Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Induces Apoptosis as a TRAIL Sensitizer via Activation of Caspase 8 and Death Receptor 5 in Human Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
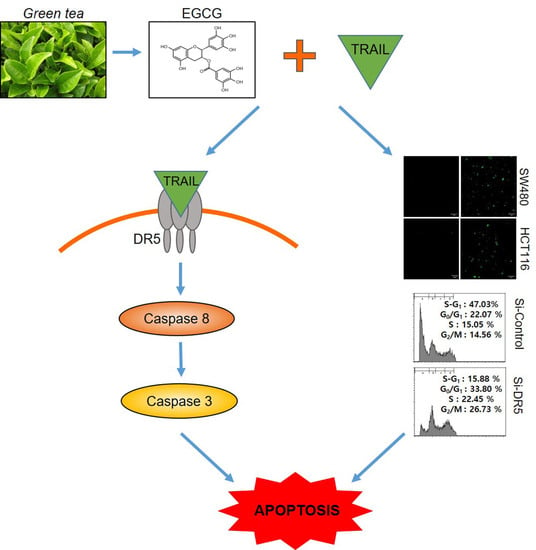
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. TUNEL Assay
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis for Sub-G1 Accumulation
2.6. FACS Analysis for Early and Late Apoptosis Detection
2.7. FACS Analysis for Cell Surface Expression of DR5
2.8. RNA Isolation and Measurement
2.9. Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. RNA Interference
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cotreatment of TRAIL and EGCG Synergistically Increased Cytotoxicity in CRCs
3.2. Cotreatment of EGCG and TRAIL Dramatically Increased TUNEL-Positive Cells, Cleaved PARP and Activated Caspase 8 in SW480 and HCT116 Cells
3.3. Cotreatment of EGCG and TRAIL Upregulated DR5 in Colon Cancer Cells
3.4. Depletion of DR5 Reduced the Ability of EGCG and TRAIL Cotreatment to Induce Cytotoxicity, Cleaved-PARP and Increase Sub G1 Population in Colon Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bockbrader, K.M.; Tan, M.; Sun, Y. A small molecule Smac-mimic compound induces apoptosis and sensitizes TRAIL- and etoposide-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7381–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brooks, A.D.; Sayers, T.J. Reduction of the antiapoptotic protein cFLIP enhances the susceptibility of human renal cancer cells to TRAIL apoptosis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopin, V.; Slomianny, C.; Hondermarck, H.; Le Bourhis, X. Synergistic induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells by cotreatment with butyrate and TNF-alpha, TRAIL, or anti-Fas agonist antibody involves enhancement of death receptors’ signaling and requires P21(waf1). Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 298, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossati, S.; Ghiso, J.; Rostagno, A. TRAIL death receptors DR4 and DR5 mediate cerebral microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis induced by oligomeric Alzheimer’s Abeta. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridlender, M.; Kapulnik, Y.; Koltai, H. Plant derived substances with anti-cancer activity: From folklore to practice. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, J.; Sowa, Y.; Horinaka, M.; Koyama, M.; Wakada, M.; Miki, T.; Sakai, T. The anti-obesity drug orlistat promotes sensitivity to TRAIL by two different pathways in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, B.; Ding, Q.; Xia, G.; Fang, Z. EGCG inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma through TFPI-2 overexpression. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Herbeuval, J.P.; Grivel, J.C.; Boasso, A.; Hardy, A.W.; Chougnet, C.; Dolan, M.J.; Yagita, H.; Lifson, J.D.; Shearer, G.M. CD4+ T-cell death induced by infectious and noninfectious HIV-1: Role of type 1 interferon-dependent, TRAIL/DR5-mediated apoptosis. Blood 2005, 106, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Antosiewicz, A.; Singh, S.V. Signal transduction pathways leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in cancer cells by Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds: A review. Mutat. Res. 2004, 555, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.K.; Ryu, B.J.; Kim, S.H. AW00179 potentiates TRAIL-mediated death of human lung cancer H1299 cells through ROS-JNK-c-Jun-mediated up-regulation of DR5 and down-regulation of anti-apoptotic molecules. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz, A.L.; Trauzold, A.; Hillenbrand, A.; Knippschild, U.; Henne-Bruns, D.; von Karstedt, S.; Lemke, J. TRAILblazing Strategies for Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.H.M.; Kong, W.Y.; Fang, C.M.; Loh, H.S.; Chuah, L.H.; Abdullah, S.; Ngai, S.C. The TRAIL to cancer therapy: Hindrances and potential solutions. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 143, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Pezzani, R.; Redaelli, M.; Zorzan, M.; Imran, M.; Ahmed Khalil, A.; Salehi, B.; Sharopov, F.; Cho, W.C.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Preclinical Pharmacological Activities of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate in Signaling Pathways: An Update on Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, K.J.; Kwon, T.K. Anticancer effects and molecular mechanisms of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Integr. Med. Res. 2014, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sang, S.; Lambert, J.D.; Ho, C.T.; Yang, C.S. The chemistry and biotransformation of tea constituents. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 64, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, B.; Ghildiyal, A.; Sahabjada, S.S.; Arshad, M.; Mahdi, A.A.; Tiwari, S. Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Effect of Curcumin and TRAIL (TNF Related Apoptosis inducing Ligand) in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemic Cells. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, XC01–XC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, B.U.; Habib, S.; Ahmad, P.; Allarakha, S.; Moinuddin, A.A. Pathophysiological Role of Peroxynitrite Induced DNA Damage in Human Diseases: A Special Focus on Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP). Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.H.; Yun, M.; Choo, E.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Jung, D.B.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.O.; Kato, N.; Kim, B.; et al. A derivative of epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis via SHP-1-mediated suppression of BCR-ABL and STAT3 signalling in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3565–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Park, Y.R.; Seo, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, S.W. Parthenolide enhances sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to TRAIL by inducing death receptor 5 and promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Yun, M.; Kim, E.O.; Jung, D.B.; Won, G.; Kim, B.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.H. Decursin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through oxidative stress mediated- endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling in non-small cell lung cancers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Kong, H.; Guo, Z.; Liu, S.; Cao, X. Anti-apoptotic hPEBP4 silencing promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells by activating ERK and JNK pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Roginsky, A.B.; Ding, X.Z.; Woodward, C.; Collin, P.; Newman, R.A.; Bell, R.H., Jr.; Adrian, T.E. Review of the apoptosis pathways in pancreatic cancer and the anti-apoptotic effects of the novel sea cucumber compound, Frondoside A. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1138, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterov, A.; Lu, X.; Johnson, M.; Miller, G.J.; Ivashchenko, Y.; Kraft, A.S. Elevated AKT activity protects the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP from TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10767–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, M.; Ohtsubo, M.; Takayanagi, A.; Tachibana, M.; Shimizu, N.; Murai, M. Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB prevents TRAIL-induced apoptosis in renal cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3888–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Cho, D.H.; Andera, L.; Suh, N.; Kim, I. Curcumin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells by regulating apoptosis-related proteins. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2013, 383, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Thome, M.; Burns, K.; Bodmer, J.L.; Hofmann, K.; Kataoka, T.; Holler, N.; Tschopp, J. TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity 1997, 7, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, E.A.; Sohn, E.J.; Won, G.; Choi, J.U.; Jeong, M.; Kim, B.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.H. Upregulation of microRNA135a-3p and death receptor 5 plays a critical role in Tanshinone I sensitized prostate cancer cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5624–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegelin, M.D.; Reuss, D.E.; Habel, A.; Herold-Mende, C.; von Deimling, A. The flavonoid kaempferol sensitizes human glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by proteasomal degradation of survivin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.N.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.Y.; Yue, P.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Choi Kim, H.R.; Lotan, R.; Wu, G.S. Overexpression of BCL2 blocks TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yan, C.; Jia, S.; Hu, J. Correlation analysis of peripheral DPYD gene polymorphism with 5-fluorouracil susceptibility and side effects in colon cancer patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5857–5861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szliszka, E.; Czuba, Z.P.; Domino, M.; Mazur, B.; Zydowicz, G.; Krol, W. Ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) enhances the apoptosis- inducing potential of TRAIL in cancer cells. Molecules 2009, 14, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szliszka, E.; Krol, W. Polyphenols Isolated from Propolis Augment TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 731940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwary, R.; Yu, W.; Li, J.; Park, S.K.; Sanders, B.G.; Kline, K. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in alpha-TEA mediated TRAIL/DR5 death receptor dependent apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Twomey, J.D.; Kim, S.R.; Zhao, L.; Bozza, W.P.; Zhang, B. Spatial dynamics of TRAIL death receptors in cancer cells. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 19, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, S.M.; Jung, J.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Sohn, E.J.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.H. Tanshinone IIA induces autophagic cell death via activation of AMPK and ERK and inhibition of mTOR and p70 S6K in KBM-5 leukemia cells. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, O.S.; Jung, J.H.; Shin, E.A.; Park, J.E.; Park, W.Y.; Kim, S.-H. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Induces Apoptosis as a TRAIL Sensitizer via Activation of Caspase 8 and Death Receptor 5 in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040084
Kwon OS, Jung JH, Shin EA, Park JE, Park WY, Kim S-H. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Induces Apoptosis as a TRAIL Sensitizer via Activation of Caspase 8 and Death Receptor 5 in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040084
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Oh Sung, Ji Hoon Jung, Eun Ah Shin, Ji Eon Park, Woon Yi Park, and Sung-Hoon Kim. 2020. "Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Induces Apoptosis as a TRAIL Sensitizer via Activation of Caspase 8 and Death Receptor 5 in Human Colon Cancer Cells" Biomedicines 8, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040084
APA StyleKwon, O. S., Jung, J. H., Shin, E. A., Park, J. E., Park, W. Y., & Kim, S.-H. (2020). Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Induces Apoptosis as a TRAIL Sensitizer via Activation of Caspase 8 and Death Receptor 5 in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Biomedicines, 8(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040084