Neurodevelopmental Outcomes after Congenital Heart Disease Surgery in Infancy: A 2-Year Serial Follow-Up
Abstract
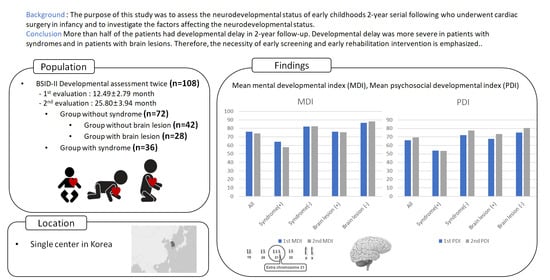
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Bayley Scales of Infant Development II (BSID-II)
2.3. Other Measurements
2.4. Subgroups of the Patients
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Neurodevelopment Outcomes in Children after Heart Surgery
3.3. Comparison of the Neurodevelopment Outcomes between the Patients with and without Syndrome
3.4. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in the Group of Full-Term Patients According to the Presence of the Syndrome (n = 49)
3.5. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in the Group without Syndrome According to the Presence of Brain Lesion
3.6. Factors Associated with the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Patients without Syndrome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boneva, R.S.; Botto, L.D.; Moore, C.A.; Yang, Q.; Correa, A.; Erickson, J.D. Mortality Associated With Congenital Heart Defects in the United States. Circulation 2001, 103, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marino, B.S.; Lipkin, P.; Newburger, J.W.; Peacock, G.; Gerdes, M.; Gaynor, J.W.; Mussatto, K.A.; Uzark, K.; Goldberg, C.S.; Johnsonjr, W.H.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Children With Congenital Heart Disease: Evaluation and Management. Circulation 2012, 126, 1143–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellinger, D.C.; Wypij, D.; Rivkin, M.J.; DeMaso, D.R.; Robertson, R.L., Jr.; Dunbar-Masterson, C.; Rappaport, L.A.; Wernovsky, G.; Jonas, R.A.; Newburger, J.W. Adolescents With d-Transposition of the Great Arteries Corrected With the Arterial Switch Procedure. Circulation 2011, 124, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, G.R.; Harrison, M.J.; Williamson, D.L. Is “Treat your child normally” helpful advice for parents of survivors of treatment of hypoplastic left heart syndrome? Cardiol. Young 2009, 19, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snookes, S.H.; Gunn, J.K.; Eldridge, B.J.; Donath, S.M.; Hunt, R.W.; Galea, M.P.; Shekerdemian, L. A Systematic Review of Motor and Cognitive Outcomes after Early Surgery for Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e818–e827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, J.W.; Stopp, C.; Wypij, D.; Andropoulos, D.B.; Atallah, J.; Atz, A.M.; Beca, J.; Donofrio, M.T.; Duncan, K.; Ghanayem, N.S.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery in Infancy. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majnemer, A.; Limperopoulos, C.; Shevell, M.; Rohlicek, C.; Rosenblatt, B.; Tchervenkov, C. Developmental and Functional Outcomes at School Entry in Children with Congenital Heart Defects. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, R.E.; Clark, B.G.; Robertson, C.M.; Moddemann, D.M.; Dinu, I.A.; Joffe, A.R.; Sauve, R.S.; Creighton, D.E.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Ross, D.B.; et al. Five-year neurocognitive and health outcomes after the neonatal arterial switch operation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 1413–1421.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naef, N.; Liamlahi, R.; Beck, I.; Bernet, V.; Dave, H.; Knirsch, W.; Latal, B. Neurodevelopmental Profiles of Children with Congenital Heart Disease at School Age. J. Pediatr. 2017, 188, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, N. Manual for the Bayley Scales of Infant Development, 2nd ed.; Pyschological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development; Pearson Education: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Yum, M.-S.; Jeong, S.-J.; Ko, T.-S. Assessment of children with developmental delay: Korean infant and child development test (KICDT) and Korean Bayley scale of infant development-II (K-BSID-II). Korean J. Pediatr. 2009, 52, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Biarge, M.; Jowett, V.C.; Cowan, F.M.; Wusthoff, C. Neurodevelopmental outcome in children with congenital heart disease. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papile, L.-A.; Burstein, J.; Burstein, R.; Koffler, H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: A study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorna, O.; Baldwin, H.S.; Neumaier, J.; Gogliotti, S.; Powers, D.; Mouvery, A.; Bichell, D.; Maitre, N.L. Feasibility of a Team Approach to Complex Congenital Heart Defect Neurodevelopmental Follow-Up. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2016, 9, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chock, V.; Lee, H.C. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes for Infants Born With Congenital Heart Disease. NeoReviews 2014, 15, e344–e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, C.K.; Newburger, J.W. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Congenital Heart Disease. Circulation 2014, 130, e124–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mussatto, K.A.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Hoffman, G.M.; Tweddell, J.S.; Bear, L.; Cao, Y.; Brosig, C. Risk and Prevalence of Developmental Delay in Young Children With Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e570–e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visconti, K.J.; Rimmer, D.; Gauvreau, K.; del Nido, P.; Mayer, J.E., Jr.; Hagino, I.; Pigula, F.A. Regional Low-Flow Perfusion Versus Circulatory Arrest in Neonates: One-Year Neurodevelopmental Outcome. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Bove, E.L.; Devaney, E.J.; Mollen, E.; Schwartz, E.; Tindall, S.; Nowak, C.; Charpie, J.; Brown, M.B.; Kulik, T.J.; et al. A randomized clinical trial of regional cerebral perfusion versus deep hypothermic circulatory arrest: Outcomes for infants with functional single ventricle. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 133, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanner, K.; Sabrine, N.; Wren, C. Cardiovascular Malformations Among Preterm Infants. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e833–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kecskes, Z. Poor outcome of very low birthweight babies with serious congenital heart disease. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002, 87, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbess, J.M.; Visconti, K.J.; Hancock-Friesen, C.; Howe, R.C.; Bellinger, D.C.; Jonas, R.A. Neurodevelopmental Outcome After Congenital Heart Surgery: Results From an Institutional Registry. Circulation 2002, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.; Nord, A.; Gerdes, M.; Wernovsky, G.; Jarvik, G.P.; Bernbaum, J.; Zackai, E.; Gaynor, J.W. Predictors of impaired neurodevelopmental outcomes at one year of age after infant cardiac surgery. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2009, 36, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, A.; Cruz, G.; Patel, Y.; Cahalin, L.P.; Moore, J.G. Sternal Precautions and Prone Positioning of Infants Following Median Sternotomy: A Nationwide Survey. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2020, 32, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Demographics | All Patients | Without Syndrome (n = 72) | With Any Syndrome (n = 36) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male/female | 58 (53.7)/50 (46.3) | 43 (59.7)/29 (40.3) | 15 (41.7)/21 (58.3) | 0.077 |
| Birth weight (g) | 1901.54 ± 1024.33 | 1620.36 ± 1014.04 | 2463.89 ± 796.17 | 0.000 * |
| Normal (≥2500) | 40 (36.7) | 20 (27.8) | 20 (55.6) | |
| LBW (<2500) | 22 (20.2) | 10 (13.9) | 12 (33.3) | |
| VLBW (<1500) | 9 (8.3) | 8 (11.1) | 1 (2.8) | |
| ELBW (<1000) | 37 (33.9) | 34 (47.2) | 3 (8.3) | |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks) | 0.000 * | |||
| Preterm (<37 weeks) | 59 (54.1) | 50 (69.4) | 9 (25.0) | |
| Term (≥37 weeks) | 49 (45.0) | 22 (30.6) | 27 (75.0) | |
| 1-min Apgar score | 5.25 ± 2.49 | 4.94 ± 2.54 | 6.45 ± 1.93 | 0.016 * |
| 5-min Apgar score | 7.01 ± 1.98 | 6.74 ± 2.06 | 7.95 ± 1.36 | 0.015 * |
| Maternal age | 33.7 ± 3.90 | 33.19 ± 4.25 | 34.82 ± 2.73 | 0.047 * |
| Maternal education | ||||
| High school or higher | 108 (100) | 36 (100) | 72 (100) | |
| Cardiac diagnosis | 0.008 * | |||
| VSD | 9 (8.3) | 3 (4.2) | 6 (16.7) | |
| PDA | 42 (38.9) | 37 (51.4) | 5 (13.9) | |
| ASD | 4 (3.7) | 2 (2.8) | 2 (5.6) | |
| Cyanotic | 53 (49.1) | 30 (41.6) | 23 (63.8) | |
| Age at surgery (days) | 53.71 ± 66.78 | 33.24 ± 47.59 | 95.83 ± 80.36 | 0.000 * |
| Age at first assessment (month) | 12.49 ± 2.79 | 12.72 ± 2.64 | 12.03 ± 3.06 | 0.224 |
| Age at second assessment (month) | 25.80 ± 3.94 | 25.85 ± 4.01 | 25.69 ± 3.84 | 0.850 |
| Number of operations | 1.95 ± 1.76 | 1.63 ± 1.22 | 2.63 ± 2.41 | 0.005 * |
| Preop US or MRI (n = 30/70) | 0.811 | |||
| Nonspecific finding | 61 (61) | 42 (60) | 19 (63.3) | |
| ICH, PVH | 19 (19) | 15 (21.4) | 4 (13.3) | |
| Etc. | 20 (20) | 13 (18.6) | 7 (23.4) | |
| Hemorrhage grade | 0.124 | |||
| I | 18 (94.7) | 14 (93.3) | 4 (100) | |
| II | 1 (5.3) | 1 (6.7) | 0 | |
| III | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IV | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Rehabilitation experience (have/did not have) | 98 (90.7)/10 (9.3) | 66 (91.7)/6 (8.3) | 32 (88.9)/4 (11.1) | 0.642 |
| Perioperative risk | ||||
| Cardiac arrest duration (n = 21/29) | 54.52 ± 34.90 | 44.69 ± 36.61 | 0.336 | |
| ECC duration (n = 23/31) | 114.26 ± 60.72 | 86.58 ± 52.43 | 0.079 |
| BSID-II. | First Evaluation | Second Evaluation | p-Value between the Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | N (%) | N (%) | p-Value |
| MDI | |||
| Mean ± SD | 76.11 ± 20.17 | 73.98 ± 22.53 | 0.465 |
| Within normal limits | 39 (36.1) | 39 (36.1) | - |
| Mild DD | 29 (26.9) | 20 (18.5) | - |
| Significant DD | 40 (37.1) | 49 (45.4) | - |
| PDI | |||
| Mean ± SD | 65.95 ± 18.34 | 69.48 ± 20.86 | 0.188 |
| Within normal limits | 21 (19.4) | 30 (27.8) | - |
| Mild DD | 22 (20.4) | 18 (16.7) | - |
| Significant DD | 65 (60.1) | 60 (55.5) | - |
| Group | Without SD (n = 72) | With Any SD (n = 36) | p-Value between Group | Adjusted p-Value between Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSID-II | First | Second | p-Value | First | Second | p-Value | First | Second | First | Second |
| MDI (n (%)) | ||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 82.13 ± 19.05 | 82.27 ± 21.57 | 0.964 | 64.08 ± 16.88 | 57.68 ± 13.54 | 0.068 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.001 * | 0.006 * |
| Within normal limits | 34 (47.2) | 37 (51.4) | 5 (13.89) | 2(5.56) | ||||||
| Mild DD | 20 (27.8) | 15 (20.8) | 9 (25.00) | 5 (13.89) | ||||||
| Significant DD | 18 (25.0) | 20 (27.8) | 22 (61.11) | 29 (80.55) | ||||||
| PDI (n (%)) | ||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 72.03 ± 18.95 | 77.44 ± 20.40 | 0.101 | 53.80 ± 8.50 | 53.55 ± 9.72 | 0.908 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.067 | 0.011 * |
| Within normal limits | 21 (29.2) | 29 (40.3) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.78) | ||||||
| Mild DD | 18 (25.0) | 16 (22.2) | 4 (11.11) | 2 (5.56) | ||||||
| Significant DD | 33 (45.8) | 27 (37.5) | 32 (88.88) | 33 (91.66) | ||||||
| Without SD (n = 22) | With Any SD (n = 27) | p-Value between Group | Adjusted p-Value between Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSID-II | First | Second | p-Value | First | Second | p-Value | First | Second | First | Second |
| MDI (n (%)) | ||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 79.32 ± 18.45 | 79.77 ± 20.25 | 0.938 | 62.11 ± 17.00 | 55.44 ± 11.80 | 0.100 | 0.005 * | 0.000 * | 0.006 * | 0.013 * |
| Within normal limits | 10 (45.5) | 10 (45.5) | 3 (11.1) | 1 (3.7) | ||||||
| Mild DD | 6 (27.3) | 5 (22.7) | 5 (18.5) | 2 (7.4) | ||||||
| Significant DD | 6 (27.3) | 7 (31.8) | 19 (70.4) | 24 (88.9) | ||||||
| PDI (n (%)) | ||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 65.82 ± 18.20 | 70.23 ± 16.91 | 0.410 | 53.74 ± 8.77 | 52.07 ± 9.38 | 0.503 | 0.022 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| Within normal limits | 4 (18.2) | 4 (18.2) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (3.7) | ||||||
| Mild DD | 6 (27.3) | 8 (36.4) | 4 (14.8) | 1 (3.7) | ||||||
| Significant DD | 12 (54.5) | 10 (45.5) | 23 (85.2) | 25 (92.6) | ||||||
| Without Brain Lesions (n = 42) | With Brain Lesions (n = 28) | p-Value between Groups | Adjusted p-Value between Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSID-II | First | Second | p-Value | First | Second | p-Value | First | Second | First | Second |
| MDI (n (%)) | ||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 86.38 ± 18.01 | 88.07 ± 20.00 | 0.685 | 75.89 ± 19.33 | 75.43 ± 21.47 | 0.933 | 0.023 * | 0.014 * | 0.003 * | 0.004 * |
| Within normal limits | 24 (57.1) | 27 (64.3) | 9 (32.1) | 10 (35.7) | ||||||
| Mild DD | 10 (23.8) | 8 (19.0) | 10 (35.7) | 7 (25.0) | ||||||
| Significant DD | 8 (19.1) | 7 (16.6) | 9 (32.2) | 11 (39.3) | ||||||
| PDI (n (%)) | ||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 75.14 ± 19.84 | 80.43 ± 19.84 | 0.226 | 67.54 ± 17.10 | 73.29 ± 21.47 | 0.273 | 0.102 | 0.158 | 0.025 * | 0.040 * |
| Within normal limits | 14 (33.3) | 18 (42.9) | 6 (21.4) | 11 (39.3) | ||||||
| Mild DD | 12 (28.6) | 10 (23.8) | 6 (21.4) | 5 (17.9) | ||||||
| Significant DD | 16 (38.0) | 14 (33.4) | 16 (57.1) | 12 (42.8) | ||||||
| MDI | PDI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Normal Development (n = 37) | Developmental Delay (n = 35) | p-Value | Normal Development (n = 29) | Developmental Delay (n = 43) | p-Value |
| Sex (male/female) | 21 (56.8)/16 (43.2) | 22 (62.9)/13 (37.1) | 0.604 | 16 (55.2)/13 (44.8) | 27 (62.8)/16 (37.2) | 0.518 |
| Birth weight (g) | 0.889 | 0.019 * | ||||
| Normal (≥2500) | 10 (27.0) | 10 (28.6) | 3 (10.3) | 17 (39.5) | ||
| LBW (<2500) | 5 (13.5) | 5 (14.3) | 4 (13.8) | 6 (14.0) | ||
| VLBW (<1500) | 6 (16.2) | 2 (5.7) | 6 (20.7) | 2 (4.7) | ||
| ELBW (<1000) | 16 (43.2) | 18 (51.4) | 16 (55.2) | 18 (41.9) | ||
| Gestational age (weeks) | 0.511 | 0.011 * | ||||
| Preterm (<37 weeks) | 27 (73.0) | 23 (65.7) | 25 (86.2) | 25 (58.1) | ||
| Term (≥37 weeks) | 10 (27.0) | 12 (34.3) | 4 (13.8) | 18 (41.9) | ||
| 1-min Apgar score | 5.36 ± 2.37 | 4.50 ± 2.67 | 0.157 | 4.52 ± 2.46 | 5.24 ± 2.58 | 0.240 |
| 5-min Apgar score | 7.00 ± 1.88 | 6.47 ± 2.22 | 0.285 | 6.45 ± 1.90 | 6.95 ± 2.16 | 0.317 |
| Maternal age | 33.00 ± 4.17 | 33.40 ± 4.37 | 0.692 | |||
| Cardiac diagnosis | 0.708 | 0.091 | ||||
| VSD | 2 (5.4) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (6.9) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| PDA | 19 (51.4) | 18 (51.4) | 21 (72.4) | 16 (37.2) | ||
| ASD | 0 (0) | 2 (5.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.7) | ||
| Cyanotic | 16 (43.2) | 14 (40.0) | 6 (20.7) | 24 (55.8) | ||
| Preoperative US or MRI diagnosis (n = 70) | 0.009 * | 0.597 | ||||
| Nonspecific findings | 27 (73.0) | 15 (42.9) | 18 (62.1) | 24 (55.8) | ||
| Brain lesions | 10 (27.0) | 20 (57.1) | 11 (37.9) | 19 (44.2) | ||
| Hemorrhage grade (n = 28) | 0.004 * | 0.201 | ||||
| I | 11 (68.8) | 3 (25.0) | 9 (56.3) | 5 (41.7) | ||
| II | 4 (25.0) | 3 (25.0) | 5 (31.3) | 2 (16.7) | ||
| III | 0 (0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| IIII | 1 (6.3) | 6 (50.0) | 2 (12.5) | 5 (41.7) | ||
| Age at operation (day) | 33.84 ± 45.51 | 32.60 ± 50.36 | 0.913 | 36.76 ± 50.54 | 30.86 ± 45.95 | 0.609 |
| Number of operations | 1.65 ± 1.42 | 1.60 ± 0.98 | 0.867 | 1.14 ± 0.44 | 1.95 ± 1.45 | 0.004 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, K.J.; Kim, M.G.; Ko, E.J.; Sung, I.Y. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes after Congenital Heart Disease Surgery in Infancy: A 2-Year Serial Follow-Up. Children 2021, 8, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100911
Song KJ, Kim MG, Ko EJ, Sung IY. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes after Congenital Heart Disease Surgery in Infancy: A 2-Year Serial Follow-Up. Children. 2021; 8(10):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100911
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Kyeong Joo, Min Gi Kim, Eun Jae Ko, and In Young Sung. 2021. "Neurodevelopmental Outcomes after Congenital Heart Disease Surgery in Infancy: A 2-Year Serial Follow-Up" Children 8, no. 10: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100911
APA StyleSong, K. J., Kim, M. G., Ko, E. J., & Sung, I. Y. (2021). Neurodevelopmental Outcomes after Congenital Heart Disease Surgery in Infancy: A 2-Year Serial Follow-Up. Children, 8(10), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100911