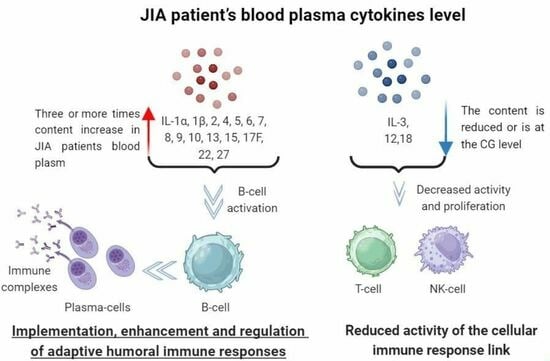
Specific Features of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients’ Cytokine Profile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Causes the expansion of antigen-specific clones (T-helpers which have clusters of differentiation-4 (CD4), T-killers (CD8)).
- Increases production of other cytokines (T-helpers (CD4), T-killers (CD8), and natural killer (NK) cells).
- Required for differentiation in the T-helper1 and T-helper2 (Th1 and Th2) subsets, as well as for the development and differentiation of T regulatory cells (T-helpers (CD4)).
- Increases cytolytic activity (T-killers (CD8) and NK cells).
- Promotes proliferation (B-cells and NK cells).
- Enhances the secretion of antibodies and initiates transcription of immunoglobulin J-chain in B-cells.
- Induces proliferation of memory cells (T-killers (CD8)) [14].
2. Materials and Methods
- Common cytokines, including ILs, the change in the levels of which in patients diagnosed with JIA was previously described in the literature and currently serves to confirm the diagnosis: IL-1α, 1ß, 6, and 18 and TNF-α.
- Proinflammatory cytokines: IL-2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12(p40), 15, 17, and 22, which are divided into the following subgroups:
- IL-2 family: IL-2, 7, 9, and 15
- IL-3 family: IL-3 and IL-5
- Not integrated into families: IL-8, 12(p40), 17, and 22
- Anti-inflammatory cytokines: IL-4, 10, 13, and 27
3. Results
3.1. Content of the Common Cytokines
3.2. Content of the Proinflammatory Cytokines
3.2.1. Content of the IL-2 Family
3.2.2. IL-3 Family
3.2.3. Cytokines Which Are Not Integrated into Families
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martini, A.; Lovell, D.J.; Albani, S.; Brunner, H.I.; Hyrich, K.L.; Thompson, S.D.; Ruperto, N. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barut, K.; Adrovic, A.; Şahin, S.; Kasapçopur, Ö. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Balk. Med. J. 2017, 34, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowdie, P.J.; Tse, S.M.L. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 59, 301–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manners, P.J.; Diepeveen, D.A. Prevalence of Juvenile Chronic Arthritis in a Population of 12-Year-Old Children in Urban Australia. Pediatrics 1996, 98, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, W. The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Syphilis. Br. J. Vener. Dis. 1976, 52, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, C.M.; Binder, S.R. ANA Testing in the Presence of Acute and Chronic Infections. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2016, 37, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, S.A.; Binstadt, B.A. Autoantibodies in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Prognosis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Wasiliew, P.; Kracht, M. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Pathway. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Hashizume, M.; Yoshida, H.; Suzuki, M.; Shiina, M. IL-6/IL-6 Receptor System and Its Role in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Clin. Sci. 2011, 122, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEGG PATHWAY: IL-17 Signaling Pathway—Reference Pathway. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map04657+K05405 (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Jang, D.-I.; Lee, A.-H.; Shin, H.-Y.; Song, H.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L.; Liu, K.D. Overview of Interleukin-2 Function, Production and Clinical Applications. Cytokine 2004, 28, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, T.R. The Biology of Interleukin-2. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessler, H.; Bergman, M.; Salman, H. Interleukin-3 and Stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2000, 54, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Fu, T.; Ji, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z. The role of interleukin-4 in rheumatic diseases. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsu, K. Interleukin-5. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1992, 4, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsu, K. Interleukin-5 and IL-5 Receptor in Health and Diseases. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2011, 87, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Tang, T.-X.; Deng, H.; Yang, X.-P.; Tang, Z.-H. Interleukin-7 Biology and Its Effects on Immune Cells: Mediator of Generation, Differentiation, Survival, and Homeostasis. Front, Immunol. 2021, 2, 747324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, J.T.; Durum, S.K.; Seddon, B. Flip the Coin: IL-7 and IL-7R in Health and Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, M. The Role of Interleukin-8 in Inflammation and Mechanisms of Regulation. J. Periodontol. 1993, 64, 456–460. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, C.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Teijeira, Á.; Oñate, C.; González, Á.; Ponz, M.; Schalper, K.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Melero, I. Interleukin-8 in Cancer Pathogenesis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 60, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.; Gupta, R.; Malhotra, R.; Sharma, V.; Farooque, K.; Kumar, V.; Chakraborty, S.; Mitra, D.K. Interleukin-9 Facilitates Osteoclastogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, Q.; Brady, T.J.; Xiao, H.; Wakefield, M.R.; Fang, Y. The Role of Interleukin-9 in Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and Therapeutic Potential of Interleukin-10. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, C.; Scheffold, A.; Rutz, S. Functions and Regulation of T Cell-Derived Interleukin-10. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 44, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, D.A.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-12 Family Cytokines: Immunological Playmakers. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12 and the Regulation of Innate Resistance and Adaptive Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaszko, M.; Biały, S.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Significance of Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 in Inflammatory Arthritis. Cells 2021, 10, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, M.; Yadav, N.; Dalai, S.K. Interleukin 15: A Key Cytokine for Immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard-Chamard, H.; Mishra, H.K.; Nandi, M.; Mayhue, M.; Menendez, A.; Ilangumaran, S.; Ramanathan, S. Interleukin-15 in Autoimmunity. Cytokine 2020, 136, 155258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, N.; Garg, A.V.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H.; Saijo, S.; Nakae, S. Functional Specialization of Interleukin-17 Family Members. Immunity 2011, 34, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubanov, A.A.; Bakulev, A.L.; Samtsov, A.V.; Khairutdinov, V.R.; Sokolovskiy, E.V.; Kokhan, M.M.; Artemyeva, A.V.; Chernyaeva, E.V.; Ivanov, R.A. Netakimab—New IL-17a inhibitor: 12-week results of phase III clinical study BCD-085-7/PLANETA in patients with moderate-tosevere plaque psoriasis. Vestnik Dermatol. i Venerol. 2019, 95, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEGG PATHWAY: Rheumatoid Arthritis—Reference Pathway. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map05323+K05482 (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Wu, Y.; Min, J.; Ge, C.; Shu, J.; Tian, D.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, D. Interleukin 22 in Liver Injury, Inflammation and Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.-W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Huang, P. Interleukin-22: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Atherosclerosis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudakov, J.A.; Hanash, A.M.; van den Brink, M.R.M. Interleukin-22: Immunobiology and Pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 747–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, H.; Olsson, T. Interleukin-22 Influences the Th1/Th17 Axis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 618110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Hunter, C.A. The Immunobiology of Interleukin-27. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 417–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Yu, K.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; Ba, X.; Lin, W.; Huang, Y.; Shen, P.; Huang, Y.; et al. Interleukin 27 Signaling in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Good or Evil? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 787252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.A.; Bour-Jordan, H. Current and Future Immunomodulation Strategies to Restore Tolerance in Autoimmune Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D.; Romano, M.; Gattinara, M.; Gerloni, V. Biologics for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 5860–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardapane, A.; Breda, L.; Lucantoni, M.; Chiarelli, F. TNF-α Polymorphisms in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Which Potential Clinical Implications? Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 756291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, Q.W.; Alubaidi, G.; Humadi, Y. Level of Interleukin-35, Interleukin-36, and the Interleukin-35/Interleukin-36 Ratio in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, F.; Kessel, C.; Lavric, M.; Holzinger, D.; Foell, D. Review of biomarkers in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Helpful tools or just playing tricks? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, H.-J.v.D.; de Jager, W.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Prakken, B.J.; de Boer, R.J. Differential cytokine profiles in juvenile idiopathic arthritis subtypes revealed by cluster analysis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, M.; Strothmann, L.; Sonnenschein, A.; Mannhardt-Laakmann, W. Distinct Cytokine Profiles in Patients with Oligoarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis after in Vitro Blockade of Interleukin (IL)-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α. World J. Vaccines 2014, 4, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostik, M.M.; Makhova, M.A.; Maletin, A.S.; Magomedova, S.M.; Sorokina, L.S.; Tsukasaki, M.; Okamoto, K.; Takayanagi, H.; Vasiliev, D.S.; Kozlova, D.I.; et al. Cytokine Profile in Patients with Chronic Non-Bacterial Osteomyelitis, Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, and Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Cytokine 2021, 143, 155521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacraz, S.; Nicod, L.; Rochemonteix, B.G.-D.; Baumberger, C.; Dayer, J.M.; Welgus, H.G. Suppression of metalloproteinase biosynthesis in human alveolar macrophages by interleukin-4. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| IL-1α (pg/mL) | IL-1ß (pg/mL) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | IL-18 (pg/mL) | TNF-α (pg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIA | 278.4 (188.1; 375.0) * | 17.31 (11.79; 28.82) * | 102.8 (56.58; 132.1) * | 185.1 (148.5; 205.1) | 88.29 (60.05; 126.2) * |
| CG | 87.0 (73.7; 93.7) | 1.93 (0.95; 3.9) | 8.37 (6.0; 11.7) | 216.0 (114.2; 285.1) | 45.4 (37.5; 55.1) |
| IL-2 (pg/mL) | IL-7 (pg/mL) | IL-9 (pg/mL) | IL-15 (pg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIA | 3.7 ± 1.3 ** | 11.1 ± 2.3 ** | 472.9 (242.2; 719.5) * | 43.0 ± 15.4 ** |
| CG | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 5.8 ± 1.1 | 35.7 (29.8; 40.2) | 10.0 ± 4.4 |
| IL-3, pg/mL | IL-5, pg/mL | |
|---|---|---|
| JIA | 11.8 (7.0; 16.4) * | 11.0 (5.5; 13.4) * |
| CG | 73.6 (44.7; 139.8) | 2.6 (1.6; 3.2) |
| IL-8 (pg/mL) | IL-12(p40) (pg/mL) | IL-17A (pg/mL) | IL-17F (pg/mL) | IL-22, (pg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIA | 29.0 ± 8.1 ** | 1075 (1026; 1102) | 53.1 ± 29.1 | 158.0 (106.8; 216.1) * | 27.8 ± 11.4 ** |
| CG | 14.3 ± 3.3 | 1080 (971; 1169) | 53.4 ± 22.7 | 29.3 (28.7; 30.7) | 14.7 ± 1.5 |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | IL-10 (pg/mL) | IL-13 (pg/mL) | IL-27 (pg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIA | 34.0 ± 12.4 ** | 73.5 (48.9; 91.2) * | 31.2 (22.9; 59.0) * | 12,215 (11,130; 13,859) * |
| CG | 20.0 ± 6.0 | 19.0 (14.2; 25.3) | 14.5 (10.7; 17.7) | 2240 (1467; 3595) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozlova, D.I.; Rybakov, A.V.; Yureva, K.A.; Khizha, V.V.; Sorokina, L.S.; Kostik, M.M.; Guslev, A.B. Specific Features of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients’ Cytokine Profile. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010135
Kozlova DI, Rybakov AV, Yureva KA, Khizha VV, Sorokina LS, Kostik MM, Guslev AB. Specific Features of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients’ Cytokine Profile. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozlova, Daria I., Arseny V. Rybakov, Karina A. Yureva, Vitaly V. Khizha, Lybov S. Sorokina, Mikhail M. Kostik, and Alexandr B. Guslev. 2024. "Specific Features of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients’ Cytokine Profile" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010135
APA StyleKozlova, D. I., Rybakov, A. V., Yureva, K. A., Khizha, V. V., Sorokina, L. S., Kostik, M. M., & Guslev, A. B. (2024). Specific Features of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients’ Cytokine Profile. Biomedicines, 12(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010135