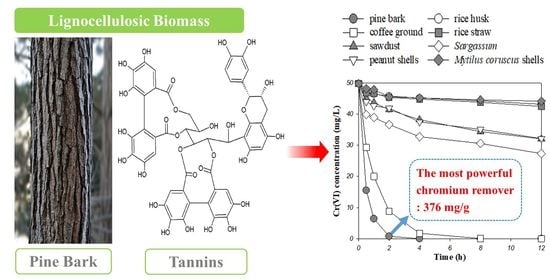
Superior Removal of Toxic Cr(VI) from Wastewaters by Natural Pine Bark
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Biomass
2.2. Batch Biosorption Studies
2.3. Chromium Analysis
2.4. FTIR Analysis
2.5. XPS Analysis
2.6. SEM-EDX Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Pine Bark
3.2. Removal Behaviors of Cr(VI) by Pine Bark
3.3. FTIR Spectroscopic Study
3.4. XPS Study
3.5. SEM-EDX Study
3.6. Evaluation of Cr(VI)-Reducing Power of Pine Bark
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.X.; Dou, J.F.; Xu, H.B. Removal of Cr(VI) ions by sewage sludge compost biomass from aqueous solutions: Reduction to Cr(III) and biosorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Fan, X.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Shen, S.; Hu, D. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water by quaternized chitin/branched polyethylenimine biosorbent with hierarchical pore structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.V.; Phung, O.J. Effect of chromium supplementation on glycated hemoglobin and fasting plasma glucose in patients with diabetes mellitus. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnhart, J. Occurrences, uses, and properties of chromium. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1997, 26, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, C.; Fiol, N.; Poch, J.; Villaescusa, I. Modeling of kinetics of Cr(VI) sorption onto grape stalk waste in a stirred batch reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Park, S.; Hong, H.J.; Choi, Y.E.; Yang, J.W. Biosorption of chromium (Cr(III)/Cr(VI)) on the residual microalga Nannochloris oculata after lipid extraction for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11155–11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzahuatl-Muñoz, A.R.; Aranda-García, E.; Cristiani-Urbina, M.D.C.; Barragán-Huerta, B.E.; Villegas-Garrido, T.L.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Removal of hexavalent and total chromium from aqueous solutions by Schinus molle Bark. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 2911–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.S.; Park, J.M. Reduction of hexavalent chromium with the brown seaweed Ecklonki biomass. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4860–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.S.; Jo, J.H.; Park, J.M. Mechanism of hexavalent chromium removal by dead fungal biomass of Aspergillus niger. Water Res. 2005, 39, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.-S.; Park, J.M. Use of dead fungal biomass for the detoxification of hexavalent chromium: Screening and kinetics. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Guo, X.; Lautner, S.; Saake, B. Removal of hexavalent chromium by different modified spruce bark adsorbents. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2014, 34, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Braghiroli, F.L.; Amaral-Labat, G.; Boss, A.F.N.; Lacoste, C.; Pizzi, A. Tannin gels and their carbon derivatives: A review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arbenz, A.; Avérous, L. Chemical modification of tannins to elaborate aromatic biobased macromolecular architectures. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2626–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Nuñez, P.V.; Aranda-García, E.; Cristiani-Urbina, M.C.; Morales-Barrera, L.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Removal of hexavalent and total chromium from aqueous solutions by plum (P. domestica L.) tree bark. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Wong, Y.S.; Wong, M.H.; Tam, N.F.Y. Biosorption and bioreduction of Cr(VI) by a microalgal isolate, Chlorella miniata. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzahuatl-Muñoz, A.R.; Morales-Barrera, L.; Cristiani-Urbina, M.d.C.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Hexavalent chromium reduction and chromium biosorption by Prunus serotina bark. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, P.; Baquero, L.P.; Larrota, H.R. Flavonoids: Potential therapeutic agents by their antioxidant capacity. In Bioactive Compounds: Health Benefits and Potential Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 265–288. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.S.; Wang, S.L.; Huang, S.T.; Tzou, Y.M.; Huang, J.H. Biosorption of Cr(VI) by coconut coir: Spectroscopic investigation on the reaction mechanism of Cr(VI) with lignocellulosic material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; Pereira, H.; Olivella, M.A.; Villaescusa, I. Heavy metals removal in aqueous environments using bark as a biosorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aronniemi, M.; Sainio, J.; Lahtinen, J. Chemical state quantification of iron and chromium oxides using XPS: The effect of the background subtraction method. Surf. Sci. 2005, 578, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.; Paul, D.; Singh, A.; Gupta, T. Removal of hexavalent chromium upon interaction with biochar under acidic conditions: Mechanistic insights and application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16786–16797. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, X. Biochar as both electron donor and electron shuttle for the reduction transformation of Cr (VI) during its sorption. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.; Lo, W.-H.; Babel, S. Physico–chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.L.; Lee, C.K.; Low, K.S.; Zainal, Z. Sorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) in aqueous solution by ethylenediamine modified RCE hull. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobya, M. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hazelnut shell activated carbon: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, T.; Rajgopal, S.; Miranda, L.R. Chromium(VI) adsorption from aqueous solution by Hevea Brasilinesis sawdust activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 124, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Singh, D.; Garg, V.K. A comparative study for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by agriculture wastes' carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Doi, S.; Cho, N.S.; Kim, H.E. Removal of hexavalent chromium from dilute aqueous solution by coniferous leaves. Holzforschung 1999, 53, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakiky, M.; Khamis, M.; Manassra, A.; Mer'eb, M. Selective adsorption of chromium(VI) in industrial wastewater using low-cost abundantly available adsorbents. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, R.; Narimura, K.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K.; Watari, T.; Inoue, K. Grape waste as a biosorbent for removing Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, J.R.; Memon, S.Q.; Bhanger, M.I.; El-Turki, A.; Hallam, K.R.; Allen, G.C. Banana peel: A green and economical sorbent for the selective removal of Cr(VI) from industrial wastewater. Colloids Surf. B 2009, 70, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 5.651 |
| Ash (%) | 21.25 |
| Volatile organic matter (%) | 73.10 |
| Carbon (%) | 55.57 |
| Hydrogen (%) | 5.549 |
| Nitrogen (%) | 0.080 |
| Sulfur (%) | 0.077 |
| Oxygen (%) | 37.19 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −27 |
| Point of zero charge (pHpzc) | 3.79 |
| Biomass | Proposed Mechanism of the Cr(VI) Removal | Cr(VI) Removal Capacity (mg/g) | pH | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethylenediamine-modified rice hull | Adsorption a | 23.4 | 2.0 | [25] |
| Hazelnut shell | Adsorption a | 170 | 1.0 | [26] |
| Sawdust activated carbon | Adsorption a | 65.8 | 2.0 | [27] |
| Sugar beet pulp | Adsorption a | 17.2 | 2.0 | [28] |
| Maize cob | Adsorption a | 13.8 | 1.5 | [29] |
| Sugarcane baggase | Adsorption a | 13.4 | 2.0 | [30] |
| Coniferous leaves | Adsorption a | 6.3 | 3.0 | [29] |
| Pine needle | Adsorption a | 21.5 | 2.0 | [30] |
| Grape waste | Adsorption-coupled reduction b | 99.3 | 4.0 | [31] |
| Banana peel | Adsorption-coupled reduction b | 96.2 | 2.0 | [32] |
| Pine bark | Adsorption-coupled reduction b | 376.3 | 2.0 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Kim, N.; Park, D. Superior Removal of Toxic Cr(VI) from Wastewaters by Natural Pine Bark. Separations 2023, 10, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080430
Yang H, Kim N, Park D. Superior Removal of Toxic Cr(VI) from Wastewaters by Natural Pine Bark. Separations. 2023; 10(8):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080430
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hanui, Namgyu Kim, and Donghee Park. 2023. "Superior Removal of Toxic Cr(VI) from Wastewaters by Natural Pine Bark" Separations 10, no. 8: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080430
APA StyleYang, H., Kim, N., & Park, D. (2023). Superior Removal of Toxic Cr(VI) from Wastewaters by Natural Pine Bark. Separations, 10(8), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080430