Noncanonical NF-κB in Cancer
Abstract
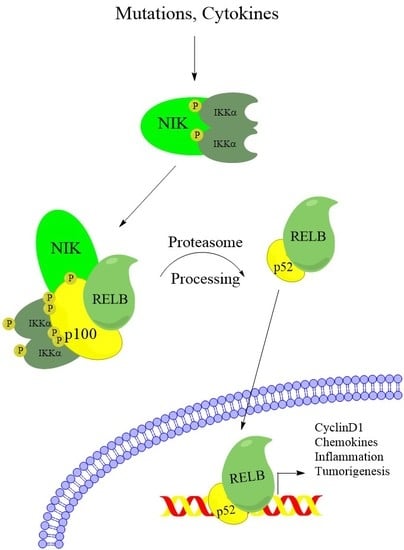
:1. Introduction
2. Noncanonical NF-κB Activation in Multiple Myeloma
3. Noncanonical NF-κB in Other Cancers
4. RelB-p52 and EZH2 Cooperation in Cancer
5. Noncanonical IκB Proteins
6. Alternative Functions of the Noncanonical Kinases
6.1. Other Functions of IKKα
6.2. Alternative Roles for NIK
7. Crosstalk between Canonical and Noncanonical NF-κB
8. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libermann, T.A.; Baltimore, D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttridge, D.C.; Albanese, C.; Reuther, J.Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 5785–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catz, S.D.; Johnson, J.L. Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor κB and its significance in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7342–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Authier, H.; Billot, K.; Derudder, E.; Bordereaux, D.; Rivière, P.; Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Nahmias, C.; Baud, V. IKK phosphorylates RelB to modulate its promoter specificity and promote fibroblast migration downstream of TNF receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14794–14799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; DeMartino, G.N.; Greene, W.C. Cotranslational Biogenesis of NF-κB p50 by the 26S Proteasome. Cell 1998, 92, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senftleben, U.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, G.; Greten, F.R.; Krähn, G.; Bonizzi, G.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C.; et al. Activation by IKKalpha of a Second, Evolutionary Conserved, NF-kappa B Signaling Pathway. Science 2001, 293, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudio, E.; Brown, K.; Park, S.; Wang, H.; Siebenlist, U. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-κB2 in maturing B cells. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejardin, E.; Droin, N.M.; Delhase, M.; Haas, E.; Cao, Y.; Makris, C.; Li, Z.-W.; Karin, M.; Ware, C.F.; Green, D.R. The Lymphotoxin-β Receptor Induces Different Patterns of Gene Expression via Two NF-κB Pathways. Immunity 2002, 17, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coope, H.J.; Atkinson, P.G.P.; Huhse, B.; Belich, M.; Janzen, J.; Holman, M.J.; Klaus, G.G.B.; Johnston, L.H.; Ley, S.C. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100 to p52. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5375–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitoh, T.; Nakayama, M.; Nakano, H.; Yagita, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamaoka, S. TWEAK induces NF-kappaB2 p100 processing and long lasting NF-kappaB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36005–36012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novack, D.V.; Yin, L.; Hagen-Stapleton, A.; Schreiber, R.D.; Goeddel, D.V.; Ross, F.P.; Teitelbaum, S.L. The IkappaB function of NF-kappaB2 p100 controls stimulated osteoclastogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Zhang, M.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.-C. Regulation of the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26243–26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, S.J.; Albrecht, J.-C.; Giehler, F.; Kieser, A.; Sticht, H.; Biesinger, B. Noncanonical NF- B Activation by the Oncoprotein Tio Occurs Through a Nonconserved TRAF3-Binding Motif. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.Q.; Zarnegar, B.; Oganesyan, G.; Saha, S.K.; Yamazaki, S.; Doyle, S.E.; Dempsey, P.W.; Cheng, G. Rescue of TRAF3-null mice by p100 NF-κB deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarnegar, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Mahoney, D.J.; Dempsey, P.W.; Cheung, H.H.; He, J.; Shiba, T.; Yang, X.; Yeh, W.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Noncanonical NF-κB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vince, J.E.; Wong, W.W.-L.; Khan, N.; Feltham, R.; Chau, D.; Ahmed, A.U.; Benetatos, C.A.; Chunduru, S.K.; Condon, S.M.; McKinlay, M.; et al. IAP Antagonists Target cIAP1 to Induce TNFα-Dependent Apoptosis. Cell 2007, 131, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Blankenship, J.W.; Wayson, S.M.; Fedorova, A.V.; Kayagaki, N.; Garg, P.; Zobel, K.; Dynek, J.N.; Elliott, L.O.; Wallweber, H.J.A.; et al. IAP Antagonists Induce Autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-κB Activation, and TNFα-Dependent Apoptosis. Cell 2007, 131, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.D.; Hostager, B.S.; Bishop, G.A. Differential signaling and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) degradation mediated by CD40 and the Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, M.; Sun, S.-C. β-TrCP binding and processing of NF-κB2/p100 involve its phosphorylation at serines 866 and 870. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.-C. Induction of p100 processing by NF-kappaB-inducing kinase involves docking IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) to p100 and IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30099–30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, A.; Sun, S.-C. Genetic evidence for the essential role of beta-transducin repeat-containing protein in the inducible processing of NF-kappa B2/p100. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22111–22114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, S.; Passos, D.O.; Huang, D.-B.; Mulero, M.C.; Mazumder, A.; Biswas, T.; Verma, I.M.; Lyumkis, D.; Ghosh, G. Structural Basis for the Activation of IKK1/α. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, V.F.-S.; Tsui, R.; Caldwell, A.; Hoffmann, A. A single NFκB system for both canonical and non-canonical signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.; Teixeira, A.; Oikonomopoulos, S.; Humburg, P.; Lone, I.; Saliba, D.; Siggers, T.; Bulyk, M.; Angelov, D.; Dimitrov, S.; et al. Extensive characterization of NF-κB binding uncovers non-canonical motifs and advances the interpretation of genetic functional traits. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, T.H.; Hoffmann, A.; Baltimore, D. One Nucleotide in a κB Site Can Determine Cofactor Specificity for NF-κB Dimers. Cell 2004, 118, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, Z.; Fusco, A.; Huang, D.-B.; Gupta, K.; Kim, D.Y.; Ware, C.F.; Van Duyne, G.D.; Ghosh, G. p100/IκBδ sequesters and inhibits NF-κB through kappaBsome formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15946–15951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cildir, G.; Low, K.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling in Health and Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Tänzer, S.; Busslinger, M.; Weih, F. Lack of nuclear factor-kappa B2/p100 causes a RelB-dependent block in early B lymphopoiesis. Blood 2008, 112, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Kim, H.; Kearns, J.D.; Tergaonkar, V.; O’Dea, E.; Werner, S.L.; Benedict, C.A.; Ware, C.F.; Ghosh, G.; Verma, I.M.; et al. A Fourth IκB Protein within the NF-κB Signaling Module. Cell 2007, 128, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyawaki, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuka, H.; Koba, M.; Shibata, Y.; Yasumizu, R.; Ikehara, S. A new mutation, aly, that induces a generalized lack of lymph nodes accompanied by immunodeficiency in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, R.; Nishimura, T.; Yasumizu, R.; Tanaka, H.; Hataba, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Miyawaki, S.; Miyasaka, M. The splenic marginal zone is absent in alymphoplasticaly mutant mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoso, G.; Carlson, L.; Poljak, L.; Shores, E.W.; Epstein, S.; Leonardi, A.; Grinberg, A.; Tran, T.; Scharton-Kersten, T.; Anver, M.; et al. Mice deficient in nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B/p52 present with defects in humoral responses, germinal center reactions, and splenic microarchitecture. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caamaño, J.H.; Rizzo, C.A.; Durham, S.K.; Barton, D.S.; Raventós-Suárez, C.; Snapper, C.M.; Bravo, R. Nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B2 (p100/p52) is required for normal splenic microarchitecture and B cell-mediated immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, N.S.; Anderson, M.M.; Carette, A.; Silva, K.; Heise, N.; Bhagat, G.; Klein, U. Transcription factors of the alternative NF-κB pathway are required for germinal center B-cell development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9063–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal Centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaileh, M.; Sen, R. NF-κB function in B lymphocytes. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.; Uchiyama, H.; Akbarali, Y.; Urashima, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Libermann, T.; Anderson, K. Multiple myeloma cell adhesion-induced interleukin-6 expression in bone marrow stromal cells involves activation of NF-kappa B. Blood 1996, 87, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landowski, T.H.; Olashaw, N.E.; Agrawal, D.; Dalton, W.S. Cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) is associated with activation of NF-κB (RelB/p50) in myeloma cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2417–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croucher, P.I.; Shipman, C.M.; Lippitt, J.; Perry, M.; Asosingh, K.; Hijzen, A.; Brabbs, A.C.; van Beek, E.J.; Holen, I.; Skerry, T.M.; et al. Osteoprotegerin inhibits the development of osteolytic bone disease in multiple myeloma. Blood 2001, 98, 3534–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keats, J.J.; Fonseca, R.; Chesi, M.; Schop, R.; Baker, A.; Chng, W.-J.; Van Wier, S.; Tiedemann, R.; Shi, C.-X.; Sebag, M.; et al. Promiscuous mutations activate the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, C.M.; Davis, R.E.; Demchenko, Y.; Bellamy, W.; Gabrea, A.; Zhan, F.; Lenz, G.; Hanamura, I.; Wright, G.; Xiao, W.; et al. Frequent Engagement of the Classical and Alternative NF-κB Pathways by Diverse Genetic Abnormalities in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinman, R.I.; Cogswell, P.C.; Lofquist, A.K.; Baldwin, A.S. Role of transcriptional activation of I kappa B alpha in mediation of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids. Science 1995, 270, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auphan, N.; DiDonato, J.A.; Rosette, C.; Helmberg, A.; Karin, M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: Inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science 1995, 270, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab, M.S.; Podar, K.; Breitkreutz, I.; Richardson, P.G.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple myeloma. Lancet 2009, 374, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, C.; Mimura, N.; Bobb, K.; Kong, S.-Y.; Gorgun, G.; Cirstea, D.; Hu, Y.; Minami, J.; Ohguchi, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Dual Inhibition of Canonical and Noncanonical NF- B Pathways Demonstrates Significant Antitumor Activities in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4669–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Bonizzi, G.; Seagroves, T.N.; Greten, F.R.; Johnson, R.; Schmidt, E.V.; Karin, M. IKKalpha provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 2001, 107, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demicco, E.G.; Kavanagh, K.T.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Wang, X.; Shin, S.R.; Landesman-Bollag, E.; Seldin, D.C.; Sonenshein, G.E. RelB/p52 NF- B Complexes Rescue an Early Delay in Mammary Gland Development in Transgenic Mice with Targeted Superrepressor I B- Expression and Promote Carcinogenesis of the Mammary Gland. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10136–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sovak, M.A.; Bellas, R.E.; Kim, D.W.; Zanieski, G.J.; Rogers, A.E.; Traish, A.M.; Sonenshein, G.E. Aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression and the pathogenesis of breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2952–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, F.; González-Pérez, A.; Furriol, J.; Nicolau, M.J.; Ferrer, J.; Burgués, O.; Sabbaghi, M.; González-Navarrete, I.; Cristobal, I.; Serrano, L.; et al. Non-canonical NF-κB pathway activation predicts outcome in borderline oestrogen receptor positive breast carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Belguise, K.; Kersual, N.; Kirsch, K.H.; Mineva, N.D.; Galtier, F.; Chalbos, D.; Sonenshein, G.E. Oestrogen signalling inhibits invasive phenotype by repressing RelB and its target BCL2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurtado, A.; Holmes, K.A.; Ross-Innes, C.S.; Schmidt, D.; Carroll, J.S. FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi, A.; Meyer, M.; Dowhan, D.H. Cross-regulation between FOXA1 and ErbB2 signaling in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Belguise, K.; O’Neill, C.F.; Sanchez-Morgan, N.; Romagnoli, M.; Eddy, S.F.; Mineva, N.D.; Yu, Z.; Min, C.; Trinkaus-Randall, V.; et al. RelB NF- B Represses Estrogen Receptor Expression via Induction of the Zinc Finger Protein Blimp1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3832–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kendellen, M.F.; Bradford, J.W.; Lawrence, C.L.; Clark, K.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Canonical and non-canonical NF-κB signaling promotes breast cancer tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, C.L.; Baldwin, A.S. Non-Canonical EZH2 Transcriptionally Activates RelB in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E. Androgen receptor: Structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.P.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B. Androgen deprivation therapy: Progress in understanding mechanisms of resistance and optimizing androgen depletion. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadiminty, N.; Lou, W.; Sun, M.; Chen, J.; Yue, J.; Kung, H.-J.; Evans, C.P.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, A.C. Aberrant activation of the androgen receptor by NF-kappaB2/p52 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3309–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, L.; Mundade, R.; Korc, M.; Loehrer, P.J.; Lu, T. Critical role of NF-κB in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10969–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wharry, C.E.; Haines, K.M.; Carroll, R.G.; May, M.J. Constitutive non-canonical NFkappaB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döppler, H.; Liou, G.-Y.; Storz, P. Downregulation of TRAF2 Mediates NIK-Induced Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation and Tumorigenicity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, D.; Wilson, W.; Ryan, M.; Yeh, J.J.; Baldwin, A.S. GSK-3α promotes oncogenic KRAS function in pancreatic cancer via TAK1-TAB stabilization and regulation of noncanonical NF-κB. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Valenta, J.; Parney, I.F.; Bayless, K.J.; Sitcheran, R. The NF-κB RelB Protein Is an Oncogenic Driver of Mesenchymal Glioma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsu, N.; Nakatani, Y.; Yamashita, D.; Ohue, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Kondo, T. Eva1 Maintains the Stem-like Character of Glioblastoma-Initiating Cells by Activating the Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, M.; Saitoh, Y.; Mochida, K.; Tsuruyama, E.; Kiyono, T.; Imoto, I.; Inazawa, J.; Yuasa, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yamaoka, S. NF-κB Inducing Kinase, a Central Signaling Component of the Non-Canonical Pathway of NF-κB, Contributes to Ovarian Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.-L.; Liu, S.-H.; Ai, Z.-H.; Tao, M.-F.; Ma, L.; Wen, S.-Y.; Dai, M.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.-S.; Jiang, R.-Z.; et al. RelB/NF-κB links cell cycle transition and apoptosis to endometrioid adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2402–e2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Greenman, C.D.; Raine, K.; Jones, D.; Hinton, J.; Marshall, J.; Stebbings, L.A.; et al. Breast Cancer Working Group of the International Cancer Genome Consortium Mutational processes molding the genomes of 21 breast cancers. Cell 2012, 149, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.J.R.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L.; et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, R.S.; Liddament, M.T. Retroviral restriction by APOBEC proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, B.; McCann, J.L.; Starrett, G.J.; Kosyakovsky, L.; Luengas, E.M.; Molan, A.M.; Burns, M.B.; McDougle, R.M.; Parker, P.J.; Brown, W.L.; et al. The PKC/NF-κB signaling pathway induces APOBEC3B expression in multiple human cancers. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4538–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Role of telomeres and telomerase in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.W.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Prowse, K.R.; Harley, C.B.; West, M.D.; Ho, P.L.; Coviello, G.M.; Wright, W.E.; Weinrich, S.L.; Shay, J.W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.W.; Hodis, E.; Xu, M.J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Chin, L.; Garraway, L.A. Highly recurrent TERT promoter mutations in human melanoma. Science 2013, 339, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, S.; Figl, A.; Rachakonda, P.S.; Fischer, C.; Sucker, A.; Gast, A.; Kadel, S.; Moll, I.; Nagore, E.; Hemminki, K.; et al. TERT promoter mutations in familial and sporadic melanoma. Science 2013, 339, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.-L.; Sun, W.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Cheng, H.S.; Ying, Z.; Lakshmanan, M.; Raju, A.; Tenen, D.G.; Cheng, S.-Y.; et al. Non-canonical NF-κB signalling and ETS1/2 cooperatively drive C250T mutant TERT promoter activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, G.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Jin, H.; Zhu, J.; Che, X.; Huang, C. Tumor-suppressor NFκB2 p100 interacts with ERK2 and stabilizes PTEN mRNA via inhibition of miR-494. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4080–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hua, X.; Xu, J.; Tian, Z.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Wu, X.-R.; Huang, C.; Xu, J.; et al. Inhibition of PHLPP2/cyclin D1 protein translation contributes to the tumor suppressive effect of NF-κB2 (p100). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34112–34130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Jones, R.S.; Zhang, Y. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 2002, 298, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Hart, C.M.; Francis, N.J.; Vargas, M.L.; Sengupta, A.; Wild, B.; Miller, E.L.; O’Connor, M.B.; Kingston, R.E.; Simon, J.A. Histone Methyltransferase Activity of a Drosophila Polycomb Group Repressor Complex. Cell 2002, 111, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmichev, A.; Nishioka, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Reinberg, D. Histone methyltransferase activity associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the Enhancer of Zeste protein. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czermin, B.; Melfi, R.; McCabe, D.; Seitz, V.; Imhof, A.; Pirrotta, V. Drosophila Enhancer of Zeste/ESC Complexes Have a Histone H3 Methyltransferase Activity that Marks Chromosomal Polycomb Sites. Cell 2002, 111, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bracken, A.P.; Kleine-Kohlbrecher, D.; Dietrich, N.; Pasini, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Beekman, C.; Theilgaard-Mönch, K.; Minucci, S.; Porse, B.T.; Marine, J.-C.; et al. The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iannetti, A.; Ledoux, A.C.; Tudhope, S.J.; Sellier, H.; Zhao, B.; Mowla, S.; Moore, A.; Hummerich, H.; Gewurz, B.E.; Cockell, S.J.; et al. Regulation of p53 and Rb Links the Alternative NF-κB Pathway to EZH2 Expression and Cell Senescence. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Donatis, G.M.; Pape, E.L.; Pierron, A.; Cheli, Y.; Hofman, V.; Hofman, P.; Allegra, M.; Zahaf, K.; Bahadoran, P.; Rocchi, S.; et al. NF-kB2 induces senescence bypass in melanoma via a direct transcriptional activation of EZH2. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, W.; Howard, T.P.; Vazquez, F.; Tsherniak, A.; Wu, J.N.; Wang, W.; Haswell, J.R.; Walensky, L.D.; Hahn, W.C.; et al. SWI/SNF-mutant cancers depend on catalytic and non-catalytic activity of EZH2. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, M.E.; Moore, H.M.; Li, X.; Toy, K.A.; Huang, W.; Sabel, M.S.; Kidwell, K.M.; Kleer, C.G. EZH2 expands breast stem cells through activation of NOTCH1 signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3098–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, B.; Liang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; et al. Integration of Estrogen and Wnt Signaling Circuits by the Polycomb Group Protein EZH2 in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 5105–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Y.; Xia, W.; Chen, C.-T.; Xie, X.; Chao, C.-H.; Woodward, W.A.; Hsu, J.-M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.-C. EZH2 Promotes Expansion of Breast Tumor Initiating Cells through Activation of RAF1-β-Catenin Signaling. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wu, Z.J.; Groner, A.C.; He, H.H.; Cai, C.; Lis, R.T.; Wu, X.; Stack, E.C.; Loda, M.; Liu, T.; et al. EZH2 Oncogenic Activity in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells Is Polycomb-Independent. Science 2012, 338, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.T.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Aau, M.; Guan, P.; Karuturi, R.K.M.; Liou, Y.C.; Yu, Q. Context-Specific Regulation of NF-κB Target Gene Expression by EZH2 in Breast Cancers. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, G.P.; Fujita, T.; Bhatia, K.; Huppi, C.; Liou, H.C.; Scott, M.L.; Baltimore, D. The bcl-3 proto-oncogene encodes a nuclear I kappa B-like molecule that preferentially interacts with NF-kappa B p50 and p52 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, L.D.; Duckett, C.S.; Wamsley, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chiao, P.; Nabel, G.; McKeithan, T.W.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Verma, I.M. The proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes an I kappa B protein. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatada, E.N.; Nieters, A.; Wulczyn, F.G.; Naumann, M.; Meyer, R.; Nucifora, G.; McKeithan, T.W.; Scheidereit, C. The ankyrin repeat domains of the NF-kappa B precursor p105 and the protooncogene bcl-3 act as specific inhibitors of NF-kappa B DNA binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessells, J.; Baer, M.; Young, H.A.; Claudio, E.; Brown, K.; Siebenlist, U.; Johnson, P.F. BCL-3 and NF-κB p50 Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49995–50003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hishiki, T.; Ohshima, T.; Ego, T.; Shimotohno, K. BCL3 acts as a negative regulator of transcription from the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat through interactions with TORC3. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28335–28343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, A.R.; Lu, M.; Hai, T.; Lu, Y.; Boldogh, I. NF-kappa B-inducible BCL-3 expression is an autoregulatory loop controlling nuclear p50/NF-kappa B1 residence. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32080–32093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Nolan, G.P.; Liou, H.C.; Scott, M.L.; Baltimore, D. The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a transcriptional coactivator that activates through NF-kappa B p50 homodimers. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogswell, P.C.; Guttridge, D.C.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Baldwin, A.S. Selective activation of NF-κB subunits in human breast cancer: Potential roles for NF-κB2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashatus, D.; Cogswell, P.; Baldwin, A.S. Expression of the Bcl-3 proto-oncogene suppresses p53 activation. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westerheide, S.D.; Mayo, M.W.; Anest, V.; Hanson, J.L.; Baldwin, A.S. The Putative Oncoprotein Bcl-3 Induces Cyclin D1 To Stimulate G1 Transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8428–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocha, S.; Martin, A.M.; Meek, D.W.; Perkins, N.D. p53 represses cyclin D1 transcription through down regulation of Bcl-3 and inducing increased association of the p52 NF-kappaB subunit with histone deacetylase 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4713–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budunova, I.V.; Perez, P.; Vaden, V.R.; Spiegelman, V.S.; Slaga, T.J.; Jorcano, J.L. Increased expression of p50-NF-κB and constitutive activation of NF-κB transcription factors during mouse skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7423–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pallares, J.; Martínez-Guitarte, J.L.; Dolcet, X.; Llobet, D.; Rue, M.; Palacios, J.; Prat, J.; Matias-Guiu, X. Abnormalities in the NF-κB family and related proteins in endometrial carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, N.J.; Pathmanathan, R.; Raab-Traub, N. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8293–8301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canoz, O.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Admirand, J.H.; Medeiros, L.J. Immunohistochemical detection of BCL-3 in lymphoid neoplasms: A survey of 353 cases. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heissmeyer, V.; Krappmann, D.; Wulczyn, F.G.; Scheidereit, C. NF-kappa B p105 is a target of Ikappa B kinases and controls signal induction of Bcl-3-p50 complexes. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4766–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, V.Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Kim, D.; Zhong, X.; Du, Q.; Ghassemian, M.; Ghosh, G. Bcl3 Phosphorylation by Akt, Erk2, and IKK Is Required for Its Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, H.; Kanehira, K.; Okita, K.; Morimatsu, M.; Saito, M. MAIL, a novel nuclear I kappa B protein that potentiates LPS-induced IL-6 production. FEBS Lett. 2000, 485, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, M.; Dubois, N.; Musumeci, L.; Bours, V.; Robe, P.A. IκBζ: An emerging player in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66310–66322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, S.; Muta, T.; Matsuo, S.; Takeshige, K. Stimulus-specific induction of a novel nuclear factor-kappaB regulator, IkappaB-zeta, via Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor is mediated by mRNA stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, A.; Muta, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Takeshige, K. Essential roles for NF-κB and a Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-specific signal(s) in the induction of IκB-ζ. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Uematsu, S.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Kuwata, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Takeshige, K.; et al. Regulation of Toll/IL-1-receptor-mediated gene expression by the inducible nuclear protein IκBζ. Nature 2004, 430, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, D.V.; Zhu, N.; Farhang, G.; Kim, B.J.; Huxford, T. The Nuclear IκB Protein IκBζ Specifically Binds NF-κB p50 Homodimers and Forms a Ternary Complex on κB DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 379, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, S.; Muta, T.; Takeshige, K. A novel IkappaB protein, IkappaB-zeta, induced by proinflammatory stimuli, negatively regulates nuclear factor-kappaB in the nuclei. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27657–27662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogai, H.; Wenzel, S.-S.; Hailfinger, S.; Grau, M.; Kaergel, E.; Seitz, V.; Wollert-Wulf, B.; Pfeifer, M.; Wolf, A.; Frick, M.; et al. IκB-ζ controls the constitutive NF-κB target gene network and survival of ABC DLBCL. Blood 2013, 122, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Baud, V.; Delhase, M.; Zhang, P.; Deerinck, T.; Ellisman, M.; Johnson, R.; Karin, M. Abnormal Morphogenesis But Intact IKK Activation in Mice Lacking the IKK Subunit of IB Kinase. Science 1999, 284, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhase, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Chen, Y.; Karin, M. Positive and negative regulation of IkappaB kinase activity through IKKbeta subunit phosphorylation. Science 1999, 284, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Massa, P.E.; Hanidu, A.; Peet, G.W.; Aro, P.; Savitt, A.; Mische, S.; Li, J.; Marcu, K.B. IKKα, IKKβ, and NEMO/IKKγ Are Each Required for the NF-κB-mediated Inflammatory Response Program. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45129–45140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkhofer, E.C.; Cogswell, P.; Baldwin, A.S. Her2 activates NF-kappaB and induces invasion through the canonical pathway involving IKKalpha. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adli, M.; Merkhofer, E.; Cogswell, P.; Baldwin, A.S. IKKα and IKKβ Each Function to Regulate NF-κB Activation in the TNF-Induced/Canonical Pathway. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbach, A.; Gold, P.; Binder, B.R.; Hofer, E.; de Martin, R.; Schmid, J.A. Signaling Molecules of the NF-κB Pathway Shuttle Constitutively between Cytoplasm and Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10842–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Verma, U.N.; Prajapati, S.; Kwak, Y.-T.; Gaynor, R.B. Histone H3 phosphorylation by IKK-α is critical for cytokine-induced gene expression. Nature 2003, 423, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anest, V.; Hanson, J.L.; Cogswell, P.C.; Steinbrecher, K.A.; Strahl, B.D.; Baldwin, A.S. A nucleosomal function for IκB kinase-α in NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Nature 2003, 423, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoberg, J.E.; Yeung, F.; Mayo, M.W. SMRT Derepression by the IκB Kinase α: A Prerequisite to NF-κB Transcription and Survival. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Majada, V.; Aguilera, C.; Villanueva, A.; Vilardell, F.; Robert-Moreno, A.; Aytés, A.; Real, F.X.; Capella, G.; Mayo, M.W.; Espinosa, L.; et al. Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, P.; Fernández-Majada, V.; Villanueva, A.; Garcia-Carbonell, R.; Iglesias, M.; López, L.; Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Villà-Freixa, J.; Mulero, M.C.; Andreu, M.; et al. A Truncated Form of IKKα Is Responsible for Specific Nuclear IKK Activity in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.-L.; Tan, W.; Ricono, J.M.; Korchynskyi, O.; Zhang, M.; Gonias, S.L.; Cheresh, D.A.; Karin, M. Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKα controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin. Nature 2007, 446, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puto, L.A.; Reed, J.C. Daxx represses RelB target promoters via DNA methyltransferase recruitment and DNA hypermethylation. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croxton, R.; Puto, L.A.; de Belle, I.; Thomas, M.; Torii, S.; Hanaii, F.; Cuddy, M.; Reed, J.C. Daxx represses expression of a subset of antiapoptotic genes regulated by nuclear factor-kappaB. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9026–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.D.; Noothi, S.K.; Pullum, D.A.; Lawrie, C.H.; Pallapati, R.; Potluri, V.; Kuntzen, C.; Khan, S.; Plas, D.R.; Orlowski, R.Z.; et al. Transcriptional repression by the HDAC4–RelB–p52 complex regulates multiple myeloma survival and growth. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birbach, A.; Bailey, S.T.; Ghosh, S.; Schmid, J.A. Cytosolic, nuclear and nucleolar localization signals determine subcellular distribution and activity of the NF-kappaB inducing kinase NIK. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Ito, T.; Azuma, S.; Ito, E.; Honma, R.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Kawamura, M.; Imai, J.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-κB is preferentially involved in the proliferation of basal-like subtype breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vazquez-Santillan, K.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Jimenez-Hernandez, L.E.; Gaytan-Cervantes, J.; Muñoz-Galindo, L.; Piña-Sanchez, P.; Martinez-Ruiz, G.; Torres, J.; Garcia-Lopez, P.; Gonzalez-Torres, C.; et al. NF-kappaΒ-inducing kinase regulates stem cell phenotype in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzman, M.L.; Neering, S.J.; Upchurch, D.; Grimes, B.; Howard, D.S.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Luger, S.M.; Jordan, C.T. Nuclear factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2001, 98, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, F.; Borcherding, N.; Zhang, W.; Boyce, B.; Xue, H.-H.; Zhao, C. Stabilization of NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Suppresses MLL-AF9-Induced Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-U.; Ravi, S.; Lee, D.W.; McFadden, K.; Kamradt, M.L.; Toussaint, L.G.; Sitcheran, R. NIK/MAP3K14 Regulates Mitochondrial Dynamics and Trafficking to Promote Cell Invasion. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 3288–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Q.; Wu, Q.; Horbinski, C.M.; Flavahan, W.A.; Yang, K.; Zhou, W.; Dombrowski, S.M.; Huang, Z.; Fang, X.; Shi, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial control by DRP1 in brain tumor initiating cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kashatus, J.A.; Nascimento, A.; Myers, L.J.; Sher, A.; Byrne, F.L.; Hoehn, K.L.; Counter, C.M.; Kashatus, D.F. Erk2 phosphorylation of Drp1 promotes mitochondrial fission and MAPK-driven tumor growth. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bren, G.D.; Solan, N.J.; Miyoshi, H.; Pennington, K.N.; Pobst, L.J.; Paya, C.V. Transcription of the RelB gene is regulated by NF-κB. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7722–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Pauza, M.E.; Feng, L.; Lo, D. RelB regulation of chemokine expression modulates local inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Mackman, N.; Ku, G.; Lo, D.; Feng, L. RelB modulation of IkappaBalpha stability as a mechanism of transcription suppression of interleukin-1alpha (IL-1alpha), IL-1beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 7688–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marienfeld, R.; May, M.J.; Berberich, I.; Serfling, E.; Ghosh, S.; Neumann, M. RelB forms transcriptionally inactive complexes with RelA/p65. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 19852–19860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacque, E.; Tchenio, T.; Piton, G.; Romeo, P.-H.; Baud, V. RelA repression of RelB activity induces selective gene activation downstream of TNF receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14635–14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maier, H.J.; Marienfeld, R.; Wirth, T.; Baumann, B. Critical role of RelB serine 368 for dimerization and p100 stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39242–39250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savinova, O.V.; Hoffmann, A.; Ghosh, G. The Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 proteins p105 and p100 function as the core of high-molecular-weight heterogeneous complexes. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legarda-Addison, D.; Ting, A.T. Negative regulation of TCR signaling by NF-kappaB2/p100. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7767–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C.; Ganchi, P.A.; Béraud, C.; Ballard, D.W.; Greene, W.C.; Ware, C.F.; Van Duyne, G.D.; Ghosh, G. Autoregulation of the NF-kappa B transactivator RelA (p65) by multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors containing ankyrin motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, V.; Collares, D. Post-Translational Modifications of RelB NF-κB Subunit and Associated Functions. Cells 2016, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. A Structural Guide to Proteins of the NF- B Signaling Module. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Natoli, G.; Ghosh, G. Transcriptional regulation via the NF-κB signaling module. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6706–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beg, A.A.; Baldwin, A.S. Activation of multiple NF-kappa B/Rel DNA-binding complexes by tumor necrosis factor. Oncogene 1994, 9, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Z.B.; Weih, D.S.; Sivakumar, V.; Weih, F. RelB is required for Peyer’s patch development: Differential regulation of p52-RelB by lymphotoxin and TNF. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.B.; Huxford, T.; Chen, Y.Q.; Ghosh, G. The role of DNA in the mechanism of NFkappaB dimer formation: Crystal structures of the dimerization domains of the p50 and p65 subunits. Structure 1997, 5, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.-B.; Vu, D.; Ghosh, G. NF-κB RelB Forms an Intertwined Homodimer. Structure 2005, 13, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.; Basak, S.; James, E.S.; Quiambo, R.S.; Kinsella, M.C.; Alegre, M.-L.; Weih, F.; Franzoso, G.; Hoffmann, A.; Fu, Y.-X. Coordination between NF-kappaB family members p50 and p52 is essential for mediating LTbetaR signals in the development and organization of secondary lymphoid tissues. Blood 2006, 107, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Petrovas, C.; Sonenshein, G.E. RelB-p50 NF-kappa B complexes are selectively induced by cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein 1: Differential regulation of Bcl-x(L) promoter activity by NF-kappa B family members. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5737–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, S.; Rescigno, M.; Granucci, F.; Citterio, S.; Francolini, M.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Differential activation of NF-kappa B subunits in dendritic cells in response to Gram-negative bacteria and to lipopolysaccharide. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, E.; Dejardin, E.; Pritchard, L.L.; Green, D.R.; Körner, M.; Baud, V. RelB/p50 Dimers Are Differentially Regulated by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Lymphotoxin-β Receptor Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23278–23284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schjerven, H.; Tran, T.N.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Johansen, F.-E. De novo synthesized RelB mediates TNF-induced up-regulation of the human polymeric Ig receptor. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, V.F.-S.; Davis-Turak, J.; Macal, M.; Huang, J.Q.; Ponomarenko, J.; Kearns, J.D.; Yu, T.; Fagerlund, R.; Asagiri, M.; Zuniga, E.I.; et al. Control of RelB during dendritic cell activation integrates canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tegowski, M.; Baldwin, A. Noncanonical NF-κB in Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6020066
Tegowski M, Baldwin A. Noncanonical NF-κB in Cancer. Biomedicines. 2018; 6(2):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6020066
Chicago/Turabian StyleTegowski, Matthew, and Albert Baldwin. 2018. "Noncanonical NF-κB in Cancer" Biomedicines 6, no. 2: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6020066
APA StyleTegowski, M., & Baldwin, A. (2018). Noncanonical NF-κB in Cancer. Biomedicines, 6(2), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6020066