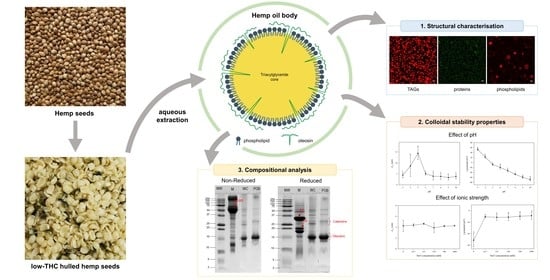
Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Oil Bodies from Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Hemp Milk and Isolation of Oil Bodies
2.2.2. Microstructure
Cryo-SEM
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.2.3. Compositional Analysis of Hemp Seed Oil Bodies
Proximate Composition
Fatty Acid Composition
2.2.4. Protein Composition of Hemp Seed Oil Bodies by Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.2.5. Physicochemical Characterisation and Stability of Oil Bodies
Particle Size
ζ-Potential
Effect of pH and Ionic Strength on Colloidal Stability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Hemp Seed
3.2. Microstructure of Hemp Seed Oil Bodies
3.3. Proximate Composition of Hemp Seed Oil Bodies
3.4. Fatty Acid Composition of Lipids in Hemp Seed Oil Bodies
3.5. Protein Composition
3.6. Physicochemical Properties of Hemp Seed Oil Bodies
3.6.1. Particle Size and ζ-Potential
3.6.2. Effect of pH and Ionic Strength on Colloidal Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callaway, J.C. Hempseed as a nutritional resource: An overview. Euphytica 2004, 140, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E. Cannabis: A Complete Guide; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, S.-S.; Birch, J. Physicochemical and quality characteristics of cold-pressed hemp, flax and canola seed oils. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 30, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.H.C. Oil bodies and oleosins in seeds. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 43, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzen, J.T.C.; Huang, A.H.C. Surface structure and properties of plant seed oil bodies. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 117, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, A.H.C. Structure of plant seed oil bodies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1994, 4, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzen, J.T.C.; Cao, Y.Z.; Laurent, P.; Ratnayake, C.; Huang, A.H.C. Lipids, proteins, and structure of seed oil bodies from diverse species. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurer, S.; Waschatko, G.; Schach, D.; Zielbauer, B.I.; Dahl, J.; Weidner, T.; Bonn, M.; Vilgis, T.A. The role of intact oleosin for stabilization and function of oleosomes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 13872–13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ono, T. Simple extraction method of non-allergenic intact soybean oil bodies that are thermally stable in an aqueous medium. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7402–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chirico, S.; di Bari, V.; Foster, T.; Gray, D. Enhancing the recovery of oilseed rape seed oil bodies (oleosomes) using bicarbonate-based soaking and grinding media. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhotu, R.; Shi, X.; Hu, Q.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Guo, S. Aggregation behaviour and stability of maize germ oil body suspension. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y. Effects of pH on protein components of extracted oil bodies from diverse plant seeds and endogenous protease-induced oleosin hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.A.; Payne, G.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Lad, M. Oxidative stability of Echium plantagineum seed oil bodies. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, D.; Gray, D.A.; Fisk, I.D.; Decker, E.A.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Extraction and characterization of oil bodies from soy beans: A natural source of pre-emulsified soybean oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8711–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.H.C. Oleosins and oil bodies in seeds and other organs. Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Efthymiou, C.; Williams, M.A.K.; McGrath, K.M. Revealing the structure of high-water content biopolymer networks: Diminishing freezing artefacts in cryo-SEM images. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, S.; Gordon, K.C.; Singh, H. Chemical and structural characterisation of almond oil bodies and bovine milk fat globules. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1996–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalli, A.; Contarini, G. Determination of phospholipids in dairy products by SPE/HPLC/ELSD. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1071, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, A.; Verrier, T.; Singh, H. Free fatty acid profiles of emulsified lipids during in vitro digestion with pancreatic lipase. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzen, J.T.; Peng, C.-C.; Cheng, D.-J.; Chen, E.C.; Chiu, J.M. A new method for seed oil body purification and examination of oil body integrity following germination. J. Biochem. 1997, 121, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manderson, G.; Hardman, M.; Creamer, L. Effect of heat treatment on the conformation and aggregation of β-lactoglobulin A, B, and C. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 5052–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterlini, P.; Jaime, G.S.; Aden, C.; Olivaro, C.; Gómez, M.I.; Cruz, K.; Tonello, U.; Romero, C.M. Seeds characterization of wild species Jatropha peiranoi endemic of arid areas of Monte Desert Biome, Argentina. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 141, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, E.; Pellegrini, N.; Ntone, E.; Nikiforidis, C.V. In vitro lipid digestion in raw and roasted hazelnut particles and oil bodies. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforidis, C.V.; Kiosseoglou, V.; Scholten, E. Oil bodies: An insight on their microstructure—Maize germ vs sunflower seed. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforidis, C.V. Structure and functions of oleosomes (oil bodies). Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 274, 102039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallier, S.; Tate, H.; Singh, H. In Vitro Gastric and Intestinal Digestion of a Walnut Oil Body Dispersion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, A.C.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. Structural and interfacial characteristics of oil bodies in coconuts (Cocos nucifera L.). Food Chem. 2019, 276, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomah, B.D.; Busson, M.; Godfrey, D.V.; Drover, J.C.G. Characteristics of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Esteban, J.I.; González-Fernández, M.J.; Fabrikov, D.; Torija-Isasa, E.; Sánchez-Mata, M.d.C.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Varieties: Fatty Acid Profiles and Upgrading of γ-Linolenic Acid–Containing Hemp Seed Oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraliakbari, H.; Shahidi, F. Lipid class compositions, tocopherols and sterols of tree nut oils extracted with different solvents. J. Food Lipids 2008, 15, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Appukuttan Aachary, A.; Thiyam-Holländer, U. Hemp seed oil: Minor components and oil quality. Lipid Technol. 2015, 27, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentzen, M. Phosphatidylglycerol and sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol: Anionic membrane lipids and phosphate regulation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Benedetti, B.; Cannazza, G.; Cerrato, A.; Citti, C.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A. New insights in hemp chemical composition: A comprehensive polar lipidome characterization by combining solid phase enrichment, high-resolution mass spectrometry, and cheminformatics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H.; Ten, Z.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, X.Q. Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadnađev, M.; Dapčević-Hadnađev, T.; Lazaridou, A.; Moschakis, T.; Michaelidou, A.M.; Popović, S.; Biliaderis, C.G. Hempseed Meal Protein Isolates Prepared by Different Isolation Techniques. Part I. physicochemical properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, F.; Lubbers, S.; Husson, F.; Saurel, R. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Protein Extraction Conditions Affect Extraction Yield and Protein Quality. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3682–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malomo, S.A.; Aluko, R.E. A comparative study of the structural and functional properties of isolated hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) albumin and globulin fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, J.A.; Beaudoin, F.; Tatham, A.S.; Alexander, L.G.; Shewry, P.R. The Seed Oleosins: Structure, Properties and Biological Role. In Advances in Botanical Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 35, pp. 111–138. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforidis, C.V.; Matsakidou, A.; Kiosseoglou, V. Composition, properties and potential food applications of natural emulsions and cream materials based on oil bodies. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25067–25078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikiforidis, C.V.; Karkani, O.A.; Kiosseoglou, V. Exploitation of maize germ for the preparation of a stable oil-body nanoemulsion using a combined aqueous extraction-ultrafiltration method. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Gao, Q.; Ma, N.; Hao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; Ho, C.-T. Structures and physicochemical characterization of enzyme extracted oil bodies from rice bran. LWT 2021, 135, 109982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-J.; Liao, P.-C.; Yang, H.-H.; Tzen, J.T.C. Determination and analyses of the N-termini of oil-body proteins, steroleosin, caleosin and oleosin. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Demetriades, K.; Coupland, J.N.; McClements, D.J. Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforidis, C.V.; Kiosseoglou, V. Aqueous extraction of oil bodies from maize germ (Zea mays) and characterization of the resulting natural oil-in-water emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Qiang, W.; Yang, Y.; Gao, T.; Guo, J.; Du, L.; Noman, M.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; et al. Physicochemical stability of safflower oil body emulsions during food processing. LWT 2020, 132, 109838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, G.; Lad, M.; Foster, T.; Khosla, A.; Gray, D. Composition and properties of the surface of oil bodies recovered from Echium plantagineum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Parameter | Composition (%, Wet Basis) |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 22.80 ± 2.09 |
| Fat | 79.30 ± 2.78 |
| Crude protein | 1.50 ± 0.22 |
| Ash | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| Fatty Acid | Total Fat Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Lipids | Neutral Lipids | Polar Lipids | |
| C16:0 Palmitic acid | 6.10 ± 0.02 | 5.95 ± 0.03 | 8.46 ± 0.05 |
| C18:0 Stearic acid | 2.91 ± 0.03 | 2.86 ± 0.06 | 2.98 ± 0.07 |
| C18:1n9 Oleic acid | 15.10 ± 0.06 | 15.00 ± 0.15 | 13.44 ± 0.20 |
| C18:2n6 Linoleic acid | 60.74 ± 0.32 | 61.07 ± 0.20 | 47.36 ± 0.47 |
| C18:3n6 γ-Linolenic acid | 0.039 ± 0.005 | 0 | 1.23 ± 0.04 |
| C18:3n3 α-Linolenic acid | 11.66 ± 0.33 | 11.70 ± 0.23 | 23.62 ± 0.96 |
| C20:0 Arachidic acid | 1.98 ± 0.01 | 1.99 ± 0.06 | 1.59 ± 0.01 |
| C20:1 Eicosenoic acid | 1.00 ± 0.03 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.68 ± 0.10 |
| C20:2 Eicosadienoic acid | 0.486 ± 0.035 | 0.467 ± 0.015 | 0.644 ± 0.082 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, F.L.; Ma, S.; Dave, A.; Acevedo-Fani, A. Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Oil Bodies from Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.). Foods 2021, 10, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122930
Garcia FL, Ma S, Dave A, Acevedo-Fani A. Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Oil Bodies from Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.). Foods. 2021; 10(12):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122930
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Francesca Louise, Sihan Ma, Anant Dave, and Alejandra Acevedo-Fani. 2021. "Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Oil Bodies from Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.)" Foods 10, no. 12: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122930
APA StyleGarcia, F. L., Ma, S., Dave, A., & Acevedo-Fani, A. (2021). Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Oil Bodies from Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.). Foods, 10(12), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122930