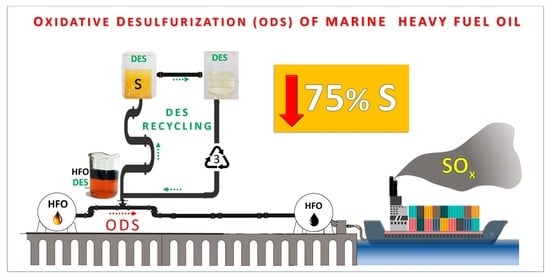
High-Degree Oxidative Desulfurization of a Commercial Marine Fuel Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Recycling Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Presence of Sulfur in Fuels
1.2. Technologies for Sulfur Removal from Fuels
1.3. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Petroleum Distillates
1.4. Regeneration of Deep Eutectic Solvents
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oxidation and Extraction
2.2. Recycling DESs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Oxidation Conditions on the Desulfurization Efficiency of HFO
3.1.1. Effect of the H2O2/S Molar Ratio
3.1.2. Effect of Catalyst Type
3.1.3. Effect of the H2O2/Acid Molar Ratio
3.1.4. Effect of Oxidation Temperature and Time
3.2. The Effect of Extraction Conditions on the Desulfurization Efficiency of HFO
3.2.1. Effect of the Type of DES on the Desulfurization Efficiency of HFO
3.2.2. Effect of Solvent/Oil Mass Ratio
3.2.3. Effect of Extraction Temperature and Time
3.3. DES Recyclability
3.3.1. Liquid–Liquid Extraction
3.3.2. Anti-Solvent Addition
3.3.3. Consecutive Cycles of Oxidative Desulfurization and Solvent Regeneration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahim, M.A.; Al-Sahhaf, T.A.; Elkilani, A.S. Refinery Feedstocks and Products. In Fundamentals of Petroleum Refining; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W. Sulfur in Petroleum. In Applying Nanotechnology to Desulfurization Process in Petroleum Engineering, 1st ed.; Saleh, T.A., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Union Law. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32009L0030 (accessed on 31 May 2023).
- International Maritime Organization. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/MediaCentre/PressBriefings/pages/34-IMO-2020-sulphur-limit-.aspx (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Song, C.; Turaga, U.; Ma, X. Desulfurization. In Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing, 1st ed.; Lee, S., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.A. Characterization, determination and elimination technologies for sulfur from petroleum: Toward cleaner fuel and a safe environment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 25, e00080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, R.; Kiran, N.; Ahmed, S.; Muhammad, A.; Jatoi, A.S.; Mazari, S.A.; Salma, U.; Plechkova, N.V. Extractive desulfurization of fuel oils using deep eutectic solvents—A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J. Deep desulfurization of fuels with cobalt chloride-choline chloride/polyethylene glycol metal deep eutectic solvents. Fuel 2018, 225, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houda, S.; Lancelot, C.; Blanchard, P.; Poinel, L.; Lamonier, C. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Oils with High Sulfur Content: A Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortezaee, A.; Movahedirad, S.; Sobati, M.A. Challenges of oxidative/extractive desulphurization of heavy fuel oil. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 101, 1802–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.; Waqas, A.; Muhammad, I. Desulfurization of liquid fuels using air-assisted performic acid oxidation and emulsion catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritt-Rasmussen, J.; Wegeberg, S.; Gustavson, K.; Sørheim, K.R.; Daling, P.S.; Jørgensen, K.; Tonteri, O.; Holst-Andersen, J.P. Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO); TemaNord; 2018:549; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018; ISBN 978-92-893-5851-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mirshafiee, F.; Movahedirad, S.; Sobati, M.A.; Alaee, R.; Zarei, S.; Sargazi, H. Current status and future prospects of oxidative desulfurization of naphtha: A review. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, R.; Darian, J.T.; Ghaedian, M.; Shafeghat, A.; Safavi, M. Desulfurization of Heavy Oil by Using Combination of Oxidation and Mild Thermolysis. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2019, 62, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vedachalam, S.; Dalai, A.K. Hydrotreating and Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Fuel Oil into Low Sulfur Marine Fuel over Dual Function NiMo/γ–Al2O3 Catalyst. Catalysis Today 2023, 407, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Saxena, S.; Xiao, C.; Mei, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Duan, A.; Roberts, W.L. Molecular characteristics of sulfur compounds in oxidative desulfurization for heavy fuel oil based on APPI FT-ICR MS analysis. Catal. Today 2022, 404, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlaja, A.S.; Alade, O.S.; Tshentu, Z.R. Vanadium(IV) catalysed oxidation of organosulfur compounds in heavy fuel oil. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2017, 20, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Racha, S.M.; Shown, B.; Mandal, S.; Das, A.K. New insights on oxidative desulfurization for low sulfur residual oil production. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedachalam, S.; Boahene, P.E.; Dalai, A.K. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Gas Oil over a Ti–TUD-1-Supported Keggin-Type Molybdenum Heteropolyacid. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15299–15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshi, A.; Shiralizadeh, P. Sulfur reduction of heavy fuel oil by oxidative desulfurization (ODS) method. Pet. Coal 2015, 57, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, D.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.; Mubarak, N.M.; Dharaskar, S.; Wong, W.Y.; Gupta, T.C.S.M. Deep eutectic solvents for extraction-desulphurization: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.; Branco, L.C.; Silvestre, A.J.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep desulfurization of fuels: Are deep eutectic solvents the alternative for ionic liquids? Fuel 2021, 293, 120297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, M.; Shan, W.; Deng, C.; Ren, W.; Shi, Z.; Lü, H. L-proline-based deep eutectic solvents (DESs) for deep catalytic oxidative desulfurization (ODS) of diesel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhu, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Hua, M.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhu, W.; et al. Synergistic effect of dual Brønsted acidic deep eutectic solvents for oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Guo, T.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Oxidative desulfurization of fuels promoted by choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 424, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, F.; Tian, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. One-pot extractive and oxidative desulfurization of fuel with ternary dual-acid deep eutectic solvent. Fuel 2022, 329, 125513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid-based DESs as extractants and catalysts for removal of DBT from model oil. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12805–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Deakyne, C.A.; Baker, G.A. Quantum Chemical Evaluation of Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extractive Desulfurization of Fuel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7525–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, Z.; Su, T.; Liao, W.; Hao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W.; Ge, H.; Lü, H. Novel acidic eutectic mixture as peroxidase mimetics for oxidative desulfurization of model diesel. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 255, 117747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.Y.; Ali, A.M.; Albayati, T.M. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents for ultrasonic-assisted oxidative desulfurization of actual heavy crude oil. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 182, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.Y.; Majid, M.F.; Rajasuriyan, S.; Zaid, H.F.M.; Jumbri, K.; Chong, F.K. Desulfurization Performance of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Presence of Graphene Oxide. Environments 2020, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isci, A.; Kaltschmitt, M. Recovery and recycling of deep eutectic solvents in biomass conversions: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 197–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słupek, E.; Makoś, P. Absorptive Desulfurization of Model Biogas Stream Using Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calemma, V.; Rausa, R.; D’Anton, P.; Montanari, L. Characterization of Asphaltenes Molecular Structure. Energy Fuels 1998, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenzin, H.; Mullins, O.C. Asphaltene Molecular Size and Structure. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Kamble, P.D.; Basu, J.K.; Sengupta, S. Kinetic Study and Optimization of Oxidative Desulfurization of Benzothiophene Using Mesoporous Titanium Silicate-1 Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Table A.1. In Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtarpour, M.; Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Golgoun, S. Solubility and solvation behavior of some drugs in choline based deep eutectic solvents at different temperatures. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, T.; Shahbaz, K.; Farid, M.M. Improving the production of propyl and butyl ester-based biodiesel by purification using deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, G.; Ashokkumar, M.; Alizadeh, A. Ultrasound-assisted oxidative-adsorptive desulfurization using highly acidic graphene oxide as a catalyst-adsorbent. Fuel 2017, 210, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimov, I.N.; Losev, A.P. On the Nature of UV/Vis Absorption Spectra of Asphaltenes. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2007, 25, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Oxidation | Extraction | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. | Fuel | Oxidant | Oxidant Concentration | Catalyst | Catalyst Concentration | T (°C) | Time | Solvent | S/O | T (°C) | Time | S Removal Degree |
| [10] | HFO (3.1 wt.% S) | H2O2 30% | O/S = 0.25–5 | FA, AA, H2SO4 | C/S = 40 | 50 °C | 2 h | DMF | 1/1 | RT | 30 min | Not reported |
| [11] | HGO (4 wt.% S) | H2O2 30% | Oil/H2O2: 4/1 v/v | FA, POM | Oil/FA: 20/6.5 v/v | 60 °C | 1 h | MeOH/H2O: 80/20 | 1/1 | RT | 10 min | 40–70% |
| [14] | VGO (2.81 wt.% S) | H2O2 30% | O/S = 4/1 | FA | O/C = 2/1 | 55 °C | 2 h | - | - | - | - | 65% |
| [15] | HDS-HFO (1.14 wt.%) | Cumene hydroperoxide | O/S = 5.8/1 | NiMo/γ–Al2O3 | C/HFO = 2/40 w/w | 68 °C | 96 min | acetonitrile | 2/1 | 50 °C | - | <0.5 wt.% S |
| [16] | HFO | H2O2 30% | O/S = 10 | Mo/Al2O3 | C/Oil = 1.5/30 w/w | 60 °C | 4 h | acetonitrile | 2/1 | 60 °C | 1 h | 30.7% |
| [17] | HFO (~1.8 wt.% S) | TBHP | O/S = 10/1 | Solid catalyst | - | 70 °C | - | - | - | - | - | ~50% |
| [18] | Residual oil (S > 1.5 wt.%) | Cumene hydroperoxide, H2O2, TBHP | 20–30% v/v | V2O5/Al2O3, FA, AA | 4–30% v/v acid | 60–80 °C | 2–3 h | MeOH, acetonitrile | 1/1 | RT | 1 h | Up to 73.2% |
| [19] | HDS-HGO | Cumene hydroperoxide, H2O2, TBHP, O2 | H2O2/Oil = 14/40 w/w, 10/1 molar | Mesoporous solid catalyst | C/Oil = 2/40 w/w | 70 °C | 2 h | MeOH | 1/1 | RT | - | ~70% |
| [20] | HFO (2.75 wt.% S) | H2O2 30% | 15–40 wt.% | FA, AA | 8–50% | 60 °C | 90 min | acetonitrile | 1/1 | RT | 10 min | Final: 1.14 wt.% S |
| Νο. | HFO (wt.%) | H2O2 (wt.%) | Acetic (A) or Formic (F) Acid (wt.%) | H2O2/S (Molar Ratio) | H2O2/Acid (Molar Ratio) | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | S Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70.10 | 18.70 | (A) 11.20 | 2.50 | (A) 1.0 | 60 | 90 | 56.5 |
| 2 | 56.50 | 15.26 | (A) 28.24 | 2.50 | (A) 0.33 | 60 | 90 | 72.4 |
| 3 | 75.40 | 20.40 | (A) 4.20 | 2.50 | (A) 3.0 | 60 | 90 | 41.6 |
| 4 | 56.50 | 15.26 | (A) 28.24 | 2.50 | (A) 0.33 | 80 | 90 | 58.6 |
| 5 | 56.50 | 15.26 | (A) 28.24 | 2.50 | (A) 0.33 | 45 | 90 | 75.7 |
| 6 | 56.50 | 15.26 | (A) 28.24 | 2.50 | (A) 0.33 | 60 | 180 | 74.5 |
| 7 | 76.27 | 20.54 | (F) 3.20 | 2.50 | (F) 3.0 | 60 | 90 | 47.6 |
| 8 | 100 | - | - | - | - | 60 | 90 | 50.9 |
| Νο. | DES | Solvent/Oil Mass Ratio | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | S Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | ChCl/EG (1/2) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | 72.4 |
| 9 | ChCl/LA (1/2) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | 62.6 |
| 10 | ChCl/LA (1/4) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | 49.6 |
| 11 | ChCl/LA/CA (1/2/1) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | X |
| 12 | ChCl/LA/CA (1/4/1) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | X |
| 13 | ChlCl/PEG400 (1/6) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | 60.5 |
| 14 | ChlCl/PEG400 (1/6) + H2O (1/1 w/w) | 5/1 | 60 | 90 | 70.3 |
| 15 | ChCl/EG (1/2) | 2/1 | 60 | 90 | X |
| 16 | ChCl/EG (1/2) | 0.5/1 | 60 | 90 | X |
| 17 | ChCl/EG (1/2) | 5/1 | 60 | 180 | 71.1 |
| 18 | ChCl/EG (1/2) | 5/1 | 80 | 90 | 69.6 |
| No. | DES | Method | Solvent | Solvent/DES Mass Ratio | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | ChCl/EG = 1/2 (From Exp. No. 2) | Liquid–liquid extraction | Acetone | 1/1 | Room T | 60 |
| 20 | ChCl/EG = 1/2 (From Exp. No. 2) | Liquid–liquid extraction | Toluene | 1/1 | Room T | 60 |
| 21 | ChCl/EG = 1/2 (From Exp. No. 2) | Anti-solvent addition | Ethanol | 1/1 | Room T | 60 |
| 22 | ChCl/EG = 1/2 (From Exp. No. 2) | Anti-solvent addition | Water | 1/1 | Room T | 60 |
| 23 | ChCl/EG = 1/2 (From Exp. No. 2) | Anti-solvent addition | Water | 5/1 | Room T | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thoda, O.; Svinterikos, E.; Sakkas, K.M.; Moschovi, A.M.; Yakoumis, I. High-Degree Oxidative Desulfurization of a Commercial Marine Fuel Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Recycling Process. Separations 2023, 10, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080445
Thoda O, Svinterikos E, Sakkas KM, Moschovi AM, Yakoumis I. High-Degree Oxidative Desulfurization of a Commercial Marine Fuel Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Recycling Process. Separations. 2023; 10(8):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080445
Chicago/Turabian StyleThoda, Olga, Efstratios Svinterikos, Konstantinos Miltiadis Sakkas, Anastasia Maria Moschovi, and Iakovos Yakoumis. 2023. "High-Degree Oxidative Desulfurization of a Commercial Marine Fuel Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Recycling Process" Separations 10, no. 8: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080445
APA StyleThoda, O., Svinterikos, E., Sakkas, K. M., Moschovi, A. M., & Yakoumis, I. (2023). High-Degree Oxidative Desulfurization of a Commercial Marine Fuel Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Recycling Process. Separations, 10(8), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10080445