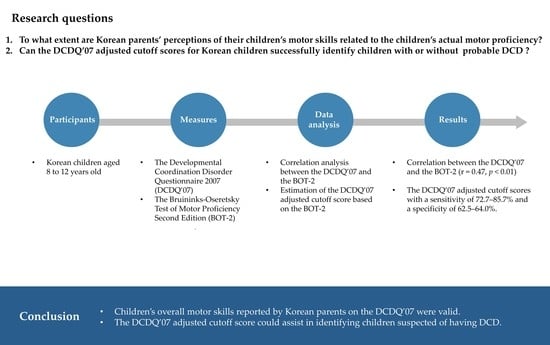
Relationship between the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 and the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition in Korean Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. The Bruininks−Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition (BOT-2)
2.2.2. The Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 (DCDQ’07)
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, (DSM-5), 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Pub: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, J.G.; Missiuna, C.; Harris, S.R.; Boyd, L.A. Developmental coordination disorder: A review and update. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, B.J.; Wilson, B.N.; Dewey, D.; Crawford, S.G. DCD may not be a discrete disorder. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1998, 17, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Brina, C.; Averna, R.; Rampoldi, P.; Rossetti, S.; Penge, R. Reading and writing skills in children with specific learning disabilities with and without developmental coordination disorder. Motor Control 2018, 22, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watemberg, N.; Waiserberg, N.; Zuk, L.; Lerman-Sagie, T. Developmental coordination disorder in children with attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder and physical therapy intervention. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwicker, J.G.; Harris, S.R.; Klassen, A.F. Quality of life domains affected in children with developmental coordination disorder: A systematic review. Child Care Health Dev. 2013, 39, 562–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwicker, J.G.; Suto, M.; Harris, S.R.; Vlasakova, N.; Missiuna, C. Developmental coordination disorder is more than a motor problem: Children describe the impact of daily struggles on their quality of life. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2018, 81, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Yeger, B.; Hanna Kasis, A. The relationship between developmental co-ordination disorders, child’s perceived self-efficacy and preference to participate in daily activities. Child Care Health Dev. 2010, 36, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, D.; Kaplan, B.J.; Crawford, S.G.; Wilson, B.N. Developmental coordination disorder: Associated problems in attention, learning, and psychosocial adjustment. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2002, 21, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.H.; Howe, T.H.; Chuang, I.C.; Hsieh, C.L. Cooccurrence of problems in activity level, attention, psychosocial adjustment, reading and writing in children with developmental coordination disorder. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2007, 30, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.H.; Ruddock, S.; Smits-Engelsman, B.; Polatajko, H.; Blank, R. Understanding performance deficits in developmental coordination disorder: A meta-analysis of recent research. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunford, C.; Missiuna, C.; Street, E.; Sibert, J. Children’s perceptions of the impact of developmental coordination disorder on activities of daily living. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2005, 68, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, E.A.; Chesson, R.A. ’Always the guiding hand’: Parent’s accounts of the long-term implications of developmental co-ordination disorder for their children and families. Child Care Health Dev. 2008, 34, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarus, T.; Lourie-Gelberg, Y.; Engel-Yeger, B.; Bart, O. Participation patterns of school-aged children with and without DCD. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.L.; Brown, D.; Sorgardt, K.S. A preliminary investigation of quality of life satisfaction reports in emerging adults with and without developmental coordination disorder. J. Adult Dev. 2011, 18, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrowell, I.; Hollén, L.; Lingam, R.; Emond, A. Mental health outcomes of developmental coordination disorder in late adolescence. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.J.; Zwicker, J.G. Early identification of children with/at risk of developmental coordination disorder: A scoping review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, R.; Barnett, A.L.; Cairney, J.; Green, D.; Kirby, A.; Polatajko, H.; Rosenblum, S.; Smits-Engelsman, B.; Sugden, D.; Wilson, P.; et al. International clinical practice recommendations on the definition, diagnosis, assessment, intervention, and psychosocial aspects of developmental coordination disorder. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 242–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.E.; Sugden, D.A.; Barnett, A. Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2; Pearson Assessment: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bruininks, R.H.; Bruininks, B.D. Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency, 2nd ed.; Pearson Assessment: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, E.; Jung, M.; Park, S.; Choi, E. Current trends of occupational therapy assessment tool by Korean occupational therapist. Korea. J. Occup. Ther. 2006, 14, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, E.; Jeong, Y.; Choi, Y.; Yoo, E. Current trends of occupational therapy assessment tool by Korean pediatric occupational therapist. J. Korean Soc. Occup. Ther. Child Sch. 2015, 6, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.N.; Crawford, S.G.; Green, D.; Roberts, G.; Aylott, A.; Kaplan, B.J. Psychometric properties of the revised Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2009, 29, 182–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toftegaard-Stoeckel, J.; Groenfeldt, V.; Andersen, L.B. Children’s self-perceived bodily competencies and associations with motor skills, body mass index, teachers’ evaluations, and parents’ concerns. J. Sports. Sci. 2010, 28, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Brown, T.; Chien, C. Motor skill assessment of children: Is there an association between performance-based, child-report, and parent-report measures of children’s motor skills? Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2012, 32, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.; Lane, H. Comparing a parent-report and a performance-based measure of children’s motor skill abilities: Are they associated? Occup. Ther. Health Care 2014, 28, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Gabbard, C.; Vieira, J.L.; Tamplain, P. Associations between the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire—Brazilian version (DCDQ-BR) and motor competence in school-age children. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2020, 40, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.N.; Kaplan, B.J.; Crawford, S.G.; Campbell, A.; Dewey, D. Reliability and validity of a parent questionnaire on childhood motor skills. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2000, 54, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lalor, A.; Brown, T.; Murdolo, Y. Relationship between children’s performance-based motor skills and child, parent, and teacher perceptions of children’s motor abilities using self/informant-report questionnaires. Aust. Occup. Ther. J. 2016, 63, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Gabbard, C. Adaptation and preliminary testing of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ) for children in India. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2017, 37, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Gabbard, C.; Vieira, J.L.; Silva, P.N.; Cheuczuk, F.; Rocha, F.F.; Souza, V.F.; Cacola, P. Reconsidering the use of cut-off scores: DCDQ—Brazil. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2019, 25, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, B.N.; Crawford, S.G. The Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007: Administration Manual for the DCDQ’07 with Psychometric Properties. Available online: www.dcdq.ca (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Park, K.J.; Kweon, K.; Lee, S.; Lim, Y.S.; Joung, Y.S.; Kim, H.W. Effect of pharmacological treatment for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder on motor coordination: Open label study. J. Korean Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 28, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratner, B. The correlation coefficient: Its values range between +1/−1, or do they? J. Target Meas. Anal. Market. 2009, 17, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DCD Assessment Information Sheet. Available online: https://www.caot.ca/document/6143/DCD_Assessment_InfoSheet_FNL.pdf. (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Schoemaker, M.M.; Smits-Engelsman, B.C.; Jongmans, M.J. Psychometric properties of the movement assessment battery for children-checklist as a screening instrument for children with a developmental co-ordination disorder. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 73, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.J.; Schisterman, E.F. The inconsistency of “optimal’ cutpoints obtained using two criteria based on the receiver operating characteristic curve. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estevan, I.; Molina-García, J.; Bowe, S.J.; Álvarez, O.; Castillo, I.; Barnett, L.M. Who can best report on children’s motor competence: Parents, teachers, or the children themselves? Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2018, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueckriegel, S.M.; Blankenburg, F.; Burghardt, R.; Ehrlich, S.; Henze, G.; Mergl, R.; Driever, P.H. Influence of age and movement complexity on kinematic hand movement parameters in childhood and adolescence. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2008, 26, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy-Behr, A.; Wilson, B.N.; Rodger, S.; Mickan, S. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 for German-speaking countries: DCDQ-G. Neuropediatrics 2013, 44, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Caravale, B.; Baldi, S.; Capone, L.; Presaghi, F.; Balottin, U.; Zoppello, M. Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ-Italian). Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 36, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravale, B.; Baldi, S.; Gasparini, C.; Wilson, B.N. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and predictive validity of the Italian version of Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ). Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2014, 18, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Lee, W.; Woon, J.; Kim, Y. Development of Korean version of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ-K). J. Korean. Phys. Ther. 2020, 32, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, C.K.; Altunalan, T.; Acar, G.; Elbasan, B.; Gucuyener, K. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire in Turkish children. Percept. Mot. Skills 2019, 126, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Lobete, L.; Santos-del-Riego, S.; Pértega-Díaz, S.; Montes-Montes, R. Prevalence of suspected developmental coordination disorder and associated factors in Spanish classrooms. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 86, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| 8 to 9 Age | 10 to 12 Age | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCDQ’07 | |||
| Control during movement | 23.45 (4.84) | 24.96 (4.50) | 24.17 (4.74) |
| Fine motor/handwriting | 16.90 (3.31) | 17.72 (2.84) | 17.29 (3.12) |
| General coordination | 18.28 (4.51) | 20.16 (3.93) | 19.17 (4.34) |
| Total | 58.62 (11.00) | 62.84 (9.80) | 60.63 (10.64) |
| BOT-2 | |||
| Fine manual control | 52.19 (8.02) | 49.58 (6.94) | 50.95 (7.62) |
| Fine motor precision | 16.33 (4.41) | 15.22 (3.65) | 15.80 (4.10) |
| Fine motor integration | 15.54 (3.34) | 14.83 (3.54) | 15.20 (3.45) |
| Manual coordination | 47.47 (7.83) | 47.70 (8.91) | 47.58 (8.35) |
| Manual dexterity | 17.43 (3.89) | 16.63 (3.76) | 17.05 (3.84) |
| Upper-limb coordination | 10.40 (3.90) | 11.68 (4.47) | 11.01 (4.22) |
| Body coordination | 47.22 (8.03) | 49.18 (7.93) | 48.16 (8.03) |
| Bilateral coordination | 15.02 (3.68) | 16.03 (3.68) | 15.50 (3.71) |
| Balance | 13.03 (4.20) | 13.41 (4.20) | 13.21 (4.20) |
| Strength and agility | 53.75 (8.78) | 54.27 (7.08) | 54.00 (8.00) |
| Running speed and agility | 17.69 (3.75) | 17.86 (3.05) | 17.77 (3.43) |
| Strength | 15.04 (4.24) | 15.85 (3.72) | 15.43 (4.02) |
| Total motor composite | 49.99 (7.87) | 49.79 (7.32) | 49.89 (7.60) |
| Variables | 8 to 9 Age | 10 to 12 Age | Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMC | MC | BC | SA | BOT-2 Total | FMC | MC | BC | SA | BOT-2 Total | FMC | MC | BC | SA | BOT-2 Total | |
| Control during movement | 0.32 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.03 | 0.47 ** | 0.16 | 0.39 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.17 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.46 ** |
| Fine motor/handwriting | 0.45 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.30 ** | 0.19 * | 0.38 ** | 0.21* | 0.14 | −0.02 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.32 ** | 0.20 ** | 0.18 ** | 0.13 * | 0.27 ** |
| General coordination | 0.42 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.50 ** | 0.19 * | 0.39 ** | 0.21* | 0.30 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.34 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.45 ** |
| DCDQ’07 total | 0.45 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.15 | 0.41 ** | 0.15 | 0.31 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.35 ** | 0.47 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, D.; Kim, M.; Ji, S.; Choi, D.; Joung, Y.-S.; Kim, E.Y. Relationship between the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 and the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition in Korean Children. Children 2022, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020255
Yoon D, Kim M, Ji S, Choi D, Joung Y-S, Kim EY. Relationship between the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 and the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition in Korean Children. Children. 2022; 9(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Deukgeun, Misun Kim, Seokyeon Ji, Dabin Choi, Yoo-Sook Joung, and Eun Young Kim. 2022. "Relationship between the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 and the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition in Korean Children" Children 9, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020255
APA StyleYoon, D., Kim, M., Ji, S., Choi, D., Joung, Y. -S., & Kim, E. Y. (2022). Relationship between the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire 2007 and the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition in Korean Children. Children, 9(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020255