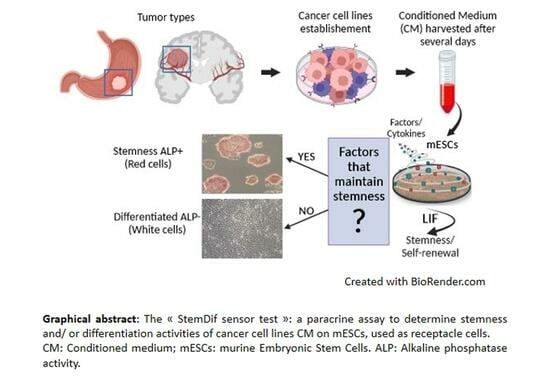
The “StemDif Sensor Test”: A Straightforward, Non-Invasive Assay to Characterize the Secreted Stemness and/or Differentiation Activities of Tumor-Derived Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cancer Stem Cells
2.2. LIF ELISA Test
2.3. “StemDif Sensor Test”
2.4. RNA Preparation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Protein Lysate Preparation
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. LIF Secretion by Adult and Pediatric Glioma-Initiating Cells (GICs)
3.2. LIF-Dependent Induction of STAT3 in mESCs Treated with GIC CM
3.3. “StemDif Sensor Test” Set up in mESCs
3.4. Gastric Adenocarcinoma-Derived Cell Lines Exhibit Heterogeneity in LIF Secretion, and Their CM Could Display Dual Functions on mESCs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Cancer Stem Cells Revisited. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, O.; Smith, B.D. Eliminating Cancer Stem Cells by Targeting Embryonic Signaling Pathways. Stem Cell Rev. 2017, 13, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Moriya, C.; Igarashi, H.; Saitoh, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Adachi, Y.; Imai, K. Cancer Stem Cells in Human Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudás, J.; Skvortsov, S.; Ganswindt, U.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.-I. Therapy Resistance Mediated by Cancer Stem Cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, A.; Acker, T.; Garvalov, B.K. The Cancer Stem Cell Niche(s): The Crosstalk between Glioma Stem Cells and Their Microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2496–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirant, C.; Bessette, B.; Varlet, P.; Puget, S.; Cadusseau, J.; Tavares, S.D.R.; Studler, J.-M.; Silvestre, D.C.; Susini, A.; Villa, C.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Tumor Cells with Stem-like Properties in Pediatric Brain Tumors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikfalvi, A.; da Costa, C.A.; Avril, T.; Barnier, J.-V.; Bauchet, L.; Brisson, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Castel, H.; Chevet, E.; Chneiweiss, H.; et al. Challenges in Glioblastoma Research: Focus on the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Luo, W.; Pehlivan, K.C.; Hoang, H.; Rajappa, P.; Cripe, T.P.; Cassady, K.A.; Lee, D.A.; Cairo, M.S. Pediatric versus Adult High Grade Glioma: Immunotherapeutic and Genomic Considerations. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1038096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Veiga, M.-A.; Rogister, B.; Lombard, A.; Neirinckx, V.; Piette, C. Glioma Stem Cells in Pediatric High-Grade Gliomas: From Current Knowledge to Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeniou, M.; Fève, M.; Mameri, S.; Dong, J.; Salomé, C.; Chen, W.; El-Habr, E.A.; Bousson, F.; Sy, M.; Obszynski, J.; et al. Chemical Library Screening and Structure-Function Relationship Studies Identify Bisacodyl as a Potent and Selective Cytotoxic Agent Towards Quiescent Human Glioblastoma Tumor Stem-Like Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad Kahn, S.; Costa, S.L.; Gholamin, S.; Nitta, R.T.; Dubois, L.G.; Fève, M.; Zeniou, M.; Coelho, P.L.C.; El-Habr, E.; Cadusseau, J.; et al. The Anti-Hypertensive Drug Prazosin Inhibits Glioblastoma Growth via the PKCδ-Dependent Inhibition of the AKT Pathway. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zebaze, L.N.; Dong, J.; Chézeau, L.; Inquimbert, P.; Hugel, S.; Niu, S.; Bihel, F.; Boutant, E.; Réal, E.; et al. WNK1 Kinase and Its Partners Akt, SGK1 and NBC-Family Na+/HCO3− Cotransporters Are Potential Therapeutic Targets for Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells Linked to Bisacodyl Signaling. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27197–27219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeneevassen, L.; Bessède, E.; Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P.; Dubus, P.; Varon, C. Gastric Cancer: Advances in Carcinogenesis Research and New Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessède, E.; Dubus, P.; Mégraud, F.; Varon, C. Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Stem Cells at the Origin of Gastric Cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaishi, S.; Okumura, T.; Tu, S.; Wang, S.S.W.; Shibata, W.; Vigneshwaran, R.; Gordon, S.A.K.; Shimada, Y.; Wang, T.C. Identification of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells Using the Cell Surface Marker CD44. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2009, 27, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, I.; Giudice, V.; Delahaye, E.; Wianny, F.; Aubry, M.; Mure, M.; Chen, J.; Jauch, R.; Bogu, G.K.; Nolden, T.; et al. Klf4 and Klf5 Differentially Inhibit Mesoderm and Endoderm Differentiation in Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.; Smith, A. Naive and Primed Pluripotent States. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, R. Celebrating 10 Years of hESC Lines: An Interview with Rudolf Jaenisch. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2008, 26, 3005–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brons, I.G.; Smithers, L.E.; Trotter, M.W.; Rugg-Gunn, P.; Sun, B.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; Howlett, S.K.; Clarkson, A.; Ahrlund-Richter, L.; Pedersen, R.A.; et al. Derivation of Pluripotent Epiblast Stem Cells from Mammalian Embryos. Nature 2007, 448, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, C.M.; Layton, M.J.; Metcalf, D.; Lock, P.; Willson, T.A.; Gough, N.M.; Nicola, N.A. Inter-Species Chimeras of Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor Define a Major Human Receptor-Binding Determinant. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3487–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillas, M.; Saucourt, C.; Guillotin, B.; Gauthereau, X.; Taupin, J.-L.; Moreau, J.-F.; Boeuf, H. The LIF Cytokine: Towards Adulthood. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2009, 20, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, S.; Anido, J.; Prieto-Sánchez, R.M.; Folch, G.; Barba, I.; Cuartas, I.; García-Dorado, D.; Poca, M.A.; Sahuquillo, J.; Baselga, J.; et al. TGF-Beta Increases Glioma-Initiating Cell Self-Renewal through the Induction of LIF in Human Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulluoglu, S.; Sahin, M.; Tuysuz, E.C.; Yaltirik, C.K.; Kuskucu, A.; Ozkan, F.; Sahin, F.; Ture, U.; Bayrak, O.F. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Promotes Aggressiveness of Chordoma. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, W.; Lytle, N.K.; Huang, P.; Yuan, X.; Dann, A.M.; Ridinger-Saison, M.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Antal, C.E.; Liang, G.; et al. Targeting LIF-Mediated Paracrine Interaction for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy and Monitoring. Nature 2019, 569, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrengues, J.; Bourget, I.; Pons, C.; Butet, V.; Hofman, P.; Tartare-Deckert, S.; Feral, C.C.; Meneguzzi, G.; Gaggioli, C. LIF Mediates Proinvasive Activation of Stromal Fibroblasts in Cancer. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1664–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, P.; Rezaeian, A.H.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Gupta, S.; Liang, H.; Lin, H.-K.; Hung, M.-C.; et al. LIFR Is a Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Upstream of the Hippo-YAP Pathway and a Prognostic Marker. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, S. LIF-Ting Hippo Averts Metastasis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Jing, X.; Shen, B.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, B.; Fu, Z.; Peng, C.; Qiu, W. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor Negatively Regulates the Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeneevassen, L.; Giraud, J.; Molina-Castro, S.; Sifré, E.; Tiffon, C.; Beauvoit, C.; Staedel, C.; Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P.; Martin, O.C.B.; et al. Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells Tumorigenic Properties through Hippo Kinases Activation in Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Maihle, N.J.; Huang, Y. Pluripotency Factors Lin28 and Oct4 Identify a Sub-Population of Stem Cell-like Cells in Ovarian Cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, S. Nanog, Gli, and P53: A New Network of Stemness in Development and Cancer. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2475–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Goldstein, B.G.; Chao, H.H.; Katz, J.P. KLF4 and KLF5 Regulate Proliferation, Apoptosis and Invasion in Esophageal Cancer Cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Jia, J.; Huang, Z.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Guo, P. KLF5 Promotes Cell Migration by Up-Regulating FYN in Bladder Cancer Cells. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patru, C.; Romao, L.; Varlet, P.; Coulombel, L.; Raponi, E.; Cadusseau, J.; Renault-Mihara, F.; Thirant, C.; Leonard, N.; Berhneim, A.; et al. CD133, CD15/SSEA-1, CD34 or Side Populations Do Not Resume Tumor-Initiating Properties of Long-Term Cultured Cancer Stem Cells from Human Malignant Glio-Neuronal Tumors. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirant, C.; Galan-Moya, E.-M.; Dubois, L.G.; Pinte, S.; Chafey, P.; Broussard, C.; Varlet, P.; Devaux, B.; Soncin, F.; Gavard, J.; et al. Differential Proteomic Analysis of Human Glioblastoma and Neural Stem Cells Reveals HDGF as a Novel Angiogenic Secreted Factor. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taupin, J.L.; Gualde, N.; Moreau, J.F. A Monoclonal Antibody Based Elisa for Quantitation of Human Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor. Cytokine 1997, 9, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taupin, J.L.; Acres, B.; Dott, K.; Schmitt, D.; Kieny, M.P.; Gualde, N.; Moreau, J.F. Immunogenicity of HILDA/LIF Either in a Soluble or in a Membrane Anchored Form Expressed in Vivo by Recombinant Vaccinia Viruses. Scand. J. Immunol. 1993, 38, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, J.F.; Donaldson, D.D.; Bennett, F.; Witek-Giannotti, J.; Clark, S.C.; Wong, G.G. Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor Is Identical to the Myeloid Growth Factor Human Interleukin for DA Cells. Nature 1988, 336, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, A.A.; Kirstein, N.; Mournetas, V.; Darracq, A.; Broc, S.; Blanchard, C.; Zeineddine, D.; Mortada, M.; Boeuf, H. Murine Embryonic Stem Cell Plasticity Is Regulated through Klf5 and Maintained by Metalloproteinase MMP1 and Hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillas, M.; Saucourt, C.; Guillotin, B.; Gauthereau, X.; Ding, L.; Buchholz, F.; Doss, M.X.; Sachinidis, A.; Hescheler, J.; Hummel, O.; et al. Three LIF-Dependent Signatures and Gene Clusters with Atypical Expression Profiles, Identified by Transcriptome Studies in Mouse ES Cells and Early Derivatives. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourillot, P.Y.; Aksoy, I.; Schreiber, V.; Wianny, F.; Schulz, H.; Hummel, O.; Hubner, N.; Savatier, P. Novel STAT3 Target Genes Exert Distinct Roles in the Inhibition of Mesoderm and Endoderm Differentiation in Cooperation with Nanog. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 1760–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.; Dobrin, R.; Lu, R.; Kotenko, I.; Levorse, J.; DeCoste, C.; Schafer, X.; Lun, Y.; Lemischka, I.R. Dissecting Self-Renewal in Stem Cells with RNA Interference. Nature 2006, 442, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, H.; Burdon, T.; Chambers, I.; Smith, A. Self-Renewal of Pluripotent Embryonic Stem Cells Is Mediated via Activation of STAT3. Genes.Dev. 1998, 12, 2048–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, J.; Molina-Castro, S.; Seeneevassen, L.; Sifré, E.; Izotte, J.; Tiffon, C.; Staedel, C.; Boeuf, H.; Fernandez, S.; Barthelemy, P.; et al. Verteporfin Targeting YAP1/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Activity Inhibits the Tumorigenic Properties of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2255–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, I.S.; Wei, S.-J.; Kang, M.H. Role of OCT4 in Cancer Stem-like Cells and Chemotherapy Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monferrer, E.; Burgos-Panadero, R.; Blanquer-Maceiras, M.; Cañete, A.; Navarro, S.; Noguera, R. High Oct4 Expression: Implications in the Pathogenesis of Neuroblastic Tumours. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, E.P.; Rizzino, A. Sox2 Dosage: A Critical Determinant in the Functions of Sox2 in Both Normal and Tumor Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19298–19306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Kong, F.; Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Dong, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H.; Xu, Y.; Chu, Y.; et al. A KLF4/PiHL/EZH2/HMGA2 Regulatory Axis and Its Function in Promoting Oxaliplatin-Resistance of Colorectal Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.-E.; Saucourt, C.; Mournetas, V.; Gauthereau, X.; Thézé, N.; Praloran, V.; Thiébaud, P.; Bœuf, H. LIF-Dependent Signaling: New Pieces in the Lego. Stem Cell Rev. 2012, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.-B.; Yang, Y.; Liang, W.-Q.; Zhang, K.-C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.-T. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion via the LIFR-Hippo-YAP Pathway. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1484, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, D.; Reinhardt, B.; Kedinger, C.; Boeuf, H. Role of Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling (Socs) in Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) -Dependent Embryonic Stem Cell Survival. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, D.; Duval, G.; Kedinger, C.; Poch, O.; Boeuf, H. The “PINIT” Motif, of a Newly Identified Conserved Domain of the PIAS Protein Family, Is Essential for Nuclear Retention of PIAS3L. FEBS Lett. 2003, 554, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy—Promise and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou Hammoud, A.; Giraud, J.; Gauthereau, X.; Blanchard, C.; Daburon, S.; Zese, M.; Molina-Castro, S.; Dubus, P.; Varon, C.; Boeuf, H. The “StemDif Sensor Test”: A Straightforward, Non-Invasive Assay to Characterize the Secreted Stemness and/or Differentiation Activities of Tumor-Derived Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123293
Abou Hammoud A, Giraud J, Gauthereau X, Blanchard C, Daburon S, Zese M, Molina-Castro S, Dubus P, Varon C, Boeuf H. The “StemDif Sensor Test”: A Straightforward, Non-Invasive Assay to Characterize the Secreted Stemness and/or Differentiation Activities of Tumor-Derived Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123293
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou Hammoud, Aya, Julie Giraud, Xavier Gauthereau, Camille Blanchard, Sophie Daburon, Marco Zese, Silvia Molina-Castro, Pierre Dubus, Christine Varon, and Helene Boeuf. 2023. "The “StemDif Sensor Test”: A Straightforward, Non-Invasive Assay to Characterize the Secreted Stemness and/or Differentiation Activities of Tumor-Derived Cancer Cell Lines" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123293
APA StyleAbou Hammoud, A., Giraud, J., Gauthereau, X., Blanchard, C., Daburon, S., Zese, M., Molina-Castro, S., Dubus, P., Varon, C., & Boeuf, H. (2023). The “StemDif Sensor Test”: A Straightforward, Non-Invasive Assay to Characterize the Secreted Stemness and/or Differentiation Activities of Tumor-Derived Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123293