Multiplex PCR and Antibiotic Use in Children with Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Definitions and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
- Acute onset of fever ≥ 39 °C
- Pleuritic chest pain or equivalent (abdominal pain, meningismus)
- Focal lung auscultation (tubal murmur, hypoventilation or crackles)
- Focal consolidation in chest radiographs
- Leucocytosis > 12,000/mm3 with neutrophilia > 6000/mm3
- C-reactive protein (CRP) level > 60 mg/L
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Patients and Controls
3.2. Multiplex PCR Results
3.3. Antibiotic Prescription
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katz, S.E.; Williams, D.J. Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia in the United States: Changing Epidemiology, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges, and Areas for Future Research. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruuskanen, O.; Lahti, E.; Jennings, L.C.; Murdoch, D.R. Viral pneumonia. Lancet 2011, 377, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, D.A.; Peetluk, L.S.; Deppen, S.; Slaughter, J.C.; Katz, S.; Halasa, N.B.; Khankari, N.K. Diagnostic models predicting paediatric viral acute respiratory infections: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e067878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.W.; Wallihan, R.; Juergensen, A.; Mejias, A.; Ramilo, O. Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children: Myths and Facts. Am. J. Perinatol. 2019, 36, S54–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhedin, S.; Lindstrand, A.; Rotzén-Östlund, M.; Tolfvenstam, T.; Ohrmalm, L.; Rinder, M.R.; Zweygberg-Wirgart, B.; Ortqvist, A.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Broliden, K.; et al. Clinical utility of PCR for common viruses in acute respiratory illness. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e538–e545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gageldonk-Lafeber, A.B.; Heijnen, M.-L.A.; Bartelds, A.I.M.; Peters, M.F.; van der Plas, S.M.; Wilbrink, B. A case-control study of acute respiratory tract infection in general practice patients in The Netherlands. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Argentiero, A.; Rebecchi, F.; Fainardi, V.; Pisi, G.; Principi, N. The remaining unsolved problems for rational antibiotic therapy use in pediatric community-acquired pneumonia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigadoi, G.; Gastaldi, A.; Moi, M.; Barbieri, E.; Rossin, S.; Biffi, A.; Cantarutti, A.; Giaquinto, C.; Da Dalt, L.; Donà, D. Point-of-Care and Rapid Tests for the Etiological Diagnosis of Respiratory Tract Infections in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Xie, L.; Cao, Q.; Tao, Y.; et al. Evaluation of Molecular Point-of-Care Testing for Respiratory Pathogens in Children With Respiratory Infections: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 778808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriacko, P.; Saiman, L.; Zachariah, P. Antibiotic Use in Hospitalized Children With Respiratory Viruses Detected by Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramony, A.; Zachariah, P.; Krones, A.; Whittier, S.; Saiman, L. Impact of Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing for Respiratory Pathogens on Healthcare Resource Utilization for Pediatric Inpatients. J. Pediatr. 2016, 173, 196–201.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Suzuki, R.; Onaka, M.; Nishiyama, A.; Kitagawa, D.; Oka, M.; Masuo, K.; Yoshida, S. The impact analysis of a multiplex PCR respiratory panel for hospitalized pediatric respiratory infections in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.T.; Nunes, J.C.F.; Estrela, M.; Figueiras, A.; Roque, F.; Herdeiro, M.T. Comparing Hospital and Primary Care Physicians’ Attitudes and Knowledge Regarding Antibiotic Prescribing: A Survey within the Centre Region of Portugal. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Lago, J.M.; Lopez-Vazquez, P.; López-Durán, A.; Taracido-Trunk, M.; Figueiras, A. Attitudes of primary care physicians to the prescribing of antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance: A qualitative study from Spain. Fam. Pract. 2012, 29, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Echevarría, A.; García de Miguel, M.J.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; del Castillo Martí, F. Neumonía comunitaria. In Protocolos Diagnóstico-Terapeúticos de Infectología Pediátrica; Sociedad Española de Infectología Pediátrica-Asociación Española de Pediatría: Madrid, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Leber, A.L.; Everhart, K.; Daly, J.A.; Hopper, A.; Harrington, A.; Schreckenberger, P.; McKinley, K.; Jones, M.; Holmberg, K.; Kensinger, B. Multicenter Evaluation of BioFire FilmArray Respiratory Panel 2 for Detection of Viruses and Bacteria in Nasopharyngeal Swab Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01945-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Jang, K.M.; Hau, Y.S.; Lee, J.M. Rapid Molecular Tests for Detecting Respiratory Pathogens Reduced the Use of Antibiotics in Children. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, S.A.; Marin, J.R.; Hall, M.; Ralston, S.L. Trends Over Time in Use of Nonrecommended Tests and Treatments Since Publication of the American Academy of Pediatrics Bronchiolitis Guideline. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2037356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, T.; Stark, E.; Pattemore, P.; Jennings, L. Missed opportunities for antimicrobial stewardship in pre-school children admitted to hospital with lower respiratory tract infection. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 53, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotons, P.; Villaronga, M.; Henares, D.; Armero, G.; Launes, C.; Jordan, I.; Muñoz-Almagro, C. Clinical impact of rapid viral respiratory panel testing on pediatric critical care of patients with acute lower respiratory infection. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 40, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echavarría, M.; Marcone, D.N.; Querci, M.; Seoane, A.; Ypas, M.; Videla, C.; O’Farrell, C.; Vidaurreta, S.; Ekstrom, J.; Carballal, G. Clinical impact of rapid molecular detection of respiratory pathogens in patients with acute respiratory infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 108, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.R.; Hassan, F.; Jackson, M.A.; Selvarangan, R. Impact of multiplex molecular assay turn-around-time on antibiotic utilization and clinical management of hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 110, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schram, L.; Novak-Weekley, S.; Chen, Q.; Han, P. Impact of a Rapid Respiratory Pathogen Panel on Antibiotic and Chest Radiography Usage and Hospital Length of Stay in the Pediatric Inpatient Setting. Perm. J. 2022, 26, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, J.M.; Florin, T.A.; Moss, A.; Suresh, K.; Ramgopal, S.; Navanandan, N.; Shah, S.S.; Ruddy, R.M.; Ambroggio, L. Factors Associated With Antibiotic Use for Children Hospitalized With Pneumonia. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2021054677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratnam, L.C.; Robinson, J.L.; Hawkes, M.T. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Biomarkers for Pediatric Pneumonia. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, M.L.; Pérez-Arenas, E.; Pérez-Hernandez, P.; Falces-Romero, I.; Ruiz, S.; Pozo, F.; Casas, I.; Calvo, C. Human Metapneumovirus Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, D.; Groendahl, B.; Puppe, W.; Off, H.N.T.; Poplawska, K.; Knuf, M.; Meyer, C.U.; Reischl, A.T.; Gehring, S. High antibiotic prescription rates in hospitalized children with human metapneumovirus infection in comparison to RSV infection emphasize the value of point-of-care diagnostics. Infection 2019, 47, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wils, J.; Saegeman, V.; Schuermans, A. Impact of multiplexed respiratory viral panels on infection control measures and antimicrobial stewardship: A review of the literature. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, T.S.; Stevens, M.P.; Bearman, G. Syndromic Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (mPCR) Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship: Current Practice and Future Directions. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.J.; Uyeki, T.M.; Chu, H.Y. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patients (n = 64) | Controls (n = 50) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, months | 26 (18–43) | 26 (15–50.5) | 0.895 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 36 (56%) | 24 (48%) | 0.381 |
| Prematurity, n (%) | 12 (19%) | 5 (10%) | 0.193 |
| Underlying medical conditions, n (%) | 14 (22%) | 10 (20%) | 0.807 |
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Breathing difficulty, n (%) | 62 (97%) | 45 (90%) | 0.237 |
| Wheezing, n (%) | 51 (80%) | 38 (76%) | 0.655 |
| Appears unwell a, n (%) | 12 (19%) | 4 (8%) | 0.113 |
| Hypoxaemia b, n (%) | 59 (92%) | 42 (84%) | 0.237 |
| Laboratory results | |||
| Leukocyte count/mm3 | 10,310 (7700–13,828) | 11,800 (8000–15,850) | 0.642 |
| Neutrophil count/mm3 | 6815 (4565–9858) | 7397 (3603–11,755) | 0.947 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 28.7 (13.5–72) | 12.5 (4.7–23.6) | <0.0001 |
| Chest X-ray results | |||
| Infiltrates, n (%) | 31 (48%) | 35 (70%) | 0.002 |
| Focal consolidation, n (%) | 32 (50%) | 14 (28%) | 0.0175 |
| Pleural effusion, n (%) | 1 (1.6%) | 1 (2%) | 1 |
| ICU admission, n (%) | 7 (11%) | 5 (10%) | 1 |
| Hospital stay, days | 4 (3–6) | 3 (2–4.3) | <0.0001 |
| Patients (n = 64) | Controls (n = 50) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
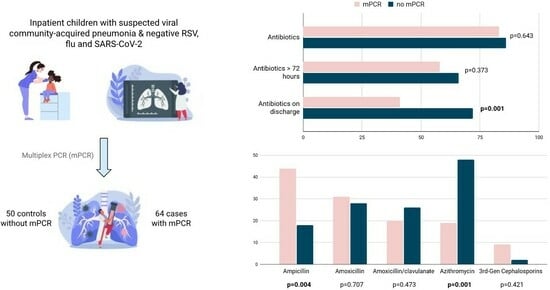
| Any antibiotic treatment | 53 (83%) | 43 (86%) | 0.643 |
| Antibiotics ≥ 72 h | 37 (58%) | 33 (66%) | 0.373 |
| Antibiotics after discharge | 26 (41%) | 36 (72%) | 0.001 |
| Total antibiotic duration, days; median (IQR) | 7 (2–8.5) | 6 (3–8) | 0.764 |
| Antibiotics | |||
| Ampicillin | 28 (44%) | 9 (18%) | 0.004 |
| Amoxicillin | 20 (31%) | 14 (28%) | 0.707 |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanate | 13 (20%) | 13 (26%) | 0.473 |
| Azithromycin | 12 (19%) | 24 (48%) | 0.001 |
| Cefotaxime or ceftriaxone | 6 (9%) | 1 (2%) | 0.421 |
| RV/EV, CoV, ADV (n = 21) | Other Pathogens (n = 34) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any antibiotic treatment, n (%) | 18 (86%) | 28 (82%) | 1 |
| Antibiotics ≥ 72 h, n (%) | 10 (48%) | 20 (59%) | 0.578 |
| Antibiotics after discharge, n (%) | 6 (29%) | 14 (41%) | 0.399 |
| Total antibiotic duration | 5.5 (1–8.25) | 7 (2–8) | 0.459 |
| Hospital stay, days | 5 (4–6.5) | 4 (2–7) | 0.372 |
| Antibiotics (n = 96) | No antibiotics (n = 18) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, months | 26.5 (17.3–48.8) | 22 (9.5–42.3) | 0.104 |
| Leukocyte count/mm3 | 11,730 (7850–15,910) | 9515 (7072–10,730) | 0.034 |
| Neutrophil count/mm3 | 7425 (4515–11,755) | 5920 (4296–7602) | 0.067 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 23.9 (10.5–50.6) | 12.3 (6.1–18.9) | 0.005 |
| ICU admission, n (%) | 11 (12%) | 1 (6%) | 0.688 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
del Rosal, T.; Bote-Gascón, P.; Falces-Romero, I.; Sainz, T.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Rodríguez-Molino, P.; Méndez-Echevarría, A.; Bravo-Queipo-de-Llano, B.; Alonso, L.A.; Calvo, C. Multiplex PCR and Antibiotic Use in Children with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Children 2024, 11, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020245
del Rosal T, Bote-Gascón P, Falces-Romero I, Sainz T, Baquero-Artigao F, Rodríguez-Molino P, Méndez-Echevarría A, Bravo-Queipo-de-Llano B, Alonso LA, Calvo C. Multiplex PCR and Antibiotic Use in Children with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Children. 2024; 11(2):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020245
Chicago/Turabian Styledel Rosal, Teresa, Patricia Bote-Gascón, Iker Falces-Romero, Talía Sainz, Fernando Baquero-Artigao, Paula Rodríguez-Molino, Ana Méndez-Echevarría, Blanca Bravo-Queipo-de-Llano, Luis A. Alonso, and Cristina Calvo. 2024. "Multiplex PCR and Antibiotic Use in Children with Community-Acquired Pneumonia" Children 11, no. 2: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020245
APA Styledel Rosal, T., Bote-Gascón, P., Falces-Romero, I., Sainz, T., Baquero-Artigao, F., Rodríguez-Molino, P., Méndez-Echevarría, A., Bravo-Queipo-de-Llano, B., Alonso, L. A., & Calvo, C. (2024). Multiplex PCR and Antibiotic Use in Children with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Children, 11(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020245