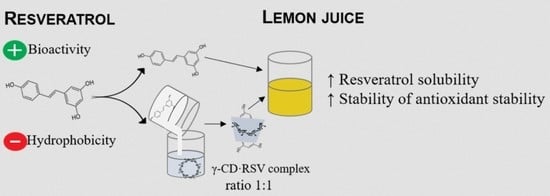
Inclusion Complex of Resveratrol with γ-Cyclodextrin as a Functional Ingredient for Lemon Juices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of the Inclusion Complex (γ-CD·RSV) and Physical Mixture
2.3. Characterisation of the Inclusion Complexes
2.3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.2. Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD)
2.3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.4. Formulation of Lemon Juices
2.5. Physicochemical Analysis of the Liquid Samples
2.6. Stability Studies
2.6.1. Quantification of RSV
2.6.2. Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Solid-State Characterisation of the γ-CD Inclusion Complex with RSV
3.1.1. FT-IR
3.1.2. PXRD
3.1.3. TGA
3.2. Stability of RSV in Formulated Juices
3.2.1. RSV Integrated in Juice Matrix
3.2.2. Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, A.; Cucciolla, V.; Della Ragione, F.; Galletti, P. Dietary polyphenols: Focus on resveratrol, a promising agent in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases and control of glucose homeostasis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Resveratrol: An overview of its anti-cancer mechanisms. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, M. The Phenolic Substances of white Hellebore (Veratrum Grandiflorum Loes fil.) II. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1939, 60, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H.; Lean, M.E.J.; Crozier, A. Plant Foods and Herbal Sources of Resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langcake, P.; Pryce, R.J. The production of resveratrol by Vitis vinifera and other members of the Vitaceae as a response to infection or injury. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1976, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J. Stability and solubility of trans-resveratrol are strongly influenced by pH and temperature. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, A. Sur la fermentation de la fécule par l’action du fermentbutyrique. Comptes Rendus l’Académie des Sci. 1891, 112, 536. [Google Scholar]
- Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savić-Gajić, I.; Savić, I.; Nikolić, V.; Nikolić, L.; Popsavin, M.; Rakić, S. The improvement of photostability and antioxidant activity of trans-resveratrol by cyclodextrins. Adv. Technol. 2017, 6, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, R.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zou, G. Study of the complexation of resveratrol with cyclodextrins by spectroscopy and molecular modeling. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Cheng, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, G. Complexation of resveratrol with cyclodextrins: Solubility and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Abellán, C.; Fortea, I.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Núñez-Delicado, E. Cyclodextrins as resveratrol carrier system. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, D.; Li, L. Microcalorimetric and spectrographic studies on host–guest interactions of α-, β-, γ- and Mβ-cyclodextrin with resveratrol. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 510, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacche, V.; Lorenzi, N.; Nava, D.; Pini, E.; Sinico, C. Host–guest interaction study of resveratrol with natural and modified cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 55, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, E.; Mathiron, D.; Bertaut, E.; Landy, D.; Cailleu, D.; Pilard, S.; Clément, C.; Courot, E.; Bonnet, V.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. Physico-chemical studies of resveratrol, methyljasmonate and cyclodextrin interactions: An approach to resveratrol bioproduction optimization. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catenacci, L.; Sorrenti, M.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Hunt, L.; Caira, M.R. Inclusion of the phytoalexin trans-resveratrol in native cyclodextrins: A thermal, spectroscopic, and X-ray structural study. Molecules 2020, 25, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishihira, V.S.K.; Mezzomo, N.J.; Baldissera, M.D.; Vaucher, R.A.; Pinto, G.C.; Pohl, A.R.; Gomes, P.; Rodrigues Junior, L.F.; Frizzo, C.P.; Bender, C.R.; et al. Resveratrol inclusion complex with β-cyclodextrin (RCD): Characterization and evaluation of toxicity in Wistar rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 9, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trollope, L.; Cruickshank, D.L.; Noonan, T.; Bourne, S.A.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Caira, M.R. Inclusion of trans-resveratrol in methylated cyclodextrins: Synthesis and solid-state structures. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 3136–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.; Martinho, A.; Luís, Â.; Figueiras, A.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C.; Silva, F. Resveratrol encapsulation with methyl-β-cyclodextrin for antibacterial and antioxidant delivery applications. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuti, V.; Cannavà, C.; Cristiano, M.C.; Fresta, M.; Majolino, D.; Paolino, D.; Stancanelli, R.; Tommasini, S.; Ventura, C.A. A characterization study of resveratrol/sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex and in vitro anticancer activity. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2014, 115, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, R.; Fu, R.; Xiong, J.; Hu, Y. Cytotoxicity and inhibition of lipid peroxidation activity of resveratrol/cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 73, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiqian Yang, Z.; Argenziano, M.; Salamone, P.; Pirro, E.; Sprio, A.E.; Di Scipio, F.; Carere, M.E.; Quaglino, E.; Cavallo, F.; Cavalli, R.; et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetics comparison between resveratrol 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex and resveratrol suspension after oral administration. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2016, 86, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Abellán, C.; Fortea, M.I.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Núñez-Delicado, E. Complexation of resveratrol by native and modified cyclodextrins: Determination of complexation constant by enzymatic, solubility and fluorimetric assays. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, F.; Lin, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.-P. Investigating the oxyresveratrol β-cyclodextrin and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexes: The effects on oxyresveratrol solution, stability, and antibrowning ability on fresh grape juice. LWT 2019, 100, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matencio, A.; Navarro-Orcajada, S.; Conesa, I.; Muñoz-Sánchez, I.; Laveda-Cano, L.; Cano-Yelo, D.; García-Carmona, F.; López-Nicolás, J.M. Evaluation of juice and milk “food models” fortified with oxyresveratrol and β-Cyclodextrin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saokham, P.; Loftsson, T. γ-Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Thymol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibrous webs: Enhanced water solubility, high thermal stability and antioxidant property of thymol. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pais, J.M.; Pereira, B.; Paz, F.A.A.; Cardoso, S.M.; Braga, S.S. Solid γ-cyclodextrin inclusion compound with gingerols, a multi-component guest: Preparation, properties and application in yogurt. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koontz, J.L.; Marcy, J.E.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Duncan, S.E. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Formation and Solid-State Characterization of the Natural Antioxidants α-Tocopherol and Quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, M.R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Petruzzi, L.; Casanova, F.P.; Sinigaglia, M. Functional Beverages: The Emerging Side of Functional Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, R.P.; Santos, M.D.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Mota, M.J.; Lopes, R.P.; Inácio, R.S.; Delgadillo, I.; Saraiva, J.A. Hyperbaric storage of melon juice at and above room temperature and comparison with storage at atmospheric pressure and refrigeration. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saada, M.; Falleh, H.; Catarino, M.; Cardoso, S.; Ksouri, R. Plant Growth Modulates Metabolites and Biological Activities in Retama raetam (Forssk.) Webb. Molecules 2018, 23, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, O.; Catarino, M.; Afonso, A.; Silva, A.; Cardoso, S. Salvia elegans, Salvia greggii and Salvia officinalis Decoctions: Antioxidant Activities and Inhibition of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Enzymes. Molecules 2018, 23, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhakar, N.K.; Matencio, A.; Caldera, F.; Argenziano, M.; Cavalli, R.; Dianzani, C.; Zanetti, M.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Trotta, F. Comparative evaluation of solubility, cytotoxicity and photostability studies of resveratrol and oxyresveratrol loaded nanosponges. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caira, M.R. On the isostructurality of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes and its practical utility. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2001, 46, 371–386. [Google Scholar]
- González-Molina, E.; Moreno, D.A.; García-Viguera, C. Aronia-Enriched Lemon Juice: A New Highly Antioxidant Beverage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11327–11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Codex General Standard for Fruit Juices and Nectars (CODEX STAN 247-2005); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005.
- Gironés-Vilaplana, A.; Mena, P.; Moreno, D.A.; García-Viguera, C. Evaluation of sensorial, phytochemical and biological properties of new isotonic beverages enriched with lemon and berries during shelf life. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, O.; Svanberg, U.; Sahlström, A. Effect of oxygen and fluorescent light on the quality of orange juice during storage at 8 °C. Food Chem. 1995, 53, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserhalmi, Z.; Sass-Kiss, Á.; Tóth-Markus, M.; Lechner, N. Study of pulsed electric field treated citrus juices. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2006, 7, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Malanga, M.; Manet, I.; Manoli, F.; Tuza, K.; Aykaç, A.; Ladavière, C.; Fenyvesi, E.; Vargas-Berenguel, A.; Gref, R.; et al. Citric acid–γ-cyclodextrin crosslinked oligomers as carriers for doxorubicin delivery. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmi, C.; Centini, M.; Maggiore, M.; Gaggelli, N.; Andreassi, M.; Buonocore, A.; Beretta, G.; Facino, R.M. Non-covalent inclusion of ferulic acid with α-cyclodextrin improves photo-stability and delivery: NMR and modeling studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Formulation | pH | °Brix | Browning | Cloudiness | ᐃE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSV-juice | 2.52 ± 0.06 a | 8.7 ± 0.1 a | 0.19 ± 0.03 a | 0.14 ± 0.00 a | 5.56 ± 1.24 a |
| γ-CD·RSV-juice | 2.50 ± 0.04 a | 9.0 ± 0.1 a | 0.20 ± 0.02 a | 0.28 ± 0.01 ab | 6.00 ± 2.21 a |
| RSV-CA | 2.45 ± 0.33 a | 3.5 ± 0.1 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 8.51 ± 1.76 a |
| γ-CD·RSV-CA | 2.56 ± 0.30 a | 3.7 ± 0.0 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.51 ± 0.07 b | 8.40 ± 0.98 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.F.R.; Monteiro, M.; Resende, D.; Braga, S.S.; Coimbra, M.A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Inclusion Complex of Resveratrol with γ-Cyclodextrin as a Functional Ingredient for Lemon Juices. Foods 2021, 10, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010016
Silva AFR, Monteiro M, Resende D, Braga SS, Coimbra MA, Silva AMS, Cardoso SM. Inclusion Complex of Resveratrol with γ-Cyclodextrin as a Functional Ingredient for Lemon Juices. Foods. 2021; 10(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Andreia F. R., Mariana Monteiro, Daniela Resende, Susana S. Braga, Manuel A. Coimbra, Artur M. S. Silva, and Susana M. Cardoso. 2021. "Inclusion Complex of Resveratrol with γ-Cyclodextrin as a Functional Ingredient for Lemon Juices" Foods 10, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010016
APA StyleSilva, A. F. R., Monteiro, M., Resende, D., Braga, S. S., Coimbra, M. A., Silva, A. M. S., & Cardoso, S. M. (2021). Inclusion Complex of Resveratrol with γ-Cyclodextrin as a Functional Ingredient for Lemon Juices. Foods, 10(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010016