Decreased Incidence of Pediatric Intussusception during COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Measures and Outcomes
2.3. Data Analyses
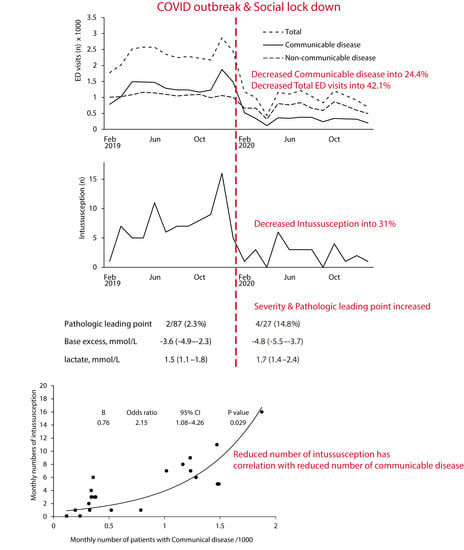
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Outbreak at the Study Location
3.2. Incidence of Intussusception and Its Association with Monthly ED Visits
3.3. Clinical Characteristics of Intussusception before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Acute Intussusception in Infants and Children: Incidence, Clinical Presentation and Management: A Global Perspective. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/67720 (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Kliegman, R.M.; Geme, J.W.S.; Blum, N.J.; Shah, S.S.; Tasker, R.C.; Wilson, K.M. Ileus, adhesions, intussusception, and closed-loop obstructions. In Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 21st ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1965–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz, H.-I.; Soriano-Gabarró, M.; Grimprel, E.; Franco, E.; Mezner, Z.; Desselberger, U.; Smit, Y.; Bosch, J.W.-V.D.; De Vos, B.; Giaquinto, C. Intussusception Among Young Children in Europe. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 25, S22–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.K.; Ko, D.-H.; Hyun, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Song, W.; Kim, H.S. Associations of Adenovirus Genotypes in Korean Acute Gastroenteritis Patients with Respiratory Symptoms and Intussusception. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombo, L.A.; Gerber, M.A.; Pickering, L.K.; Atreya, C.D.; Breiman, R.F. Intussusception, infection, and immunization: Summary of a workshop on rotavirus. PEDIATRICS 2001, 108, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Kao, C.-L.; Huang, L.-M.; NI, Y.-H.; Lai, H.-S.; Lin, F.-Y.; Chang, M.-H. Viral etiology of intussusception in Taiwanese childhood. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1998, 17, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Lim, I.S.; Chae, S.A.; Yun, S.W.; Lee, N.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Characteristics of intussusception among children in Korea: A nationwide epidemiological study. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.-L.; Zhang, S.-F.; Li, J.-E.; Wang, J. Association of Meteorological Factors with Pediatric Intussusception in Subtropical China: A 5-Year Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, G.Y.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Zeidman, A.; Atar, E.; Marcus, O.; Joubran, S.; Ram, E. Sex differences in the epidemiology, seasonal variation, and trends in the management of patients with acute appendicitis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2012, 397, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Shahzad, N.; Arshad, S.; Shariff, A.H. Seasonal Variation in Acute Cholecystitis: An Analysis of Cholecystectomies Spanning Three Decades. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 246, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Statistics 2020: A Visual Summary. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/whs-2020-visual-summary (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Zhang, K.; Vilches, T.N.; Tariq, M.; Galvani, A.P.; Moghadas, S.M. The impact of mask-wearing and shelter-in-place on COVID-19 outbreaks in the United States. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Khang, Y.-H.; Lim, H.-K. Impact of the 2015 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Outbreak on Emergency Care Utilization and Mortality in South Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanzer, D.L.; Schwartz, B. Impact of Seasonal and Pandemic Influenza on Emergency Department Visits, 2003–2010, Ontario, Canada. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2013, 20, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galvin, C.J.; Li, Y.-C.; Malwade, S.; Syed-Abdul, S. COVID-19 preventive measures showing an unintended decline in infectious diseases in Taiwan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ye, Y.; Liao, Y.; Bin Wang, P. Fewer paediatric intussusception cases during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2020, 56, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Heo, K.; Seo, Y. COVID-19 in South Korea: Lessons for developing countries. World Dev. 2020, 135, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, M.; Barbi, E.; Apicella, A.; Marchetti, F.; Cardinale, F.; Trobia, G. Delayed access or provision of care in Italy resulting from fear of COVID-19. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, e10–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopfer, C.; Wetzke, M.; Scharff, A.Z.; Mueller, F.; Dressler, F.; Baumann, U.; Sasse, M.; Hansen, G.; Jablonka, A.; Happle, C. COVID-19 related reduction in pediatric emergency healthcare utilization—A concerning trend. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, A.; Rousseau, M.R.; Bartier, S.; Dabi, Y.; Challine, A.; Haddad, B.; Herta, N.; Souied, E.; Ortala, M.; Epaud, S.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 on surgical emergencies: Nationwide analysis. BJS Open 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgard, M.; Cherbanyk, F.; Nassiopoulos, K.; Malekzadeh, S.; Pugin, F.; Egger, B. An effect of the COVID-19 pandemic: Significantly more complicated appendicitis due to delayed presentation of patients! PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Milanović, K.; Veršić, A.B.; Pasini, M.; Divković, D.; Pavlović, O.; Lučev, J.; Žufić, V. Is there an increased incidence of orchiectomy in pediatric patients with acute testicular torsion during COVID-19 pandemic?—A retrospective multicenter study. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2021, 17, 479.e1–479.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.L.; Kong, M.S.; Lin, J.N.; Wang, K.L.; Lou, C.C.; Wong, H.F. Intussusception in infants and children: Risk factors leading to surgical reduction. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1994, 93, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lampl, B.S.; Glaab, J.; Ayyala, R.S.; Kanchi, R.; Ruzal-Shapiro, C.B. Is Intussusception a Middle-of-the-Night Emergency? Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2017, 35, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Byun, Y.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, J.S.; Ryu, J.-M.; Choi, S.J. Lactic acid level as an outcome predictor in pediatric patients with intussusception in the emergency department. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, M.; Pellerin, M.; Kimball, Z.; de la Garza-Jordan, J.; Tubbs, R.S.; Jordan, R. Intussusception: An anatomical perspective with review of the literature. Clin. Anat. 2011, 24, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, T.S.; Huh, H.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, G.J.; Sung, H.; Roh, K.H.; et al. Guidelines for Laboratory Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y. COVID-19 in South Korea. Postgrad. Med. J. 2020, 96, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease-19, Republic of Korea. Available online: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en (accessed on 28 January 2021).
- Chen, S.C.-C.; Wang, J.-D.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Leong, M.-M.; Tok, T.-S.; Chin, Y.-Y. Epidemiology of Childhood Intussusception and Determinants of Recurrence and Operation: Analysis of National Health Insurance Data Between 1998 and 2007 in Taiwan. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2010, 51, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.S.; Chung, J.-Y.; Chang, S.; Lee, K.; Choe, B.-H.; Hong, S.J.; Song, J.S.; Park, K.Y. Epidemiological Correlation between Fecal Adenovirus Subgroups and Pediatric Intussusception in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, R.D.; Grafstein, E.; Barclay, N.; Irvine, M.A.; Portales-Casamar, E. Paediatric patients seen in 18 emergency departments during the COVID-19 pandemic. Emerg. Med. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.-L.; Soo, J.S.L.; Allen, J.C.; Ganapathy, S.; Lee, K.P.; Tyebally, A.; Yung, C.F.; Thoon, K.C.; Ng, Y.H.; Oh, J.Y.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 on pediatric emergencies and hospitalizations in Singapore. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, S.; Hyodo, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kobayashi, M. Association of viral isolates from stool samples with intussusception in children. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e641–e645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bazuaye-Ekwuyasi, E.A.; Camacho, A.C.; Rios, F.S.; Torck, A.; Choi, W.J.; Aigbivbalu, E.E.; Mehdi, M.Q.; Shelton, K.J.; Radhakrishnan, G.L.; Radhakrishnan, R.S.; et al. Intussusception in a child with COVID-19 in the USA. Emerg. Radiol. 2020, 27, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzam, Z.; Salim, A.; Ashraf, A.; Jehan, F.; Arshad, M. Intussusception in an infant as a manifestation of COVID-19. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 59, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Rong, Z.; Li, W. Clinical Characteristics of 5 COVID-19 Cases With Non-respiratory Symptoms as the First Manifestation in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castaño, I.; Calabuig-Barbero, E.; Gonzálvez-Piñera, J.; López-Ayala, J.M. COVID-19 Infection Is a Diagnostic Challenge in Infants With Ileocecal Intussusception. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2020, 36, e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hviid, A.; Svanström, H. Antibiotic use and intussusception in early childhood. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahidi, S.H.; Williams, J.S.; Hassani, F. Physical activity during COVID-19 quarantine. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, K.E. Intussusception in children: Evidence-based diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr. Radiol. 2009, 39, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.H.; Lowenstein, S.R.; Koziol-McLain, J.; Barta, D.C.; Steiner, J. Chart Reviews in Emergency Medicine Research: Where Are the Methods? Ann. Emerg. Med. 1996, 27, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pre-Pandemic Period | Pandemic Period | |
|---|---|---|
| Feb. 2019 to Jan. 2020 | Feb. 2020 to Jan. 2021 | |
| Total visits | 28,018 | 11,800 (42.1% a) |
| Communicable disease | 15,932 | 3880 (24.4% a) |
| proportion b, % | 56.9 | 32.9 (57.8% a) |
| Non-communicable disease | 12,994 | 8050 (62.0%) |
| proportion b, % | 46.4 | 68.2 (147% a) |
| Intussusception | 87 | 27 (31% a) |
| COVID-19 confirmed | 0 | 0 (0% a) |
| Variables | Non-Pandemic | Pandemic | Total | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 87 | n = 27 | n = 114 | |||
| Age, month | 25 (16–37) | 24 (14–31) | 24.5 (16–36) | 0.582 | |
| Sex, male | 63 (72.4) | 23 (85.2) | 86 (75.4) | 0.210 | |
| Past history of intussusception | 9 (10.3) | 6 (22.2) | 15 (13.2) | 0.188 | |
| Rotavirus vaccination | 78 (89.7) | 24 (88.9) | 102 (89.5) | 1.000 | |
| Concomitant GITI | 21 (24.1) | 6 (22.2) | 27 (23.7) | 1.000 | |
| Concomitant URTI | 13 (14.9) | 4 (14.8) | 17 (14.9) | 1.000 | |
| Duration of illness | 13 (4–48) | 9 (4–24) | 12 (4–24) | 0.140 | |
| Symptoms | |||||
| Abdominal pain | 83 (95.4) | 25 (92.6) | 108 (94.7) | 0.626 | |
| Cyclic irritability | 74 (85.1) | 22 (81.5) | 96 (84.2) | 0.763 | |
| Vomit | 31 (35.6) | 11 (40.7) | 42 (36.8) | 0.653 | |
| Hematochezia | 14 (16.1) | 8 (29.6) | 22 (19.3) | 0.161 | |
| EDLOS, h | 9.5 (7.9–11.4) | 9.2 (7.7–11.5) | 9.4 (7.8–11.4) | 0.886 | |
| ED course | |||||
| Time to diagnosis | 0.6 (0.3–1) | 0.8 (0.4–1.6) | 0.6 (0.4–1.1) | 0.063 | |
| Time to air reduction | 2.6 (1.8–3.6) | 3.1 (2.5–4.5) | 2.9 (2.0–3.7) | 0.000 | |
| Success to air reduction | 86 (98.9) | 25 (92.6) | 111 (97.4) | 0.139 | |
| Admission | 4 (4.6) | 5 (18.5) | 9 (7.9) | 0.033 | |
| Pathologic leading point | 2 (2.3) | 4 (14.8) | 6 (5.3) | 0.027 | |
| Laboratory test | |||||
| WBC, ×103/µL | 10 (7.6–12.9) | 10.5 (8–15.6) | 10.3 (7.9–13.2) | 0.437 | |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.2 (0.1–0.6) | 0.3 (0.1–0.7) | 0.2 (0.1–0.6) | 0.839 | |
| Bicarbonate, mmol/L | 19.6 (18.4–21.1) | 19.2 (17.7–20.9) | 19.6 (18.3–21.1) | 0.454 | |
| BE, mmol/L | −3.6 (−4.9–−2.3) | −4.8 (−5.5–−3.7) | −4 (−5.1–−2.6) | 0.030 | |
| lactate, mmol/L | 1.5 (1.1–1.8) | 1.7 (1.4–2.4) | 1.5 (1.2–1.9) | 0.016 | |
| COVID-19 confirmed | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NA | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.S.; Byun, Y.-H.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Ryu, J.-M.; Lee, J.-Y. Decreased Incidence of Pediatric Intussusception during COVID-19. Children 2021, 8, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8111072
Park JS, Byun Y-H, Choi SJ, Lee JS, Ryu J-M, Lee J-Y. Decreased Incidence of Pediatric Intussusception during COVID-19. Children. 2021; 8(11):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8111072
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jun Sung, Young-Hoon Byun, Seung Jun Choi, Jong Seung Lee, Jeong-Min Ryu, and Jeong-Yong Lee. 2021. "Decreased Incidence of Pediatric Intussusception during COVID-19" Children 8, no. 11: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8111072
APA StylePark, J. S., Byun, Y. -H., Choi, S. J., Lee, J. S., Ryu, J. -M., & Lee, J. -Y. (2021). Decreased Incidence of Pediatric Intussusception during COVID-19. Children, 8(11), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8111072