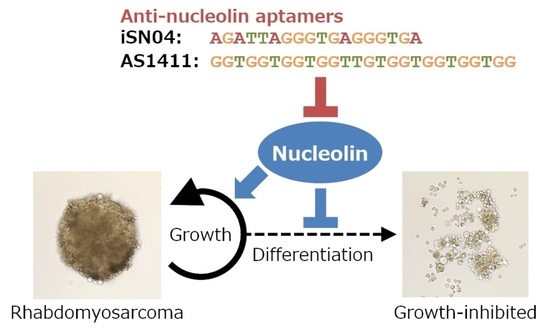
Myogenetic Oligodeoxynucleotides as Anti-Nucleolin Aptamers Inhibit the Growth of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oligodeoxynucleotides
2.2. Two-Dimensional (2D) Cell Culture
2.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.4. Cell Counting
2.5. EdU (5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) Staining
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qPCR)
2.7. Three-Dimensional (3D) Culture of RD Tumorspheres
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nucleolin Expression and Localization in ERMS Cells
3.2. iSN04 and AS1411 Inhibit the Growth of ERMS Cells
3.3. iSN04 Alters the Gene Expression in ERMS Cells
3.4. iSN04 and AS1411 Disturb the Formation of RD Tumorspheres
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.; Guo, W.; Shen, J.K.; Mankin, H.J.; Hornicek, F.J.; Duan, Z. Rhabdomyosarcoma: Advances in molecular and cellular biology. Sarcoma 2015, 2015, 232010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaQuaglia, M.P.; Gerstle, J.T. Advances in the treatment of pediatric solid tumors: A 50-year perspective. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 126, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenau, D.M.; Keefe, M.D.; Storer, N.Y.; Guyon, J.R.; Kutok, J.L.; Le, X.; Goessling, W.; Neuberg, D.S.; Kunkel, L.M.; Zon, L.I. Effects of RAS on the genesis of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohashi, K.; Oda, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Tamiya, S.; Takahira, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Tajiri, T.; Taguchi, T.; Suita, S.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Alterations of RB1 gene in embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: Special reference to utility of pRB immunoreactivity in differential diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma subtype. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Takita, J.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Kato, M.; Koh, K.; Hanada, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, K.; Maeda, D.; Fukayama, M.; et al. Characterization of genetic lesions in rhabdomyosarcoma using a high-density single nucleotide polymorphism array. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.P.; Nishijo, K.; Chen, H.I.; Yi, X.; Schuetze, D.P.; Pal, R.; Prajapati, S.I.; Abraham, J.; Arenkiel, B.R.; Chen, Q.R.; et al. Evidence for an unanticipated relationship between undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, C.; Guttridge, D.C. Mechanisms of impaired differentiation in rhabdomyosarcoma. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4323–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, N.Y.; White, R.M.; Uong, A.; Price, E.; Nielsen, G.P.; Langenau, D.M.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish rhabdomyosarcoma reflects the developmental stage of oncogene expression during myogenesis. Development 2013, 140, 3040–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vita, A.; Ferrari, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Vanni, S.; Domizio, C.; Fonzi, E.; Fausti, V.; Recine, F.; Bassi, M.; Campobassi, A.; et al. Identification of a novel RAB3IP-HMGA2 fusion transcript in an adult head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 2052–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, A.; Vanni, S.; Fausti, V.; Cocchi, C.; Recine, F.; Miserocchi, G.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Bassi, M.; Gessaroli, M.; et al. Deciphering the genomic landscape and pharmacological profile of uncommon entities of adult rhabdomyosarcomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagha, M.; Sato, T.; Bajard, L.; Daubas, P.; Esner, M.; Montarras, D.; Relaix, F.; Buckingham, M. Regulation of skeletal muscle stem cell behavior by Pax3 and Pax7. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2008, 73, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, F.; Saab, R.; Hussein, N.; Clezardin, P.; Cohen, P.A.; Ghayad, S.E. Non-coding RNA in rhabdomyosarcoma progression and metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 971174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malempati, S.; Hawkins, D.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma: Review of the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) Soft-Tissue Sarcoma Committee experience and rationale for current COG studies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Garcia, H.D.; Scheer, M.; Henssen, A.G. Current and future treatment strategies for rhabdomyosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Fu, X.; Huang, J.; Zeng, P.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, C. Advances in screening and development of therapeutic aptamers against cancer cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 662791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinji, S.; Umezawa, K.; Nihashi, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Shimosato, T.; Takaya, T. Identification of the myogenetic oligodeoxynucleotides (myoDNs) that promote differentiation of skeletal muscle myoblasts by targeting nucleolin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 616706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Yonekura, S.; Shimosato, T.; Takaya, T. Myogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide (myoDN) recovers the differentiation of skeletal muscle myoblasts deteriorated by diabetes mellitus. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 679152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihashi, Y.; Shinji, S.; Umezawa, K.; Shimosato, T.; Ono, T.; Kagami, H.; Takaya, T. Myogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide complexed with berberine promotes differentiation of chicken myoblasts. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Shimosato, T.; Takaya, T. Myogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide restores differentiation and reverses inflammation of myoblasts aggravated by cancer-conditioned medium. Muscles 2022, 1, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Q.; Gao, L. New perspectives of physiological and pathological functions of nucleolin (NCL). Life Sci. 2017, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.M.; Gaume, X.; Bouvet, P. The roles of nucleolin subcellular localization in cancer. Biochimie 2015, 113, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farin, K.; Schokoroy, S.; Haklai, R.; Cohen-Or, I.; Elad-Sfadia, G.; Reyes-Reyes, M.E.; Bates, P.J.; Cox, A.D.; Kloog, Y.; Pinkas-Kramarski, R. Oncogenic synergism between ErbB1, nucleolin, and mutant Ras. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wise, J.F.; Berkova, Z.; Mathur, R.; Zhu, H.; Braun, F.K.; Tao, R.H.; Sabichi, A.L.; Ao, X.; Maeng, H.; Samaniego, F. Nucleolin inhibits Fas ligand binding and suppresses Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo via a surface nucleolin-Fas complex. Blood 2013, 121, 4729–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, P.J.; Laber, D.A.; Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.D.; Trent, J.O. Discovery and development of the G-rich oligonucleotide AS1411 as a novel treatment for cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willmer, T.; Damerell, V.; Smyly, S.; Sims, D.; Du Toit, M.; Ncube, S.; Sinkala, M.; Govender, D.; Sturrock, E.; Blackburn, J.M.; et al. Targeting the oncogenic TBX3: Nucleolin complex to treat multiple sarcoma subtypes. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 5680–5700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nihashi, Y.; Miyoshi, M.; Umezawa, K.; Shimosato, T.; Takaya, T. Identification of a novel osteogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide (osteoDN) that promotes osteoblast differentiation in a TLR9-independent manner. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girvan, A.C.; Teng, Y.; Casson, L.K.; Thomas, S.D.; Juliger, S.; Ball, M.W.; Klein, J.B.; Pierce, W.M., Jr.; Barve, S.S.; Bates, P.J. AGRO100 inhibits activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) by forming a complex with NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) and nucleolin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekiguchi, M.; Shiroko, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Imada, M.; Miyahara, M.; Fujii, G. Characterization of a human rhabdomyosarcoma cell strain in tissue culture. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1985, 39, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, R.M.; Melnyk, J.; Finkelstein, J.Z.; Adams, E.C., Jr.; Gardner, M.B. Cultivation in vitro of cells derived from a human rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer 1969, 24, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinji, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nihashi, Y.; Umezawa, K.; Takaya, T. Berberine and palmatine inhibit the growth of human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nihashi, Y.; Umezawa, K.; Shinji, S.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Kono, T.; Ono, T.; Kagami, H.; Takaya, T. Distinct cell proliferation, myogenic differentiation, and gene expression in skeletal muscle myoblasts of layer and broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yosef, R.; Pilpel, N.; Tokarsky-Amiel, R.; Biran, A.; Ovadya, Y.; Cohen, S.; Vadai, E.; Dassa, L.; Shahar, E.; Condiotti, R.; et al. Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL-W and BCL-XL. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Xiong, L.; Li, Q.; Lin, L.; Miao, X.; Yan, S.; Hong, Z.; Yang, L.; Wen, Y.; Deng, X. 3D modeling of cancer stem cell niche. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1326–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, T.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Fernandes, D.J.; Spicer, E.K. Identification of nucleolin as an AU-rich element binding protein involved in bcl-2 mRNA stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 10855–10863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Tsaprailis, G.; Bowden, G.T. Nucleolin stabilizes Bcl-XL messenger RNA in response to UVA irradiation. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, R.; Das, S.; Ugrinova, I.; Kumar, S.; Mongelard, F.; Wong, J.; Bouvet, P. Interaction of nucleolin with ribosomal RNA genes and its role in RNA polymerase I transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9441–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.D.; Zhao, H.G.; Yang, Y.S.; Hu, T.; Yang, Q.C. GSK3β negatively regulates HIF1α mRNA stability via nucleolin in the MG63 osteosarcoma cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, C.; Mercatali, L.; Spadazzi, C.; La Manna, F.; De Vita, A.; Riva, N.; Calpona, S.; Ricci, M.; Bongiovanni, A.; Gunelli, E.; et al. CSF-1 blockade impairs breast cancer osteoclastogenic potential in co-culture systems. Bone 2014, 66, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Giles, A.; Reid, C.; Kaplan, R. CSF-1R inhibition blocks rhabdomyoscarcoma metastasis by polarizing macrophage differentiation. Cancer Res. 2015, 75 (Suppl. 15), 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.H.; Baker, T.; Laszlo, C.; Chambers, S.K. Nucleolin mediates microRNA-directed CSF-1 mRNA deadenylation but increases translation of CSF-1 mRNA. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, H.H.; Lee, S.C.; Gibson, S.J.; Chambers, S.K. Expression of the cytoplasmic nucleolin for post-transcriptional regulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA in ovarian and breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawash, M.; Jaradat, N.; Eid, A.M.; Abubaker, A.; Mufleh, O.; Al-Hroub, Q.; Sobuh, S. Synthesis of novel isoxazole-carboxamide derivatives as promising agents for melanoma and targeted nano-emulgel conjugate for improved cellular permeability. BMC Chem. 2022, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codenotti, S.; Zizioli, D.; Mignani, L.; Rezzola, S.; Tabellini, G.; Parolini, S.; Giacomini, A.; Asperti, M.; Poli, M.; Mandracchia, D.; et al. Hyperactive Akt1 signaling increases tumor progression and DNA repair in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma RD line and confers susceptibility to glycolysis and mevalonate pathway inhibitors. Cells 2022, 11, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, R.R.; Gargollo, P.C.; Ahmed, M.E.; Kim, Y.; Baer, E.; Phelps, D.A.; Charlesworth, C.M.; Madden, B.J.; Wang, L.; Houghton, P.J.; et al. Surfaceome profiling of rhabdomyosarcoma reveals B7-H3 as a mediator of immune evasion. Cancers 2021, 13, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Larcher, L.M.; Barrero, R.A.; Veedu, R.N. Three decades of nucleic acid aptamer technologies: Lessons learned, progress and opportunities on aptamer development. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Jang, G.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Song, G. Predicting aptamer sequences that interact with target proteins using an aptamer-protein interaction classifier and a Monte Carlo tree search approach. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliano, R.L. Intracellular trafficking and endosomal release of oligonucleotides: What we know and what we don’t. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018, 28, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Girvan, A.C.; Casson, L.K.; Pierce, W.M., Jr.; Qian, M.; Thormas, S.D.; Bates, P.J. AS1411 alters the localization of a complex containing protein arginine methyltransferase 5 and nucleolin. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10491–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagiwara, H.; Saito, F.; Masaki, T.; Ikeda, M.; Nakamura-Ohkuma, A.; Shimizu, T.; Matsumura, K. Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A enhances myogenesis by coordinating muscle regulatory factors and myogenic repressors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marampon, F.; Di Nisho, V.; Pietrantoni, I.; Petragnano, F.; Fasciani, I.; Scicchitano, B.M.; Ciccarelli, C.; Gravina, G.L.; Festuccia, C.; Del Fattore, A.; et al. Pro-differentiating and radiosensitizing effects of inhibiting HDACs by PXD-101 (Belinostat) in in vitro and in vivo models of human rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2019, 461, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohira, N.; Shinji, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nihashi, Y.; Shimosato, T.; Takaya, T. Myogenetic oligodeoxynucleotides as anti-nucleolin aptamers inhibit the growth of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cells. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| BAX | GCTGGACATTGGACTTCCTC CTCAGCCCATCTTCTTCCAG | [30] |
| BCL2 | AACATCGCCCTGTGGATGAC GGCCGTACAGTTCCACAAAG | [32] |
| BCL2L1 | GGCCACTTACCTGAATGACC AAGAGTGAGCCCAGCAGAAC | [30] |
| CDKN1C | GGCCTCTGATCTCCGATTTCTTC GGGTCTGCTCCACCGAG | [30] |
| GAPDH | TGTCAAGCTCATTTCCTGGTA GTGAGGGTCTCTCTCTTCCTCTTGT | [30] |
| MKI67 | AAGAGGTGTGCAGAAAATCCAAAG CTTCACTGTCCCTATGACTTCTGGTT | [30] |
| MYH3 | GGACAGGAAGAATGTGCTGAGATT GCCTCTTGTAGGACTTGACTTTCAC | [16] |
| MYOD1 | TGCTCCGACGGCATGATGGAC TCGACACCGCCGCACTCT | [16] |
| MYOG | AACCCAGGGGATCATCTGCTCAC GTTGGGCATGGTTTCATCTGGGAAG | [16] |
| NCL | ATTGGTAGCAACTCCTGGTAAG CACTGTCATCATCCTCCTCTTC | [16] |
| PAX3 | AGGAAGGAGGCAGAGGAAAG CAGCTGTTCTGCTGTGAAGG | [17] |
| PAX7 | GACCCCTGCCTAACCACATC GTCTCCTGGTAGCGGCAAAG | [16] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nohira, N.; Shinji, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nihashi, Y.; Shimosato, T.; Takaya, T. Myogenetic Oligodeoxynucleotides as Anti-Nucleolin Aptamers Inhibit the Growth of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112691
Nohira N, Shinji S, Nakamura S, Nihashi Y, Shimosato T, Takaya T. Myogenetic Oligodeoxynucleotides as Anti-Nucleolin Aptamers Inhibit the Growth of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(11):2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112691
Chicago/Turabian StyleNohira, Naoki, Sayaka Shinji, Shunichi Nakamura, Yuma Nihashi, Takeshi Shimosato, and Tomohide Takaya. 2022. "Myogenetic Oligodeoxynucleotides as Anti-Nucleolin Aptamers Inhibit the Growth of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells" Biomedicines 10, no. 11: 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112691
APA StyleNohira, N., Shinji, S., Nakamura, S., Nihashi, Y., Shimosato, T., & Takaya, T. (2022). Myogenetic Oligodeoxynucleotides as Anti-Nucleolin Aptamers Inhibit the Growth of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. Biomedicines, 10(11), 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112691