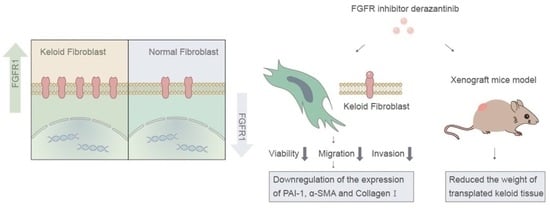
Derazantinib Inhibits the Bioactivity of Keloid Fibroblasts via FGFR Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunofluorescence Assay of Keloid Tissue and Normal Skin Tissue
2.2. Isolation and In Vitro Culture of Fibroblasts from Human Keloid
2.3. Chemical Reagents
2.4. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay of KFs
2.5. Cell Migration Assay of KFs
2.6. Cell Invasion Assay of KFs
2.7. Cell Viability Staining
2.8. Immunofluorescence Assay of KFs
2.9. Quantitative Reverse Transcription (RT)-PCR Analysis of KFs
2.10. Western Blot of KFs
2.11. Local Injection Treatment of Keloids with Derazantinib versus Glucocorticoid in an Athymic Nude Mouse Model
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. FGFR1 Demonstrated Higher Expression in Keloid Tissue
3.2. Derazantinib Reduced the Viability and Promoted the Apoptosis of KFs
3.3. Derazantinib Inhibited the Migration and Invasion of KFs
3.4. Derazantinib Suppressed the Activation of KFs
3.5. Derazantinib Inhibited Collagen Production and Disrupted Angiogenesis of Keloid Tissue in the Athymic Nude Mouse Model
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, J.P.; Marttala, J.; Macarak, E.; Rosenbloom, J.; Uitto, J. Keloids: The paradigm of skin fibrosis—Pathomechanisms and treatment. Matrix Biol. 2016, 51, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ud-Din, S.; Bayat, A. Strategic management of keloid disease in ethnic skin: A structured approach supported by the emerging literature. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169 (Suppl. 3), 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, R. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.C.; Hu, Y.F.; Zhu, D.H.; Cheng, Q.; Gu, J.J.; Feng, Q.L.; Zhang, L.X.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, D.; Rong, Z.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals fibroblast heterogeneity and increased mesenchymal fibroblasts in human fibrotic skin diseases. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Shan, M.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, Z.; He, K.; Wei, Y.; Song, K.; Meng, T.; Liu, H.; Hao, Y.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals distinct immunology profiles in human keloid. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 940645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, F.B.; Spauwen, P.H.; Schalkwijk, J.; Kon, M. On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: A review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 104, 1435–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilgus, T.A.; Ud-Din, S.; Bayat, A. A Review of the Evidence for and against a Role for Mast Cells in Cutaneous Scarring and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 18, 219673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.C. Keloids and hypertrophic scars. Clin. Dermatol. 1994, 12, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.S.; Wang, F.S.; Yang, K.D.; Huang, C.C.; Kuo, Y.R. Dexamethasone induction of keloid regression through effective suppression of VEGF expression and keloid fibroblast proliferation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, R. The Most Current Algorithms for the Treatment and Prevention of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: A 2020 Update of the Algorithms Published 10 Years Ago. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 79e–94e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaluno, L.; Urwyler, C.; Werner, S. Fibroblast growth factors: Key players in regeneration and tissue repair. Development 2017, 144, 4047–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Balordi, F.; Su, N.; Chen, L.; Fishell, G.; Hébert, J.M. Astrocyte activation is suppressed in both normal and injured brain by FGF signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2987–E2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, B.; Korfei, M.; Henneke, I.; Sibinska, Z.; Tian, X.; Hezel, S.; Dilai, S.; Wasnick, R.; Schneider, B.; Wilhelm, J.; et al. Increased FGF1-FGFRc expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, D.W.; Booijink, R.; Pater, L.; Wols, I.; Vrynas, A.; Storm, G.; Prakash, J.; Bansal, R. Fibroblast growth factor 2 conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (FGF2-SPIONs) ameliorate hepatic stellate cells activation in vitro and acute liver injury in vivo. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Droz Dit Busset, M.; Cotsoglou, C.; Harris, W.P.; Damjanov, N.; Masi, G.; Rimassa, L.; Personeni, N.; Braiteh, F.; et al. Derazantinib (ARQ 087) in advanced or inoperable FGFR2 gene fusion-positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourd, E. Derazantinib for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, K.P.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Tolcher, A.W.; Patnaik, A.; Rasco, D.W.; Harvey, R.D.; LoRusso, P.M.; Sachdev, J.C.; Abbadessa, G.; Savage, R.E.; et al. A Phase 1 study of ARQ 087, an oral pan-FGFR inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balek, L.; Gudernova, I.; Vesela, I.; Hampl, M.; Oralova, V.; Kunova Bosakova, M.; Varecha, M.; Nemec, P.; Hall, T.; Abbadessa, G.; et al. ARQ 087 inhibits FGFR signaling and rescues aberrant cell proliferation and differentiation in experimental models of craniosynostoses and chondrodysplasias caused by activating mutations in FGFR1, FGFR2 and FGFR3. Bone 2017, 105, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hall, T.; Eathiraj, S.; Wick, M.J.; Schwartz, B.; Abbadessa, G. In-vitro and in-vivo combined effect of ARQ 092, an AKT inhibitor, with ARQ 087, a FGFR inhibitor. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2017, 28, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, J.M.; Schjenken, J.E.; Civiti, T.D.; Clifton, V.L.; Smith, R. Column-based method to simultaneously extract DNA, RNA, and proteins from the same sample. Biotechniques 2007, 43, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tubuly, A.A. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting. Methods Mol. Med. 2000, 40, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiling, H.; Werner, S. Fibroblast growth factors: Key players in epithelial morphogenesis, repair and cytoprotection. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimbori, C.; Bellaye, P.S.; Xia, J.; Gauldie, J.; Ask, K.; Ramos, C.; Becerril, C.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Kolb, M. Fibroblast growth factor-1 attenuates TGF-β1-induced lung fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmawan, C.C.; Montenegro, S.E.; Jo, G.; Kusumaningrum, N.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, J.H.; Mun, J.H. Adiponectin-Based Peptide (ADP355) Inhibits Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Induced Fibrosis in Keloids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kal, H.B.; Veen, R.E.; Jürgenliemk-Schulz, I.M. Dose-effect relationships for recurrence of keloid and pterygium after surgery and radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Zeng, Q.; Ma, B.; Li, Z.; Meng, T.; Chen, J.; Yu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Long, X. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Reveals Lineage-Specific Regulatory Changes of Fibroblasts and Vascular Endothelial Cells in Keloids. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 124–135.e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.G.; Yu, Y.; Eathiraj, S.; Wang, Y.; Savage, R.E.; Lapierre, J.M.; Schwartz, B.; Abbadessa, G. Preclinical Activity of ARQ 087, a Novel Inhibitor Targeting FGFR Dysregulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, C.; Fiaccadori, K.; Pastore, M.; Correnti, M.; Piombanti, B.; Forti, E.; Navari, N.; Abbadessa, G.; Hall, T.; Destro, A.; et al. Antitumor Activity of a Novel Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Song, K.H.; Park, J.I.; Ahn, J.; Kim, E.H.; Park, J.K.; Hwang, S.G.; Woo, H.J.; Song, J.Y. A new FGFR inhibitor disrupts the TGF-β1-induced fibrotic process. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes Barreto, D.; Struijk, D.G.; Krediet, R.T. Peritoneal effluent MMP-2 and PAI-1 in encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Fang, H. Adiponectin, but Not TGF-β1, CTGF, IL-6 or TNF-α, May Be a Potential Anti-Inflammation and Anti-Fibrosis Factor in Keloid. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Li, W.B.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, J.; Song, S.X.; Bai, L.L.; Hu, Y.Y.; Yuan, Y.D.; Zhang, M. siRNA against plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, A.D.; Albornoz, F.; Griffin, J.P.; Crandall, D.L.; Elokdah, H.; Fogo, A.B.; Vaughan, D.E.; Brown, N.J. Pharmacological inhibition and genetic deficiency of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 attenuates angiotensin II/salt-induced aortic remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Giacoia, E.; Miyake, M.; Goodison, S.; Rosser, C.J. Targeting plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in a human cancer xenograft model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeier, C.; Escher, F.; Aleshcheva, G.; Pietsch, H.; Schultheiss, H.P. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 reduces cardiac fibrosis and promotes M2 macrophage polarization in inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotini, M.P.; Bachmann, F.; Spickermann, J.; McSheehy, P.M.; Affolter, M. Probing the Effects of the FGFR-Inhibitor Derazantinib on Vascular Development in Zebrafish Embryos. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Gene | Primer Sequence | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| H-GAPDH-S | GGAAGCTTGTCATCAATGGAAATC | 168 |
| H-GAPDH-A | TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC | |
| H-VEGFR1-S | GCACCTTGGTTGTGGCTGA | 155 |
| H-VEGFR1-A | CTCTCCTTCCGTCGGCATT | |
| H-FGFR1-S | GAGGCTACAAGGTCCGTTATGC | 292 |
| H-FGFR1-A | CCAATCTTGCTCCCATTCACCT | |
| H-CTGF-S | GCCCAGACCCAACTATGATTAGAG | 207 |
| H-CTGF-A | GGATGCACTTTTTGCCCTTCT | |
| H-PAI-1-S | CCCCACTTCTTCAGGCTGTT | 189 |
| H-PAI-1-A | GCCGTTGAAGTAGAGGGCAT | |
| H-COL1-S | CCCCTGGAAAGAATGGAGATG | 104 |
| H-COL1-A | AGCTGTTCCGGGCAATCCT | |
| H-COL3-S | CCCCGTATTATGGAGATGAACC | 109 |
| H-COL3-A | CCATCAGGACTAATGAGGCTTTC | |
| H-α-SMA-S | CAATGTCCTATCAGGGGGCAC | 209 |
| H-α-SMA-A | CGGCTTCATCGTATTCCTGTT | |
| H-PI3K-S | TACACTGTCCTGTGCTGGCTA | 295 |
| H-PI3K-A | GAGATTCCCATGCCGTCGTA | |
| H-TGFβ1-S | GGAGAAGAACTGCTGCGTGC | 132 |
| H-TGFβ1-A | TCCAGGCTCCAAATGTAGGG | |
| H-SMAD2-S | TGCCACGGTAGAAATGACAAG | 230 |
| H-SMAD2-A | TAACAGACTGAGCCAGAAGAGC | |
| H-SMAD3-S | CTACCAGTTGACCCGAATGTGC | 74 |
| H-SMAD3-A | TCTGTCTCCTGTACTCCGCTCC | |
| H-JNK-S | TCTCCAACACCCGTACATCAA | 151 |
| H-JNK-A | CTCCTCCAAGTCCATAACTTCCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Qi, S.; Shu, B. Derazantinib Inhibits the Bioactivity of Keloid Fibroblasts via FGFR Signaling. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123220
Xu S, Zhu Y, Wang P, Qi S, Shu B. Derazantinib Inhibits the Bioactivity of Keloid Fibroblasts via FGFR Signaling. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123220
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shuqia, Yongkang Zhu, Peng Wang, Shaohai Qi, and Bin Shu. 2023. "Derazantinib Inhibits the Bioactivity of Keloid Fibroblasts via FGFR Signaling" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123220
APA StyleXu, S., Zhu, Y., Wang, P., Qi, S., & Shu, B. (2023). Derazantinib Inhibits the Bioactivity of Keloid Fibroblasts via FGFR Signaling. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123220