Song, H.O.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, S.P. Silver nanoparticle-functionalized poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Polystyrene film on glass substrate for electrochemical determination of nitrite. Org. Electron. 2019, 75, 105374–105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.Y.; Xu, J.K.; Xu, Q.; Duan, X.M.; Jiang, F.X.; Lu, L.M.; Jia, H.Y.; Jia, Y.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.F. A poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate)-based electrochemical sensor for tert.-butylhydroquinone. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, J.K.; Wen, Y.P.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, J.; Ding, W.C. Conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene-sulfonate) film electrode with superior long-term electrode stability in water and synergistically enhanced electrocatalytic ability for application in electrochemical sensors. Synth. Met. 2015, 204, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.K.; Wen, Y.P.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, H.; Ding, W.C. Voltammetric determination of phytoinhibitor maleic hydrazide using PEDOT:PSS composite electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 751, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.S.; Cui, Y. A PEDOT: PSS functionalized capacitive sensor for humidity. Measurement 2020, 160, 107782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, G.U.; Sajid, M.; Ali, J.; Kim, S.W.; Doh, Y.H.; Choi, K.H. Wide range highly sensitive relative humidity sensor based on series combination of MoS2 and PEDOT:PSS sensors array. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 266, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Lu, Z.; Lau, G.-K. High humidity sensing by ‘hygromorphic’ dielectric elastomer actuator. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2021, 329, 129268–129275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, N.J.; Rivera, D.; Melendez, A.; Ramos, I.; Lim, J.H.; Johnson, A.T.C. Electrical response of electrospun PEDOT-PSSA nanofibers to organic and inorganic gases. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2011, 156, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.S.; Tang, N.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.N.; Duan, X.X. Rapid response flexible humidity sensor for respiration monitoring using nano-confined strategy. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 125302–125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, H.M.; Duan, X.X. Conductive polymer nanowire gas sensor fabricated by nanoscale soft lithography. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 485301–485326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccola, S.; Greco, F.; Zucca, A.; Innocenti, C.; Fernandez Cde, J.; Campo, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V. Characterization of free-standing PEDOT:PSS/iron oxide nanoparticle composite thin films and application as conformable humidity sensors. ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 6324–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.I.; Kotin, I.A.; Nebogatikova, N.A.; Smagulova, S.A.; Antonova, I.V. Graphene-PEDOT:PSS humidity sensors for high sensitive, low-cost, highly-reliable, flexible, and printed electronics. Materials 2019, 12, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Dai, Y.-Z.; Niu, L.-G.; Lv, C.; Xia, H.; Liu, T. Fast-response humidity sensor based on laser printing for respiration monitoring. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8910–8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panapoy, M.; Singsang, W.; Ksapabutr, B. Electrically conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrene sulfonate)/polyacrylonitrile fabrics for humidity sensors. Phys. Scripta 2010, T139, 014056–014060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Peng, B.; Chi, H.; Li, C.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.Y. Layer-by-layer inkjet printing SPS:PEDOT NP/RGO composite film for flexible humidity sensors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 113298–113306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cui, Y. A flexible calligraphy-integrated in situ humidity sensor. Measurement 2019, 147, 106853–106858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Chang, D.E.; Doh, Y.H.; Kang, C.U.; Choi, K.H. Humidity sensor based on PEDOT: PSS and zinc stannate nano-composite. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 3992–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Sajid, M.; Aziz, S.; Yang, B.-S. Wide range high speed relative humidity sensor based on PEDOT: PSS-PVA composite on an IDT printed on piezoelectric substrate. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 2015, 228, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, F.J.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Becherer, M.; Morales, D.P.; Rodriguez, N. Fabrication and Characterization of Humidity Sensors Based on Graphene Oxide-PEDOT: PSS Composites on a Flexible Substrate. Micromachines 2020, 11, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, G.; Sajid, M.; Choi, C. Highly sensitive and full range detectable humidity sensor using PEDOT: PSS, methyl red and graphene oxide materials. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15227–15236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mombrú, D.; Romero, M.; Faccio, R.; Mombrú, A.W. Transition from positive to negative electrical resistance response under humidity conditions for PEDOT:PSS-MoS2 nanocomposite thin films. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 2019, 30, 5959–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Q.; Abdullah, S.M.; Azmer, M.I.; Najeeb, M.A.; Qadir, K.W.; Sulaiman, K. Influence of relative humidity on the electrical response of PEDOT:PSS based organic field-effect transistor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 255, 2652–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, K.; Elshaer, A.M.; Anas, M.; Ebrahim, S. Fabrication, characterization, and electrical measurements of gas ammonia sensor based on organic field effect transistor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 30, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.W.; Chen, W.G.; Shen, W.F.; Peng, M.Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Wang, R.F.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Song, W.J.; Tan, R.Q. Enhanced flexible room temperature ammonia sensor based on PEDOT:PSS thin film with FeCl3 additives prepared by inkjet printing. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 298, 126890–126897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdee, U.; Thaibunnak, A. Growth of MWCNTs on plasma ion-bombarded thin gold films and their enhancements of ammonia-sensing properties using inkjet printing. J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seekaew, Y.; Lokavee, S.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Low-cost and flexible printed graphene-PEDOT:PSS gas sensor for ammonia detection. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehsari, H.S.; Gavgani, J.N.; Hasani, A.; Mahyari, M.; Shalamzari, E.K.; Salehi, A.; Taromi, F.A. Copper(ii) phthalocyanine supported on a three-dimensional nitrogen-doped graphene/PEDOT-PSS nanocomposite as a highly selective and sensitive sensor for ammonia detection at room temperature. RSC. Adv. 2015, 5, 79729–79737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Khasim, S.; Khan, F.A.; Dhananjaya, N. Fabrication of gas sensor device using poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly (styrenesulfonate)-doped reduced graphene oxide organic thin films for detection of ammonia gas at room temperature. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Liu, W.J.; Guo, X.J. Enabling low cost flexible smart packaging system with internet-of-things connectivity via flexible hybrid integration of silicon RFID chip and printed polymer sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5004–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarzadeh, R.; Panahi, F.; Javadpour, S.; Ali, K.-N.; Noh, H.-B.; Shim, Y.-B. The interaction of CO to the Co(salen) complex in to PEDOT:PSS film and sensor application. B. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arabloo, F.; Javadpour, S.; Memarzadeh, R.; Panahi, F.; Davazdah Emami, M.; Shariat, M.H. The interaction of carbon monoxide to Fe(III)(salen)-PEDOT:PSS composite as a gas sensor. Synth. Met. 2015, 209, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarzadeh, R.; Noh, H.-B.; Javadpour, S.; Panahi, F.; Feizpour, A.; Shim, Y.-B. Carbon monoxide sensor based on a B2HDDT-doped PEDOT: PSS layer. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Jang, Y.; Lee, G.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Jung, J.; Oh, J. Tunable chemical grafting of three-dimensional poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly (4-styrenesulfonate)-multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite with faster charge-carrier transport for enhanced gas sensing performance. Sensors 2020, 20, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; Di Pasquale, G.; Pollicino, A.; Graziani, S.; Gugliuzzo, C.; Lombardo, C.; Marletta, V. Direct printing of a multi-layer sensor on pet substrate for CO2 detection. Energies 2019, 12, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, W.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Su, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Chiu, H.-W.; Lu, S.-S.; Lin, C.-T. A low-power PEDOT: PSS/EB-PANI for CO2 sensing material integrated with a self-powered sensing platform. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Zheng, C.-X.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Lin, K.-M.; Koinkar, P.M. Room-temperature and flexible PEDOT: PSS-WO3 gas sensor for nitrogen dioxide detection. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 33, 1940013–1940018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.K.; Shen, L.; Chen, Q.; Shi, W.Z. Fully gravure-printed NO2 gas sensor on a polyimide foil using WO3-PEDOT:PSS nanocomposites and Ag electrodes. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 216, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetti, E.; Pantalei, S.; Muzyczuk, A.; Bearzotti, A.; De Cesare, F.; Spinella, C.; Macagnano, A. A high sensitive NO2 gas sensor based on PEDOT-PSS/TiO2 nanofibres. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 176, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavgani, J.N.; Dehsari, H.S.; Hasani, A.; Mahyari, M.; Shalamzari, E.K.; Salehi, A.; Taromi, F.A. A room temperature volatile organic compound sensor with enhanced performance, fast response and recovery based on N-doped graphene quantum dots and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 57559–57567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, A.; Dehsari, H.S.; Gavgani, J.N.; Shalamzari, E.K.; Salehi, A.; Afshar Taromi, F.; Mahyari, M. Sensor for volatile organic compounds using an interdigitated gold electrode modified with a nanocomposite made from poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) and ultra-large graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Satapathy, D.K.; Jaiswal, M. Nanostructuring mechanical cracks in a flexible conducting polymer thin film for ultra-sensitive vapor sensing. Nanoscale 2018, 11, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Sun, K.M.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Gogotsi, Y. Ti3C2T/PEDOT: PSS hybrid materials for room-temperature methanol sensor. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cui, Y. Cotton-based wearable PEDOT: PSS electronic sensor for detecting acetone vapor. Flex. Print. Electron. 2017, 2, 042001–042018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsorn, K.; Wongchoosuk, C. Inkjet printing of room-temperature gas sensors for identification of formalin contamination in squids. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 2019, 30, 4782–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, S.; Singhal, P.; Verma, A.L. Synthesis of PEDOT: PSS (poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene))/poly(4-styrene sulfonate))/ngps (nanographitic platelets) nanocomposites as chemiresistive sensors for detection of nitroaromatics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Xue, Z.X.; Gao, N.; Yu, J.R.; Liu, H.T.; Zhang, W.N.; Xu, J.K.; Chen, S. Effects of conductivity-enhancement reagents on self-healing properties of PEDOT:PSS films. Synth. Met. 2020, 268, 116503–116510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, N.; Yu, J.; Tian, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Zang, L. Application of PEDOT:PSS and Its Composites in Electrochemical and Electronic Chemosensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040079
Gao N, Yu J, Tian Q, Shi J, Zhang M, Chen S, Zang L. Application of PEDOT:PSS and Its Composites in Electrochemical and Electronic Chemosensors. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(4):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040079
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Nan, Jiarui Yu, Qingyun Tian, Jiangfan Shi, Miao Zhang, Shuai Chen, and Ling Zang. 2021. "Application of PEDOT:PSS and Its Composites in Electrochemical and Electronic Chemosensors" Chemosensors 9, no. 4: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040079
APA StyleGao, N., Yu, J., Tian, Q., Shi, J., Zhang, M., Chen, S., & Zang, L. (2021). Application of PEDOT:PSS and Its Composites in Electrochemical and Electronic Chemosensors. Chemosensors, 9(4), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040079