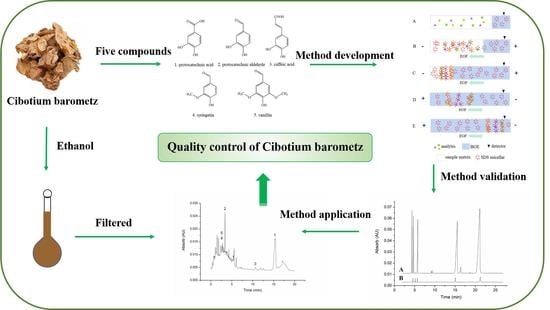
Simultaneous Separation and Analysis of Five Compounds in Cibotium barometz by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography with Large-Volume Sample Stacking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of Solutions and Samples
2.4. Electrophoretic Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Type and Concentration of Background Electrolytes (BGE)
3.2. Optimization of the pH of BGE
3.3. Optimization of MEKC Conditions
3.4. Optimization of LVSS Stacking Time and Injection Time
3.5. The Principles of This LVSS-MEKC Method
3.6. Stacking Efficiency
3.7. Method Validation
3.8. Analysis of Sample and Recoveries of Spiked Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Yi, P.; Yan, C.; Huang, D. Structural characterization and osteoprotective effects of a novel oligo-glucomannan obtained from the rhizome of Cibotium barometz by alkali extraction. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 113, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Wajeeh, N.S.; Hajrezaei, M.; Al-Henhena, N.; Kamran, S.; Bagheri, E.; Zahedifard, M.; Saremi, K.; Noor, S.M.; Ali, H.M.; Abdulla, M.A. The antiulcer effect of Cibotium barometz leaves in rats with experimentally induced acute gastric ulcer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.-B.; He, Q.; Cao, P.; Lei, W. Anti-osteoporosis activity of Cibotium barometz extract on ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.; Chen, D.; Li, X. Antioxidant Activity of Rhizoma Cibotii in vitro. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 2, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Wajeeh, N.S.; Hajerezaie, M.; Noor, S.M.; Halabi, M.F.; Al-Henhena, N.; Azizan, A.H.S.; Kamran, S.; Hassandarvish, P.; Shwter, A.N.; Ali, H.M.; et al. The gastro protective effects of Cibotium barometz hair on ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.; Zheng, C.; Lin, J.; Ye, J.; Mei, Y.; Pan, C.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Ye, H.; Liu, X. Cibotium barometz polysaccharides stimulate chondrocyte proliferation in vitro by promoting G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3027–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Markus, J.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y.-J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Aceituno, V.C.; Ahn, S.; Yang, D.C. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Cibotium barometz root. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Yang, S. Advances in Research of Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Cibotium baromatz. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med Formulae 2010, 16, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Hou, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, C. Two novel polysaccharides from rhizomes of Cibotium barometz promote bone formation via activating the BMP2/SMAD1 signaling pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115732–115743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Pei, Q.; Ju, C.; Zhang, F.; Jia, T. Detection on effect of different processed Cibotium barometz on osteoblasts by CCK-8. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 4319–4323. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Luo, R.; He, Z. The Study of Processing Technology of Cibotium barometz. Clin. Med. Eng. 2011, 18, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.; He, Z. Determinations of Protocatechuic Acid and Protocatechualdehyde in Cibotium barometz. from Different Areas by HPLC. Clin. Med. Eng. 2011, 18, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Shan, G.; Ju, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jia, T. Analysis on sublimation and volatile components of Cibotium barometz using UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2013, 16, 2308–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Sun, N.; Zhao, M.; Ju, C.; Jia, T. Analysis of Chemical Compositionin MethanoI Extract of Yellow Hai from Rhizome of Cibotii Rhizoma by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, Y.W.; Ban, J.J.; Khoo, K.S.; Sit, N.W. Biological activities and phytochemical content of the rhizome hairs of Cibotium barometz (Cibotiaceae). Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 153, 112612–112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, Y. Screening bioactive compounds from natural product and its preparations using capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabanes, H.; Guidote, A.; Quirino, J. Capillary electrophoresis of natural products: Highlights of the last five years (2006–2010). Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harstad, R.; Johnson, A.; Weisenberger, M.; Bowser, M. Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řemínek, R.; Foret, F. Capillary electrophoretic methods for quality control analyses of pharmaceuticals: A review. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, A. Simultaneous separation and analysis of camptothecin alkaloids in real samples by large-volume sample stacking in capillary electrophoresis. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2018, 32, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semail, N.-F.; Noordin, S.S.; Keyon, A.S.A.; Waras, M.N.; Saad, B.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Zain, N.N.M.; Azizi, J.; Aziz, M.Y.; Yahaya, N. A simple and efficient sequential electrokinetic and hydrodynamic injections in micellar electrokinetic chromatography method for quantification of anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil and its metabolite in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2020, 35, e5050. [Google Scholar]
- Pieckowski, M.; Kowalski, P.; Bączek, T. Combination of large volume sample stacking with polarity switching and cyclodextrin electrokinetic chromatography (LVSS-PS-CDEKC) for the determination of selected preservatives in pharmaceuticals. Talanta 2020, 211, 120673–120679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlampová, A.; Malá, Z.; Gebauer, P. Recent progress of sample stacking in capillary electrophoresis (2016–2018). Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Ye, H.; Yu, L.; Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, G. Field-amplified sample stacking in capillary electrophoresis for the determination of alkaloids in Sinomenium acutum. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5267–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, X.; Mu, C.; Wu, D.; Wang, C.; QL, Q.Z. Rapid Fabrication of Gold Nanoflowers Tuned by pH: Insights Into the Growth Mechanism. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 2761–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Fan, M.; Zhu, Z.; Zhan, S.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; et al. Quantifying the efficiency of o-benzoquinones reaction with amino acids and related nucleophiles by cyclic voltammetry. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braschi, I.; Martucci, A.; Blasioli, S.; Mzini, L.; Ciavatta, C.; Cossi, M. Effect of humic monomers on the adsorption of sulfamethoxazole sulfonamide antibiotic into a high silica zeolite Y: An interdisciplinary study. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, W.; Jiang, S.; Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y. Determining ultraviolet absorbents in sunscreen products by combining direct injection with micelle collapse on-line preconcentration capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1383, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbay, C.; Hoyos, Y.; Hooper, E.; Arslan, H.; Rizvi, S. Cationic gemini surfactants as pseudostationary phases in micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Part I: Effect of head group. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5279–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzera, M. Quality control of herbal medicines by capillary electrophoresis: Potential, requirements and applications. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 3489–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, G.; Smyth, W. Large-volume sample stacking of selected drugs of forensic significance by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1996, 681, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, N.P. Chinese Pharmacopoeia, 11th ed.; Kuang, L., Li, C., Eds.; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 235. [Google Scholar]








| Representative Number | Analyte | Structure | pKa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | protocatechuic acid |  | 4.26 |
| 2 | protocatechuic aldehyde |  | 7.26 [25] |
| 3 | caffeic acid |  | 4.58 [26] |
| 4 | syringetin |  | 7.39 |
| 5 | vanillin |  | 7.80 [27] |
| Analyte | Content (μg/mL) | Intra-Day Peak Area RSD (%) | Inter-Day Peak Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| protocatechuic acid | 0.5 | 0.68 | 5.47 |
| protocatechuic aldehyde | 0.5 | 0.47 | 3.50 |
| caffeic acid | 0.5 | 0.94 | 5.07 |
| syringetin | 0.5 | 0.47 | 2.05 |
| vanillin | 0.5 | 0.48 | 2.71 |
| Analyte | Calibration Curve | Determination Coefficient (R2) | Linearity Range(μg/mL) | Detection Limit(μg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Work | Reference | ||||
| protocatechuic acid | y = 48,389x + 1603.2 | 0.999 | 0.25–10 | 6.5 × 10−5 | 0.032 [11], 0.0124 [12] |
| protocatechuic aldehyde | y = 52,313x + 6216.2 | 0.9927 | 0.25–10 | 6.5 × 10−5 | 0.0144 [11], 0.0102 [12] |
| caffeic acid | y = 61,388x + 11,869 | 0.9985 | 0.25–10 | 6.5 × 10−5 | ND 1 |
| syringetin | y = 163,658x − 38,019 | 0.9961 | 0.25–10 | 3.3 × 10−5 | ND 1 |
| vanillin | y = 293,371x + 51,259 | 0.9993 | 0.25–10 | 3.3 × 10−5 | ND 1 |
| Number | Protocatechuic Acid (mg/g) | Caffeic Acid (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| 2 | 0.12 | 0.04 |
| 3 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| average | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| RSD (%) | 3.81 | 3.39 |
| Analyte | Spiked (μg/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| protocatechuic acid | 0.5 | 97.4 | 1.1 |
| 1.0 | 96.4 | 2.7 | |
| 1.5 | 83.2 | 3.1 | |
| caffeic acid | 0.5 | 95.4 | 3.2 |
| 0.7 | 81.5 | 4.1 | |
| 1.0 | 84.4 | 4.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Yu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, H.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Peng, J. Simultaneous Separation and Analysis of Five Compounds in Cibotium barometz by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography with Large-Volume Sample Stacking. Separations 2021, 8, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090147
Wang L, Xu H, Yu L, Zhu Z, Ye H, Liu L, Li X, Peng J. Simultaneous Separation and Analysis of Five Compounds in Cibotium barometz by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography with Large-Volume Sample Stacking. Separations. 2021; 8(9):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090147
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lili, Huifeng Xu, Lishuang Yu, Zaishi Zhu, Hongzhi Ye, Linglong Liu, Xihai Li, and Jun Peng. 2021. "Simultaneous Separation and Analysis of Five Compounds in Cibotium barometz by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography with Large-Volume Sample Stacking" Separations 8, no. 9: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090147
APA StyleWang, L., Xu, H., Yu, L., Zhu, Z., Ye, H., Liu, L., Li, X., & Peng, J. (2021). Simultaneous Separation and Analysis of Five Compounds in Cibotium barometz by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography with Large-Volume Sample Stacking. Separations, 8(9), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090147