Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Aptamers versus Antibodies
3. Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential Enrichment (SELEX) Library Design
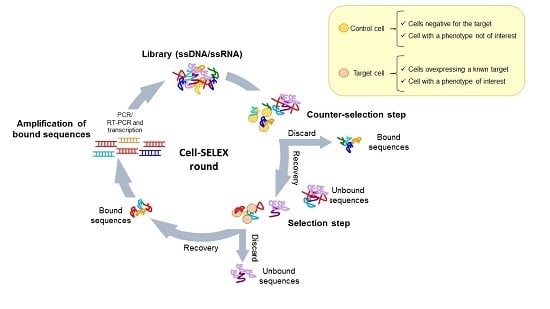
4. Cell-Based SELEX Methods
4.1. Whole-Cell SELEX Strategy
4.2. Cell-SELEX Variants
4.2.1. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)-SELEX
4.2.2. Cell Internalization SELEX
4.2.3. Ligand-Guided Selection (LIGS)
4.2.4. Microfluidic-Based System
4.3. 3D Cell-SELEX and In Vivo SELEX
5. Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
6. Post-SELEX Modifications Optimization
7. Clinical Applications of Aptamers
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Yang, S. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vater, A.; Jarosch, F.; Buchner, K.; Klussmann, S. Short bioactive Spiegelmers to migraine-associated calcitonin gene-related peptide rapidly identified by a novel approach: Tailored-SELEX. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosch, F.; Buchner, K.; Klussmann, S. In vitro selection using a dual RNA library that allows primerless selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Clawson, G.A. Primer-free aptamer selection using a random DNA library. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 629, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.T.; DeStefano, J.J. A primer-free method that selects high-affinity single-stranded DNA aptamers using thermostable RNA ligase. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 414, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, C.; Dang, L.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G. Development of cell-SELEX technology and its application in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.N.; Jensen, K.B.; Julin, C.M.; Weil, M.; Gold, L. High affinity ligands from in vitro selection: Complex targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2902–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohuchi, S.P.; Ohtsu, T.; Nakamura, Y. Selection of RNA aptamers against recombinant transforming growth factor-beta type III receptor displayed on cell surface. Biochimie 2006, 88, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Sakota, E.; Nakamura, Y. The efficient cell-SELEX strategy, Icell-SELEX, using isogenic cell lines for selection and counter-selection to generate RNA aptamers to cell surface proteins. Biochimie 2016, 131, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicke, B.J.; Marion, C.; Chang, Y.F.; Gould, T.; Lynott, C.K.; Parma, D.; Schmidt, P.G.; Warren, S. Tenascin-C aptamers are generated using tumor cells and purified protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48644–48654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilner, S.E.; Wengerter, B.; Maier, K.; De Lourdes Borba Magalhães, M.; Del Amo, D.S.; Pai, S.; Opazo, F.; Rizzoli, S.O.; Yan, A.; Levy, M. An RNA alternative to human transferrin: A new tool for targeting human cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clawson, G.A.; Abraham, T.; Pan, W.; Tang, X.; Linton, S.S.; McGovern, C.O.; Loc, W.S.; Smith, J.P.; Butler, P.J.; Kester, M.; et al. A Cholecystokinin B Receptor-Specific DNA Aptamer for Targeting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldevilla, M.M.; Villanueva, H.; Casares, N.; Lasarte, J.J.; Bendandi, M.; Inoges, S.; López-Díaz de Cerio, A.; Pastor, F. MRP1-CD28 bi-specific oligonucleotide aptamers: Target costimulation to drug-resistant melanoma cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 23182–23196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Jacobson, O.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Niu, G.; Chen, X. Combinatorial Screening of DNA Aptamers for Molecular Imaging of HER2 in Cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cao, Z.C.; Chen, H.W.; Mallikaratchy, P.; Sefah, K.; Yang, C.J.; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11838–11843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.W.; Medley, C.D.; Sefah, K.; Shangguan, D.; Tang, Z.; Meng, L.; Smith, J.E.; Tan, W. Molecular recognition of small-cell lung cancer cells using aptamers. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefah, K.; Meng, L.; Lopez-Colon, D.; Jimenez, E.; Liu, C.; Tan, W. DNA aptamers as molecular probes for colorectal cancer study. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Ren, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.; Jia, W.; Gao, M.; Zeng, F.; Zeng, L.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. CD109 is identified as a potential nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarker using aptamer selected by cell-SELEX. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55328–55342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Armstrong, B.; Habib, N.; Rossi, J.J. Blind SELEX approach identifies rna aptamers that regulate emt and inhibit metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerchia, L.; Esposito, C.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Tavitian, B.; De Franciscis, V. Differential SELEX in human glioma cell lines. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; An, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhu, Z.; Hao, L.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D.; Ji, T.; Yang, C.J. Evolution of DNA aptamers through in vitro metastatic-cell-based systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment for metastatic cancer recognition and imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4941–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, K.; Meng, X.; Huang, Z.; Wen, X. Metastatic cancer cell and tissue-specific fluorescence imaging using a new DNA aptamer developed by Cell-SELEX. Talanta 2017, 170, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Long, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Lin, W.; Han, D.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamer for metastatic prostate cancer recognition and tissue imaging. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36436–36446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.F.; Yin, C.Q.; Wang, B.C.; Peng, C.W.; Liu, S.P.; Wang, F.B. Identification of an aptamer through whole cell-SELEX for targeting high metastatic liver cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8282–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Wu, Q.; Hamerlik, P.; Hitomi, M.; Sloan, A.E.; Barnett, G.H.; Weil, R.J.; Leahy, P.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Rich, J.N. Aptamer identification of brain tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4923–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Quan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Ren, J. A novel molecular marker of breast cancer stem cells identified by cell-SELEX method. Cancer Biomark. 2015, 15, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, D.E.; Kim, J.M.; Song, S.Y. The DNA aptamer binds stemness-enriched cancer cells in pancreatic cancer. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 30, e2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Bing, T.; Shen, L.; Song, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Tan, W.; Shangguan, D. Intercellular Connections Related to Cell-Cell Crosstalk Specifically Recognized by an Aptamer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 3914–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Meyer, S.; Propson, N.E.; Nie, J.; Jiang, P.; Stewart, R.; Thomson, J.A. Characterization and target identification of a DNA aptamer that labels pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Tan, W. Aptamers generated from cell-SELEX for molecular medicine: A chemical biology approach. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, G.; Ahmed, M.S.; Dolf, A.; Endl, E.; Knolle, P.A.; Famulok, M. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting for aptamer SELEX with cell mixtures. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, S.K.; Lee, D.; Oh, K.J.; Kim, W.K.; Han, B.S.; Chi, S.W.; Lee, S.C.; et al. Identification of DNA aptamers toward epithelial cell adhesion molecule via cell-SELEX. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sefah, K.; Altman, M.B.; Chen, T.; You, M.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, C.Z.; Tan, W. Aptamer-conjugated nanorods for targeted photothermal therapy of prostate cancer stem cells. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 2417–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Cheng, J.; Teply, B.A.; Sherifi, I.; Jon, S.; Kantoff, P.W.; Richie, J.P.; Langer, R. Targeted nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer chemotherapy in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6315–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagalkot, V.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R.; Jon, S. An aptamer-doxorubicin physical conjugate as a novel targeted drug-delivery platform. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 8149–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.C.; Marks, J.W.; Lavery, L.A.; Faulkner, S.; Rosenblum, M.G.; Ellington, A.D.; Levy, M. Aptamer: Toxin conjugates that specifically target prostate tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5989–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Dellamaggiore, K.R.; Ouellette, C.P.; Sedano, C.D.; Lizadjohry, M.; Chernis, G.A.; Gonzales, M.; Baltasar, F.E.; Fan, A.L.; Myerowitz, R.; et al. Aptamer-based endocytosis of a lysosomal enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15908–15913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicke, B.J.; Stephens, A.W.; Gould, T.; Chang, Y.F.; Lynott, C.K.; Heil, J.; Borkowski, S.; Hilger, C.S.; Cook, G.; Warren, S.; et al. Tumor targeting by an aptamer. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tong, G.J.; Hsiao, S.C.; Carrico, Z.M.; Francis, M.B. Viral capsid DNA aptamer conjugates as multivalent cell-targeting vehicles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11174–11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, K.W.; Giangrande, P.H. Intracellular delivery of RNA-based therapeutics using aptamers. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.C.; Twu, K.Y.; Ellington, A.D.; Levy, M. Aptamer mediated siRNA delivery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.O.; Andrechek, E.R.; Wang, Y.; Viles, K.D.; Rempel, R.E.; Gilboa, E.; Sullenger, B.A.; Giangrande, P.H. Cell type-specific delivery of siRNAs with aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Zaia, J.; Rossi, J.J. Novel dual inhibitory function aptamer-siRNA delivery system for HIV-1 therapy. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullner, U.; Neef, I.; Eller, A.; Kleines, M.; Tur, M.K.; Barth, S. Cell-specific induction of apoptosis by rationally designed bivalent aptamer-siRNA transcripts silencing eukaryotic elongation factor 2. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Swiderski, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Neff, C.P.; Akkina, R.; Rossi, J.J. Selection, characterization and application of new RNA HIV gp 120 aptamers for facile delivery of Dicer substrate siRNAs into HIV infected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3094–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassie, J.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Thomas, G.S.; Whitaker, R.M.; Thiel, K.W.; Stockdale, K.R.; Meyerholz, D.K.; McCaffrey, A.P.; McNamara, J.O., II; Giangrande, P.H. Systemic administration of optimized aptamer-siRNA chimeras promotes regression of PSMA-expressing tumors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ribas, J.; Chowdhury, W.H.; Castanares, M.; Zhang, Z.; Laiho, M.; DeWeese, T.L.; Lupold, S.E. Prostate-targeted radiosensitization via aptamer-shRNA chimeras in human tumor xenografts. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, L.A.; Trifonova, R.; Vrbanac, V.; Basar, E.; McKernan, S.; Xu, Z.; Seung, E.; Deruaz, M.; Dudek, T.; Einarsson, J.I.; et al. Inhibition of HIV transmission in human cervicovaginal explants and humanized mice using CD4 aptamer-siRNA chimeras. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, C.P.; Zhou, J.; Remling, L.; Kuruvilla, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Smith, D.D.; Swiderski, P.; Rossi, J.J.; Akkina, R. An aptamer-siRNA chimera suppresses HIV-1 viral loads and protects from helper CD4 (+) T cell decline in humanized mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 66ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Shibata, T.; Kabashima, T.; Kai, M. Inhibition of HIV-1 protease expression in T cells owing to DNA aptamer-mediated specific delivery of siRNA. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 56, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, K.W.; Hernandez, L.I.; Dassie, J.P.; Thiel, W.H.; Liu, X.; Stockdale, K.R.; Rothman, A.M.; Hernandez, F.J.; McNamara, J.O., II; Giangrande, P.H. Delivery of chemo-sensitizing siRNAs to HER2+-breast cancer cells using RNA aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6319–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Neff, C.P.; Swiderski, P.; Li, H.; Smith, D.D.; Aboellail, T.; Remling-Mulder, L.; Akkina, R.; Rossi, J.J. Functional in vivo delivery of multiplexed anti-HIV-1 siRNAs via a chemically synthesized aptamer with a sticky bridge. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ding, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Ye, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Second-generation aptamer-conjugated PSMA-targeted delivery system for prostate cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y. Reversal of paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells by a MUC1 aptamer-let-7i chimera. Cancer Investig. 2012, 30, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shan, N.; Chen, Y. Anticancer role of MUC1 aptamer-miR-29b chimera in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells through regulation of PTEN methylation. Target. Oncol. 2012, 7, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaboni, M.; Fontanella, R.; Rienzo, A.; Capuozzo, M.; Nuzzo, S.; Santamaria, G.; Catuogno, S.; Condorelli, G.; De Franciscis, V.; Esposito, C.L. Targeting Insulin Receptor with a Novel Internalizing Aptamer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.; White, R.R. Cell-SELEX Identifies a “Sticky” RNA Aptamer Sequence. J. Nucleic Acids 2017, 2017, 4943072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranches, G.; Lukasser, M.; Schramek, M.; Ploner, A.; Stasyk, T.; Mayer, G.; Mayer, G.; Hüttenhofer, A. In Vitro Selection of Cell-Internalizing DNA Aptamers in a Model System of Inflammatory Kidney Disease. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumrut, H.E.; Ara, M.N.; Maio, G.E.; Van, N.A.; Batool, S.; Mallikaratchy, P.R. Ligand-guided selection of aptamers against T-cell Receptor-cluster of differentiation 3 (TCR-CD3) expressed on Jurkat.E6 cells. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 512, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumrut, H.E.; Ara, M.N.; Fraile, M.; Maio, G.; Mallikaratchy, P. Ligand-Guided Selection of Target-Specific Aptamers: A Screening Technology for Identifying Specific Aptamers Against Cell-Surface Proteins. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016, 26, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosing, R.K.; Mendonsa, S.D.; Bowser, M.T. Capillary electrophoresis-SELEX selection of aptamers with affinity for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6107–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonsa, S.D.; Bowser, M.T. In vitro evolution of functional DNA using capillary electrophoresis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jo, M.; Lee, D.K.; Lis, J.T.; Craighead, H.G.; Kim, S. Selection and elution of aptamers using nanoporous sol-gel arrays with integrated microheaters. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.S.; Qian, J.; Lou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Soh, H.T. Generation of highly specific aptamers via micromagnetic selection. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5490–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, L.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Che, Y.J.; Fu, C.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Wang, K.; Lee, G.B. Screening of aptamers specific to colorectal cancer cells and stem cells by utilizing On-chip cell-SELEX. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinathan, P.; Hung, L.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chiang, N.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Shan, Y.; Lee, G.B. Automated selection of aptamers against cholangiocarcinoma cells on an integrated microfluidic platform. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 044101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.G.; Marangoni, K.; Fujimura, P.T.; Alves, P.T.; Silva, M.J.; Bastos, V.A.; Goulart, L.R.; Goulart, V.A. 3D Cell-SELEX: Development of RNA aptamers as molecular probes for PC-3 tumor cell line. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 341, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, J.; Liu, Y.; Rabbani, Z.N.; Yang, Z.; Urban, J.H.; Sullenger, B.A.; Clary, B.M. In vivo selection of tumor-targeting RNA motifs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, J.; Ray, P.; Liu, J.; Kuan, C.T.; Xu, J.; Hsu, D.; Sullenger, B.A.; White, R.R.; Clary, B.M. In vivo selection against human colorectal cancer xenografts identifies an aptamer that targets rna helicase protein DHX9. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A.; Davidson, B.L. In vivo SELEX for identification of brain-penetrating aptamers. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner Zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, Z.; Breaker, R.R. R2R—Software to speed the depiction of aesthetic consensus RNA secondary structures. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, W.H.; Bair, T.; Peek, A.S.; Liu, X.; Dassie, J.; Stockdale, K.R.; Behlke, M.A.; Miller, F.J., Jr.; Giangrande, P.H. Rapid identification of cell-specific, internalizing RNA aptamers with bioinformatics analyses of a cell-based aptamer selection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, W.H.; Bair, T.; Wyatt Thiel, K.; Dassie, J.P.; Rockey, W.M.; Howell, C.A.; Liu, X.Y.; Dupuy, A.J.; Huang, L.; Owczarzy, R.; et al. Nucleotide bias observed with a short SELEX RNA aptamer library. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011, 21, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, B.; Gesell, T.; Chen, D.; Lorenz, C.; Schroeder, R. Monitoring genomic sequences during SELEX using high-throughput sequencing: Neutral SELEX. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoinka, J.; Dao, P.; Przytycka, T.M. AptaGUI-A graphical user interface for the efficient analysis of HT-SELEX data. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AptaTools. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/CBBresearch/Przytycka/index.cgi#aptatools (accessed on 6 June 2015).
- Thiel, W.H.; Giangrande, P.H. Analyzing HT-SELEX data with the Galaxy Project tools—A web based bioinformatics platform for biomedical research. Methods 2016, 97, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goecks, J.; Nekrutenko, A.; Taylor, J.; Galaxy Team. Galaxy: A comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenberg, D.; Von Kuster, G.; Coraor, N.; Ananda, G.; Lazarus, R.; Mangan, M.; Nekrutenko, A.; Taylor, J. Galaxy: A web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Slinger, B.L.; Meyer, M.M. Recognizing RNA structural motifs in HT-SELEX data for ribosomal protein S15. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassanfar, M.; Szostak, J.W. An RNA motif that binds ATP. Nature 1993, 364, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockey, W.M.; Hernandez, F.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Cao, S.; Howell, C.A.; Thomas, G.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Lapteva, N.; Spencer, D.M.; McNamara, J.O.; et al. Rational truncation of an RNA aptamer to prostate-specific membrane antigen using computational structural modeling. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011, 21, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Sullenger, B.A. Isolation of a nuclease-resistant decoy RNA that can protect human acetylcholine receptors from myasthenic antibodies. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagratis, N.C.; Bell, C.; Chang, Y.F.; Jennings, S.; Fitzwater, T.; Jellinek, D.; Dang, C. Potent 2′-amino-, and 2′-fluoro-2′-deoxyribonucleotide RNA inhibitors of keratinocyte growth factor. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelliserrykattil, J.; Ellington, A.D. Evolution of a T7 RNA polymerase variant that transcribes 2′-O-methyl RNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, P.E.; Lewis, S.D.; Silva, R.F.; Preiss, J.R.; Horwitz, L.R.; Pendergrast, P.S.; McCauley, T.G.; Kurz, J.C.; Epstein, D.M.; Wilson, C.; et al. Direct in vitro selection of a 2′-O-methyl aptamer to VEGF. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Cload, S.T. SELEX with modified nucleotides. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, C.; Zydek, M.; Rothkegel, M.; Wu, Z.; Gallin, C.; Geßner, R.; Lisdat, F.; Fürste, J.P. Properties of an LNA-modified ricin RNA aptamer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maasch, C.; Buchner, K.; Eulberg, D.; Vonhoff, S.; Klussmann, S. Physicochemical stability of NOX-E36, a 40mer L-RNA (Spiegelmer) for therapeutic applications. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 2008, 52, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, J.M.; Lewis, S.D.; Kurz, M.; Boomer, R.M.; Thompson, K.M.; Wilson, C.; McCauley, T.G. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of novel aptamer compositions. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 2234–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Yang, J.; Hwang, M.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.O.; Jang, E.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, S.H.; Suh, J.S.; Huh, Y.M.; et al. Aptamer-modified magnetic nanoprobe for molecular MR imaging of VEGFR2 on angiogenic vasculature. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Rajendran, R.; Jeong, M.S.; Ko, H.Y.; Joo, J.Y.; Cho, S.; Chang, Y.; Kim, S. Bioimaging of targeting cancers using aptamer-conjugated carbon nanodots. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6543–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ke, X.; Wang, H.; Tinnefeld, P.; He, Z. One-pot synthesized aptamer-functionalized CdTe: Zn2+ quantum dots for tumor-targeted fluorescence imaging in vitro and in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5843–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medley, C.D.; Smith, J.E.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Bamrungsap, S.; Tan, W. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for the direct detection of cancerous cells. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Arumugam, S.R.; Senapati, D.; Singh, A.K.; Arbneshi, T.; Khan, S.A.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Multifunctional oval-shaped gold-nanoparticle-based selective detection of breast cancer cells using simple colorimetric and highly sensitive two-photon scattering assay. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Dobrucki, L.W.; Chaudhury, I.; Yin, Q.; Yao, C.; Lezmi, S.; Helferich, W.G.; Fan, T.M.; Cheng, J. Aptamer-functionalized, ultra-small, monodisperse silica nanoconjugates for targeted dual-modal imaging of lymph nodes with metastatic tumors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 12721–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melancon, M.P.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, C.; Allen, P.; Wen, X.; Huang, Q.; Wallace, M.; Myers, J.N.; Stafford, R.J.; et al. Selective uptake and imaging of aptamer- and antibody-conjugated hollow nanospheres targeted to epidermal growth factor receptors overexpressed in head and neck cancer. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4530–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01848106?term=REG1&rank=2 (accessed on 2 May 2013).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01940887?term=E10030&rank=6 (accessed on 9 September 2013).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02686658?term=aptamer&rank=4 (accessed on 2 February 2016).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00740441?term=AS1411&rank=1 (accessed on 22 August 2008).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01547897?term=NOX-E36&rank=3 (accessed on 27 February 2012).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01486797?term=NOX+A-12&rank=2 (accessed on 1 December 2011).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00056199?term=aptamer&rank=11 (accessed on 7 March 2003).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01191372?term=aptamer&rank=29 (accessed on 26 August 2010).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01372137?term=NOX+H-94&rank=1 (accessed on 8 June 2011).
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Cell-type-specific, aptamer-functionalized agents for targeted disease therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Aptamer Name | Composition | Medical Condition | Current Phase | Sponsor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pegnivacogen | RNA with 5′-PEG and 3′ inverted dT | Coronary artery disease | Phase III completed | Regado Biosciences | [103] |
| E10030 | DNA with 2′-O-methyl, 5′-PEG, 3′ inverted dT | Wet age-related macular degeneration | Phase III | Ophthotech Corporation | [104] |
| Zimura | RNA with 5′-PEG, 3′ inverted dT | Dry age-related macular degeneration | Phase II/III | Ophthotech Corporation | [105] |
| AS1411 | DNA | Renal cell carcinoma | Phase II | Antisoma Research | [106] |
| NOX-E36 | L-RNA with 3′-PEG | Type 2 diabetes mellitus and albumenuria | Phase II completed | Noxxon Pharma AG | [107] |
| NOX-A12 | L-RNA with 3′-PEG | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | Phase II | Noxxon Pharma AG | [108] |
| EYE001 | RNA with 5′-PEG | Wet age-related macular degeneration | Phase I completed | National Eye Institute | [109] |
| ARC19499 | DNA with 5′-PEG and 3′ inverted dT | Hemophilia | Phase I completed | Baxalta US Inc. | [110] |
| NOX-H94 | L-RNA with 5′-PEG | Anemia of chronic inflammation | Phase I completed | Noxxon Pharma AG | [111] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L. Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030049
Catuogno S, Esposito CL. Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances. Biomedicines. 2017; 5(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatuogno, Silvia, and Carla Lucia Esposito. 2017. "Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances" Biomedicines 5, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030049
APA StyleCatuogno, S., & Esposito, C. L. (2017). Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances. Biomedicines, 5(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030049