Improving the Age Estimation Efficiency by Calculation of the Area Ratio Index Using Semi-Automatic Segmentation of Knee MRI Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
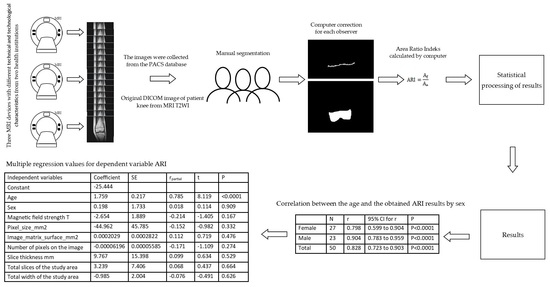
2. Materials and Methods
- Segmenting the distal epiphysis of the femur under the growth plate closure.
- Segmenting the growth plate closure.
Statistical Analysis and Data Management
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmeling, A.; Grundmann, C.; Fuhrmann, A.; Kaatsch, H.J.; Knell, B.; Ramsthaler, F.; Reisinger, W.; Riepert, T.; Ritz-Timme, S.; Rosing, F.W.; et al. Criteria for age estimation in living individuals. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2008, 122, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B. Forensic Anthropology; House, C., Ed.; Chelsea House: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, E.; Baccino, E.; Martrille, L.; Ramsthaler, F.; Prieto, J.; Schuliar, Y.; Lynnerup, N.; Cattaneo, C. The problem of aging human remains and living individuals: A review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 193, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focardi, M.; Pinchi, V.; De Luca, F.; Norelli, G.A. Age estimation for forensic purposes in Italy: Ethical issues. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2014, 128, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focardi, M.; Pinchi, V.; De Luca, F.; Norelli, G.A. Reply to the letter to the editor. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2015, 129, 1275–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, E. Comments to Focardi et al., Age estimation for forensic purposes in Italy: Ethical issues. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2015, 129, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedouit, F.; Auriol, J.; Rousseau, H.; Rouge, D.; Crubezy, E.; Telmon, N. Age assessment by magnetic resonance imaging of the knee: A preliminary study. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 217, 232.e1–232.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Schmeling, A.; Zwiesigk, P.; Pfeiffer, H.; Schulz, R. Sonographic evaluation of apophyseal ossification of the iliac crest in forensic age diagnostics in living individuals. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2011, 125, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Schiborr, M.; Pfeiffer, H.; Schmeling, A.; Schulz, R. Age dependence of epiphyseal ossification of the distal radius in ultrasound diagnostics. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2013, 127, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Muhler, M.; Schmeling, A.; Reisinger, W.; Schulz, R. Magnetic resonance imaging of the clavicular ossification. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2007, 121, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Martin, P.; Rerolle, C.; Pucheux, J.; Dedouit, F.; Telmon, N. Contribution of distal femur MRI to the determination of the 18-year limit in forensic age estimation. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2015, 129, 619–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Martin, P.; Rerolle, C.; Dedouit, F.; Rousseau, H.; Rouge, D.; Telmon, N. Evaluation of an automatic method for forensic age estimation by magnetic resonance imaging of the distal tibial epiphysis—A preliminary study focusing on the 18-year threshold. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2014, 128, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Martin, P.; Rerolle, C.; Dedouit, F.; Bouilleau, L.; Rousseau, H.; Rouge, D.; Telmon, N. Age estimation by magnetic resonance imaging of the distal tibial epiphysis and the calcaneum. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2013, 127, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.A.; Schmidt, S.; Jurgens, K.U.; Lentschig, M.; Schmeling, A.; Vieth, V. Forensic age estimation in living individuals using 3.0 T MRI of the distal femur. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2014, 128, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.A.; Schmidt, S.; Jurgens, K.U.; Lentschig, M.; Schmeling, A.; Vieth, V. The use of magnetic resonance imaging to examine ossification of the proximal tibial epiphysis for forensic age estimation in living individuals. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2014, 10, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillewig, E.; Degroote, J.; Van der Paelt, T.; Visscher, A.; Vandemaele, P.; Lutin, B.; D’Hooghe, L.; Vandriessche, V.; Piette, M.; Verstraete, K. Magnetic resonance imaging of the sternal extremity of the clavicle in forensic age estimation: Towards more sound age estimates. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2013, 127, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillewig, E.; De Tobel, J.; Cuche, O.; Vandemaele, P.; Piette, M.; Verstraete, K. Magnetic resonance imaging of the medial extremity of the clavicle in forensic bone age determination: A new four-minute approach. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottow, C.; Schulz, R.; Pfeiffer, H.; Heindel, W.; Schmeling, A.; Vieth, V. Forensic age estimation by magnetic resonance imaging of the knee: The definite relevance in bony fusion of the distal femoral- and the proximal tibial epiphyses using closest-to-bone T1 TSE sequence. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 5041–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopp, E.; Schröder, I.; Maas, R.; Adam, G.; Püschel, K.J.R. Proximale Tibiaepiphyse im Magnetresonanztomogramm. Rechtsmedizin 2010, 20, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Zhang, K.; Peng, Z.; Cui, J.H.; Hu, N.; Deng, Z.H. Forensic age estimation of living persons from the knee: Comparison of MRI with radiographs. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 268, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekizoglu, O.; Hocaoglu, E.; Inci, E.; Can, I.O.; Aksoy, S.; Kazimoglu, C. Forensic age estimation via 3-T magnetic resonance imaging of ossification of the proximal tibial and distal femoral epiphyses: Use of a T2-weighted fast spin-echo technique. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 260, 102.e1–102.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameriere, R.; Cingolani, M.; Giuliodori, A.; De Luca, S.; Ferrante, L. Radiographic analysis of epiphyseal fusion at knee joint to assess likelihood of having attained 18 years of age. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2012, 126, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmeling, A.; Olze, A.; Reisinger, W.; Konig, M.; Geserick, G. Statistical analysis and verification of forensic age estimation of living persons in the Institute of Legal Medicine of the Berlin University Hospital Charite. Leg. Med. 2003, 5 (Suppl. S1), S367–S371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laor, T.; Chun, G.F.; Dardzinski, B.J.; Bean, J.A.; Witte, D.P. Posterior distal femoral and proximal tibial metaphyseal stripes at MR imaging in children and young adults. Radiology 2002, 224, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallora, A.L.; Berglund, J.S.; Brogren, M.; Kvist, O.; Diaz Ruiz, S.; Dübbel, A.; Anderberg, P. Age Assessment of Youth and Young Adults Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee: A Deep Learning Approach. JMIR Med. Inform. 2019, 7, e16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.; van Ginneken, B.; Sanchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Trundle, P.; Ren, J. Medical image analysis with artificial neural networks. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. Off. J. Comput. Med. Imaging Soc. 2010, 34, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setiono, R.; Liu, H. Neural-network feature selector. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prove, P.L.; Jopp-van Well, E.; Stanczus, B.; Morlock, M.M.; Herrmann, J.; Groth, M.; Saring, D.; Auf der Mauer, M. Automated segmentation of the knee for age assessment in 3D MR images using convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2019, 133, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ording Muller, L.-S.; Adolfsson, J.; Forsberg, L.; Bring, J.; Dahlgren, J.; Domeij, H.; Gornitzki, C.; Wernersson, E.; Odeberg, J. Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee for chronological age estimation—A systematic review. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 5258–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Saindane, A.M. Standardizing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protocols Across a Large Radiology Enterprise: Barriers and Solutions. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2020, 49, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, O.F.; Dallora, A.L.; Nilsson, O.; Anderberg, P.; Berglund, J.S.; Flodmark, C.E.; Diaz, S. Comparison of reliability of magnetic resonance imaging using cartilage and T1-weighted sequences in the assessment of the closure of the growth plates at the knee. Acta Radiol. Open 2020, 9, 2058460120962732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Crucilla, S.; Gandhi, T.; Rose, D.; Singh, A.; Ganesh, S.; Mathur, U.; Bex, P. Mechanisms underlying simultaneous brightness contrast: Early and innate. Vis. Res. 2020, 173, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DICOM Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine. Available online: https://www.dicomstandard.org/ (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Kulseng, C.P.S.; Nainamalai, V.; Grøvik, E.; Geitung, J.-T.; Årøen, A.; Gjesdal, K.-I. Automatic segmentation of human knee anatomy by a convolutional neural network applying a 3D MRI protocol. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajalid, R.; Zhang, M.; Shan, J. Fully Automatic Knee Bone Detection and Segmentation on Three-Dimensional MRI. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DICOM Standard Browser. Available online: https://dicom.innolitics.com/ciods/ct-image/image-plane/00280030 (accessed on 23 July 2019).
- Richard, S. Computer Vision Algorithms and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guenter, S.; Andreas, S.; Ernst, R. Medical Age Assessment of Juvenile Migrants; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, M.S.; Prescott, J.W.; Best, T.M.; Powell, K.; Jackson, R.D.; Haq, F.; Gurcan, M.N. Semi-automated segmentation to assess the lateral meniscus in normal and osteoarthritic knees. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heckelman, L.N.; Soher, B.J.; Spritzer, C.E.; Lewis, B.D.; DeFrate, L.E. Design and validation of a semi-automatic bone segmentation algorithm from MRI to improve research efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliamanis, T.V.; Apostolidis, K.D.; Papakostas, G.A. How Resilient Are Deep Learning Models in Medical Image Analysis? The Case of the Moment-Based Adversarial Attack (Mb-AdA). Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Su, C.P.; Lai, C.C.; Chen, W.R.; Chen, C.; Ho, L.Y.; Chu, W.C.; Lien, C.Y. Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Hand X-ray Images Conforming to Modified Total Sharp/van der Heijde Score. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sex | N | Mean ± SD | 95% CI Mean | SEM | Median | Min | Max | 95% CI Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 27 | 15.852 ± 4.194 | [14.193;17.511] | 0.807 | 14.000 | 10.000 | 26.000 | [13.953;17.000] |
| Male | 23 | 15.217 ± 3.397 | [13.748;16.686] | 0.708 | 15.000 | 11.000 | 23.000 | [13.000;16.651] |
| Total | 50 | 15.560 ± 3.823 | [14.473;16.647] | 0.540 | 15.000 | 10.000 | 26.000 | [14.000;16.000] |
| MRI Device | N | Magnetic Field Strength (T) | Pixel Size (mm) | Image Matrix (pix.) | Slice Thickness (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skyra, Siemens | 11 | 3 T | 0.484–0.500 | 320 × 320 | 3–4 | |
| Avanto, Siemens | 30 | 1.5 T | 0.273–0.446 | 512 × 512 | 3–4 | |
| Panorama, Philips | 9 | 1.0 T | 0.484–0.625 | 288 × 288 | 3–4 | |
| Technological Characteristics of the MRI Devices | N | Mean ± SD | 95% CI Mean | Median | Min | Max |
| Magnetic field strength (T) | 50 | 1.740 ± 0.702 | [1.541;1.939] | 1.500 | 1.000 | 3.000 |
| Pixel size (mm2) | 50 | 0.180 ± 0.091 | [0.154;0.206] | 0.148 | 0.075 | 0.391 |
| Total number of pixels on the image | 50 | 189,173.760 ± 82,265.344 | [165,794.208;212,553.312] | 262,144.000 | 65,536.000 | 262,144.000 |
| Image matrix area (mm2) | 50 | 27,133.132± 4887.933 | [25,743.991;28,522.272] | 25,681.986 | 19,537.300 | 40,076.800 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 50 | 3.760 ± 0.431 | [3.637;3.883] | 4.000 | 3.000 | 4.000 |
| Total slices of the study area | 50 | 6.780 ± 0.9–75 | [6.503;7.057] | 7.000 | 5.000 | 9.000 |
| Total width of the study area (mm) | 50 | 25.260 ± 3.193 | [24.353;26.167] | 24.000 | 18.000 | 32.000 |
| Group, Element | Title |
|---|---|
| [0028:0010] | Rows |
| [0028:0011] | Columns |
| [0028:0030] | Pixel Spacing |
| [0018:0050] | Slice Thickness |
| [0018:0087] | Magnetic Field Strength |
| Kappa | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|
| Obs1 vs. Obs2 | 0.959 | 0.953 to 0.965 |
| Obs1 vs. Obs3 | 0.939 | 0.9154 to 0.963 |
| Obs2 vs. Obs3 | 0.916 | 0.891 to 0.941 |
| N | r | 95% CI for r | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 27 | 0.798 | 0.599 to 0.904 | p < 0.0001 |
| Male | 23 | 0.904 | 0.783 to 0.959 | p < 0.0001 |
| Total | 50 | 0.828 | 0.723 to 0.903 | p < 0.0001 |
| Independent Variables | Coefficient | SE | rpartial | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −25.444 | ||||
| Age | 1.759 | 0.217 | 0.785 | 8.119 | <0.0001 |
| Sex | 0.198 | 1.733 | 0.018 | 0.114 | 0.909 |
| Magnetic field strength T | −2.654 | 1.889 | −0.214 | −1.405 | 0.167 |
| Pixel_size_mm2 | −44.962 | 45.785 | −0.152 | −0.982 | 0.332 |
| Image_matrix_surface_mm2 | 0.0002029 | 0.0002822 | 0.112 | 0.719 | 0.476 |
| Number of pixels on the image | −0.00006196 | 0.00005585 | −0.171 | −1.109 | 0.274 |
| Slice thickness mm | 9.767 | 15.398 | 0.099 | 0.634 | 0.529 |
| Total slices of the study area | 3.239 | 7.406 | 0.068 | 0.437 | 0.664 |
| Total width of the study area | −0.985 | 2.004 | −0.076 | −0.491 | 0.626 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matijaš, T.; Pinjuh, A.; Dolić, K.; Radović, D.; Galić, T.; Božić Štulić, D.; Mihanović, F. Improving the Age Estimation Efficiency by Calculation of the Area Ratio Index Using Semi-Automatic Segmentation of Knee MRI Images. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11072046
Matijaš T, Pinjuh A, Dolić K, Radović D, Galić T, Božić Štulić D, Mihanović F. Improving the Age Estimation Efficiency by Calculation of the Area Ratio Index Using Semi-Automatic Segmentation of Knee MRI Images. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11072046
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatijaš, Tatjana, Ana Pinjuh, Krešimir Dolić, Darijo Radović, Tea Galić, Dunja Božić Štulić, and Frane Mihanović. 2023. "Improving the Age Estimation Efficiency by Calculation of the Area Ratio Index Using Semi-Automatic Segmentation of Knee MRI Images" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11072046
APA StyleMatijaš, T., Pinjuh, A., Dolić, K., Radović, D., Galić, T., Božić Štulić, D., & Mihanović, F. (2023). Improving the Age Estimation Efficiency by Calculation of the Area Ratio Index Using Semi-Automatic Segmentation of Knee MRI Images. Biomedicines, 11(7), 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11072046