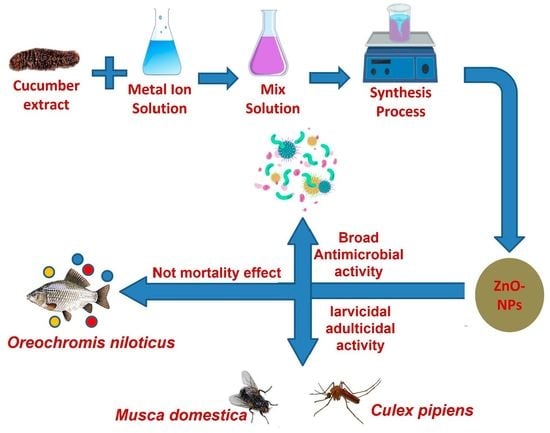
Biosynthesized ZnO-NPs Using Sea Cucumber (Holothuria impatiens): Antimicrobial Potential, Insecticidal Activity and In Vivo Toxicity in Nile Tilapia Fish, Oreochromis niloticus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Preservation and Identification of Sea Cucumber
2.2. Holothuria Impatiens Aqueous Extract Preparation
2.3. Biosynthesis of ZnO-NPs Using Holothuria Impatiens Extract
2.4. Characterization of Hi-ZnO-NPs
2.5. Antimicrobial Activities of Hi-ZnO-NPs
2.6. Insecticidal Bioassays of Hi-ZnO-NPs
2.7. Toxicity of Hi-ZnO-NPs
2.7.1. Water Quality Parameters
2.7.2. Experimental Diet
2.7.3. Histological and Hematological Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Sea Cucumber
3.2. Characterization of Biosynthesized Hi-ZnO-NPs
3.3. Antimicrobial Activities of Biosynthesized Hi-ZnO-NPs
3.4. Insecticidal Assay of Biosynthesized Hi-ZnO-NPs
3.5. Toxicity of Biosynthesized Hi-ZnO-NPs
3.5.1. Gill Histopathology
3.5.2. Liver Histopathology
3.5.3. Hematological Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chausali, N.; Saxena, J.; Prasad, R. Recent trends in nanotechnology applications of bio-based packaging. J. Agri. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, M.H.; El-Naggar, H.A.; El-Gayar, E.E.; Masood, M.F.; Mohamed, E.N.E. Effect of human activities on biodiversity in Nabq Protected Area, South Sinai, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, M.M.S.; El-Naggar, H.A.; Abou-Mahmoud, M.M.A.; Alabssawy, A.N.; Ahmed, H.O.; Abo-Taleb, H.A.; Kostas, K. Marine biodiversity patterns off Alexandria area, southeastern Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, H.A.; Salem, E.-S.S.; El-Kafrawy, S.B.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Shaban, W.M.; El-Gayar, E.E.; Ahmed, H.O.; Ashour, M.; Abou-Mahmoud, M.E. An integrated field data and remote sensing approach for impact assessment of human activities on epifauna macrobenthos biodiversity along the western coast of Aqaba Gulf. Ecohydrology 2021, 15, e2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Naggar, H.A.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Rady, I.; El-Wetidy, M.S.; Suleiman, W.B.; Al-Otibi, F.O.; Al-Rashed, S.A.; Abd El-Maoula, L.M.; Salem, E.S.; Attia, E.M.H.; et al. Two Red Sea Sponge Extracts (Negombata magnifica and Callyspongia siphonella) Induced Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.S.; El-Naggar, H.A.; El-Damhougy, K.A.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Ashour, M.; Abo-Taleb, H.A.H. GC-MS analysis of bioactive components in six different crude extracts from the Soft Coral (Sinularia maxim) collected from Ras Mohamed, Aqaba Gulf, Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liang, M.; Yan, J.; Chen, B. Nutrient requirements and growth of the sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. In Advances in Sea Cucumber Aquaculture and Management; Lovatelli, A., Conand, C., Purcell, S., Uthicke, S., Hamel, J.-R., Mercier, A., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.W.; Conand, C.; Samyn, Y. Commercially Important Sea Cucumber of the World; FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes No. 6. Rome; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; 150p. [Google Scholar]
- Hasaballah, A.I.; El-Naggar, H.A. Antimicrobial activities of some marine sponges, and its biological, repellent effects against Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Ann. Res. Rev. Biol. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, H.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Rady, I.; El-Naggar, H.A.; Abd El-Maoula, L.M.; Mehany, A.B.M. Antiproliferative activity, proapoptotic effect, and cell cycle arrest in human cancer cells of some marine natural product extract. Oxid. Med. Cell. Long. 2020, 2020, 7948705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-State, M.A.; Mahdy, H.M.; Ezzat, S.M.; Abd El Shakour, E.H.; El-Bahnasawy, M.A. Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from Rosetta Branch of river Nile, Egypt. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, S.M.; Abo-State, M.A.; Mahdy, H.M.; Abd EL-Shakour, E.H.; El-Bahnasawy, M.A. The effect of ionizing radiation on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from aquatic environments in Egypt. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2014, 4, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Dwivedi, S.; Azam, A.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Said, M.S.; Alkhedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J. Aloe vera extract functionalized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nano antibiotics against multi-drug resistant clinical bacterial isolates. J. Coll. Inter. Sci. 2016, 472, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Elbahnasawy, M.A.; Hasaballah, A.I. Green Phytosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Echinochloa stagnina Extract with Reference to Their Antibacterial, Cytotoxic, and Larvicidal Activities. Bionanoscience 2021, 11, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.M.; Sivasankarapillai, V.S.; Rahdar, A.; Joseph, J.; Sadeghfar, F.; Rajesh, K.; Kyzas, G.Z. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and antifungal activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1211, 128107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dappula, S.S.; Kandrakonda, Y.R.; Shaik, J.B.; Mothukuru, S.L.; Lebaka, V.R.; Mannarapu, M.; Amooru, G.D. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Andrographis alata: Characterization, optimization and assessment of their antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic and anti-Alzheimer’s properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1273, 134264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G. Research in mosquito control: Current challenges for a brighter future. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2801–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaballah, A.I. Impact of gamma irradiation on the development and reproduction of Culex pipiens (Diptera; Culicidae). Int. J. Rad. Biol. 2018, 94, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaballah, A.I. Impact of paternal transmission of gamma radiation on reproduction, oogenesis and spermatogenesis of the housefly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Int. J. Rad. Biol. 2021, 97, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintalchere, J.M.; Dar, M.A.; Pandit, R.S. Biocontrol efficacy of bay essential oil against housefly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2020, 81, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotedar, R.; Banerjee, U.; Singh, S.; Shriniwas, A.; Verma, A.K. The house fly Musca domestica as a carrier of pathogenic microorganisms in a Hospital Environment. J. Hosp. Infect. 1992, 20, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.C. Echinoderms of the Red Sea; Edwards, A.J., Head, S.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 215–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cherbonnier, G. Echinodermes: Holothuries; IRD Editions: Paris, France, 1988; 292p. [Google Scholar]
- Erwin, D.G.; Picton, B.E. Guide to Inshore Marine Life; IMMEL Publishing: London, UK, 1990; p. 219. [Google Scholar]
- Lieske, E.; Myers, R.F. Coral Reef Guide Red Sea: The Definitive Guide to over 1200 Species of Underwater Life; Harper Collins Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2004; 211p. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine, D.L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Velez, S.M.; Alexander, E.; Guevara, P. Antibiotic activity of lipid-soluble extracts from Caribbean marine algae. Hydrobiologia 1987, 151, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaba, M.H.; Moghannem, S.A.; El-Hawary, A.S.; Radwan, A.A.; Sharaf, M.H.; Shaban, A.S. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles mediated by Streptomyces plicatus: Characterizations, antimicrobial and nematicidal activities and cytogenetic effects. Plants 2021, 10, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, M.; Kalaivani, R.; Manikandan, S.; Kumaraguru, A.K. Metallic silver nanoparticle: A therapeutic agent in combination with antifungal drug against human fungal pathogen. Bioprocess Biosys. Eng. 2013, 36, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzinjy, A.A.; Azeez, H.H. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globulus Labill. leaf extract and zinc nitrate hexahydrate salt. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, M.H.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Kalaba, M.H.; Radwan, A.A.; Hashem, A.H. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic Activities and Phytochemical Analysis of Fungal Endophytes Isolated from Ocimum basilicum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 194, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasaballah, A.I.; El Naggar, H.A.; Abdelbary, S.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Selim, T.A. Eco friendly Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles by Marine Sponge, Spongia offcinalis: Antimicrobial and Insecticidal Activities against the Mosquito Vectors, Culex pipiens and Anopheles pharoensis. BioNanoScience 2021, 12, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaballah, A.I.; Selim, T.A.; Tanani, M.A.; Nasr, E.E. Lethality and Vitality Efficiency of Different Extracts of Salix safsaf Leaves against the House Fly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Afr. Èntomol. 2021, 29, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Laboratory and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.W. The WHO Programme for the Evaluation and Testing of New Insecticides. Bull. World Heal. Organ. 1971, 44, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mount, D.I. Methods for Aquatic Toxicity Identification Evaluations: Phase I: Toxicity Characterization Procedures; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA; Environmental Research Laboratory: Narragansett, DC, USA; National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center United States: Duluth, MN, USA, 1988; Volume 88.
- Al-Motabagani, M.A. Histological and histochemical studies on the effects of methotrexate on the liver of adult male albino rat. Int. J. Morphol. 2006, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusof, H.; Rahman, A.; Mohamad, R.; Zaidan, U.H.; Samsudin, A.A. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by cell-biomass and supernatant of Lactobacillus plantarum TA4 and its antibacterial and biocompatibility properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, S.; Sajjad, M. Bioinspired synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle and its combined efficacy with different antibiotics against multidrug resistant bacteria. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 8, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Belely, E.F.; Farag, M.; Said, H.A.; Amin, A.S.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Arthrospira platensis (Class: Cyanophyceae) and evaluation of their biomedical activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.K.; Malodia, L. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea: Characterization and its evaluation on tree seedling growth in nursery stage. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Nakara, A.; Menon, S.; Shanmugam, V. Eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cinnamomum Tamala leaf extract and its promising effect towards the antibacterial activity. J. Drug. Del. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, K.; Kalyanasundharam, S. Effect of chemically synthesis compared to biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles using aqueous extract of C. halicacabum and their antibacterial activity. OpenNano 2019, 4, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahnasawy, M.A.; Shehabeldine, A.M.; Khattab, A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Hashem, A.H. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using novel endophytic Rothia endophytica: Characterization and anticandidal activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Es’haghi, Z.; Hooshmand, S. Green and chemical synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and size evaluation by UV–vis spectroscopy. J. Nanomed. Res. 2018, 7, 00175. [Google Scholar]
- Jayarambabu, N.; Kumari, B.S.; Rao, K.V.; Prabhu, Y.T. Germination and growth characteristics of mungbean seeds (Vigna radiata L.) affected by synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 4, 2347–5161. [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath, A.; Perumal, E. Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: A promise for the future. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2017, 49, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.; Korenkov, V.; Judy, J.D.; Bertsch, P.M. Nanoparticles composed of Zn and ZnO inhibit Peronospora tabacina spore germination in vitro and P. tabacina infectivity on tobacco leaves. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro. Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, V.; Mishra, N.; Gadani, K.; Solanki, P.S.; Shah, N.A.; Tiwari, M. Mechanism of anti-bacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticle against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Liu, Y.; Mustapha, A.; Lin, M. Antifungal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 166, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.L.; Abuçafy, M.P.; Manaia, E.B.; Junior, J.A.O.; Chiari-Andréo, B.G.; Pietro, R.C.R.; Chiavacci, L.A. Relationship Between Structure And Antimicrobial Activity Of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: An Overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9395–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babayevska, N.; Przysiecka, Ł.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jarek, M.; Janiszewska, E.; Jurga, S. ZnO size and shape effect on antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity profile. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaballah, A.I.; Gobara, I.M.; El-Naggar, H.A. Larvicidal activity and ultrastructural abnormalities in the ovaries of the housefly “Musca domestica” induced by the soft coral “Ovabunda macrospiculata” synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, E.I.; Unlu, E. Sublethal effects of commercial deltamethrin on the structure of the gill, liver and gut tissues of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis: A microscopic study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 21, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilak, K.S.; Veeraiah, K.; Yacobu, K. Studies o histopathological changes in the gill, liver and kidney of Ctenopharyngodon idellus (Valenciennes) exposed to technical fenvalerate and EC 20%. Pollut. Res. 2001, 20, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ikele, C.B.; Mgbenka, B.O.; Oluah, N.S. Histopathological effects of diethyl phthalate on Clarias gariepinus juveniles. Anim. Re. Inter. 2011, 8, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, B.; Chatterjee, A.; Adhikari, S.; Ayyappan, S. Carbofuran- and cypermethrin-induced histopathological alterations in the liver of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) and its recovery. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Duysak, M.; Akbulut, M.; Yılmaz, S.; Gürkan, M.; Arslan, Z.; Ateş, M. Effects of subchronic exposure to zinc nanoparticles on tissue accumulation, serum biochemistry, and histopathological changes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Duan, Z.; Qi, R.; Li, Y.; Lang, Y. Comparative toxicity of several metal oxide nanoparticle aqueous suspensions to zebra fish (Danio rerio) early developmental stage. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2008, 43, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y. The impact of ZnO nanoparticle aggregates on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 195103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Chen, L. Oxidative stress responses in different organs of carp (Cyprinus carpio) with exposure to ZnO nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Diet Ingredients (%) | |
|---|---|
| Fish meal | 18.0 |
| Soybean meal | 29.0 |
| Yellow corn | 20.0 |
| Wheat bran | 15.0 |
| Alfalfa hay | 12.0 |
| Sunflower oil | 3.0 |
| Minerals mixture | 1.0 |
| Vitamin mixture | 1.0 |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | 1.0 |
| Total | 100 |
| Chemical Composition (g/kg) | |
| Crude protein | 30.11 |
| Ether extract | 12.35 |
| Ash | 14.34 |
| NFE 1 | 43.20 |
| GE 2 | 4600 Kcal/kg |
| Microorganism | Mean ± SD of Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) of the Tested Compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hi-ZnO-NPs (NPs) | Aqueous Extract of Sea Cucmber (F) | Zinc Acetate Solution (S) | Antibiotic Control (C) | |
| S. typhi | 22.3 ± 0.88 | 0 | 0 | 23.3 ± 0.88 |
| K. pneumonia | 27.0 ± 1.15 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 ± 0.88 |
| E. coli | 29.0 ± 0.57 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 30.3 ± 0.33 | 0 | 0 | 27.3 ± 0.33 |
| E. feacalis | 29.3 ± 0.88 | 0 | 0 | 21.6 ± 0.33 |
| A. niger | 23.6 ± 1.45 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Concentrations (ppm) | n | Larval Mortality % ± (SE) | LC50 (LCL–UCL) (ppm) | LC90 (LCL–UCL) (ppm) | χ2 (df = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 125 | 1.7 ± 0.97 a | 2.756 (2.463–3.103) | 9.294 (7.644–11.897) | 23.943 ns |
| Temephos | 125 | 100 ± 0.0 f | |||
| 0.5 | 125 | 6.3 ± 0.97 a | |||
| 1 | 125 | 16.8 ± 0.8 b | |||
| 2 | 125 | 29.6 ± 0.97 c | |||
| 4 | 125 | 55.2 ± 1.49 d | |||
| 8 | 125 | 96.0 ± 1.26 e |
| Concentrations (μg/adult) | n | Adult Mortality % ± (SE) | LD50 (LCL–UCL) (ppm) | LD90 (LCL–UCL) (ppm) | χ2 (df = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 50 | 2.0 ± 2.0 a | 4.285 (3.361–5.883) | 22.847 (13.875–52.051) | 5.852 ns |
| Cypermethrin | 50 | 100 ± 0.0 f | |||
| 0.5 | 50 | 6.0 ± 2.11 ab | |||
| 1 | 50 | 14.0 ± 2.45 b | |||
| 2 | 50 | 26.0 ± 1.58 c | |||
| 4 | 50 | 44.0 ± 2.45 d | |||
| 8 | 50 | 72.0 ± 2.0 e |
| Type of Gill Change | Control | Treatments (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | ||
| Lamellar fusion | - | ++ | +++ | + | + |
| Epithelium lifting | - | + | ++ | + | + |
| Vasodilatation | - | - | + | - | ++ |
| Aneurisms | - | - | - | + | - |
| Edema | - | - | + | - | - |
| Necrosis | - | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Hyperplasia | - | + | ++ | + | ++ |
| Type of Liver Change | Control | Treatments (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | ||
| Cytoplasmic vacuolation | - | + | +++ | + | ++ |
| Hemorrhage | - | + | ++ | + | + |
| Pyknotic nuclei | - | + | + | + | + |
| Necrosis | - | + | + | ++ | ++ |
| Parameters | Treatments (ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | |
| RBCs (×10/mm3) | 4.12 | 2.87 | 3.16 | 3.05 | 2.98 |
| Hb (g/100 mL) | 12.6 | 8.64 | 9.5 | 9.12 | 9.11 |
| PCV (%) | 40 | 28 | 31 | 30 | 29 |
| MCV (μm3/cell) | 97.09 | 97.56 | 98.1 | 98.36 | 97.32 |
| MCH (pg/cell) | 30.58 | 30.1 | 30.06 | 29.9 | 30.57 |
| MCHC (%) | 31.5 | 30.86 | 30.65 | 30.4 | 31.41 |
| WBCs (×103/mm3) | 10.76 | 9.33 | 8.68 | 9.15 | 10.25 |
| Heterophil (×103/mm3) | 2.15 | 2.71 | 2.34 | 2.01 | 2.67 |
| Lymphocyte (×103/mm3) | 7.53 | 5.6 | 5.38 | 6.22 | 6.56 |
| Monocyte (×103/mm3) | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.82 |
| Basophil (×103/mm3) | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.1 |
| Esinophil (×103/mm3) | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.1 |
| Parameters | Treatments (ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | |
| lysozyme (µg/mL) | 6.29 | 3.98 | 4.29 | 4.19 | 4.25 |
| phagocytic index (%) | 1.3 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1 | 1.05 |
| phagocytic activity (%) | 12.24 | 8.05 | 7.94 | 8.3 | 9.11 |
| IgM (µg/mL) | 5.26 | 1.35 | 2.58 | 3.01 | 4.15 |
| Parameters | Treatments (ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 4.19 | 3.41 | 3.46 | 2.98 | 3.7 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 1.66 | 1.39 | 1.33 | 1.21 | 1.41 |
| Globulin (g/dL) | 2.53 | 2.02 | 2.13 | 1.77 | 2.29 |
| AST (U/L) | 30.11 | 51.25 | 49.68 | 53.15 | 39.86 |
| ALT (U/L) | 30.16 | 41.03 | 38.46 | 50.14 | 37.98 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 2.19 | 3.05 | 3.16 | 3.12 | 3.2 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.4 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| Lipase (U/L) | 29.86 | 20.19 | 26.87 | 29.78 | 29.65 |
| Amylas (U/L) | 61.01 | 40.16 | 42.85 | 51.39 | 46.82 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 10.25 | 11.35 | 15.99 | 12.34 | 10.98 |
| Cholestrol (mg/dL) | 69.86 | 74.34 | 91.34 | 81.64 | 80.15 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 103.15 | 81.34 | 85.99 | 90.14 | 88.69 |
| Parameters | Treatments (ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | |
| MDA nmol/g | 16.54 | 25.64 | 29.86 | 19.86 | 20.01 |
| CAT U/gm | 18.17 | 13.56 | 14.25 | 14.29 | 12.99 |
| SOD U/gm | 23.58 | 14.85 | 15.98 | 18.64 | 17.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbahnasawy, M.A.; El-Naggar, H.A.; Abd-El Rahman, I.E.; Kalaba, M.H.; Moghannem, S.A.; Al-Otibi, F.; Alahmadi, R.M.; Abdelzaher, O.F.; Mabrouk, M.M.; Gewida, A.G.A.; et al. Biosynthesized ZnO-NPs Using Sea Cucumber (Holothuria impatiens): Antimicrobial Potential, Insecticidal Activity and In Vivo Toxicity in Nile Tilapia Fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Separations 2023, 10, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030173
Elbahnasawy MA, El-Naggar HA, Abd-El Rahman IE, Kalaba MH, Moghannem SA, Al-Otibi F, Alahmadi RM, Abdelzaher OF, Mabrouk MM, Gewida AGA, et al. Biosynthesized ZnO-NPs Using Sea Cucumber (Holothuria impatiens): Antimicrobial Potential, Insecticidal Activity and In Vivo Toxicity in Nile Tilapia Fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Separations. 2023; 10(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030173
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbahnasawy, Mostafa A., Hussein A. El-Naggar, Ibrahim E. Abd-El Rahman, Mohamed H. Kalaba, Saad A. Moghannem, Fatimah Al-Otibi, Reham M. Alahmadi, Othman F. Abdelzaher, Mohamed M. Mabrouk, Ahmed G. A. Gewida, and et al. 2023. "Biosynthesized ZnO-NPs Using Sea Cucumber (Holothuria impatiens): Antimicrobial Potential, Insecticidal Activity and In Vivo Toxicity in Nile Tilapia Fish, Oreochromis niloticus" Separations 10, no. 3: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030173
APA StyleElbahnasawy, M. A., El-Naggar, H. A., Abd-El Rahman, I. E., Kalaba, M. H., Moghannem, S. A., Al-Otibi, F., Alahmadi, R. M., Abdelzaher, O. F., Mabrouk, M. M., Gewida, A. G. A., AbdEl-Kader, M. F., & Hasaballah, A. I. (2023). Biosynthesized ZnO-NPs Using Sea Cucumber (Holothuria impatiens): Antimicrobial Potential, Insecticidal Activity and In Vivo Toxicity in Nile Tilapia Fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Separations, 10(3), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030173