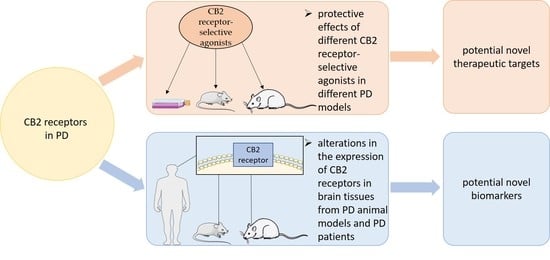
The Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
2. The Cannabinoid Type 2 (CB2) Receptors in PD
3. Preclinical Studies
3.1. Studies in PD Cellular Models
3.2. Studies in PD Animal Models
3.3. Studies in Animal Models of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia (LID)
3.4. Studies Investigating CB2 Receptor Heteromers in Animal Models of PD and LID
4. Clinical Studies
4.1. In Silico and Post-Mortem Studies in PD Patients
4.2. Clinical Trials
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tolosa, E.; Garrido, A.; Scholz, S.W.; Poewe, W. Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.-W.W.; Yuan, Y.-H.H.; Chen, N.-H.H. The therapeutic role of cannabinoid receptors and its agonists or antagonists in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 96, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tysnes, O.-B.; Storstein, A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarkov, A.; Barreto, G.E.; Grizzell, J.A.; Echeverria, V. Strategies for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: Beyond Dopamine. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H.V. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Schwarzschild, M.A. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and prevention. Lancet. Neurol. 2016, 15, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mao, S.; Xiang, D.; Fang, C. Association between depression and the subsequent risk of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Azim, F.; Saju, H.; Zargaran, A.; Shirzad, M.; Kamal, M.; Fatema, K.; Rehman, S.; Azad, M.A.M.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S. Pesticides and Parkinson’s disease: Current and future perspective. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 115, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Di Matteo, V.; Benigno, A.; Pierucci, M.; Crescimanno, G.; Di Giovanni, G. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 205, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes-Colli, Y.; Aguiar, A.F.L.; Isaac, A.R.; Ferreira, B.K.; Campos, R.M.P.; Trindade, P.M.P.; de Melo, R.A.R.; Sampaio, L.S. Phytocannabinoids and Cannabis-Based Products as Alternative Pharmacotherapy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Hypothesis to Clinical Practice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 917164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s disease: Etiopathogenesis and treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosi, G.; Cerri, S.; Blandini, F. A further update on the role of excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmina, A.B.; Kapkaeva, M.R.; Vetchinova, A.S.; Illarioshkin, S.N. Novel Approaches Used to Examine and Control Neurogenesis in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alborghetti, M.; Nicoletti, F. Different Generations of Type-B Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Parkinson’s Disease: From Bench to Bedside. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.T. Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, E.M.; Hung, S.-Y. Current Therapies in Clinical Trials of Parkinson’s Disease: A 2021 Update. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.; Grealish, S.; Henchcliffe, C. The future of stem cell therapies for Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.P.; Villanueva, E.B.; Klegeris, A. Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids in the Treatment of Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinsons Disease. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z. Roles of the Cannabinoid System in the Basal Ganglia in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 832854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhmann, C.; Mainka, T.; Ebersbach, G.; Gandor, F. Evidence for the use of cannabinoids in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bega, D.; Simuni, T.; Okun, M.S.; Chen, X.; Schmidt, P. Medicinal Cannabis for Parkinson’s Disease: Practices, Beliefs, and Attitudes Among Providers at National Parkinson Foundation Centers of Excellence. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2017, 4, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, C.; Almeida, C.; Tenreiro, S.; Quintas, A. Neuroprotection or Neurotoxicity of Illicit Drugs on Parkinson’s Disease. Life 2020, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.S.; Battaglia, G.; Bruno, V.; Mangano, K.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; Cavalli, E. The Dichotomic Role of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Le, W. Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease: How Good Are They? Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, D.; Noyce, A.J.; Schrag, A.; Tolosa, E. Challenges of modifying disease progression in prediagnostic Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.C.; Cinquina, V.; Palomo-Garo, C.; Rábano, A.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Identification of CB₂ receptors in human nigral neurons that degenerate in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibret, B.G.; Ishiguro, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Onaivi, E.S. New Insights and Potential Therapeutic Targeting of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors in CNS Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, T.; Calcagnini, S.; Pace, L.; De Marco, F.; Romano, A.; Gaetani, S. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Signaling in Neurodegenerative Disorders: From Pathogenesis to a Promising Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Bellini, G.; Tolone, C.; Luongo, L.; Mancusi, S.; Papparella, A.; Sturgeon, C.; Fasano, A.; Nobili, B.; Perrone, L.; et al. The cannabinoid receptor type 2 Q63R variant increases the risk of celiac disease: Implication for a novel molecular biomarker and future therapeutic intervention. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.-R.; Pan, C.-H.; Hishimoto, A.; Li, C.-Y.; Xi, Z.-X.; Llorente-Berzal, A.; Viveros, M.-P.; Ishiguro, H.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S.; et al. Species differences in cannabinoid receptor 2 (CNR2 gene): Identification of novel human and rodent CB2 isoforms, differential tissue expression and regulation by cannabinoid receptor ligands. Genes. Brain. Behav. 2009, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrisi, R.; Ceni, C.; Bertini, S.; Macchia, M.; Manera, C.; Gado, F. Medicinal Chemistry approach, pharmacology and neuroprotective benefits of CB2R modulators in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soethoudt, M.; Grether, U.; Fingerle, J.; Grim, T.W.; Fezza, F.; De Petrocellis, L.; Ullmer, C.; Rothenhäusler, B.; Perret, C.; Van Gils, N.; et al. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand profiling reveals biased signalling and off-target activity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Gao, F.; Larsen, B.; Gao, M.; Luo, Z.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. Mechanisms of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor-Mediated Reduction of Dopamine Neuronal Excitability in Mouse Ventral Tegmental Area. SSRN Electron. J. 2019, 42, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. Brain CB₂ Receptors: Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2517–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cilia, R. Molecular Imaging of the Cannabinoid System in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2018, 141, 305–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, H.; Kibret, B.G.; Horiuchi, Y.; Onaivi, E.S. Potential Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 828895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiatordi, G.F.; Intranuovo, F.; Delre, P.; Abatematteo, F.S.; Abate, C.; Niso, M.; Creanza, T.M.; Ancona, N.; Stefanachi, A.; Contino, M. Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 (CB2R) in a Multitarget Approach: Perspective of an Innovative Strategy in Cancer and Neurodegeneration. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 14448–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Morales, P.; Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Jagerovic, N.; Franco, R. Targeting Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in the Central Nervous System. Medicinal Chemistry Approaches with Focus on Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; García-Toscano, L.; Santos-García, I.; Gómez-Almería, M.; Gonzalo-Consuegra, C.; Espejo-Porras, F.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; de Lago, E. Targeting the CB2 receptor and other endocannabinoid elements to delay disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1373–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docagne, F.; Mestre, L.; Loría, F.; Hernangómez, M.; Correa, F.; Guaza, C. Therapeutic potential of CB2 targeting in multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids: Role in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibsen, M.S.; Connor, M.; Glass, M. Cannabinoid CB 1 and CB 2 Receptor Signaling and Bias. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bie, B.; Wu, J.; Foss, J.F.; Naguib, M. An overview of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor system and its therapeutic potential. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 31, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Xu, F.; Taylor, D.H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J. The impact of cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2Rs) in neuroprotection against neurological disorders. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magham, S.V.; Krishnamurthy, P.T.; Shaji, N.; Mani, L.; Balasubramanian, S. Cannabinoid receptor 2 selective agonists and Alzheimer’s disease: An insight into the therapeutic potentials. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 2888–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, R.; Lin, L.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, R. Activation of CB2R with AM1241 ameliorates neurodegeneration via the Xist/miR-133b-3p/Pitx3 axis. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 6032–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, M.S.; Rojo-Bustamante, E.; Molina, C.; Celorrio, M.; Sánchez-Arias, J.A.; Franco, R. Neuroprotective Effect of JZL184 in MPP(+)-Treated SH-SY5Y Cells Through CB2 Receptors. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2312–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, A.; Pollastro, F.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Cannabidiol exerts protective effects in an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease activating AKT/mTOR pathway. Fitoterapia 2020, 143, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patricio, F.; Morales-Andrade, A.A.; Patricio-Martínez, A.; Limón, I.D. Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Target: Evidence of its Neuroprotective and Neuromodulatory Function in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 595635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgaz, S.; García, C.; Gómez-Cañas, M.; Rolland, A.; Muñoz, E.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Neuroprotection with the Cannabidiol Quinone Derivative VCE-004.8 (EHP-101) against 6-Hydroxydopamine in Cell and Murine Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2021, 26, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, C.A.; Reich, E.-P.; Fine, J.S.; Lavey, B.; Kozlowski, J.A.; Hipkin, R.W.; Lundell, D.J.; Bober, L. Biology and therapeutic potential of cannabinoid CB 2 receptor inverse agonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mnich, K.; Finn, D.P.; Dowd, E.; Gorman, A.M. Inhibition by anandamide of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell death in PC12 cells. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 2010, 818497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Concannon, R.M.; Okine, B.N.; Finn, D.P.; Dowd, E. Differential upregulation of the cannabinoid CB₂ receptor in neurotoxic and inflammation-driven rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 269, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concannon, R.M.; Okine, B.N.; Finn, D.P.; Dowd, E. Upregulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in environmental and viral inflammation-driven rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.A.; Martinez, A.A.; Seillier, A.; Koek, W.; Acosta, Y.; Fernandez, E.; Strong, R.; Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G.; Roberts, J.L.; et al. WIN55,212-2, a cannabinoid receptor agonist, protects against nigrostriatal cell loss in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.; Palomo-Garo, C.; García-Arencibia, M.; Ramos, J.; Pertwee, R.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Symptom-relieving and neuroprotective effects of the phytocannabinoid Δ9-THCV in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simkins, T.J.; Janis, K.L.; McClure, A.K.; Behrouz, B.; Pappas, S.S.; Lehner, A.; Kaminski, N.E.; Goudreau, J.L.; Lookingland, K.J.; Kaplan, B.L.F. Comparison of the D2 receptor regulation and neurotoxicant susceptibility of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in wild-type and CB1/CB2 receptor knockout mice. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gálvez, Y.; Palomo-Garo, C.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; García, C. Potential of the cannabinoid CB(2) receptor as a pharmacological target against inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-Garo, C.; Gómez-Gálvez, Y.; García, C.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Targeting the cannabinoid CB2 receptor to attenuate the progression of motor deficits in LRRK2-transgenic mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 110, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.; Bemelmans, A.-P.; Joséphine, C.; Brouillet, E.; McKernan, D.P.; Dowd, E. Time-Course of Alterations in the Endocannabinoid System after Viral-Mediated Overexpression of α-Synuclein in the Rat Brain. Molecules 2022, 27, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Jin, L. AM1241 alleviates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease and promotes the regeneration of DA neurons in PD mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67837–67850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, Y.C.; Shin, W.-H.; Baek, J.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Baik, H.H.; Kim, S.R.; Won, S.-Y.; Jin, B.K. CB2 receptor activation prevents glial-derived neurotoxic mediator production, BBB leakage and peripheral immune cell infiltration and rescues dopamine neurons in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Arencibia, M.; González, S.; de Lago, E.; Ramos, J.A.; Mechoulam, R.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of cannabinoids in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Importance of antioxidant and cannabinoid receptor-independent properties. Brain Res. 2007, 1134, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Azimullah, S.; Haque, M.E.; Ojha, S.K. Cannabinoid Type 2 (CB2) Receptors Activation Protects against Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation Associated Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, G.; Chambers, D.; Rahman, R.; Molina-Holgado, F. Transcription Profile and Pathway Analysis of the Endocannabinoid Receptor Inverse Agonist AM630 in the Core and Infiltrative Boundary of Human Glioblastoma Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Vickstrom, C.R.; Friedman, V.; Kelly, T.J.; Bai, X.; Zhao, L.; Hillard, C.J.; Liu, Q.-S. The Neuroprotective Effects of the CB2 Agonist GW842166x in the 6-OHDA Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenfeld, T.; Price, J.; Albanese, M.; Bullman, J.; Guillard, F.; Meyer, I.; Leeson, R.; Costantin, C.; Ziviani, L.; Nocini, P.F.; et al. A randomized, controlled study to investigate the analgesic efficacy of single doses of the cannabinoid receptor-2 agonist GW842166, ibuprofen or placebo in patients with acute pain following third molar tooth extraction. Clin. J. Pain 2011, 27, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, K.H.; Real, C.C.; Ferreira, A.F.F.; Britto, L.R.; Chacur, M. Antinociceptive effects of treadmill exercise in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: The role of cannabinoid and opioid receptors. Brain Res. 2020, 1727, 146521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternianov, A.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.M.; Solesio, M.E.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Ortega-Álvaro, A.; Navarrete, F.; Leiva, C.; Galindo, M.F.; Manzanares, J. Overexpression of CB2 cannabinoid receptors results in neuroprotection against behavioral and neurochemical alterations induced by intracaudate administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 421.e1–421.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo-Bustamante, E.; Abellanas, M.A.; Clavero, P.; Thiolat, M.-L.; Li, Q.; Luquin, M.R.; Bezard, E.; Aymerich, M.S. The expression of cannabinoid type 1 receptor and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol synthesizing/degrading enzymes is altered in basal ganglia during the active phase of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 118, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentsch, P.; Stayte, S.; Egan, T.; Clark, I.; Vissel, B. Targeting the cannabinoid receptor CB2 in a mouse model of l-dopa induced dyskinesia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espadas, I.; Keifman, E.; Palomo-Garo, C.; Burgaz, S.; García, C.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Moratalla, R. Beneficial effects of the phytocannabinoid Δ9-THCV in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 141, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyagawa, C.R.M.; Grimsey, N.L. Cannabinoid receptor CB1 and CB2 interacting proteins: Techniques, progress and perspectives. Methods Cell Biol. 2021, 166, 83–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pinilla, E.; Rico, A.J.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Lillo, J.; Roda, E.; Navarro, G.; Lanciego, J.L.; Franco, R. Expression of GPR55 and either cannabinoid CB1 or CB2 heteroreceptor complexes in the caudate, putamen, and accumbens nuclei of control, parkinsonian, and dyskinetic non-human primates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.-R.; Canseco-Alba, A.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Tagliaferro, P.; Chung, M.; Dennis, E.; Sanabria, B.; Schanz, N.; Escosteguy-Neto, J.C.; Ishiguro, H.; et al. Cannabinoid type 2 receptors in dopamine neurons inhibits psychomotor behaviors, alters anxiety, depression and alcohol preference. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grünblatt, E.; Zander, N.; Bartl, J.; Jie, L.; Monoranu, C.-M.; Arzberger, T.; Ravid, R.; Roggendorf, W.; Gerlach, M.; Riederer, P. Comparison analysis of gene expression patterns between sporadic Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2007, 12, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarrete, F.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; Lanciego, J.L.; Manzanares, J. Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptors, and Monoacylglycerol Lipase Gene Expression Alterations in the Basal Ganglia of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, P.; Jost, W.H. Commentary: Roles of the Cannabinoid System in the Basal Ganglia in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 897930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, P.; Jost, W.H. Randomized controlled trials on the use of cannabis-based medicines in movement disorders: A systematic review. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, M.S.; Sancesario, A.; Morace, R.; Centonze, D.; Iezzi, E. Cannabinoids in Parkinson’s Disease. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peball, M.; Werkmann, M.; Ellmerer, P.; Stolz, R.; Valent, D.; Knaus, H.-G.; Ulmer, H.; Djamshidian, A.; Poewe, W.; Seppi, K. Nabilone for non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: A randomized placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, enriched enrolment randomized withdrawal study (The NMS-Nab Study). J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sieradzan, K.A.; Fox, S.H.; Hill, M.; Dick, J.P.; Crossman, A.R.; Brotchie, J.M. Cannabinoids reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study. Neurology 2001, 57, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peball, M.; Krismer, F.; Knaus, H.; Djamshidian, A.; Werkmann, M.; Carbone, F.; Ellmerer, P.; Heim, B.; Marini, K.; Valent, D.; et al. Collaborators of the Parkinson’s Disease Working Group Innsbruck Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease are Reduced by Nabilone. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonim, A.E.; Ligresti, A.; Rabbito, A.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Di Marzo, V.; Osman, N.A.; Abadi, A.H. Structure-activity relationships of thiazole and benzothiazole derivatives as selective cannabinoid CB2 agonists with in vivo anti-inflammatory properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiesh, H.M.; Sharma, C.; Goyal, S.N.; Jha, N.K.; Ojha, S. Pharmacological Properties, Therapeutic Potential and Molecular Mechanisms of JWH133, a CB2 Receptor-Selective Agonist. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 702675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, B.K.; Straiker, A.; Mackie, K. CB2: Therapeutic target-in-waiting. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 38, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wouters, E.; Walraed, J.; Banister, S.D.; Stove, C.P. Insights into biased signaling at cannabinoid receptors: Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 169, 113623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloczi, J.; Varga, Z.V.; Hasko, G.; Pacher, P. Neuroprotection in Oxidative Stress-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Endocannabinoid System Modulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 75–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, P.; Goya, P.; Jagerovic, N. Emerging strategies targeting CB2 cannabinoid receptor: Biased agonism and allosterism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 157, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| In Silico and Post-Mortem Studies in PD Patients | |
|---|---|
| Results | References |
| [78] |
| [28] |
| [79] |
| [61] |
| [80] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basile, M.S.; Mazzon, E. The Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112986
Basile MS, Mazzon E. The Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(11):2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112986
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasile, Maria Sofia, and Emanuela Mazzon. 2022. "The Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease" Biomedicines 10, no. 11: 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112986
APA StyleBasile, M. S., & Mazzon, E. (2022). The Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomedicines, 10(11), 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112986