Simultaneous Extraction of Four Antibiotic Compounds from Soil and Water Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Soil Characterization
2.3. Water Extraction
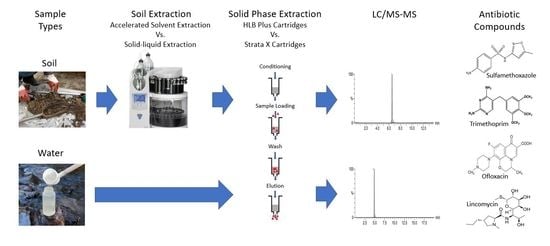
2.4. Soil Extraction
2.4.1. Equilibration Procedure
2.4.2. Extraction by LSE vs. ASE
2.4.3. Soil Characteristics and Processing Techniques Analysis
2.5. Solid Phase Extraction
2.5.1. Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) Procedure
2.5.2. Clean vs. Dirty Extraction Solutions with SPE
2.6. LC/MS/MS Quantification Procedure
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Extraction SPE Recoveries
3.1.1. HLB plus vs. Strata-X SPE Cartridges
3.1.2. Clean vs. Dirty Extracts
3.2. Soil Extraction Results
3.2.1. Determination of Extraction Method
3.2.2. Soil Type and Processing Technique
3.2.3. Matrix Effects Based on Internal Standard Signal
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Extractions
4.1.1. Comparison of SPE Cartridges
4.1.2. Comparison of Clean vs. Dirty Soil Extraction Solutions
4.2. Soil Extractions
4.2.1. Determination of Extraction Method
Sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim
Lincomycin
Ofloxacin
4.2.2. Soil Type and Processing Technique
Sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim
Lincomycin
Ofloxacin
4.2.3. Matrix Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- CDC. Antibiotic Use in the United States, 2018 Update: Progress and Opportunities; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- Food and Drug Administration. 2020 Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals; FDA: Rockville, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kümmerer, K. Significance of antibiotics in the environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, M.T.; Meyer, E.M.; Thurman, S.D.; Zaugg, L.B. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: A National reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glassmeyer, S.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Cahill, J.D.; Zaugg, S.D.; Werner, S.L. Transport of chemical and microbial contaminants from known wastewater discharge: Potential for use as indicators of human fecal contamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 36, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Standord, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Aga, D.S. Potential ecological and human health impacts of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant bacteria from wastewater treatment plants. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Crit. Rev. 2007, 10, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montforts, M.H.M.M. Environmental Risk Assessment for Veterinary Medicinal Products Part 1: Other than GMO-Containing and Immunological Products; National Institute of Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Costanzo, S.D. Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: Implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4164–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolls, J. Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: A review. Environ. Sci. 2001, 35, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Song, X.; Zhang, F.; He, L. Determination of multi-class antimicrobial residues in soil by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27584–27593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Lu, Z. Determine multiple classes of veterinary antibiotics in soil: Comparing dispersive and solid-phase extraction for sample cleanup. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.B.; Zakaria, M.P.; Latif, P.A.; Saari, N. Simultaneous determination of veterinary antibiotics and hormone in broiler manure, soil and manure compost by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P.; Zhang, H. Simultaneous extraction of four classes of antibiotics in soil, manure, and sewage sludge and analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with the isotope-labelled internal standard method. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3721–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Wong, C.K.D.; Chu, L.M. Distribution of antibiotics in wastewater-irrigated soils and their accumulation in vegetable crops in the Pearl River Delta, southern China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11062–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gu, C.; Xagoraraki, I.; Li, H. Determination of pharmaceuticals in biosolids using accelerated solvent extraction and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, T.; Schneider, R.J.; Farber, H.A.; Skutlarek, D.; Meyer, M.T.; Goldback, H.E. Determination of antibiotic residues in manure, soil, and surface waters. Clean Soil Air Water 2003, 31, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.C.; Li, X.W.; Li, L.L.; Ding, Y.Q.; Zhao, H. Simultaneous Determination of Tetracycline, Macrolide and Sulfonamide Antibiotics in Soils Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction Followed by Solid-Phase Extraction and High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. AMR 2013, 718–720, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.J.; Ferreira da Silva, B.; Ramos Stradiotto, N.; Petrovic, M.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Gros, M. Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) and QuEChERS evaluation for the analysis of antibiotics in agricultural soils. MethodsX 2020, 7, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlusener, M.P.; Spiteller, M.; Bester, K. Determination of antibiotics from soil by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1003, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyra, E.; Kowalczyk, E.; Grelik, A.; Przenioslo-Siwczynska, M.; Kwiatek, K. Screening method for the determination of tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones in animal drinking water by liquid chromatography with diode array detector. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 18, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Tao, R.; Su, H.-C.; Chen, F. Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC-MS/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 16, 3424–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1694: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Biosolids by HPLC/MS/MS; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; 77p, EPA-821-R-08-008.
- Golet, E.M.; Xifra, I.; Siegrist, H.; Alder, A.C.; Giger, W. Environmental exposure assessment of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents from sewage to soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3243–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusser, F. Effect of lincomycin and clindamycin on peptide chain initiation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1975, 7, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neil, M.J. The Merck Index—An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 13th ed.; Merck and Co., Inc.: Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2001; p. 985. ISBN 978-0911910131. [Google Scholar]
- Göbel, A.; Thomsen, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Joss, A.; Giger, W. Occurrence and sorption behavior of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in activated sludge treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3961–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowara, A.; Burhenne, J.; Spiteller, M. Binding of fluoroquinolones carboxylic acid derivatives to clay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Hoekman, L.A. Exploring QSAR—Hydrophobic, Electronic, and Steric Constants; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 71. ISBN 978-0841229914. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, N.D.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of SOILS, 11th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0023133718. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, D.; Thomas Sims, J. Recommended Soil pH and Lime Requirement Tests. In Recommended Soil Testing Procedures for the Northeastern United States; Northeast Regional Bulletin #493; Thomas Sims, J., Wolf, A., Eds.; Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Delaware: Newark, DE, USA, 1995; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D. Recommended Soil Tests for Determining Soil Cation Exchange Capacity. In Recommended Soil Testing Procedures for the Northeastern United States; Northeast Regional Bulletin #493; Thomas Sims, J., Wolf, A., Eds.; Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Delaware: Newark, DE, USA, 1995; pp. 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3—Chemical Methods; SSSA Book Series Number 5.3; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Sci Soc Am; Am Soc Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Pella, E. Elemental Organic Analysis. Part 1. Am. Lab. 1990, 22, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size Analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1—Physical and Mineralogical Methods; SSSA Book Series 5.1; Klute, A., Ed.; Soil Sci Soc Am; Am Soc Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, M.E.; Miller, W.P. Cation Exchange Capacity and Exchange Coefficients. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3—Chemical Methods; SSSA Book Series Number 5.3; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Sci Soc Am; Am Soc Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1201–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Gros, M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D. Rapid analysis of multiclass antibiotic residues and some of their metabolites in hospital, urban wastewater and river water by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Determination of antimicrobial residues and metabolites in the aquatic environment by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, H.S.; Ye, Z.; Moyer, M.T. Method Development for the Occurrence of Residual Antibiotics in Drinking Water; WRRI: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Ying, G.G.; Tao, R.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, J.R.; Zhao, L.F. Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Lin, S.S.; Dai, C.M.; Shi, L.; Zhou, X.F. Sorption-desorption and transport of trimethoprim and sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soil: Effect of soil type, dissolved organic matter, and pH. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5827–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, D.H.; Huang, M.H. Sorption and pH effect on selected antibiotics in soils. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 356–360, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, B.B.; Guy, R.D. Models for tetracycline in aquatic environments: I. Interaction with Bentonite clay systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1987, 32, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.F.; McLain, J.E.T. Soil persistence and fate of carbamazepine, lincomycin, caffeine, and ibuprofen from wastewater reuse. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, C.F.; Watson, J.E.; Nelson, S.D.; Walker, C.W. Sorption/desorption of lincomycin from three arid-region soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Roig, P.; Segarra, R.; Blasco, C.; Andreu, V.; Pico, Y. Determination of pharmaceuticals in soils and sediments by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2010, 1217, 2471–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Sorption of antimicrobial ciprofloxacin to aluminum and iron oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9166–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, C.H. Adsorption and oxidation of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents and structurally related amines with goethite. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, G.; Coronado, J.; Poyfair, T.; Degner, C. Increasing Extraction Efficiency of Organic Contaminants from Solid Substrates Using Freeze Drying: A Case Study; Columbia Analytical Services: Kelso, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aga, D.S.; Lenczewski, M.; Snow, D.; Muurinen, J.; Sallach, J.B.; Wallace, J.S. Challenges in the measurement of antibiotics and in evaluating their impacts in agroecosystems: A critical review. JEQ 2016, 45, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix effects and application of matrix effect factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Antibiotics | Sulfamethoxazole | Trimethoprim | Ofloxacin | Lincomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H11N3O3S | C14H18N4O3 | C18H20FN3O4 | C18H34N2O6S |
| Chemical Structure |  |  |  |  |
| Molecular Weight (g mol−1) 1 | 253.3 | 290.32 | 361.368 | 406.54 |
| pKaa | pKa1: 1.4 pKa2: 5.8 2 | 6.6 2 | pKa1: 6.0 pKa2: 8.0 3 | 7.6 2 |
| Log Kow 4 | 0.89 | 0.91 | −0.38 | 0.20 |
| Soil Name | Location Land Use—Horizon | pH | Carbon (%) | Nitrogen (%) | EC (uS/cm) | CEC (cmol/kg) | Texture (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | Classification | |||||||
| Bulk Soil | Rock Springs Cropped—Ap * | 5.8 | 1.14 | - | - | 14.2 | - | - | - | Silt Loam |
| Soil A | Rock Springs Cropped—Ap * | 6.5 | 0.89 | 0.097 | 79 | 25 | 22 | 59 | 18 | Silt Loam |
| Soil B | Rock Springs Cropped—B | 6.6 | 0.18 | 0.048 | 70 | 26 | 39 | 38 | 23 | Loam |
| Soil C | Astronomy Forested—A | 4.5 | 5.8 | 0.34 | 170 | 21 | 46 | 45 | 9 | Loam |
| Soil D | Astronomy Forested—B | 4.7 | 0.71 | 0.051 | 56 | 12 | 36 | 41 | 23 | Loam |
| Matrix | Pre-Process Step | Clean Up Procedures | Antibiotic Recoveries (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix pH | SPE Cartridge | Sulfamethoxazole | Trimethoprim | Lincomycin | Ofloxacin | |
| Water | 2.8 | HLB Plus | 101 ± 13 | 70 ± 12 | 65 ± 3 | 75 ± 1 |
| 7.0 | HLB Plus | 118 ± 5 | 86 ± 4 | 83 ± 5 | 35 ± 6 | |
| 2.8 | Strata X | 106 ± 5 | 82 ± 5 | 58 ± 2 | 67 ± 3 | |
| 7.0 | Strata X | 103 ± 20 | 74 ± 7 | 62 ± 4 | 34 ± 2 | |
| Clean MeOH * | 2.5 | HLB Plus | 92 ± 7 | 55 ± 10 | 2 ± 0.2 | 51 ± 8 |
| Dirty MeOH *¥ | 70 ± 23 | 46 ± 8 | 3 ± 0.3 | 47 ± 4 | ||
| Clean FA (0.1%) * | 2.8 | 101 ± 13 | 70 ± 12 | 65 ± 3 | 71 ± 1 | |
| Dirty FA (0.1%) *¥ | 104 ± 10 | 71 ± 15 | 83 ± 4 | 41 ± 9 | ||
| Clean ACN/H2O (50/50) * | 2.8 | 70 ± 15 | 8 ± 4 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 6 ± 2 | |
| Dirty ACN/H2O (50/50) * ¥ | 97 ± 6 | 84 ± 1 | 31 ± 9 | 31 ± 10 | ||
| Clean MeOH/H2O (20/80) * | 2.5 | 98 ± 5 | 77 ± 8 | 11 ± 1 | 62 ± 5 | |
| Dirty MeOH/H2O (20/80) * ¥ | 101 ± 3 | 75 ± 1 | 23 ± 2 | 46 ± 11 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franklin, A.M.; Andrews, D.M.; Williams, C.F.; Watson, J.E. Simultaneous Extraction of Four Antibiotic Compounds from Soil and Water Matrices. Separations 2022, 9, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080200
Franklin AM, Andrews DM, Williams CF, Watson JE. Simultaneous Extraction of Four Antibiotic Compounds from Soil and Water Matrices. Separations. 2022; 9(8):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080200
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranklin, Alison M., Danielle M. Andrews, Clinton F. Williams, and John E. Watson. 2022. "Simultaneous Extraction of Four Antibiotic Compounds from Soil and Water Matrices" Separations 9, no. 8: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080200
APA StyleFranklin, A. M., Andrews, D. M., Williams, C. F., & Watson, J. E. (2022). Simultaneous Extraction of Four Antibiotic Compounds from Soil and Water Matrices. Separations, 9(8), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080200