Tetracycline Antibiotics: Elucidating the Electrochemical Fingerprint and Oxidation Pathway
Abstract
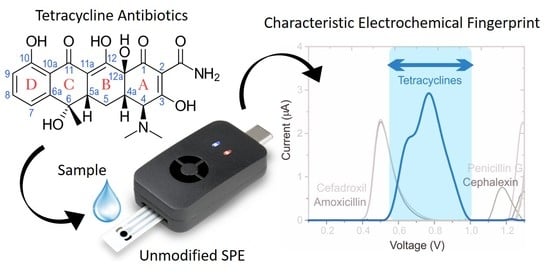
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation and Apparatus
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Electrochemical Behavior of Tetracyclines via SWV
3.2. Elucidation of the Oxidation Pathway of Tetracyclines via LC-QTOF-MS
3.3. Calibration Curves
3.4. Data Treatment towards an Enhanced Peak Analysis
3.5. Single, Binary, Tertiary, and Complex Mixtures of TCs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oka, H.; Ito, Y.; Matsumoto, H. Chromatographic analysis of tetracycline antibiotics in foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 882, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masawat, P.; Slater, J.M. The determination of tetracycline residues in food using a disposable screen-printed gold electrode (SPGE). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 124, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Pham, V.P.; La, T.H.; Phan, T.B.; Le, Q.H. Electrochemical aptasensor for detecting tetracycline in milk. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, X.; Gan, Y. Determination of tetracyclines in ovine milk by high-performance liquid chromatography with a coulometric electrode array system. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1055, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Qin, L.; Zhang, C.; Yi, H.; Li, B.; Deng, R.; Liu, S.; et al. Recent advances in sensors for tetracycline antibiotics and their applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaharn, S.; Charoenraks, T.; Wangfuengkanagul, N.; Grudpan, K.; Chailapakul, O. Flow injection analysis of tetracycline in pharmaceutical formulation with pulsed amperometric detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 499, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, D.E.; Clemons, W.M.; Carter, A.P.; Morgan-Warren, R.J.; Wimberly, B.T.; Ramakrishnan, V. The structural basis for the action of the antibiotics tetracycline, pactamycin, and hygromycin B, on the 30S ribosomal subunit. Cell 2000, 103, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, F.; He, Z. Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on the Chitosan-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection of Tetracycline. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, G.E.; Carpico, G.; Coni, E. Electrochemical sensor for the detection and presumptive identification of quinolone and tetracycline residues in milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 520, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Niazi, J.H.; Gu, M.B. Electrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline detection. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, I.G.; Fabio, P. Determination of tetracycline residues by liquid chromatography coupled with electrochemical detection and solid phase extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8735–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, K.; Sipa, K.; Brycht, M.; Borgul, P.; Skrzypek, S.; Poltorak, L. Electrochemical sensing of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Prussian Blue-Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde for the Sensitive Determination of Tetracycline. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Navarro, N.; Morais, S.; Maquieira, Á.; Puchades, R. Synthesis of haptens and development of a sensitive immunoassay for tetracycline residues. Application to honey samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 594, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridah, S.; Azura, N.; Hazana, R.; Gayah, A.R.; Norzaili, Z.; Azima, A.; Zamri, I. Electrochemical sensors for detection of tetracycline antibiotics Unbound free tetracycline and tetracycline conjugates were removed during the washing step Direct competitive ELISA method Carbon working electrode was connected to the electrochemical ayse. Malays. Soc. Anim. Prod. 2012, 15, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, D.; Qin, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Removal of tetracycline by electrochemical oxidation using a Ti/SnO2–Sb anode: Characterization, kinetics, and degradation pathway. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2017, 47, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, D.; Agüí, L.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Voltammetry and amperometric detection of tetracyclines at multi-wall carbon nanotube modified electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Snow, D.D.; Cassada, D.A.; Monson, S.J.; Spalding, R.F. Analysis of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and chlortetracycline in water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 928, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Aptamer based electrochemical sensors for emerging environmental pollutants. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, A.J.; Kronka, M.S.; Fortunato, G.V.; Lanza, M.R.V. Recent advances in electrochemical water technologies for the treatment of antibiotics: A short review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 26, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Scontri, M.; Materon, E.M.; Lanza, M.R.V.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Development and application of an electrochemical sensor modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide for the sensitive and selective detection of tetracycline. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 757, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Disposable screen printed electrochemical sensors: Tools for environmental monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 10432–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Yan, T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Q.; Sun, M.; Yan, L.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. A label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensing platform base on plasmon Au coupling with MOF-derived In2O3@g-C3N4 nanoarchitectures for tetracycline detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, X. A label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on electrodeposited gold nanoparticles and methylene blue for tetracycline detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar]
- Alawad, A.; Istamboulié, G.; Calas-Blanchard, C.; Noguer, T. A reagentless aptasensor based on intrinsic aptamer redox activity for the detection of tetracycline in water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghdisi, S.M.; Danesh, N.M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K. A novel M-shape electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetracyclines. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaopiao, C.; Yichen, X.; Xiaoxiao, C.; Shan, Z.; Yang, L.; Chaobiao, H. A “Signal On” Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor For Tetracycline Detection Based On Semiconductor Polymer Quantum Dots. J. Electrchem. Soc. 2020, 167, 067516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M. Sensitive visible light-driven photoelectrochemical aptasensor for detection of tetracycline using ZrO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposite. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yu, L.; Guo, C.; Fang, G. Sensitive and selective electrochemical aptasensor via diazonium-coupling reaction for label-free determination of oxytetracycline in milk samples. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. Fluorometric and electrochemical dual-mode nanoprobe for tetracycline by using a nanocomposite prepared from carbon nitride quantum dots and silver nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Jia, S.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Turner, A.P.F. Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of Tetracycline by an Aptamer Nano-Biosensor. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Li, D.J.; Gai, L.; Wang, J.P.; Li, Y. Bin Electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of tetracycline with multi-walled carbon nanotubes amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 162, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.; Kim, J.; Paeng, K.J.; Park, S.W.; Paeng, I.R. Biotin-avidin mediated competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect residues of tetracyclines in milk. Microchem. J. 2008, 88, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, W.; Zhao, C.; Xi, R. Preparation of anti-tetracycline antibodies and development of an indirect heterologous competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect residues of tetracycline in milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devkota, L.; Nguyen, L.T.; Vu, T.T.; Piro, B. Electrochemical determination of tetracycline using AuNP-coated molecularly imprinted overoxidized polypyrrole sensing interface. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 270, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Electrochemical Determination of Tetracycline Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Modified Carbon Nanotube-Gold Nanoparticles Electrode. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampasa, S.; Pummoree, J.; Siangproh, W.; Khongchareonporn, N.; Bgamrojanavanich, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Chaiyo, S. Chemical “Signal-On” electrochemical biosensor based on a competitive immunoassay format for the sensitive determination of oxytetracycline. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2020, 320, 128389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, K.; Cristea, C.; Tertis, M.; Feier, B.; Wieczorek, M.; Koscielniak, P.; Kochana, J. Employment of electrostriction phenomenon for label-free electrochemical immunosensing of tetracycline. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 132, 107405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alami El Hassani, N.; Baraket, A.; Boudjaoui, S.; Taveira Tenório Neto, E.; Bausells, J.; El Bari, N.; Bouchikhi, B.; Elaissari, A.; Errachid, A.; Zine, N. Development and application of a novel electrochemical immunosensor for tetracycline screening in honey using a fully integrated electrochemical Bio-MEMS. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushikawa, R.T.; Silva, M.R.; Angelo, A.C.D.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Construction of an electrochemical sensing platform based on platinum nanoparticles supported on carbon for tetracycline determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Guo, J.; Shen, F.; Sun, C. A novel colorimetric aptasensor using cysteamine-stabilized gold nanoparticles as probe for rapid and specific detection of tetracycline in raw milk. Food Control 2015, 54, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Kuang, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Yu, M.; et al. Biallelic Mutations in PATL2 Cause Female Infertility Characterized by Oocyte Maturation Arrest. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H. Ratiometric electrochemical aptasensor based on ferrocene and carbon nanofibers for highly specific detection of tetracycline residues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Hu, G.; Wagberg, T.; Zhan, S.; Xu, H.; Zhou, P. Electrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with an alginate film containing reduced graphene oxide and magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Hou, W.; Jiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X. Ultra-sensitive aptasensor based on IL and Fe3O4 nanoparticles for tetracycline detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 7426–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbani, S.; Benvidi, A. Comparison of two fabricated aptasensors based on modified carbon paste/oleic acid and magnetic bar carbon paste/Fe3O4@oleic acid nanoparticle electrodes for tetracycline detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, F.D.; Titoiu, A.M.; Marty, J.L.; Vasilescu, A. Detection of antibiotics and evaluation of antibacterial activity with screen-printed electrodes. Sensors 2018, 18, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Q.; Wang, R.; Xing, B.; Chi, H.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q. Label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline detection based on cerium doped CdS sensitized BiYWO6. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, A.S.; Sierra, T.; Domini, C.E.; Lista, A.G.; Crevillen, A.G.; Escarpa, A. Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Screen-Printed Electrodes for Total Tetracycline Determination by Adsorptive Transfer Stripping. Sensors 2020, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad-Razdari, A.; Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Rostami, S.; Izadi, Z.; Ensafi, A.A.; Siadat, M. Development of an electrochemical biosensor for impedimetric detection of tetracycline in milk. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 4697–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, P.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y. Electrochemical aptasensor based on a novel flower-like TiO2 nanocomposite for the detection of tetracycline. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, C.M.F.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Determination of Tetracycline in Bovine and Breast Milk Using a Graphite–Polyurethane Composite Electrode. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.; Gigimol, M.G.; Priyanka, R.N.; Susan, M.; Korah, B.K.; Mathew, B. In-situ fabrication of Ag3PO4 based binary composite for the efficient electrochemical sensing of tetracycline. Mater. Lett. 2020, 279, 128502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, C.M.F.; Cervini, P.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Determination of tetracycline in environmental water samples at a graphite-polyurethane composite electrode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calixto, C.M.F.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Determination of Tetracyclines in Bovine and Human Urine using a Graphite-Polyurethane Composite Electrode. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, X.; Chen, X.; Fu, L.; Lai, W.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. Platinum-catalyzed hydrogen evolution reaction for sensitive electrochemical immunoassay of tetracycline residues. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 704, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangfuengkanagul, N.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. A flow injection method for the analysis of tetracycline antibiotics in pharmaceutical formulations using electrochemical detection at anodized boron-doped diamond thin film electrode. Talanta 2004, 64, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenraks, T.; Palaharn, S.; Grudpan, K.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. Flow injection analysis of doxycycline or chlortetracycline in pharmaceutical formulations with pulsed amperometric detection. Talanta 2004, 64, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treetepvijit, S.; Preechaworapun, A.; Praphairaksit, N.; Chuanuwatanakul, S.; Einaga, Y.; Chailapakul, O. Use of nickel implanted boron-doped diamond thin film electrode coupled to HPLC system for the determination of tetracyclines. Talanta 2006, 68, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahverdiyeva, S.; Yardım, Y.; Senturk, Z. Electrooxidation of tetracycline antibiotic demeclocycline at unmodified boron-doped diamond electrode and its enhancement determination in surfactant-containing media. Talanta 2021, 223, 121695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loetanantawong, B.; Suracheep, C.; Somasundrum, M.; Surareungchai, W. Electrocatalytic Tetracycline Oxidation at a Mixed-Valent Ruthenium Oxide-Ruthenium Cyanide-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode and Determination of Tetracyclines by Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 2266–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenraks, T.; Chuanuwatanakul, S.; Honda, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Chailapakul, O. Analysis of tetracycline antibiotics using HPLC with pulsed amperometric detection. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pizan-Aquino, C.; Wong, A.; Aviles-Felix, L.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Evaluation of the performance of selective M-MIP to tetracycline using electrochemical and HPLC-UV method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 245, 122777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Wang, E. Flow injection amperometric detection based on ion transfer across a water—Solidified nitrobenzene interface for the determination of tetracycline and terramycin. Analyst 1988, 113, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüí, L.; Guzman, A.; Pedrero, M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Voltametric and flow injection determination of oxytetracycline residues in food samples using carbon fiber microelectrodes. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oungpipat, W.; Southwell-Keely, P.; Alexander, P.W. Flow injection detection of tetracyclines by electrocatalytic oxidation at a nickel-modified glassy carbon electrode. Analyst 1995, 120, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Wang, E. Liquid chromatographic determination of tetracycline antibiotics at an electrochemically pre-treated glassy carbon electrode. Analyst 1989, 114, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe Montiel, N.; Parrilla, M.; Beltran, V.; Nuyts, G.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. The opportunity of 6-monoacetylmorphine to selectively detect heroin at preanodized screen printed electrodes. Talanta 2021, 226, 122005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schram, J.; Parrilla, M.; Sleegers, N.; Samyn, N.; Bijvoets, S.M.; Heerschop, M.W.J.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Wael, K. Identifying electrochemical fingerprints of ketamine with voltammetry and LC-MS for its detection in seized samples Identifying electrochemical fingerprints of ketamine with voltammetry and LC-MS for its detection in seized samples. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13485–13492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Echelpoel, R.; de Jong, M.; Daems, D.; Van Espen, P.; De Wael, K. Unlocking the full potential of voltammetric data analysis: A novel peak recognition approach for (bio)analytical applications. Talanta 2021, 233, 122605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Skrzypek, S.; Stojanov, L. Square-wave voltammetry. ChemTexts 2018, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X. Gold modified microelectrode for direct tetracycline detection. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2012, 6, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Hu, C.; Wei, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, S. Sensitivity improvement of the oxidation of tetracycline at acetylene black electrode in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turku, I.; Sainio, T.; Paatero, E. Thermodynamics of tetracycline adsorption on silica. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadim, E.E.; Manouchehri, F.; Soleimani, G.; Hosseini, H.; Kimiagar, S.; Nafisi, S. Adsorption properties of tetracycline onto graphene oxide: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schram, J.; Parrilla, M.; Sleegers, N.; Van Durme, F.; Van Den Berg, J.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Wael, K. Electrochemical profiling and LC-MS characterization of synthetic cathinones: From methodology to detection in forensic samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Oturan, N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Oturan, M.A. Application of response surface methodology to the removal of the antibiotic tetracycline by electrochemical process using carbon-felt cathode and DSA (Ti/RuO2-IrO2) anode. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, H.; He, X.; Zhang, D. Evaluating tetracycline degradation pathway and intermediate toxicity during the electrochemical oxidation over a Ti/Ti4O7 anode. Water Res. 2018, 137, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Patel, S.; Wencewicz, T.A.; Dantas, G. The Tetracycline Destructases: A Novel Family of Tetracycline-Inactivating Enzymes. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volkers, G.; Petruschka, L.; Hinrichs, W. Recognition of drug degradation products by target proteins: Isotetracycline binding to tet repressor. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 5108–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| TET | DOXY | OXY | CHL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (µA µM−1) | 0.013 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.020 |
| R-squared | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| Linear range (µM) | 5–100 | 5–100 | 5–100 | 5–100 |
| Limit of detection (µM) | 4.17 | 2.14 | 3.07 | 2.49 |
| RSD (%) at 10 µM, N = 3 | 3.01 | 3.29 | 9.78 | 6.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cánovas, R.; Sleegers, N.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Wael, K. Tetracycline Antibiotics: Elucidating the Electrochemical Fingerprint and Oxidation Pathway. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070187
Cánovas R, Sleegers N, van Nuijs ALN, De Wael K. Tetracycline Antibiotics: Elucidating the Electrochemical Fingerprint and Oxidation Pathway. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(7):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070187
Chicago/Turabian StyleCánovas, Rocío, Nick Sleegers, Alexander L.N. van Nuijs, and Karolien De Wael. 2021. "Tetracycline Antibiotics: Elucidating the Electrochemical Fingerprint and Oxidation Pathway" Chemosensors 9, no. 7: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070187
APA StyleCánovas, R., Sleegers, N., van Nuijs, A. L. N., & De Wael, K. (2021). Tetracycline Antibiotics: Elucidating the Electrochemical Fingerprint and Oxidation Pathway. Chemosensors, 9(7), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070187