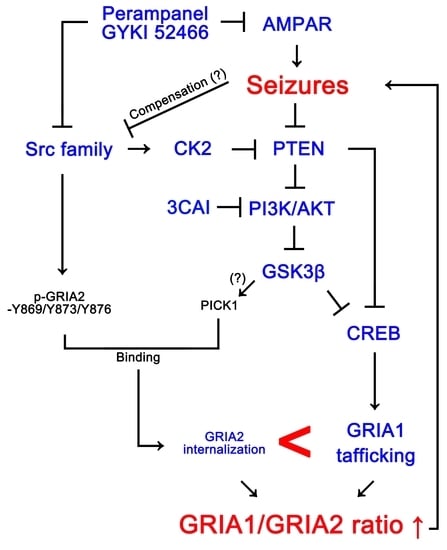
Inhibition of AKT/GSK3β/CREB Pathway Improves the Responsiveness to AMPA Receptor Antagonists by Regulating GRIA1 Surface Expression in Chronic Epilepsy Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Chemicals
2.2. Generation of Chronic Epilepsy Rats
2.3. Surgery
2.4. Drug Trials, EEG Analysis and Quantification of Behavioral Seizure Activity
2.4.1. Experiment I
2.4.2. Experiment II
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of AMPAR Antagonists on Chronic Spontaneous Seizure Activity
3.2. Effects of AMPAR Antagonists on GRIA2 Phosphorylations
3.3. Effects of AMPAR Antagonists on PKC and Src Phosphorylations
3.4. Effects of AMPAR Antagonists on PICK1 Expression
3.5. Effects of AMPAR Antagonists on GSK3β Phosphorylation
3.6. Effect of 3CAI Co-Treatment on Refractory Seizures in Non-Responders to AMPAR Antagonists
3.7. Effect of 3CAI Co-Treatment on PICK1 Expression and Phosphorylations of GSK3β and CREB in Non-Responders
3.8. Effect of 3CAI Co-Treatment on Surface GRIA Expressions in Non-Responders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aylward, R.L. Epilepsy: A review of reports, guidelines, recommendations and models for the provision of care for patients with epilepsy. Clin. Med. 2008, 8, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, R.; Norrie, J.; Stephen, L.J.; Kelly, K.; Hitiris, N.; Brodie, M.J. Mortality in adults with newly diagnosed and chronic epilepsy: A retrospective comparative study. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, R.E.; Deshpande, L.S.; Sombati, S.; Elphick, M.R.; Martin, B.R.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Prolonged exposure to WIN55,212-2 causes downregulation of the CB1 receptor and the development of tolerance to its anticonvulsant effects in the hippocampal neuronal culture model of acquired epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, R.E.; Sombati, S.; Churn, S.B.; Delorenzo, R.J. Epileptogenesis causes an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor/Ca2+-dependent decrease in Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in a hippocampal neuronal culture model of spontaneous recurrent epileptiform discharges. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 588, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberta, C.; Francesco, F. Targeting ionotropic glutamate receptors in the treatment of epilepsy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, B.; Stott, J.J.; Joelle Donofrio, J.; Rogawski, M.A. Treatment of early and late kainic acid-induced status epilepticus with the noncompetitive AMPA receptor antagonist GYKI 52466. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niquet, J.; Baldwin, R.; Norman, K.; Suchomelova, L.; Lumley, L.; Wasterlain, C.G. Simultaneous triple therapy for the treatment of status epilepticus. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 104, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, H.; Sekar, S.; Wei, Z.; Moien-Afshari, F.; Taghibiglou, C. Perampanel but not amantadine prevents behavioral alterations and epileptogenesis in pilocarpine rat model of status epilepticus. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2508–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essin, K.; Nistri, A.; Magazanik, L. Evaluation of GluR2 subunit involvement in AMPA receptor function of neonatal rat hypoglossal motoneurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greger, I.H.; Khatri, L.; Ziff, E.B. RNA editing at arg607 controls AMPA receptor exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Neuron 2002, 34, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barria, A.; Derkach, V.; Soderling, T. Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate-type glutamate receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32727–32730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidenman, K.J.; Steinberg, J.P.; Huganir, R.; Malinow, R. Glutamate receptor subunit 2 Serine 880 phosphorylation modulates synaptic transmission and mediates plasticity in CA1 pyramidal cells. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9220–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Barbarosie, M.; Kameyama, K.; Bear, M.F.; Huganir, R.L. Regulation of distinct AMPA receptor phosphorylation sites during bidirectional synaptic plasticity. Nature 2000, 405, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinow, R.; Malenka, R.C. AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyszynski, M.; Valtschanoff, J.G.; Naisbitt, S.; Dunah, A.W.; Kim, E.; Standaert, D.G.; Weinberg, R.; Sheng, M. Association of AMPA receptors with a subset of glutamate receptor-interacting protein in vivo. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6528–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Jia, R.; Yuan, F.; Wei, D.; Jiang, W. Melatonin alleviates the epilepsy-associated impairments in hippocampal LTP and spatial learning through rescue of surface GluR2 expression at hippocampal CA1 synapses. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorgen, J.Ø.; Egbenya, D.L.; Hammer, J.; Davanger, S. PICK1 facilitates lasting reduction in GluA2 concentration in the hippocampus during chronic epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 137, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Gorter, J.A.; Bennett, M.V.; Zukin, R.S. The GluR2 (GluR-B) hypothesis: Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors in neurological disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, D.S.; Park, H.; Kang, T.C. Src/CK2/PTEN-mediated GluN2B and CREB dephosphorylations regulate the responsiveness to AMPA receptor antagonists in chronic epilepsy Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Park, H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, T.C. PTEN is required for the anti-epileptic effects of AMPA receptor antagonists in chronic epileptic rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.J.; Xia, J.; Scannevin, R.H.; Zhang, X.; Huganir, R.L. Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 differentially regulates its interaction with PDZ domain-containing proteins. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7258–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Chung, H.J.; Lee, H.K.; Huganir, R.L. Interaction of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR2/3 with PDZ domains regulates hippocampal long-term depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11725–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, G.; Ju, W.; Liu, L.; Wyszynski, M.; Lee, S.H.; Dunah, A.W.; Taghibiglou, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wong, T.P.; et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of GluR2 is required for insulin-stimulated AMPA receptor endocytosis and LTD. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Huganir, R.L. Tyrosine phosphorylation and regulation of the AMPA receptor by SRC family tyrosine kinases. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6152–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.R.; Kang, T.C. Blockade of endothelin B receptor improves the efficacy of levetiracetam in chronic epileptic rats. Seizure 2015, 31, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, H.C.; Song, H.K.; Kang, T.C. Perampanel affects up-stream regulatory signaling pathways of GluA1 phosphorylation in normal and epileptic rats. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Park, H.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, T.C. Blockade of 67-kDa laminin receptor facilitates AQP4 down-regulation and BBB disruption via ERK1/2-and p38 MAPK-mediated PI3K/AKT activations. Cells 2020, 9, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Src kinase regulation by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Src protein-tyrosine kinase structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, A. Drug development targeting the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta)-mediated signal transduction pathway: Role of GSK-3beta in adult brain. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 109, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, C.A.; Jope, R.S. CREB DNA binding activity is inhibited by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and facilitated by lithium. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, C.A.; Jope, R.S. The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 391–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagishita, S.; Murayama, M.; Ebihara, T.; Maruyama, K.; Takashima, A. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β-mediated phosphorylation in the most C-terminal region of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) regulates the binding of PICK1 to glutamate receptor subunit GluA2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29438–29448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.J.; Chen, J.; Zien, A.; Sochivko, D.; Normann, S.; Schramm, J.; Elger, C.E.; Wiestler, O.D.; Blümcke, I. Correlated stage- and subfield-associated hippocampal gene expression patterns in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dubey, D.; Bermudez, C.; Porter, B.E. Suppressing cAMP response element-binding protein transcription shortens the duration of status epilepticus and decreases the number of spontaneous seizures in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middei, S.; Houeland, G.; Cavallucci, V.; Ammassari-Teule, M.; D’Amelio, M.; Marie, H. CREB is necessary for synaptic maintenance and learning-induced changes of the AMPA receptor GluA1 subunit. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P. Molecular basis of NMDA receptor functional diversity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, G.T.; Hanley, J.G. Mechanisms of AMPA Receptor Endosomal Sorting. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, E.; Passafaro, M. Recent Findings on AMPA Receptor Recycling. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greger, I.H.; Esteban, J.A. AMPA receptor biogenesis and trafficking. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J. Mechanisms of synaptic plasticity: From membrane to intracellular AMPAR trafficking. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindle, P.K.; Montminy, M.R. The CREB family of transcription activators. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1992, 2, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, P. Transcription factors responsive to cAMP. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moult, P.R.; Cross, A.; Santos, S.D.; Carvalho, A.L.; Lindsay, Y.; Connolly, C.N.; Irving, A.J.; Leslie, N.R.; Harvey, J. Leptin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking via PTEN inhibition. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4088–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacka, J.J.; Lu, J.; Xie, Z.L.; Uchiyama, Y.; Roth, K.A.; Zhang, J. Kainic acid induces early and transient autophagic stress in mouse hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 414, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Kai, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, L.H. Akt Inhibitor perifosine prevents epileptogenesis in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talos, D.M.; Jacobs, L.M.; Gourmaud, S.; Coto, C.A.; Sun, H.; Lim, K.C.; Lucas, T.H.; Davis, K.A.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Jensen, F.E. Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 and 2 in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, H.N.; El-Tanbouly, D.M.; Zaki, H.F. Topiramate mitigates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal neurotoxicity via modulation of AMPA receptors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.; Levey, A.I.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Jin, L.; Wu, D.; Nash, N.; Kuncl, R.W. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 1994, 13, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arstikaitis, P.; Gauthier-Campbell, C. BARS at the synapse: PICK-1 lipid binding domain regulates targeting, trafficking, and synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 6909–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertaso, F.; Zhang, C.; Scheschonka, A.; de Bock, F.; Fontanaud, P.; Marin, P.; Huganir, R.L.; Betz, H.; Bockaert, J.; Fagni, L.; et al. PICK1 uncoupling from mGluR7a causes absence-like seizures. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, H.C.; Song, H.K.; Kang, T.C. Cellular and regional specific changes in multidrug efflux transporter expression during recovery of vasogenic edema in the rat hippocampus and piriform cortex. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. TRPC3- and ETB receptor-mediated PI3K/AKT activation induces vasogenic edema formation following status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2017, 1672, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekaart, D.W.M.; Anink, J.J.; Baayen, J.C.; Idema, S.; de Vries, H.E.; Aronica, E.; Gorter, J.A.; van Vliet, E.A. Activation of the innate immune system is evident throughout epileptogenesis and is associated with blood-brain barrier dysfunction and seizure progression. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Saavedra, J.M.; Shi, L.; et al. MALAT1 up-regulator polydatin protects brain microvascular integrity and ameliorates stroke through C/EBPβ/MALAT1/CREB/PGC-1α/PPARγ pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fu, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, H.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, Z. NDP-MSH binding melanocortin-1 receptor ameliorates neuroinflammation and BBB disruption through CREB/Nr4a1/NF-κB pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Antigen | Host | Manufacturer (Catalog Number) | Dilution Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| CREB | Rabbit | Novus biologicals (NBP1-90364) | 1:500 (WB) |
| GRIA1 | Mouse | Synaptic systems (#182011) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| GRIA2 | Rabbit | Sigma (AB1768-I) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| GSK3β | Rabbit | Elapscience (ENT2082) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| N-cadherin | Rabbit | Abcam (ab182030) | 1:4000 (WB) |
| p-CREB S133 | Rabbit | Novus biologicals (NB110-55727) | 1:5000 (WB) |
| p-GRIA2 Y869/Y873/Y876 | Rabbit | Cell signaling (#3921) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| p-GRIA2 S880 | Rabbit | Invitrogen (#PA5-38134) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| p-GSK3β S9 | Rabbit | Biorbyt (orb14745) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| p-PKC T497 | Rabbit | Abcam (ab76016) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| p-Src family Y416 | Rabbit | Cell signaling (#6943) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| p-Src family Y527 | Rabbit | Cell signaling (#2105) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| PICK1 | Rabbit | Abcam (ab3420) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| PKC | Rabbit | Abcam (ab23511) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| Src family | Rabbit | Cell signaling (#2108) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| β-actin | Mouse | Sigma (#A5316) | 1:5000 (WB) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-E.; Lee, D.-S.; Park, H.; Kim, T.-H.; Kang, T.-C. Inhibition of AKT/GSK3β/CREB Pathway Improves the Responsiveness to AMPA Receptor Antagonists by Regulating GRIA1 Surface Expression in Chronic Epilepsy Rats. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040425
Kim J-E, Lee D-S, Park H, Kim T-H, Kang T-C. Inhibition of AKT/GSK3β/CREB Pathway Improves the Responsiveness to AMPA Receptor Antagonists by Regulating GRIA1 Surface Expression in Chronic Epilepsy Rats. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(4):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040425
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji-Eun, Duk-Shin Lee, Hana Park, Tae-Hyun Kim, and Tae-Cheon Kang. 2021. "Inhibition of AKT/GSK3β/CREB Pathway Improves the Responsiveness to AMPA Receptor Antagonists by Regulating GRIA1 Surface Expression in Chronic Epilepsy Rats" Biomedicines 9, no. 4: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040425
APA StyleKim, J. -E., Lee, D. -S., Park, H., Kim, T. -H., & Kang, T. -C. (2021). Inhibition of AKT/GSK3β/CREB Pathway Improves the Responsiveness to AMPA Receptor Antagonists by Regulating GRIA1 Surface Expression in Chronic Epilepsy Rats. Biomedicines, 9(4), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040425