The Role of Ovotransferrin in Egg-White Antimicrobial Activity: A Review
Abstract
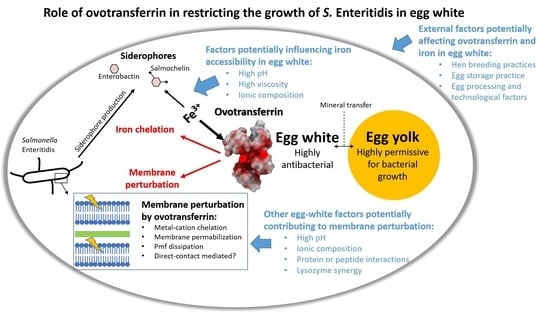
:1. Introduction
2. Structure of Ovotransferrin
3. Role of Ovotransferrin in Iron Deficiency
3.1. The Requirement for Iron
3.2. Iron Metabolism in Bacteria

3.3. Capacity of Siderophores to Capture Iron from Ovotransferrin
4. Role of Ovotransferrin in Bacterial Membrane Perturbation
4.1. Evidence for a Direct Interaction of Ovotransferrin with the Bacterial Membrane
4.2. Bacterial Membrane Perturbation in the Natural Context of Egg White
5. Impact of Egg White Conditions on Ovotransferrin
5.1. Impact of Egg White pH
5.2. Impact of the Ionic Composition of Egg White
5.3. Impact of Viscosity and the Heterogeneous Structure of Egg White
5.4. Impact of the Presence of Others Egg White Proteins
5.5. Impact of Ovotransferrin-Derived Peptides
5.6. Impact of Egg Processing and Technological Factors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaheer, K. An Updated Review on Chicken Eggs: Production, Consumption, Management Aspects and Nutritional Benefits to Human Health. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 6, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Baron, F.; Thapon, J.-L. Science et Technologie de L’oeuf, Volume 2: De L’oeuf aux Ovoproduits; Sciences et Techniques Agroalimentaire; Tec&Doc.; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA BIOHAZ Panel (EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards) Scientific Opinion on the Public Health Risks of Table Eggs Due to Deterioration and Development of Pathogens, 2014. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3782. [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Bonnassie, S.; Gautier, M.; Andrews, S.C.; Jan, S. Egg White versus Salmonella Enteritidis! A Harsh Medium Meets a Resilient Pathogen. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantois, I.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Gast, R.; Humphrey, T.J.; Van Immerseel, F. Mechanisms of Egg Contamination by Salmonella Enteritidis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 718–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, F.; Jan, S. Egg and egg product microbiology. In Improving the Safety and Quality of Eggs and Egg Products. Vol. 1: Egg Chemistry, Production and Consumption; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 330–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hincke, M.T.; Gautron, J.; Panheleux, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.; McKee, M.D.; Nys, Y. Identification and Localization of Lysozyme as a Component of Eggshell Membranes and Eggshell Matrix. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2000, 19, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Thesmar, H.S.; Kerr, W.L. Outgrowth of Salmonellae and the Physical Property of Albumen and Vitelline Membrane as Influenced by Egg Storage Conditions. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, R.K.; Holt, P.S. Influence of the Level and Location of Contamination on the Multiplication of Salmonella Enteritidis at Different Storage Temperatures in Experimentally Inoculated Eggs. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techer, C.; Baron, F.; Delbrassinne, L.; Belaïd, R.; Brunet, N.; Gillard, A.; Gonnet, F.; Cochet, M.-F.; Grosset, N.; Gautier, M.; et al. Global Overview of the Risk Linked to the Bacillus Cereus Group in the Egg Product Industry: Identification of Food Safety and Food Spoilage Markers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1344–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Guo, A.; Chen, Q.; Gu, L.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, X. The Specific Biological Characteristics of Spoilage Microorganisms in Eggs. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, J.L.; Board, R.G. Persistence of Contamination of Hens’ Egg Albumen in Vitro with Salmonella Serotypes. Epidemiol. Infect 1992, 108, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clavijo, R.I.; Loui, C.; Andersen, G.L.; Riley, L.W.; Lu, S. Identification of Genes Associated with Survival of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis in Chicken Egg Albumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, K. The Chicken Egg White Proteome. Proteomics 2007, 7, 3558–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Mann, M. In-Depth Analysis of the Chicken Egg White Proteome Using an LTQ Orbitrap Velos. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J. Proteomic Analysis of Fertilized Egg White during Early Incubation. EuPA Open Proteomics 2014, 2, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derde, M.; Lechevalier, V.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Cochet, M.-F.; Jan, S.; Baron, F.; Gautier, M.; Vié, V.; Nau, F. Hen Egg White Lysozyme Permeabilizes Escherichia coli Outer and Inner Membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9922–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervé-Grépinet, V.; Réhault-Godbert, S.; Labas, V.; Magallon, T.; Derache, C.; Lavergne, M.; Gautron, J.; Lalmanach, A.-C.; Nys, Y. Purification and Characterization of Avian β-Defensin 11, an Antimicrobial Peptide of the Hen Egg. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4401–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, D.; Wilson, P.W.; Bain, M.M.; McDade, K.; Kalina, J.; Hervé-Grépinet, V.; Nys, Y.; Dunn, I.C. Gallin; an Antimicrobial Peptide Member of a New Avian Defensin Family, the Ovodefensins, Has Been Subject to Recent Gene Duplication. BMC Immunol. 2010, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagase, H.; Harris, E.; Woessner, J.F.; Brew, K. Ovostatin: A Novel Proteinase Inhibitorfrom Chicken Egg White. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 7481–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesierska, E.; Saleh, Y.; Trziszka, T.; Kopec, W.; Siewinski, M.; Korzekwa, K. Antimicrobial Activity of Chicken Egg White Cystatin. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 21, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réhault-Godbert, S.; Labas, V.; Helloin, E.; Hervé-Grépinet, V.; Slugocki, C.; Berges, M.; Bourin, M.-C.; Brionne, A.; Poirier, J.-C.; Gautron, J.; et al. Ovalbumin-Related Protein X Is a Heparin-Binding Ov-Serpin Exhibiting Antimicrobial Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17285–17295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banks, J.; Board, R.; Sparks, N. Natural Antimicrobial Systems and Their Potential in Food Preservation of the Future. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1986, 8, 103–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garibaldi, J.A. Role of Microbial Iron Transport Compounds in the Bacterial Spoilage of Eggs. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 20, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, F.; Gautier, M.; Brule, G. Factors Involved in the Inhibition of Growth of Salmonella Enteritidis in Liquid Egg White. J. Food Prot. 1997, 60, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Loui, C.; Clavijo, R.I.; Riley, L.W.; Lu, S. Survival Characteristics of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis in Chicken Egg Albumen. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, R.T.; Giehl, T.J.; Laforce, F.M. Damage of the Outer Membrane of Enteric Gram-Negative Bacteria by Lactoferrin and Transferrin. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenti, P.; Visca, P.; Antonini, G.; Orsi, N. Interaction between Lactoferrin and Ovotransferrin and Candida Cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1986, 33, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, O.; Quiros, L.M.; Fierro, F. Transferrins Selectively Cause Ion Effux through Bacterial and Artificial Membranes. FEBS Lett. 2003, 548, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gantois, I.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis Genes Induced during Oviduct Colonization and Egg Contamination in Laying Hens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6616–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gantois, I.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F. The Salmonella Enteritidis Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis Gene RfbH Is Required for Survival in Egg Albumen. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspoet, R.; Appia-Ayme, C.; Shearer, N.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Thompson, A.; Van Immerseel, F. Microarray-Based Detection of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis Genes Involved in Chicken Reproductive Tract Colonization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Jia, B.; He, M.; Yichen, H.; Qin, X.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Yanhong, L.; Xianming, S. Transcriptional Sequencing Uncovers Survival Mechanisms of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis in Antibacterial Egg White. mSphere 2019, 4, e00700-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baron, F.; Cochet, M.-F.; Alabdeh, M.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Gautier, M.; Nau, F.; Andrews, S.C.; Bonnassie, S.; Jan, S. Egg-White Proteins Have a Minor Impact on the Bactericidal Action of Egg White toward Salmonella Enteritidis at 45°C. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauveur, B. Reproduction des Volailles et Production D’oeufs; Quae: Paris, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Tranter, H.S.; Board, R.G. The Influence of Incubation Temperature and PH on the Antimicrobial Properties of Hen Egg Albumen. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1984, 56, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giansanti, F. Physiological Roles of Ovotransferrin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiter, R.D.; Mulvihill, E.R.; McKnight, G.S.; Senear, A.W. Regulation of Gene Expression in the Chick Oviduct by Steroid Hormones. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1978, 42, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, R.R. Proteins of Iron Storage and Transport. In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Anfinsen, C.B., Edsall, J.T., Richards, F.M., Eisenberg, D.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 40, pp. 281–363. [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch, J.-M.; Chambon, P. The Complete Nucleotide Sequence of the Chicken Ovotransferrin MRNA. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 122, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, H.; Mikami, B.; Hirose, M. Crystal Structure of Diferric Hen Ovotransferrin at 2.4 Å Resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, H.; Dewan, J.C.; Mikami, B.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Hirose, M. Crystal Structure of Hen Apo-Ovotransferrin: Both Lobes Adopt an Open Conformation upon Loss of Iron. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 28445–28452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelps, C.F.; Antonini, E. A Study of the Kinetics of Iron and Copper Binding to Hen Ovotransferrin. Biochem. J. 1975, 147, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J. A Comparison of Glycopeptides from the Ovotransferrin and Serum Transferrin of the Hen. Biochem. J. 1968, 108, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera-A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, B.F.; Baker, H.M.; Morris, G.E.; Rumball, S.V.; Baker, E.N. Apolactoferrin Structure Demonstrates Ligand-Induced Conformational Change in Transferrins. Nature 1990, 344, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, J.G.; Neu, M.; Pantos, E.; Schwab, F.J.; Evans, R.W.; Townes-Andrews, E.; Lindley, P.F.; Appel, H.; Thies, W.G.; Hasnain, S.S. X-Ray Solution Scattering Reveals Conformational Changes upon Iron Uptake in Lactoferrin, Serum and Ovo-Transferrins. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 225, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, K. Alternative Structural State of Transferrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10190–10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guha Thakurta, P.; Choudhury, D.; Dasgupta, R.; Dattagupta, J.K. Structure of Diferric Hen Serum Transferrin at 2.8 Å Resolution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2003, 59, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azari, P.R.; Feeney, R.E. Resistance of Metal Complexes of Conalbumin and Transferrin to Proteolysis and to Thermal Denaturation. J. Biol. Chem. 1958, 232, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.Y.; Ahn, D.U. An Economic and Simple Purification Procedure for the Large-Scale Production of Ovotransferrin from Egg White. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.T.; Woodworth, R.C. Ultraviolet Difference Spectral Studies of Conalbumin Complexes with Transition Metal Ions. Biochemitry 1969, 8, 3711–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.C.; Robinson, A.K.; Rodr, F. Bacterial Iron Homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A.L.; Caroline, L. Raw Hen Egg White and the Role of Iron in Growth Inhibition of Shigella Dysenteriae, Staphylococcus Aureus, Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Sci. Wash. 1944, 100, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderton, G.; Ward, W.H.; Fevold, H.L. Identification of the Bacteria-Inhibiting, Iron Binding Protein of Egg White as Conalbumin. Arch Biochem 1946, 11, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nys, Y.; Sauveur, B. Valeur nutritionnelle des oeufs. INRAE Prod. Anim. 2004, 17, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciqual Table de Composition Nutritionnelle Des Aliments. Available online: https://ciqual.anses.fr/ (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Stadelman, W.J.; Cotterill, O.J. Egg Science and Technology, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Baron, F.; Thapon, J.-L. Science et Technologie de L’oeuf, Volume 1: Production et Qualité; Sciences et Techniques Agroalimentaire; Tec&Doc.; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi, J.A. Factors in Egg White Which Control Growth of Bacteria. J. Food Sci. 1960, 25, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, E.L.W.Y.N. Availability of Iron and Survival of Bacteria in Infection. Med. Microbiol. 1983, 3, 153–177. [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, A.M.; Mori, I.; Walsh, C.T. Reconstitution and Characterization of the Escherichia coli Enterobactin Synthetase from EntB, EntE, and EntF. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 2648–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumler, A.J.; Norris, T.L.; Lasco, T.; Voigt, W.; Reissbrodt, R.; Rabsch, W.; Heffron, F. IroN, a Novel Outer Membrane Siderophore Receptor Characteristic of Salmonella Enterica. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devireddy, L.R.; Gazin, C.; Zhu, X.; Green, M.R. A Cell-Surface Receptor for Lipocalin 24p3 Selectively Mediates Apoptosis and Iron Uptake. Cell 2005, 123, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetz, D.H.; Holmes, M.A.; Borregaard, N.; Bluhm, M.E.; Raymond, K.N.; Strong, R.K. The Neutrophil Lipocalin NGAL Is a Bacteriostatic Agent That Interferes with Siderophore-Mediated Iron Acquisition. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonetti, N.H.; Williams, P.H. A Cluster of Five Genes Specifying the Aerobactin Iron Uptake System of Plasmid ColV-K30. Infect Immun. 1984, 46, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skare, J.T.; Ahmer, B.M.; Seachord, C.L.; Darveau, R.P.; Postle, K. Energy Transduction between Membranes. TonB, a Cytoplasmic Membrane Protein, Can Be Chemically Cross-Linked in Vivo to the Outer Membrane Receptor FepA. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 16302–16308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Fischbach, M.A.; Liu, D.R.; Walsh, C.T. In Vitro Characterization of Salmochelin and Enterobactin Trilactone Hydrolases IroD, IroE, and Fes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11075–11084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luckey, M.; Pollack, J.R.; Wayne, I.R.; Ames, B.N.; Neilands, J.B. Iron Uptake in Salmonella Typhimurium: Utilization of Exogenous Siderochromes as Iron Carriers. J. Bacteriol. 1972, 111, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troxell, B.; Hassan, H.M. Transcriptional Regulation by Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) in Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hantke, K. Iron and Metal Regulation in Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, E.; Gottesman, S. A Small RNA Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Iron Metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4620–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bister, B.; Bischoff, D.; Nicholson, G.J.; Valdebenito, M.; Schneider, K.; Winkelmann, G.; Hantke, K.; Süssmuth, R.D. The Structure of Salmochelins: C-Glucosylated Enterobactins of Salmonella Enterica. Biometals 2004, 17, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantke, K.; Nicholson, G.; Rabsch, W.; Winkelmann, G. Salmochelins, Siderophores of Salmonella Enterica and Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains, Are Recognized by the Outer Membrane Receptor IroN. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langman, L.; Young, I.G.; Frost, G.E.; Rosenberg, H.; Gibson, F. Enterochelin System of Iron Transport in Escherichia coli: Mutations Affecting Ferric-Enterochelin Esterase. J. Bacteriol. 1972, 112, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chenaul, S.S.; Earhart, C.F. Identification of Hydrophobic Proteins FepD and FepG of the Escherichia coli Ferrienterobactin Permease. Microbiology 1992, 138, 2167–2171. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbach, M.R.; Braun, V.; Köster, W. Ferrichrome Transport in Escherichia coli K-12: Altered Substrate Specificity of Mutated Periplasmic FhuD and Interaction of FhuD with the Integral Membrane Protein FhuB. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 7186–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S.C. Iron Storage in Bacteria. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1998, 40, 281–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerken, H.; Vuong, P.; Soparkar, K.; Mistra, R. Roles of the EnvZ/OmpR Two-Component System and Porins in Iron Acquisition in Escherichia coli. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chart, H.; Buck, M.; Stevenson, P.; Griffiths, E. Iron Regulated Outer Membrane Proteins of Escherichia coli: Variations in Expression Due to the Chelator Used to Restrict the Availability of Iron. Microbiology 1986, 132, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chart, H.; Rowe, B. Iron Restriction and the Growth of Salmonella enteritidis. Epidemiol. Infect. 1993, 110, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caza, M.; Garénaux, A.; Lépine, F.; Dozois, C.M. Catecholate Siderophore Esterases Fes, IroD and IroE Are Required for Salmochelins Secretion Following Utilization, but Only IroD Contributes to Virulence of Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 97, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; Bonnassie, S.; Alabdeh, M.; Cochet, M.-F.; Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Gautier, M.; Andrews, S.C.; Jan, S. Global Gene-Expression Analysis of the Response of Salmonella Enteritidis to Egg White Exposure Reveals Multiple Egg White-Imposed Stress Responses. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; He, S.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Crucial Role of YbgC for Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis Survival in Egg White. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 289, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desert, C.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Nau, F.; Jan, G.; Val, F.; Mallard, J. Comparison of Different Electrophoretic Separations of Hen Egg White Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4553–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Pasco, M.; Mollé, D.; Désert, C.; Croguennec, T.; Nau, F. Proteomic Analysis of Hen Egg White. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3901–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, C.; Arena, S.; Scaloni, A.; Guerrier, L.; Boschetti, E.; Mendieta, M.E.; Citterio, A.; Righetti, P.G. Exploring the Chicken Egg White Proteome with Combinatorial Peptide Ligand Libraries. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3461–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, L.A.; Fau, C.; Baron, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Nau, F.; Gautier, M.; Karatzas, K.A.; Jan, S.; Andrews, S.C. The Three Lipocalins of Egg-White: Only Ex-FABP Inhibits Siderophore-Dependent Iron Sequestration by Salmonella Enteritidis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correnti, C.; Clifton, M.C.; Abergel, R.J.; Allred, B.; Hoette, T.M.; Ruiz, M.; Cancedda, R.; Raymond, K.N.; Descalzi, F.; Strong, R.K. Galline Ex-FABP Is an Antibacterial Siderocalin and a Lysophosphatidic Acid Sensor Functioning through Dual Ligand Specificities. Structure 2011, 19, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenti, P.; Visca, P.; Antonini, G.; Orsi, N. Antifungal Activity of Ovotransferrin towards Genus Candida. Mycopathologia 1985, 89, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leive, L. The Barrier Function of the Gram-Negative Envelope. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1974, 235, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaidoi, H.; Vaara, M. Molecular Basis of Bacterial Outer Membrane Permeability. Microbiol. Rev. 1985, 49, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, K.; Hill, T.; Chart, H. Interaction of Lactoferrin and Transferrins with the Outer Membrane of Bordetella Pertussis. Microbiology 1987, 133, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, P. Chemiosmotic Coupling in Oxidative and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation. Biol. Rev. 1966, 445–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, S.; Baron, F.; Alabdeh, M.; Chaari, W.; Grosset, N.; Cochet, M.-F.; Gautier, M.; Víe, V.; Nau, F. Biochemical and Micrographic Evidence of Escherichia coli Membrane Damage during Incubation in Egg White under Bactericidal Conditions. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hu, M.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Role of YoaE Gene Regulated by CpxR in the Survival of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis in Antibacterial Egg White. mSphere 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raivio, T.L.; Leblanc, S.K.D.; Price, N.L. The Escherichia coli Cpx Envelope Stress Response Regulates Genes of Diverse Function That Impact Antibiotic Resistance and Membrane Integrity. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darwin, A.J. The Phage-shock-protein Response. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Tommassen, J. Involvement of Stress Protein PspA (Phage Shock Protein A) of Escherichia coli in Maintenance of the Protonmotive Force under Stress Conditions. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epand, R.F.; Pollard, J.E.; Wright, J.O.; Savage, P.B.; Epand, R.M. Depolarization, Bacterial Membrane Composition, and the Antimicrobial Action of Ceragenins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3708–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, F.; Jan, S.; Gonnet, F.; Pasco, M.; Jardin, J. Ovotransferrin Plays a Major Role in the Strong Bactericidal Effect of Egg White against the Bacillus Cereus Group. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.F.; Powell, C.K. Increase in the PH of the White and Yolk of Hens’ Eggs. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1931, 23, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padan, E.; Zilberstein, D.; Rottenberg, H. The Proton Electrochemical Gradient in Escherichia coli Cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 63, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padan, E.; Zilberstein, D.; Schuldiner, S. PH Homesstasis in Bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Rev. Biomembr. 1981, 650, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, I.R. Regulation of Cytoplasmic PH in Bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 1985, 49, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Kirk, M.F. PH as a Primary Control in Environmental Microbiology: 1. Thermodynamic Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messens, W.; Duboccage, L.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Heyndrickx, M.; Herman, L. Growth of Salmonella Serovars in Hens’ Egg Albumen as Affected by Storage Prior to Inoculation. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdeh, M.; Lechevalier, V.; Nau, F.; Gautier, M.; Cochet, M.-F.; Gonnet, F.; Jan, S.; Baron, F. Role of Incubation Conditions and Protein Fraction on the Antimicrobial Activity of Egg White against Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, I.; Mizutani, K.; Hirose, M. Iron-Binding Process in the Amino- and Carboxyl-Terminal Lobes of Ovotransferrin: Quantitative Studies Utilizing Single Fe3+ -Binding Mutants. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11118–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinsky, T.J.; Nielsen, J.E.; McCammon, J.A.; Baker, N.A. PDB2PQR: An Automated Pipeline for the Setup of Poisson–Boltzmann Electrostatics Calculations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W665–W667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.C.; Weber, I. The Metal Combining Properties of Conalbumin1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 5094–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasa, R.; Malmström, B.G.; Saltman, P.; Vänngård, T. The Specific Binding of Iron(III) and Copper(II) to Transferrin and Conalbumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1963, 75, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.T.; Woodworth, R.C. Differences in Absorption and Emission Properties of Conalbumin and Metal-Saturated Conalbumin. J. Polym. Sci. Part C Polym. Symp. 1970, 30, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.W.; Donovan, J.W.; Williams, J. Calorimetric Studies on the Binding of Iron and Aluminium to the Amino- and Carboxyl-Terminal Fragments of Hen Ovotransferrin. FEBS Lett. 1977, 83, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirose, J.; Fujiwara, H.; Magarifuchi, T.; Iguti, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Kominami, S.; Hiromi, K. Copper Binding Selectivity of N- and C-Sites in Serum (Human)- and Ovo-Transferrin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1996, 1296, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, P.; Visca, P.; Antonini, G.; Orsi, N.; Antonini, E. The Effect of Saturation with Zn2+ and Other Metal Ions on the Antibacterial Activity of Ovotransferrin. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. (Berl.) 1987, 176, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réhault-Godbert, S.; Guyot, N.; Nys, Y. The Golden Egg: Nutritional Value, Bioactivities, and Emerging Benefits for Human Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grittins, J.E.; Overfield, N.D. The Nutrient Content of Eggs in Great Britain. In Proceedings of the 4th European Symposium on the Quality of Eggs and Eggs Products; Oosterwod, A., de Vries, A.W., Eds.; Springer: Beekbergen, The Netherland, 1991; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mongin, P.; Lacassagne, L. Equilibre acido-basique du sang et formation de la coquille de l’oeuf. Ann. Biol. Anim. Biochim. Biophys. 1966, 6, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, J.; Pace, J. The Distribution of Carbon Dioxide in the Hen’s Egg. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1938, 126, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, P.; Stasio, A.; Mastromerino, P.; Seganti, L.; Sinibaldi, L.; Orsi, N. Influence of Bicarbonate and Citrate on the Bacteriostatic Action of Ovotransferrin towards Staphylococci. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1981, 10, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.Y.; Mendonca, A.F.; Ahn, D.U. Influence of Zinc, Sodium Bicarbonate, and Citric Acid on the Antibacterial Activity of Ovotransferrin Against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria Monocytogenes in Model Systems and Ham. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 2660–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.R.; Rha, C. Apparent Shear Viscosity of Native Egg White. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1982, 17, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.S.; Monsey, J.B. Changes in the Composition of Ovomucin during Liquefaction of Thick Egg White. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1972, 23, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.S.; Monsey, J.B. The Composition and Proposed Subunit Structure of Egg-White P-Ovomucin. Biochem. J. 1975, 147, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotterill, O.J.; Winter, A.R. Egg White Lysozyme: 3. The Effect of PH on the Lysozyme-Ovomucin Interaction1. Poult. Sci. 1955, 34, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.; Hale, H.P. The Mechanical Properties of the Thick White of the Hen’s Egg. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1959, 32, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.S.; Monsey, J.B. Changes in the Composition of Ovomucin during Liquefaction of Thick Egg White: The Effect of Ionic Strength and Magnesium Salts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1972, 23, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Nakamura, R. Studies on Factors of Solubilization of Insoluble Ovomucin during Thick White Thinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1976, 24, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Ogino, K.; Kuramoto, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Degradation of the P-Glycosidally Linked Carbohydrate Units of Ovomucin during Egg White Thinning. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Ogato, S.; Matsudomi, N.; Kobayashi, K. Comparative Study of Aggregated and Disaggregated Ovomucin during Egg White Thinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Chan, E. Biochemical Basis for the Properties of Egg White. CRC Crit Rev. Poult. Biol. 1989, 2, 21–58. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Kawase, K.; Tomita, M.; Kiyosawa, I.; Okonogi, S. Collaborative Bacteriostatic Activity of Bovine Lactoferrin with Lysozyme against Escherichia coli O111. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 1705–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, R.T.; Giehl, T.J. Killing of Gram-Negative Bacteria by Lactofernn and Lysozyme. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facon, M.J.; Skura, B.J. Antibacterial Activity of Lactoferricin, Lysozyme and EDTA against Salmonella Enteritidis. Int. Dairy J. 1996, 6, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, K.J.; Rupnow, J.H.; Froning, G.W. The Effect of Lysozyme and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid on Salmonella on Broiler Parts. Poult. Sci. 1985, 64, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughey, V.L.; Wilger, P.A.; Johnson, E.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Lysozyme against Listeria Monocytogenes Scott A in Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Branen, J.K.; Davidson, P.M. Enhancement of Nisin, Lysozyme, and Monolaurin Antimicrobial Activities by Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid and Lactoferrin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 90, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.Y.; Mendonca, A.F.; Ahn, D.U. Effect of Ethylenediaminetetraacetate and Lysozyme on the Antimicrobial Activity of Ovotransferrin Against Listeria Monocytogenes. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.R.; Sugimoto, Y.; Aoki, T. Ovotransferrin Antimicrobial Peptide (OTAP-92) Kills Bacteria through a Membrane Damage Mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2000, 1523, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Guo, Y.; Fu, X.; Jin, Y. Identification and Antimicrobial Mechanisms of a Novel Peptide Derived from Egg White Ovotransferrin Hydrolysates. LWT 2020, 131, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehault-Godbert, S.; Baron, F.; Mignon-Grasteau, S.; Labas, V.; Gautier, M.; Hincke, M.T.; Nys, Y. Effect of Temperature and Time of Storage on Protein Stability and Anti-Salmonella Activity of Egg White. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yu, W.; Ren, F.; Wu, J. Formation and Characterization of Peptides in Egg White during Storage at Ambient Temperature. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; Gautier, M.; Brule, G. Rapid Growth of Salmonella Enteritidis in Egg White Reconstituted from Industrial Egg White Powder. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galyean, R.D.; Cotterill, O.J. Chromatography and Electrophoresis of Native and Spray-Dried Egg White. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.N.; Mason, A.B.; Woodworth, R.C.; Brandts, J.F. Calorimetric Studies of Serum Transferrin and Ovotransferrin. Estimates of Domain Interactions, and Study of the Kinetic Complexities of Ferric Ion Binding. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Gonnet, F.; Dubois, J.-J.; Gautier, M. Effect of Dry Heating on the Microbiological Quality, Functional Properties, and Natural Bacteriostatic Ability of Egg White after Reconstitution. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Min Concentration in Egg White (mM) * | Max Concentrationin Egg White (mM) * | |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium | 67.42 | 80.91 |
| Sulphur | 50.83 | 56.14 |
| Potassium | 35.81 | 44.25 |
| Phosphorus | 4.2 | 7.10 |
| Magnesium | 3.70 | 4.94 |
| Calcium | 1.25 | 2.99 |
| Chlorine | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| Iron | 0.0036 | 0.0179 |
| Zinc | 0.0015 | 0.0185 |
| Copper | 0.0029 | 0.0058 |
| Manganese | 0.0013 | 0.0020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Legros, J.; Jan, S.; Bonnassie, S.; Gautier, M.; Croguennec, T.; Pezennec, S.; Cochet, M.-F.; Nau, F.; Andrews, S.C.; Baron, F. The Role of Ovotransferrin in Egg-White Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040823
Legros J, Jan S, Bonnassie S, Gautier M, Croguennec T, Pezennec S, Cochet M-F, Nau F, Andrews SC, Baron F. The Role of Ovotransferrin in Egg-White Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. Foods. 2021; 10(4):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040823
Chicago/Turabian StyleLegros, Julie, Sophie Jan, Sylvie Bonnassie, Michel Gautier, Thomas Croguennec, Stéphane Pezennec, Marie-Françoise Cochet, Françoise Nau, Simon C. Andrews, and Florence Baron. 2021. "The Role of Ovotransferrin in Egg-White Antimicrobial Activity: A Review" Foods 10, no. 4: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040823
APA StyleLegros, J., Jan, S., Bonnassie, S., Gautier, M., Croguennec, T., Pezennec, S., Cochet, M. -F., Nau, F., Andrews, S. C., & Baron, F. (2021). The Role of Ovotransferrin in Egg-White Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. Foods, 10(4), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040823