HSP70 Inhibitor Suppresses IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of Osteoblasts through p44/p42 MAP Kinase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Migration Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Densitometric Analysis of Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of VER-155008 on the IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of MC3T3-E1 Cells
3.2. Effect of YM-08 on the IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of MC3T3-E1 Cells
3.3. Effects of VER-155008 on the IGF-I-Induced Phosphorylation of p44/p42 MAP Kinase or Akt in MC3T3-E1 Cells
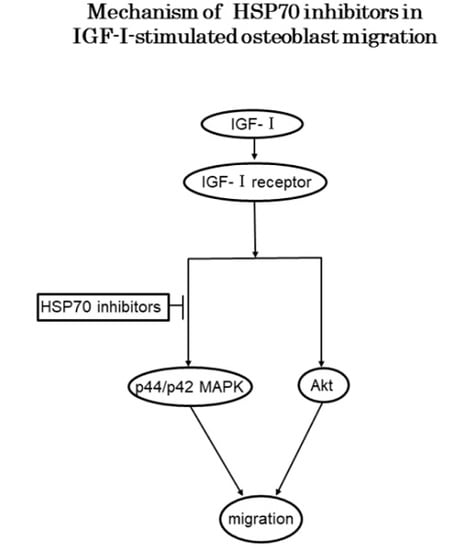
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karsenty, G.; Wangner, E.F. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev. Cell 2010, 2, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kular, J.; Tickner, J.; Chim, S.M.; Xu, J. An overview of the regulation of bone remodeling at cellular level. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.N.; Bostrom, M.P.; Lane, J.M. Bone growth factors. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 31, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.R.; Daluiski, A.; Einhorn, T.A. The role of growth factors in the repair of bone: Biology and clinical applications. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2002, 84, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, A.H.; Roodman, D.; Freeman, C.; Mohla, S. Mechanisms of tumor metastasis to the bone: Challenges and opportunities. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, T.L.; Chernausek, S.D. Genetic strategies for elucidating insulin-like growth factor action in bone. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2004, 14, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Rosen, C.J. The insulin-like growth factor-1 gene and osteoporosis: A critical appraisal. Gene 2005, 361, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, T.; Tokuda, H.; Yoshida, M.; Yasuda, E.; Hanai, Y.; Kozawa, O. Possible involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in insulin-like growth factor-I-induced alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoblasts. Horm. Metab. Res. 2005, 37, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanai, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Ishisaki, A.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Nakamura, N.; Yoshida, M.; Takai, S.; Ohta, T.; Kozawa, O. Involvement of p44/p42 MAP kinase in insulin-like growth factor-I-induced alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 251, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakasaki, M.; Yoshioka, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshikawa, H.; Itoh, K. IGF-I secreted by osteoblasts acts as a potent chemotactic factor for osteoblasts. Bone 2008, 43, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, T.; Tokuda, H.; Sakai, G.; Fujita, K.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Otsuka, T.; Kozawa, O. Repression of IGF-I-induced osteoblast migration by (−)-epigallocatechin gallate through p44/p42 MAP kinase. Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mymrikov, E.V.; Seit-Nebi, A.S.; Gusev, N.B. Large potentials of small heat shock proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1123–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radons, J. The human HSP70 family of chaperones: Where do we stand? Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 379–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ren, G.; Wang, H. The detection and role of heat shock protein 70 in various nondisease conditions and disease conditions: A literature review. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, M.Y.; Gabai, V.L. Hsp70 in cancer: Back to the future. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4153–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Xue, D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, F.; Pan, Z. Extracellular heat shock protein 70 promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the ERK signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 4088–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudo, H.; Kodama, H.; Amagai, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Kasai, S. In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 96, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozawa, O.; Tokuda, H.; Miwa, M.; Kotoyori, J.; Oiso, Y. Cross-talk regulation between cyclic AMP production and phosphoinositide hydrolysis induced by prostaglandin E2 in osteoblast-like cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1992, 198, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiosis, S.A.; Chrisler, W.B.; Bollinger, N.; Karin, N.J. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced ERK activation and chemotaxis in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts are independent of EGF receptor transactivation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Ito, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Inaguma, Y.; Kozawa, O.; Asano, T. Modulation of the stress-induced synthesis of hsp27 and αB-crystallin by cyclic AMP in C6 rat glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlecht, R.; Scholz, S.R.; Dahmen, H.; Wegener, A.; Sirrenberg, C.; Musil, D.; Bomke, J.; Eggenweiler, H.M.; Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. Functional analysis of HSP70 inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Li, X.; Lee, H.F.; Jinwal, U.K.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Seguin, S.P.; Young, Z.T.; Brodsky, J.L.; Dickey, C.A.; Sun, D.; et al. Synthesis and initial evaluation of YM-08, a blood-brain barrier permeable derivative of the heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) inhibitor MKT-177, which reduces tau levels. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.K.; Hong, S.K.; Veeranki, S.; Karkhanis, M.; Starenki, D.; Plaza, J.A.; Park, J.I. A mortalin/HSPA9-mediated switch in tumor-suppressive signaling of Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 4051–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, K.; Shiota, M.; Tanaka, M.; Otsuka, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Kato, M.; Tamada, S.; Iwao, H.; Miura, K.; Nakatani, T.; et al. Heat shock protein 70 inhibitors suppress androgen receptor expression in LNCaP95 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaglom, J.A.; Qang, Y.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Monti, S.; Alexandrov, I.; Lu, X.; Sherman, M.Y. Cancer cell responses to HSP70 inhibitor JG-98: Comparison with HSP90 inhibitors and findings synergistic drug combinations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhead, M.L.; Clark, J.C.; Myers, D.E.; Dass, C.R.; Choong, P.F. The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: A review. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 959248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliara, V.; Saide, A.; Mitidieri, E.; d’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Sorrentino, R.; Russo, G.; Russo, A. 5-FU targets rpL3 to induce mitochondrial apoptosis via cystathionine-β-synthase in colon cancer cells lacking p53. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50333–50348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, A.; Saide, A.; Cagliani, R.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G.; Russo, G. rpL3 promotes the apoptosis of p53 mutated lung cancer cells by down-regulating CBS and NFκB upon 5-FU treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spina, A.; Sorvillo, L.; Chiosi, E.; Esposito, A.; Di Maiolo, F.; Sapio, L.; Caraglia, M.; Naviglio, S. Synergistic cytotoxic effects of inorganic phosphate and chemotherapeutic drugs on human osteosarcoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uozaki, H.; Ishida, T.; Kakiuchi, C.; Horiuchi, H.; Gotoh, T.; Iijima, T.; Imamura, T.; Machinami, R. Expression of heat shock proteins in osteosarcoma and its relationship to prognosis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2000, 196, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asling, J.; Morrison, J.; Mutsaers, A.J. Targeting HSP70 and GRP78 in canine osteosarcoma cells in combination with doxorubicin chemotherapy. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Tokuda, H.; Hatakeyama, D.; Hirade, K.; Niwa, M.; Ito, H.; Kato, K.; Kozawa, O. Mechanism of simvastatin on induction of heat shock protein in osteoblasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 415, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, E.E.; Zhou, L.; Woo, N.Y. Effects of mitogenic hormones on HSP70 expression in a silver sea bream fibroblast cell line and a primary macrophage preparation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 152, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawabata, T.; Tokuda, H.; Sakai, G.; Fujita, K.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Kuroyanagi, G.; Otsuka, T.; Kozawa, O. HSP70 Inhibitor Suppresses IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of Osteoblasts through p44/p42 MAP Kinase. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040109
Kawabata T, Tokuda H, Sakai G, Fujita K, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kuroyanagi G, Otsuka T, Kozawa O. HSP70 Inhibitor Suppresses IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of Osteoblasts through p44/p42 MAP Kinase. Biomedicines. 2018; 6(4):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040109
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawabata, Tetsu, Haruhiko Tokuda, Go Sakai, Kazuhiko Fujita, Rie Matsushima-Nishiwaki, Gen Kuroyanagi, Takanobu Otsuka, and Osamu Kozawa. 2018. "HSP70 Inhibitor Suppresses IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of Osteoblasts through p44/p42 MAP Kinase" Biomedicines 6, no. 4: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040109
APA StyleKawabata, T., Tokuda, H., Sakai, G., Fujita, K., Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R., Kuroyanagi, G., Otsuka, T., & Kozawa, O. (2018). HSP70 Inhibitor Suppresses IGF-I-Stimulated Migration of Osteoblasts through p44/p42 MAP Kinase. Biomedicines, 6(4), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040109