Musculoskeletal Features without Ataxia Associated with a Novel de novo Mutation in KCNA1 Impairing the Voltage Sensitivity of Kv1.1 Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical and Genetic Analysis
2.2. Mutagenesis and Expression of Kv1.1WT and Kv1.1T268K Channels
2.3. Electrophysiology
2.4. Homology Modeling
3. Results
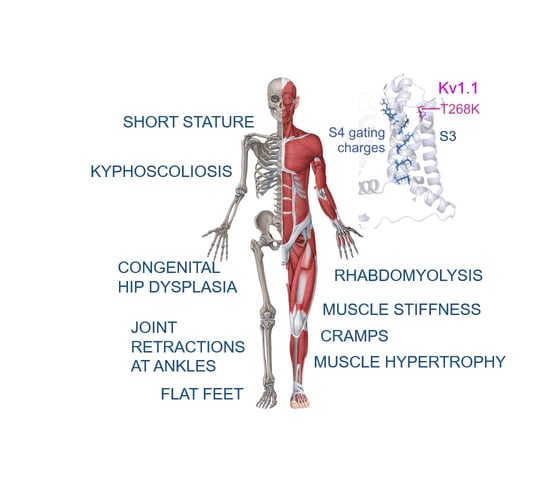
3.1. Case Report
3.2. Genetic Results
3.3. Functional Analysis of the Kv1.1T268K Channel
3.4. Structural Model of the Kv1.1T268K Channel
4. Discussion
4.1. Genotype–Phenotype Correlations and Clinical Implications
4.2. Molecular Findings and Channel Structure Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smart, S.L.; Lopantsev, V.; Zhang, C.L.; Robbins, C.A.; Wang, H.; Chiu, S.Y.; Schwartzkroin, P.A.; Messing, A.; Tempel, B.L. Deletion of the Kv1.1 potassium channel causes epilepsy in mice. Neuron 1998, 20, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herson, P.S.; Virk, M.; Rustay, N.R.; Bond, C.T.; Crabbe, J.C.; Adelman, J.P.; Maylie, J. A mouse model of episodic ataxia type-1. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, R.; Bakiri, Y.; Volynski, K.E.; Kullmann, D.M. Action potential broadening in a presynaptic channelopathy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; Mackinnon, R. Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent Shaker family K+ channel. Science 2005, 309, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paulhus, K.; Ammerman, L.; Glasscock, E. Clinical Spectrum of KCNA1 Mutations: New Insights into Episodic Ataxia and Epilepsy Comorbidity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, M.C.; Liantonio, A.; Rolland, J.-F.; Pessia, M.; Imbrici, P. Kv1.1 Channelopathies: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, D.L.; Gancher, S.T.; Nutt, J.G.; Brunt, E.R.P.; Smith, E.A.; Kramer, P.; Litt, M. Episodic ataxia/myokymia syndrome is associated with point mutations in the human potassium channel gene, KCNA1. Nat. Genet. 1994, 8, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, S.M.; Eunson, L.H.; Spauschus, A.; De Silva, R.; Tolmie, J.; Wood, N.W.; McWilliam, R.C.; Stephenson, J.B.; Stephenson, J.P.; Kullmann, D.M.; et al. A novel mutation in the human voltage-gated potassium channel gene (Kv1.1) associates with episodic ataxia type 1 and sometimes with partial epilepsy. Brain 1999, 122, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imbrici, P.; Gualandi, F.; D’Adamo, M.C.; Masieri, M.T.; Cudia, P.; De Grandis, D.; Mannucci, R.; Nicoletti, I.; Tucker, S.J.; Ferlini, A.; et al. A novel KCNA1 mutation identified in an Italian family affected by episodic ataxia type 1. Neuroscience 2008, 157, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdura, E.; Fons, C.; Schlüter, A.; Ruiz, M.; Fourcade, S.; Casasnovas, C.; Castellano, A.; Pujol, A. Complete loss of KCNA1 activity causes neonatal epileptic encephalopathy and dyskinesia. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Golumbek, P.; Cellini, E.; Doccini, V.; Guerrini, R.; Wallgren-Pettersson, C.; Thuresson, A.C.; Gurnett, C.A. De novo KCNA1 variants in the PVP motif cause infantile epileptic encephalopathy and cognitive impairment similar to recurrent KCNA2 variants. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2018, 176, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamo, M.C.; Gallenmuller, C.; Servettini, I.; Hartl, E.; Tucker, S.J.; Arning, L.; Biskup, S.; Grottesi, A.; Guglielmi, L.; Imbrici, P.; et al. Novel phenotype associated with a mutation in the KCNA1(Kv1.1) gene. Front. Physiol. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.M.; Lin, J.H.; Cao, L.; Zhang, T.M.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, K.L.; Tian, W.T.; Hu, Z.M.; Li, N.; Wang, J.L.; et al. Familial paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia is associated with mutations in the KCNA1 gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, T.A.; Manole, A.; MacDonald, H.; Riazi, S.; Kraeva, N.; Hanna, M.G.; Lang, A.E.; Männikkö, R.; Yoon, G. A novel KCNA1 mutation in a family with episodic ataxia and malignant hyperthermia. Neurogenetics 2016, 17, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Wijst, J.; Konrad, M.; Verkaart, S.A.J.; Tkaczyk, M.; Latta, F.; Altmüller, J.; Thiele, H.; Beck, B.; Schlingmann, K.P.; de Baaij, J.H.F. A de novo KCNA1 Mutation in a Patient with Tetany and Hypomagnesemia. Nephron 2018, 139, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imbrici, P.; Altamura, C.; Gualandi, F.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Neri, M.; De Maria, G.; Ferlini, A.; Padovani, A.; D’Adamo, M.C.; Nicolotti, O.; et al. A novel KCNA1 mutation in a patient with paroxysmal ataxia, myokymia, painful contractures and metabolic dysfunctions. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 83, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstein, C.A.; Beggs, A.H.; Rodan, L.; Shi, J.; Towne, M.C.; Pelletier, R.; Cao, S.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Urion, D.K.; Picker, J.; et al. Clinical heterogeneity associated with KCNA1 mutations include cataplexy and nonataxic presentations. Neurogenetics 2016, 17, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eunson, L.H.; Rea, R.; Zuberi, S.M.; Youroukos, S.; Panayiotopoulos, C.P.; Liguori, R.; Avoni, P.; McWilliam, R.C.; Stephenson, J.B.P.; Hanna, M.G.; et al. Clinical, genetic, and expression studies of mutations in the potassium channel gene KCNA1 reveal new phenotypic variability. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinali, M.; Jungbluth, H.; Eunson, L.H.; Sewry, C.A.; Manzur, A.Y.; Mercuri, E.; Hanna, M.G.; Muntoni, F. Expanding the phenotype of potassium channelopathy: Severe neuromyotonia and skeletal deformities without prominent Episodic Ataxia. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poujois, A.; Antoine, J.C.; Combes, A.; Touraine, R.L. Chronic neuromyotonia as a phenotypic variation associated with a new mutation in the KCNA1 gene. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; von Hehn, C.; Kaczmarek, L.K.; Ment, L.R.; Pober, B.R.; Hisama, F.M. Functional analysis of a novel potassium channel (KCNA1) mutation in hereditary myokymia. Neurogenetics 2007, 8, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Petitjean, D.; Haddad, G.A.; Batulan, Z.; Blunck, R. A Common Kinetic Property of Mutations Linked to Episodic Ataxia Type 1 Studied in the Shaker Kv Channel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.B.; Tao, X.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature 2007, 450, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sali, A.; Blundell, T.L. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L., 3rd; Mackerell, A.D., Jr.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The biomolecular simulation program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.C.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 044130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starace, D.M.; Bezanilla, F. A proton pore in a potassium channel voltage sensor reveals a focused electric field. Nature 2004, 427, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombola, F.; Pathak, M.M.; Isacoff, E.Y. Voltage-sensing arginines in a potassium channel permeate and occlude cation-selective pores. Neuron 2005, 45, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chanda, B.; Asamoah, O.K.; Blunck, R.; Roux, B.; Bezanilla, F. Gating charge displacement in voltage-gated ion channels involves limited transmembrane movement. Nature 2005, 436, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Blunck, R. The isolated voltage sensing domain of the Shaker potassium channel forms a voltage-gated cation channel. Elife 2016, 5, e18130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Bezanilla, F.; Roux, B. In search of a consensus model of the resting state of a voltage-sensing domain. Neuron 2011, 72, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersson, M.; Freites, J.A.; Tobias, D.J.; White, S.H. Structural Dynamics of the S4 Voltage-Sensor Helix in Lipid Bilayers Lacking Phosphate Groups. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 8732–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Wanderling, S.; Paduch, M.; Medovoy, D.; Singharoy, A.; McGreevy, R.; Villalba-Galea, C.A.; Hulse, R.E.; Roux, B.; Schulten, K.; et al. Structural mechanism of voltage-dependent gating in an isolated voltage-sensing domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrici, P.; D’Adamo, M.C.; Cusimano, A.; Pessia, M. Episodic ataxia type 1 mutation F184C alters Zn2+-induced modulation of the human K+ channel Kv1.4-Kv1.1/Kvbeta1.1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C778–C787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, T.D.; Cha, Y.H.; Hahn, A.F.; Barohn, R.; Salajegheh, M.K.; Griggs, R.C.; Bundy, B.N.; Jen, J.C.; Baloh, R.W.; Hanna, M.G.; et al. Episodic ataxia type 1: Clinical characterization, quality of life and genotype-phenotype correlation. Brain 2014, 137, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodson, P.D.; Forsythe, I.D. Presynaptic K+ channels: Electrifying regulators of synaptic terminal excitability. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, J.S. Subcellular localization of K+ channels in mammalian brain neurons: Remarkable precision in the midst of extraordinary complexity. Neuron 2015, 85, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kv1.1 knock-in ataxic mice exhibit spontaneous myokymic activity exacerbated by fatigue, ischemia and low temperature. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 47, 310–321. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.L.; Messing, A.; Chiu, S.Y. Temperature-sensitive neuromuscular transmission in Kv1.1 null mice: Role of potassium channels under the myelin sheath in young nerves. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7200–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Messing, A.; Chiu, S.Y. Determinants of excitability at transition zones in Kv1.1-deficient myelinated nerves. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5768–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abeynayake, N.; Arthur, A.; Gronthos, S. Crosstalk between skeletal and neural tissues is critical for skeletal health. Bone 2021, 142, 115645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Smerin, Y.; Swartz, K.J. Helical structure of the COOH terminus of S3 and its contribution to the gating modifier toxin receptor in voltage-gated ion channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2001, 117, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henrion, U.; Renhorn, J.; Börjesson, S.I.; Nelson, E.M.; Schwaiger, C.S.; Bjelkmar, P.; Wallner, B.; Lindahl, E.; Elinder, F. Tracking a complete voltage-sensor cycle with metal-ion bridges. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8552–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Börjesson, S.I.; Elinder, F. An electrostatic potassium channel opener targeting the final voltage sensor transition. J. Gen. Physiol. 2011, 137, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, É.; Starek, G.; McGuire, H.; Bernèche, S.; Blunck, R. A limited 4 Å radial displacement of the S4-S5 linker is sufficient for internal gate closing in Kv channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40091–40098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faure, É.; Thompson, C.; Blunck, R. Do lipids show state-dependent affinity to the voltage-gated potassium channel KvAP? J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16452–16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, D.; Jiang, Q.X.; MacKinnon, R. Phospholipids and the origin of cationic gating charges in voltage sensors. Nature 2006, 444, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosson, N.E.; Ejneby, M.S.; Wu, X.; Yazdi, S.; Konradsson, P.; Lindahl, E.; Elinder, F. A drug pocket at the lipid bilayer-potassium channel interface. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yazdi, S.; Stein, M.; Elinder, F.; Andersson, M.; Lindahl, E. The Molecular Basis of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Interactions with the Shaker Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel. PloS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoglio-Simeone, K.A.; Wilke, J.C.; Milligan, H.L.; Allen, C.N.; Rho, J.M.; Maganti, R.K. Ketogenic diet treatment abolishes seizure periodicity and improves diurnal rhythmicity in epileptic Kcna1-null mice. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imbrici, P.; Liantonio, A.; Camerino, G.M.; De Bellis, M.; Camerino, C.; Mele, A.; Giustino, A.; Pierno, S.; De Luca, A.; Tricarico, D.; et al. Therapeutic Approaches to Genetic Ion Channelopathies and Perspectives in Drug Discovery. Front. Pharm. 2016, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Voltage Dependence of Activation | Kinetic of Activation | Kinetic of Deactivation | C-Type Inactivation (Amplitude %) +40 mV | Recovery from Inactivation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1/2 (mV) | k (mV) | τV1/2 (ms) | τV1/2 (ms) | τfast (s) | τslow (s) | τ (s) | |
| WT | −25.8 ± 0.4 (10) | 7.4 ± 0.4 (10) | 7.3 ± 0.8 (16) | 25.0 ± 0.6 (10) | 3.9 ± 0.3 (51%) (9) | 32.4 ± 2.4 (49%) (9) | 3.9 ± 0.7 (6) |
| T268K | −11.8 ± 0.3 ** (14) | 9.1 ± 0.3 (14) | 4.4 ± 0.8 (12) | 17.0 ± 0.4 * (10) | 4.0 ± 0.4 (47%) (11) | 30.8 ± 5.3 (53%) (11) | 3.4 ± 0.7 (8) |
| WT + T268K | −15.9 ± 0.4 * (18) | 8.1 ± 0.4 (18) | 5.9 ± 0.6 (19) | 28.0 ± 1.0 (11) | 4.8 ± 0.5 (55%) (11) | 35.7 ± 4.1 (47%) (11) | 3.8 ± 0.8 (10) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imbrici, P.; Accogli, A.; Blunck, R.; Altamura, C.; Iacomino, M.; D’Adamo, M.C.; Allegri, A.; Pedemonte, M.; Brolatti, N.; Vari, S.; et al. Musculoskeletal Features without Ataxia Associated with a Novel de novo Mutation in KCNA1 Impairing the Voltage Sensitivity of Kv1.1 Channel. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010075
Imbrici P, Accogli A, Blunck R, Altamura C, Iacomino M, D’Adamo MC, Allegri A, Pedemonte M, Brolatti N, Vari S, et al. Musculoskeletal Features without Ataxia Associated with a Novel de novo Mutation in KCNA1 Impairing the Voltage Sensitivity of Kv1.1 Channel. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010075
Chicago/Turabian StyleImbrici, Paola, Andrea Accogli, Rikard Blunck, Concetta Altamura, Michele Iacomino, Maria Cristina D’Adamo, Anna Allegri, Marina Pedemonte, Noemi Brolatti, Stella Vari, and et al. 2021. "Musculoskeletal Features without Ataxia Associated with a Novel de novo Mutation in KCNA1 Impairing the Voltage Sensitivity of Kv1.1 Channel" Biomedicines 9, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010075
APA StyleImbrici, P., Accogli, A., Blunck, R., Altamura, C., Iacomino, M., D’Adamo, M. C., Allegri, A., Pedemonte, M., Brolatti, N., Vari, S., Cataldi, M., Capra, V., Gustincich, S., Zara, F., Desaphy, J. -F., & Fiorillo, C. (2021). Musculoskeletal Features without Ataxia Associated with a Novel de novo Mutation in KCNA1 Impairing the Voltage Sensitivity of Kv1.1 Channel. Biomedicines, 9(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010075