The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
2. Yes-Associated Protein in Human NSCLC and MPM
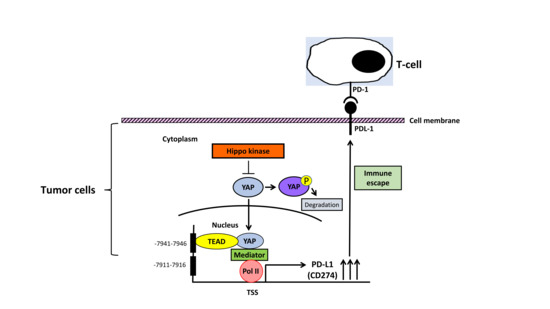
3. YAP Regulates PD-L1 Expression in Human NSCLC and MPM
4. Future perspectives: The Interactions between YAP Signaling Pathways and Immune Checkpoints
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. The PD-1-PD-L pathway in immunological tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, M.; Iwai, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Freeman, G.J.; Minato, N.; Honjo, T. Differential expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, ligands for an inhibitory receptor PD-1, in the cells of lymphohematopoietic tissues. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 84, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, Y.; Ishida, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T.; Minato, N. Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12293–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zielinski, C.; Knapp, S.; Mascaux, C.; Hirsch, F. Rationale for targeting the immune system through checkpoint molecule blockade in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, W.A.; Tran, T.; Vilain, R.E.; Madore, J.; Selinger, C.I.; Kohonen-Corish, M.; Yip, P.; Yu, B.; O’Toole, S.A.; McCaughan, B.C.; et al. PD-L1 expression is a favorable prognostic factor in early stage non-small cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passiglia, F.; Bronte, G.; Bazan, V.; Natoli, C.; Rizzo, S.; Galvano, A.; Listì, A.; Cicero, G.; Rolfo, C.; Santini, D.; et al. PD-L1 expression as predictive biomarker in patients with NSCLC: A pooled analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19738–19747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleyea, F.; Blankenshipa, L.; Millisorb, V.; Anderson, J.; Jaiyesimi, I. Programmed cell death-1/Programmed cell death ligand-1(PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors, heralding a new era of immunotherapy in the management of advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2017, 12, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Y.; Yao, R.; Zhou, L.; Lu, L.; Gao, W.; Sun, Y. The miR-3127-5p/p-STAT3 axis up-regulates PD-L1 inducing chemoresistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunger, A.; Kießler, M.; Wehner, R.; Temme, A.; Meier, F.; Bachmann, M.; Schmitz, M. Immune Monitoring of Cancer Patients Prior to and During CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitor Treatment. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrò, L.; Ceresoli, G.L.; D’Incecco, A.; Scherpereel, A.; Aerts, J.; Maio, M. Immune checkpoint therapy of mesothelioma: Pre-clinical bases and clinical evidences. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozier, J.; Zheng, H.; Adusumilli, P.S. Immunotherapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Current status and future directions. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedrés, S.; Ponce-Aix, S.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Sansano, I.; Enguita, A.; Navarro-Mendivil, A.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Martinez, P.; Felip, E. Analysis of expression of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumoulin, D.W.; Aerts, J.G.; Cornelissen, R. Is immunotherapy a viable option in treating mesothelioma? Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sui, H.; Ma, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Yang, J. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Therapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Toward Personalized Medicine and Combination Strategies. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6984948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; Ready, N.; Steins, M.; Poddubskaya, E.; Borghaei, H.; Felip, E.; Paz-Ares, L.; et al. Nivolumab Versus Docetaxel in Previously Treated Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two-Year Outcomes From Two Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trials (CheckMate 017 and CheckMate 057). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.M.; Zakowski, M.; Venkatraman, E.; Krug, L.; Rosenzweig, K.; Dycoco, J.; Lee, C.; Yeoh, C.; Bains, M.; Rusch, V. Prognostic factors in the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma at a large tertiary referral center. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudino, G.; Yang, H.; Carbone, M. HGF/Met Signaling Is a Key Player in Malignant Mesothelioma Carcinogenesis. Biomedicines 2014, 2, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, M.S.; Mao, J.H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, C.T.; Yu, J.S.; Harvard, C.; Lin, Y.C.; Bravo, D.T.; Jablons, D.M.; You, L. Cul4A is an oncogene in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.L.; Ni, J.; Hsu, P.C.; Mao, J.H.; Hsieh, D.; Xu, A.; Chan, G.; Au, A.; Xu, Z.; Jablons, D.M.; et al. Cul4A overexpression associated with Gli1 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alley, E.W.; Lopez, J.; Santoro, A.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; van Brummelen, E. Clinical safety and activity of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): Preliminary results from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatwal, M.S.; Tanvetyanon, T. Malignant mesothelioma clinical trial combines immunotherapy drugs. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quispel-Janssen, J.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Zimmerman, M.; Lalezari, F.; Thunnissen, E.; Monkhorst, K.; Schouten, R.; Schunselaar, L.; Disselhorst, M.; et al. Programmed Death 1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Patients with Recurrent Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaxas, Y.; Rivalland, G.; Mauti, L.A.; Klingbiel, D.; Kao, S.; Schmid, S.; Nowak, A.K.; Gautschi, O.; Bartnick, T.; Hughes, B.G.; et al. Pembrolizumab as Palliative Immunotherapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1784–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.; Halder, G. The two faces of Hippo: Targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Teng, L. YAP/TAZ for cancer therapy: Opportunities and challenges (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Feng, P.; Peng, A.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, X.; He, S.; Zhou, D. cAMP response element-binding protein and Yes-associated protein form a feedback loop that promotes neurite outgrowth. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.X.; Luo, J.; Mo, J.S.; Liu, G.; Kim, Y.C.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, B.; Peyman, G.; Ouyang, H.; Jiang, W.; et al. Mutant Gq/11 promote uveal melanoma tumorigenesis by activating YAP. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Degese, M.S.; Iglesias-Bartolome, R.; Vaque, J.P.; Molinolo, A.A.; Rodrigues, M.; Zaidi, M.R.; Ksander, B.R.; Merlino, G.; Sodhi, A.; et al. Hippo-independent activation of YAP by the GNAQ uveal melanoma oncogene through a trio-regulated rho GTPase signaling circuitry. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Chen, J.; Gan, C.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Kremerskothen, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. WWC2 is an independent prognostic factor and prevents invasion via Hippo signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3718–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X.; Weng, Z.; Li, S. Emerging role of Hippo signalling pathway in bladder cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.Y.; Luo, Q.Q.; Xu, Y.H.; Tang, N.W.; Niu, X.M.; Li, Z.M.; Shen, S.P.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z.W. 17-AAG suppresses growth and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells via regulation of the LATS1/YAP pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Sabnis, A.J.; Chan, E.; Olivas, V.; Cade, L.; Pazarentzos, E.; Asthana, S.; Neel, D.; Yan, J.J.; Lu, X.; et al. The Hippo effector YAP promotes resistance to RAF- and MEK-targeted cancer therapies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, B.; Yang, Y.L.; Xu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Mao, J.H.; Tetsu, O.; Li, H.; Jablons, D.M.; You, L. Inhibition of ERK1/2 down-regulates the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway in human NSCLC cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4357–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, P.C.; You, B.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, W.Q.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.T.; Li, H.; et al. YAP promotes erlotinib resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51922–51933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.Q.; Yang, Y.L.; Hang, P.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Hsu, P.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Z.; et al. YAP1 regulates ABCG2 and cancer cell side population in human lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4096–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.D.; Xue, W.; Krall, E.B.; Bhutkar, A.; Piccioni, F.; Wang, X.; Schinzel, A.C.; Sood, S.; Rosenbluh, J.; Kim, J.W.; et al. KRAS and YAP1 converge to regulate EMT and tumor survival. Cell 2014, 158, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, F.R. YAP1 takes over when oncogenic K-Ras slumbers. Cell 2014, 158, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Miao, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.L.; Xu, Z.; You, J.; Dai, Y.; Yeh, C.C.; Chan, G.; Liu, S.; et al. Inhibition of yes-associated protein suppresses brain metastasis of human lung adenocarcinoma in a murine model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3073–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felley-Bosco, E.; Stahel, R. Hippo/YAP pathway for targeted therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Dai, Y.Y.; Hsu, P.C.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Chan, G.; et al. Targeting YAP in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, G.A.; Yang, Y.L.; You, L.; Jablons, D.M. Drug development against the hippo pathway in mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, P.N., Jr.; Santoro, I.L.; Tadokoro, H.; de Lima, L.G.; Filardi, B.A.; Oliveira, P.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Mountzios, G.; de Mello, R.A. A pooled analysis of nivolumab for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and the role of PD-L1 as a predictive biomarker. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki Vareki, S.; Garrigós, C.; Duran, I. Biomarkers of response to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 116, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, T.; Harvey, K.F. Hippo Wades into Cancer Immunology. Dev. Cell 2016, 39, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, F.; Chu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Dai, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Ling, L.; Jia, J.; et al. YAP antagonizes innate antiviral immunity and is targeted for lysosomal degradation through IKKε-mediated phosphorylation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lu, X.; Dey, P.; Deng, P.; Wu, C.C.; Jiang, S.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Konaparthi, R.; Hua, S.; et al. Targeting YAP-Dependent MDSC Infiltration Impairs Tumor Progression. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Shahbazian, D.; Surana, R.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Graham, G.T.; White, S.M.; Weiner, L.M.; Yi, C. Yes-associated protein mediates immune reprogramming in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Tao, J.; Barbi, J.; Chen, Q.; Park, B.V.; Li, Z.; Zhang, N.; Lebid, A.; Ramaswamy, A.; Wei, P.; et al. YAP Is Essential for Treg-Mediated Suppression of Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1026–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Hsu, P.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Xu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chan, G.; Huang, Z.; Hu, B.; Li, H.; et al. YAP regulates PD-L1 expression in human NSCLC cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114576–114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, P.C.; Miao, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, W.Q.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, C.W.; Yang, C.T.; Huang, Z.; You, J.; Xu, Z.; et al. Inhibition of yes-associated protein down-regulates PD-L1 (CD274) expression in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3139–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Azad, T.; Ling, M.; Hao, Y.; Snetsinger, B.; Khanal, P.; Minassian, L.M.; Graham, C.H.; Rauh, M.J.; Yang, X. The Hippo Pathway Component TAZ Promotes Immune Evasion in Human Cancer through PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Z.; Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Yang, X. The Hippo Pathway: Immunity and Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Park, D.I.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.E.; Yeo, M.K.; Park, Y.H.; Lim, D.S.; Choi, W.; Lee, D.H.; Yoo, G.; et al. Hippo effector YAP directly regulates the expression of PD-L1 transcripts in EGFR-TKI-resistant lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 491, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, T.; Qin, T.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Shen, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashizawa, T.; Iizuka, A.; Nonomura, C.; Kondou, R.; Maeda, C.; Miyata, H.; Sugino, T.; Mitsuya, K.; Hayashi, N.; Nakasu, Y.; et al. Antitumor Effect of Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) Blockade in Humanized the NOG-MHC Double Knockout Mouse. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yao, L.C.; Cheng, M.; Cai, D.; Martinek, J.; Pan, C.X.; Shi, W.; Ma, A.H.; De Vere White, R.W.; Airhart, S.; et al. Humanized mice in studying efficacy and mechanisms of PD-1-targeted cancer immunotherapy. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinda, B.; Khan, I.; Parkin, B.; Konig, H. The rocky road to personalized medicine in acute myeloid leukaemia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1411–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Chong, R.; Ding, S.J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, J. CDK1 phosphorylation of YAP promotes mitotic defects and cell motility and is essential for neoplastic transformation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6722–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.G.; Carrara, M.; Yuan, W.C.; Valdes-Quezada, C.; Gurung, B.; Pepe-Mooney, B.; Zhang, T.; Geeven, G.; Gray, N.S.; de Laat, W.; et al. YAP Drives Growth by Controlling Transcriptional Pause Release from Dynamic Enhancers. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, H. The Hippo signaling pathway provides novel anti-cancer drug targets. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16084–16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaib, I.; Karachaliou, N.; Pilotto, S.; Codony Servat, J.; Cai, X.; Li, X.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Servat, C.C.; Yang, J.; Hu, C.; et al. Co-activation of STAT3 and YES-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Pathway in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibata, M.; Ham, K.; Hoque, M.O. A time for YAP1: Tumorigenesis, immunosuppression and targeted therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pandey, S.; Travers, M.; Sun, H.; Morton, G.; Madzo, J.; Chung, W.; Khowsathit, J.; Perez-Leal, O.; Barrero, C.A.; et al. Targeting CDK9 reactivates epigenetically silenced genes in cancer. Cell 2018, 175, 1244–1258.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, P.-C.; Yang, C.-T.; Jablons, D.M.; You, L. The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040114
Hsu P-C, Yang C-T, Jablons DM, You L. The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer. Biomedicines. 2018; 6(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Ping-Chih, Cheng-Ta Yang, David M. Jablons, and Liang You. 2018. "The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer" Biomedicines 6, no. 4: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040114
APA StyleHsu, P. -C., Yang, C. -T., Jablons, D. M., & You, L. (2018). The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer. Biomedicines, 6(4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040114