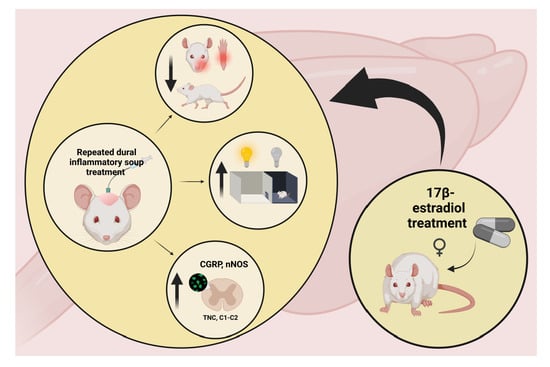
Estradiol Treatment Enhances Behavioral and Molecular Changes Induced by Repetitive Trigeminal Activation in a Rat Model of Migraine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Brief Summary of the Experiment
2.3. Experimental Groups
2.4. Ovariectomy
2.5. Implantation of the Cannula
2.6. Application of the Inflammatory Soup or Synthetic Interstitial Fluid
2.7. Behavioral Tests
2.7.1. von Frey Test (vF)
2.7.2. Hind Paw Mechanical Allodynia Test (HPMA)
2.7.3. Open Field Test (OF)
2.7.4. Light Dark Box Test (LDB)
2.8. Measurement of Estradiol Concentration
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Data Evaluation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Estradiol Concentration
3.2. Inflammatory Soup and Behavioral Changes
3.3. Inflammatory Soup and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide
3.4. Inflammatory Soup and Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CGRP | calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| E2 | 17β-estradiol |
| HPMA | hind paw mechanical allodynia test |
| IR | immunoreactive |
| IS | inflammatory soup |
| LDB | light-dark box test |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| NTG | nitroglycerin |
| OF | open field test |
| OVX | ovariectomized |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PBS-T | PBS containing 1% Triton-X-100 |
| PFA | paraformaldehyde |
| SIF | synthetic interstitial fluid |
| TNC | transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 |
| vF | von Frey test |
References
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broner, S.W.; Bobker, S.; Klebanoff, L. Migraine in Women. Semin Neurol. 2017, 37, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, M.E.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine chronification. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2011, 11, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, K.H.; Steen, A.E.; Reeh, P.W. A dominant role of acid pH in inflammatory excitation and sensitization of nociceptors in rat skin, in vitro. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15 (Pt 2), 3982–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strassman, A.M.; Raymond, S.A.; Burstein, R. Sensitization of meningeal sensory neurons and the origin of headaches. Nature 1996, 384, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, R.; Yamamura, H.; Malick, A.; Strassman, A.M. Chemical stimulation of the intracranial dura induces enhanced responses to facial stimulation in brain stem trigeminal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 964–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshinsky, M.L.; Gomonchareonsiri, S. Episodic dural stimulation in awake rats: A model for recurrent headache. Headache 2007, 47, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Z.; Tang, W.; Zhao, D.; Hu, G.; Li, R.; Yu, S. Volumetric abnormalities of the brain in a rat model of recurrent headache. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918756466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, L.; Bishop, J.; Barmettler, G.; Kainz, V.; Burstein, R.; Borsook, D. Brain network alterations in the inflammatory soup animal model of migraine. Brain Res. 2017, 1660, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spekker, E.; Laborc, K.F.; Bohár, Z.; Nagy-Grócz, G.; Fejes-Szabó, A.; Szűcs, M.; Vécsei, L.; Párdutz, Á. Effect of dural inflammatory soup application on activation and sensitization markers in the caudal trigeminal nucleus of the rat and the modulatory effects of sumatriptan and kynurenic acid. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieseler, J.; Ellis, A.; Sprunger, D.; Brown, K.; McFadden, A.; Mahoney, J.; Rezvani, N.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. A novel method for modeling facial allodynia associated with migraine in awake and freely moving rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 185, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bishop, J.; Becerra, L.; Barmettler, G.; Chang, P.C.; Kainz, V.; Burstein, R.; Borsook, D. Modulation of brain networks by sumatriptan-naproxen in the inflammatory soup migraine model. Pain 2019, 160, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundblad, C.; Haanes, K.A.; Grände, G.; Edvinsson, L. Experimental inflammation following dural application of complete Freund’s adjuvant or inflammatory soup does not alter brain and trigeminal microvascular passage. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Ran, Y.; Su, M.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Dong, Z.; Yu, S. Chronic changes in pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and related receptors in response to repeated chemical dural stimulation in rats. Mol. Pain 2017, 13, 1744806917720361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Yu, S. Depression and anxiety behaviour in a rat model of chronic migraine. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amin, F.M.; Aristeidou, S.; Baraldi, C.; Czapinska-Ciepiela, E.K.; Ariadni, D.D.; Di Lenola, D.; Fenech, C.; Kampouris, K.; Karagiorgis, G.; Braschinsky, M.; et al. European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies (EHF-SAS). The association between migraine and physical exercise. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stucky, N.L.; Gregory, E.; Winter, M.K.; He, Y.Y.; Hamilton, E.S.; McCarson, K.E.; Berman, N.E. Sex differences in behavior and expression of CGRP-related genes in a rodent model of chronic migraine. Headache 2011, 51, 674–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Melemedjian, O.K.; Price, T.J.; Dussor, G. Sensitization of dural afferents underlies migraine-related behavior following meningeal application of interleukin-6 (IL-6). Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo-Carrillo, A.; Lopez-Avila, A. A chronic animal model of migraine, induced by repeated meningeal nociception, characterized by a behavioral and pharmacological approach. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, L.M.; Gregory, E.; Winter, M.K.; McCarson, K.E.; Berman, N.E. Behavioral effects and mechanisms of migraine pathogenesis following estradiol exposure in a multibehavioral model of migraine in rat. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 263, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajdokht, F.; Babri, S.; Karimi, P.; Alipour, M.R.; Bughchechi, R.; Mohaddes, G. Chronic ghrelin treatment reduced photophobia and anxiety-like behaviors in nitroglycerin- induced migraine: Role of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossum, D.; Hanisch, U.K.; Quirion, R. Neuroanatomical localization, pharmacological characterization and functions of CGRP, related peptides and their receptors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 649–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körtési, T.; Tuka, B.; Nyári, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tajti, J. The effect of orofacial complete Freund’s adjuvant treatment on the expression of migraine-related molecules. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, S.D. Sensory neuropeptides: Their role in inflammation and wound healing. Immunopharmacology 1997, 37, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.Q.; Lawand, N.B.; Willis, W.D. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the generation and maintenance of mechanical allodynia and hyperalgesia in rats after intradermal injection of capsaicin. Pain 2003, 104, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noseda, R.; Burstein, R. Advances in understanding the mechanisms of migraine-type photophobia. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzik, T.J.; Korbut, R.; Adamek-Guzik, T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Laroux, F.S.; Lefer, D.J.; Kawachi, S.; Scalia, R.; Cockrell, A.S.; Gray, L.; Van der Heyde, H.; Hoffman, J.M.; Grisham, M.B. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of acute and chronic inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2000, 2, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Célérier, E.; González, J.R.; Maldonado, R.; Cabañero, D.; Puig, M.M. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia in a murine model of postoperative pain: Role of nitric oxide generated from the inducible nitric oxide synthase. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, A.A.; Bertels, Z.; Akerman, S. Targeted Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors for Migraine. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osborne, M.G.; Coderre, T.J. Effects of intrathecal administration of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 126, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alba, J.; Clayton, N.M.; Collins, S.D.; Colthup, P.; Chessell, I.; Knowles, R.G. GW274150, a novel and highly selective inhibitor of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), shows analgesic effects in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2006, 120, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, R.L.; Moore, P.K. Effects of selective inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase on carrageenan-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.T. New theories in the pathogenesis of menstrual migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2008, 12, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokare, D.M.; Shelkar, G.P.; Borkar, C.D.; Nakhate, K.T.; Subhedar, N.K. A simple and inexpensive method to fabricate a cannula system for intracranial injections in rats and mice. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2011, 64, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, A.; Tepe, N.; Eftekhari, S.; Boran, H.E.; Dilekoz, E.; Edvinsson, L.; Bolay, H. CGRP receptor antagonist MK-8825 attenuates cortical spreading depression induced pain behavior. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Flores, C.M.; Harding-Rose, C.A.; Goodis, H.E.; Hargreaves, K.M. Capsaicin-evoked release of immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide from rat trigeminal ganglion: Evidence for intraganglionic neurotransmission. Pain 2001, 91, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmayer, R.M.; Vanderah, T.W.; Majuta, L.; Zhang, E.-T.; Bs, B.F.; De Felice, M.; Chichorro, J.; Ossipov, M.H.; King, T.; Lai, J.; et al. Medullary pain facilitating neurons mediate allodynia in headache-related pain. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Gao, Y.J. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Fukuoka, T.; Dai, Y.; Obata, K.; Noguchi, K. P2Y12 receptor upregulation in activated microglia is a gateway of p38 signaling and neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2892–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristiansen, K.A.; Edvinsson, L. Neurogenic inflammation: A study of rat trigeminal ganglion. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, S.G.; Thomas, J.G.; Abrantes, A.M.; Lipton, R.B.; Pavlovic, J.; Smitherman, T.A.; Irby, M.B.; Penzien, D.B.; Roth, J.; O’Leary, K.C.; et al. Pain worsening with physical activity during migraine attacks in women with overweight/obesity: A prospective evaluation of frequency, consistency, and correlates. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, M.E.; Ashina, S.; Burstein, R.; Reed, M.L.; Buse, D.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B.; AMPP Group. Prevalence and characteristics of allodynia in headache sufferers: A population study. Neurology 2008, 70, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E.; Ashina, S.; Burstein, R.; Silberstein, S.; Reed, M.L.; Serrano, D.; Stewart, W.F.; American Migraine Prevalence Prevention Advisory Group. Cutaneous allodynia in the migraine population. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louter, M.A.; Bosker, J.E.; van Oosterhout, W.P.; van Zwet, E.W.; Zitman, F.G.; Ferrari, M.D.; Terwindt, G.M. Cutaneous allodynia as a predictor of migraine chronification. Brain 2013, 136 Pt 11, 3489–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scher, A.I.; Stewart, W.F.; Ricci, J.A.; Lipton, R.B. Factors associated with the onset and remission of chronic daily headache in a population-based study. Pain 2003, 106, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burstein, R.; Jakubowski, M.; Garcia-Nicas, E.; Kainz, V.; Bajwa, Z.; Hargreaves, R.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D. Thalamic sensitization transforms localized pain into widespread allodynia. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanagaite, J.; Pareja, J.A.; Støren, O.; White, L.R.; Sand, T.; Stovner, L.J. Light-induced discomfort and pain in migraine. Cephalalgia 1997, 17, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalın, O.Ö.; Uluduz, D.; Özge, A.; Sungur, M.A.; Selekler, M.; Siva, A. Phenotypic features of chronic migraine. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, A.F.; Kuburas, A.; Kaiser, E.A.; Raddant, A.C.; Recober, A. A Potential Preclinical Migraine Model: CGRP-Sensitized Mice. Mol. Cell. Pharmacol. 2009, 1, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Seybold, V.S. The role of peptides in central sensitization. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 194, 451–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, N.; Dallel, R.; Artola, A.; Monconduit, L. General trigeminospinal central sensitization and impaired descending pain inhibitory controls contribute to migraine progression. Pain 2014, 155, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, V.; Rümenapp, P.; Schaible, H.G. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is involved in the spinal processing of mechanosensory input from the rat’s knee joint and in the generation and maintenance of hyperexcitability of dorsal horn-neurons during development of acute inflammation. Neuroscience 1996, 71, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, R.; De Icco, R.; Demartini, C.; Zanaboni, A.M.; Tumelero, E.; Sances, G.; Allena, M.; Tassorelli, C. Plasma levels of CGRP and expression of specific microRNAs in blood cells of episodic and chronic migraine subjects: Towards the identification of a panel of peripheral biomarkers of migraine? J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernuda-Morollón, E.; Larrosa, D.; Ramón, C.; Vega, J.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; Pascual, J. Interictal increase of CGRP levels in peripheral blood as a biomarker for chronic migraine. Neurology 2013, 81, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Johnson, K.W. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain 2017, 158, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neeb, L.; Reuter, U. Nitric oxide in migraine. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 6, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; De Corato, A.; Lisi, L.; Tringali, G.; Navarra, P.; Dello Russo, C. Proinflammatory-activated trigeminal satellite cells promote neuronal sensitization: Relevance for migraine pathology. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, R.J.; Zuccarello, M.; Keller, J.T. Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the rat dura mater. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Ploug, K.B.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; Olesen, J.; Jansen-Olesen, I.; Gupta, S. Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the trigeminal vascular system and other brain structures related to pain in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 484, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.A.; Smith, M.L.; McGuire, B.; Tarash, I.; Evans, C.J.; Charles, A. Characterization of a novel model of chronic migraine. Pain 2014, 155, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penfield, W.; McNaughton, F.L. Dural headache and innervation of the dura mater. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1940, 44, 43–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyihár-Csillik, E.; Vécsei, L. Effect of a nitric oxide donor on nitroxergic nerve fibers in the rat dura mater. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 260, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardutz, A.; Krizbai, I.; Multon, S.; Vecsei, L.; Schoenen, J. Systemic nitroglycerin increases nNOS levels in rat trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 3071–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverman, C.S.; Brown, J.W.; Sandhir, R.; Klein, R.M.; McCarson, K.; Berman, N.E. Oestrogen increases nociception through ERK activation in the trigeminal ganglion: Evidence for a peripheral mechanism of allodynia. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liverman, C.S.; Brown, J.W.; Sandhir, R.; McCarson, K.E.; Berman, N.E. Role of the oestrogen receptors GPR30 and ERalpha in peripheral sensitization: Relevance to trigeminal pain disorders in women. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bereiter, D.A. Sex differences in brainstem neural activation after injury to the TMJ region. Cells Tissues Organs 2001, 169, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereiter, D.A.; Cioffi, J.L.; Bereiter, D.F. Oestrogen receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the trigeminal sensory system of male and cycling female rats. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.L.; McCarson, K.E. Estrogen increases nociception-evoked brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in the female rat. Neuroendocrinology 2005, 81, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fejes-Szabó, A.; Spekker, E.; Tar, L.; Nagy-Grócz, G.; Bohár, Z.; Laborc, K.F.; Vécsei, L.; Párdutz, Á. Chronic 17β-estradiol pretreatment has pronociceptive effect on behavioral and morphological changes induced by orofacial formalin in ovariectomized rats. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kou, X.X.; Wu, Y.W.; Ding, Y.; Hao, T.; Bi, R.Y.; Gan, Y.H.; Ma, X. 17β-estradiol aggravates temporomandibular joint inflammation through the NF-κB pathway in ovariectomized rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.; Mokha, S.S. Activation of the trigeminal α2-adrenoceptor produces sex-specific, estrogen dependent thermal antinociception and antihyperalgesia using an operant pain assay in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 314, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Cui, L.; Liverman, C.S.; Roby, K.F.; Klein, R.M.; Welch, K.M.A.; Berman, N.E. Ovarian steroids regulate neuropeptides in the trigeminal ganglion. Neuropeptides 2005, 39, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, M.; Puri, V.; Puri, S. Effects of estrogen on the serotonergic system and calcitonin gene-related peptide in trigeminal ganglia of rats. Ann. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermeer, L.M.; Gregory, E.; Winter, M.K.; McCarson, K.E.; Berman, N.E. Exposure to bisphenol A exacerbates migraine-like behaviors in a multibehavior model of rat migraine. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 137, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangula, P.R.; Lanlua, P.; Wimalawansa, S.; Supowit, S.; DiPette, D.; Yallampalli, C. Regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in dorsal root ganglia of rats by female sex steroid hormones. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowa, C.N.; Usip, S.; Collins, J.; Storey-Workley, M.; Hargreaves, K.M.; Papka, R.E. The effects of pregnancy and estrogen on the expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the uterine cervix, dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord. Peptides 2003, 24, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarajari, S.; Oblinger, M.M. Estrogen effects on pain sensitivity and neuropeptide expression in rat sensory neurons. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 224, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gon, G.; Giaid, A.; Steel, J.H.; O’Halloran, D.J.; Van Noorden, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Jones, P.M.; Amara, S.G.; Ishikawa, H.; Bloom, S.R. Localization of immunoreactivity for calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat anterior pituitary during ontogeny and gonadal steroid manipulations and detection of its messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuri, K.; Kawata, M. Estrogen affects calcitonin gene-related peptide- and methionine-enkephalin-immunoreactive neuron in the female rat preoptic area. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 169, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labastida-Ramírez, A.; Rubio-Beltrán, E.; Villalón, C.M.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Gender aspects of CGRP in migraine. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Durán, M.; de Frutos, T.; Díaz-Recasens, J.; García-Gálvez, G.; Jiménez, A.; Montón, M.; Farré, J.; Sánchez de Miguel, L.; González-Fernández, F.; Arriero, M.D.; et al. Estrogen stimulates neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein expression in human neutrophils. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccatelli, S.; Grandison, L.; Scott, R.E.; Pfaff, D.W.; Kow, L.M. Estradiol regulation of nitric oxide synthase mRNAs in rat hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinology 1996, 64, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spekker, E.; Bohár, Z.; Fejes-Szabó, A.; Szűcs, M.; Vécsei, L.; Párdutz, Á. Estradiol Treatment Enhances Behavioral and Molecular Changes Induced by Repetitive Trigeminal Activation in a Rat Model of Migraine. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123175
Spekker E, Bohár Z, Fejes-Szabó A, Szűcs M, Vécsei L, Párdutz Á. Estradiol Treatment Enhances Behavioral and Molecular Changes Induced by Repetitive Trigeminal Activation in a Rat Model of Migraine. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123175
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpekker, Eleonóra, Zsuzsanna Bohár, Annamária Fejes-Szabó, Mónika Szűcs, László Vécsei, and Árpád Párdutz. 2022. "Estradiol Treatment Enhances Behavioral and Molecular Changes Induced by Repetitive Trigeminal Activation in a Rat Model of Migraine" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123175
APA StyleSpekker, E., Bohár, Z., Fejes-Szabó, A., Szűcs, M., Vécsei, L., & Párdutz, Á. (2022). Estradiol Treatment Enhances Behavioral and Molecular Changes Induced by Repetitive Trigeminal Activation in a Rat Model of Migraine. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123175