Determination of Tedizolid in Bacterial Growth Medium Mueller-Hinton Broth by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application to an In Vitro Study in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model
Abstract
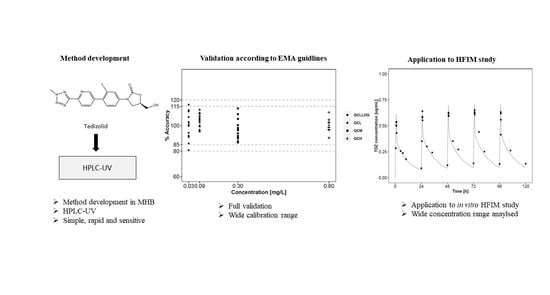
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Calibration and Quality Control Samples
2.3. Sample Treatment
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Application Study in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model
3. Results
3.1. Sample Treatment and Recovery
3.2. HPLC Instrument Method
3.3. Linearity and Sensitivity
3.4. Validation of the Bioanalytical Assay
3.5. Application to HFIM PK Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Livermore, D.M.; Mushtaq, S.; Warner, M.; Woodford, N. Activity of oxazolidinone TR-700 against linezolid-susceptible and -resistant staphylococci and enterococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prokocimer, P.; De Anda, C.; Fang, E.; Mehra, P.; Das, A. Tedizolid phosphate vs linezolid for treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections: The ESTABLISH-1 randomized trial. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 309, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Xue, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Glenschek-Sieberth, M.; Lyu, Y. Comparative in vitro potency and kill curve activity of tedizolid and linezolid against Gram-positive bacteria isolated from Chinese hospitalized patients in 2013–2016 Antimicrobial Original Research Paper Comparative in vitro potency and kill curve activity of tedizolid and linezolid against Gram-positive bacteria isolated from Chinese hospitalized patients in 2013-2016. J. Chemother. 2013, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, D.; Srivastava, S.; Nuermberger, E.; Koeuth, T.; Martin, K.R.; Cirrincione, K.N.; Lee, P.S.; Gumbo, T. Multiparameter Responses to Tedizolid Monotherapy and Moxifloxacin Combination Therapy Models of Children with Intracellular Tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, S342–S348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, A.S.; Abdelhady, W.; Li, L.; Gonzales, R.; Xiong, Y.Q. Comparative efficacies of tedizolid phosphate, linezolid, and vancomycin in a murine model of subcutaneous catheter-related biofilm infection due to methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5092–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wicha, S.G.; Kloft, C. Simultaneous determination and stability studies of linezolid, meropenem and vancomycin in bacterial growth medium by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1028, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, S.; Ca, S.; Dp, N. Development of a High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Tedizolid in Human Plasma. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 6 2015, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, M. A highly sensitive and efficient UPLC-MS/MS assay for rapid analysis of tedizolid (a novel oxazolidinone antibiotic) in plasma sample. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Pan, C.W.; Xie, Q.P.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, Y.Z.; Lin, Y.M. Simultaneous determination of tedizolid and linezolid in rat plasma by ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1011, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahre, M.; Sabarinath, S.; Grant, M.; Seubert, C.; DeAnda, C.; Prokocimer, P.; Derendorf, H. Skin and soft tissue concentrations of tedizolid (formerly torezolid), a novel oxazolidinone, following a single oral dose in healthy volunteers. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louie, A.; Liu, W.; Kulawy, R.; Drusano, G.L. In vivo pharmacodynamics of torezolid phosphate (TR-701), a new oxazolidinone antibiotic, against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in a mouse thigh infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, R.; Kai, M.; Goto, K.; Ohchi, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Tatsuta, R.; Kitano, T.; Itoh, H. High-throughput and wide-range simultaneous determination of linezolid, daptomycin and tedizolid in human plasma using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.Y.J.; Wang, J.; Jayne, J.; Fukushima, L.; Rao, A.P.; D’Argenio, D.Z.; Beringer, P.M. Pharmacokinetics of tedizolid in plasma and sputum of adults with cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Housman, S.T.; Pope, J.S.; Russomanno, J.; Salerno, E.; Shore, E.; Kuti, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P. Pulmonary disposition of tedizolid following administration of once-daily oral 200-milligram tedizolid phosphate in healthy adult volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, S.; Passarell, J.; Lu, Q.; Fiedler-Kelly, J.; Ludwig, E.; Prokocimer, P. Tedizolid population pharmacokinetics, exposure response, and target attainment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6462–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, M.; Zhang, M.; Xin, Y.; Zheng, G.; Cheng, S. Comparative pharmacokinetics of tedizolid in rat plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 107, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, C.; Schießer, S.; Wulkersdorfer, B.; Hitzenbichler, F.; Kees, M.G.; Zeitlinger, M. Determination of free clindamycin, flucloxacillin or tedizolid in plasma: Pay attention to physiological conditions when using ultrafiltration. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stainton, S.M.; Monogue, M.L.; Baummer-Carr, A.; Shepard, A.K.; Nugent, J.F.; Kuti, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P. Comparative assessment of tedizolid pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration between diabetic patients with wound infections and healthy volunteers via in vivo microdialysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milosevic, T.V.; Payen, V.L.; Sonveaux, P.; Muccioli, G.G.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. Mitochondrial Alterations (Inhibition of Mitochondrial Protein Expression, Oxidative Metabolism, and Ultrastructure) Induced by Linezolid and Tedizolid at Clinically Relevant Concentrations in Cultured Human HL-60 Promyelocytes and THP-1 Monocytes Downloa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, S.; Fang, E.; Muñoz, K.A.; Minassian, S.L.; Prokocimer, P.G. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability of tedizolid. Pharmacotherapy 2014, 34, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landersdorfer, C.B.; Rees, V.E.; Yadav, R.; Rogers, K.E.; Kim, T.H.; Bergen, P.J.; Cheah, S.E.; Boyce, J.D.; Peleg, A.Y.; Oliver, A.; et al. Optimization of a meropenem-tobramycin combination dosage regimen against hypermutable and nonhypermutable pseudomonas aeruginosa via mechanism-based modeling and the hollow-fiber infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heffernan, A.J.; Sime, F.B.; Sarovich, D.S.; Neely, M.; Guerra-Valero, Y.; Naicker, S.; Cottrell, K.; Harris, P.; Andrews, K.T.; Ellwood, D.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Plasma and Epithelial Lining Fluid Exposures of Amikacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Dynamic In Vitro Hollow-Fiber Infection Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00879-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Broeker, A.; Nowak, H.; Rahmel, T.; Nussbaumer-Pröll, A.; Österreicher, Z.; Zeitlinger, M.; Wicha, S.G. A pharmacometric approach to define target site-specific breakpoints for bacterial killing and resistance suppression integrating microdialysis, time–kill curves and heteroresistance data: A case study with moxifloxacin. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioanalytical method validation|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/bioanalytical-method-validation#current-effective-version-section (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Drusano, G.L.; Shields, R.K.; Mtchedlidze, N.; Nguyen, M.H.; Clancy, C.J.; Vicciarelli, M.; Louie, A. Pharmacodynamics of ceftazidime plus avibactam against KPC-2-bearing isolates of klebsiella pneumoniae in a hollow fiber infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Jin, B.; Ma, C.; Zhang, T.; Li, T. Identification of forced degradation products of tedizolid phosphate by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 139, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, D.; Srivastava, S.; Pasipanodya, J.G.; Lee, P.S.; Gumbo, T. Tedizolid is highly bactericidal in the treatment of pulmonary Mycobacterium avium complex disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, ii30–ii35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Inter-Day | Intra-Day | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | |||||||
| QC tier | TDZ (mg/L) | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV |
| QCLLOQ | 0.03 | 99.9 | 9.0 | 100.8 | 7.9 | 97.8 | 14.0 | 98.5 | 2.8 |
| QCL | 0.09 | 104.8 | 4.0 | 105.1 | 4.8 | 101.2 | 6.2 | 105.3 | 4.4 |
| QCM | 0.3 | 91.6 | 4.6 | 103.7 | 8.8 | 94.7 | 3.6 | 96.7 | 6.3 |
| QCH | 0.8 | 100.7 | 3.6 | 102.9 | 5.0 | 96.2 | 4.0 | 99.9 | 3.4 |
| Freeze/Thaw (3 Cycles) | Bench Top (20 °C, 6 h) | Autosampler (15 h, 4 °C) | Incubator (37 °C, 24 h) | Long-Term Stability (3 months, −80 °C) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QC tier | TDZ (mg/L) | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. % CV | Acc. (%) | Prec. %CV |
| QCL | 0.09 | 99.6 | 7.8 | 95.8 | 7.8 | 102.9 | 7.8 | 104.3 | 7.0 | 99.1 | 8.6 |
| QCM | 1.0 | 95.0 | 1.2 | 94.2 | 8.5 | 95.3 | 0.8 | 109.0 | 0.7 | 94.8 | 5.9 |
| QCH | 3.2 | 103.2 | 2.2 | 94.6 | 6.0 | 104.8 | 4.3 | 107.3 | 2.1 | 89.4 | 8.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, K.; Milioudi, A.; Martínez, E.H.; Wicha, S.G. Determination of Tedizolid in Bacterial Growth Medium Mueller-Hinton Broth by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application to an In Vitro Study in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model. Separations 2021, 8, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090141
Iqbal K, Milioudi A, Martínez EH, Wicha SG. Determination of Tedizolid in Bacterial Growth Medium Mueller-Hinton Broth by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application to an In Vitro Study in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model. Separations. 2021; 8(9):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090141
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Khalid, Aliki Milioudi, Elena Haro Martínez, and Sebastian Georg Wicha. 2021. "Determination of Tedizolid in Bacterial Growth Medium Mueller-Hinton Broth by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application to an In Vitro Study in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model" Separations 8, no. 9: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090141
APA StyleIqbal, K., Milioudi, A., Martínez, E. H., & Wicha, S. G. (2021). Determination of Tedizolid in Bacterial Growth Medium Mueller-Hinton Broth by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application to an In Vitro Study in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model. Separations, 8(9), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090141