A Population Balance Model to Describe the Evolution of Sublethal Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Parameter Estimation and Uncertainty
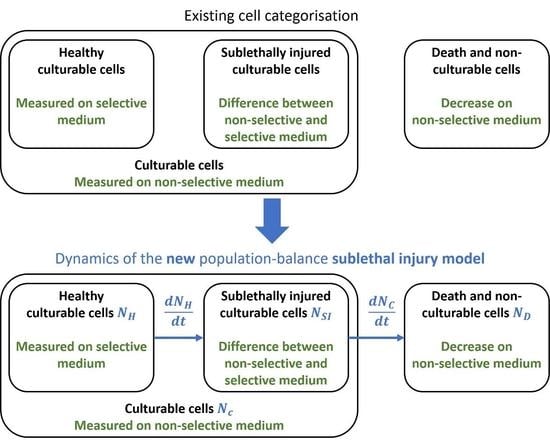
2.3. Sublethal Injury
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Sublethal Injury Model
3.2. Case Study 1: Log-Linear Inactivation
3.3. Case Study 2: Biphasic Inactivation
3.4. Case Study 3: Log-Linear Inactivation with Tailing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMeekin, T.A.; Olley, J.; Ratkowsky, D.A.; Ross, T. Predictive microbiology: Towards the interface and beyond. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 73, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, F.; Carrasco, E.; Pradhan, A.K.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Valero, A. Special issue on 10th international conference of predictive modelling in foods: Towards a new paradigm in predictive microbiology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwietering, M.H.; Garre, A.; Wiedmann, M.; Buchanan, R.L. All food processes have a residual risk, some are small, some very small and some are extremely small: Zero risk does not exist. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.C.H.; Fung, D.Y.C. Evaluation of Thin Agar Layer Method for Recovery of Heat-Injured Foodborne Pathogens. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, A. Bacterial injury: A review. Can. J. Microbiol. 1977, 23, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.D. Potential sites of damage in microorganisms exposed to chemical or physical agents. In The Revival of Injured Microbes; Andrew, M.H.E., Russell, A.D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wesche, A.M.; Gurtler, J.B.; Marks, B.P.; Ryser, E.T. Stress, Sublethal Injury, Resuscitation, and Virulence of Bacterial Foodborne Pathogens. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1121–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashears, M.M.; Amezquita, A.; Stratton, J. Validation of Methods Used To Recover Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. Subjected to Stress Conditions. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasson, V.; Rajkovic, A.; Debevere, J.; Uyttendaele, M. Kinetics of resuscitation and growth of L. monocytogenes as a tool to select appropriate enrichment conditions as a prior step to rapid detection methods. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Deisingh, A.K.; Thompson, M. Strategies for the detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in foods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasson, V.; Uyttendaele, M.; Raykovic, A.; Debevere, J. Establishment of procedures provoking sub-lethal injury of Listeria monocytogenes, Campylobacter jejuni and Escherichia coli O157 to serve method performance testing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, E.; Velliou, E.G.; Van Derlinden, E.; Mertens, L.; Van Impe, J.F. Effect of cell immobilization on heat-induced sublethal injury of Escherichia coli, Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria innocua. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, L.; Devlieghere, F.; Vandekinderen, I.; Rajtak, U.; Debevere, J. The sensory acceptability of cooked meat products treated with a protective culture depends on glucose content and buffering capacity: A case study with Lactobacillu sakei 10A. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semanchek, J.J.; Golden, D.A. Influence of growth temperature on inactivation and injury of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by heat, acid, and freezing. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, V.C.H. A review of microbial injury and recovery methods in food. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, S.V.; Donnelly, C.W. Development of a Repair-Enrichment Broth for Resuscitation of Heat-Injured Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dykes, G.A. Physical and metabolic causes of sub-lethal damage in Listeria monocytogenes after long-term chilled storage at 4 °C. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Z.; Hu, X.; Liao, X. Sublethal injury and recovery of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by high pressure carbon dioxide. Food Control 2015, 50, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.M.; Bergholz, T.M.; Hildebrandt, I.M.; Marks, B.P. Application of a Nonlinear Model to Transcript Levels of Upregulated Stress Response Gene ipbA in Stationary-Phase Salmonella enterica Subjected to Sublethal Heat Stress. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghate, V.; Leong, A.L.; Kumar, A.; Bang, W.S.; Zhou, W.; Yuk, H.-G. Enhancing the antibacterial effect of 461 and 521 nm light emitting diodes on selected foodborne pathogens in trypticase soy broth by acidic and alkaline pH conditions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J. Inactivation Kinetics of Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus in Different Media by Dielectric Barrier Discharge Non-Thermal Plasma. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, R.; Wang, D.; Zou, M.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Analysis of Bacillus cereus cell viability, sublethal injury, and death induced by mild thermal treatment. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olszewska, M.A.; Zhao, T.; Doyle, M.P. Inactivation and induction of sublethal injury of Listeria monocytogenes in biofilm treated with various sanitizers. Food Control 2016, 70, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Lv, X.; Sun, D.-W. Assessing the inactivation efficiency of Ar/O2 plasma treatment against Listeria monocytogenes cells: Sublethal injury and inactivation kinetics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Puig, M.; Moreno, P.; Pina-Pérez, M.C.; Rodrigo, D.; Martínez, A. Combined effect of high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) and antimicrobial from agro-industrial by-products against S. Typhimurium. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 77, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, H.; Yu, Q.; Li, X.; Dai, R. Inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus in phosphate buffered saline and physiological saline ohmic heating with different voltage gradient and frequency. J. Food Eng. 2020, 274, 109834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Kan, J. Sublethal injury and recovery of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and K-12 after exposure to lactic acid. Food Control 2017, 82, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Genovés, S.; Martorell, P.; Zanini, S.F.; Rodrigo, D.; Martinez, A. Sublethal injury and virulence changes in Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua treated with antimicrobials carvacrol and citral. Food Microbiol. 2015, 50, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Popo, E.; Mendonca, A.; Dickson, J.; Shaw, A.; Coleman, S.; Daraba, A.; Jackson-Davis, A.; Woods, F. Isoeugenol significantly inactivates Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica, and Listeria monocytogenes in refrigerated tyndallized pineapple juice with added Yucca schidigera extract. Food Control 2019, 106, 106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Devlieghere, F.; Geeraerd, A.; Uyttendaele, M. Thermal inactivation and sublethal injury kinetics of Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes in broth versus agar surface. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 243, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, C.; Jiao, S. Effect of radio frequency heating stress on sublethal injury of Salmonella Typhimurium in red pepper powder. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Shen, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X. Lethal and sublethal injury and kinetics of Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus in milk by pulsed electric fields. Food Control 2013, 32, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.A.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Teixeira, P.; Silva, C.L.M. Recovery of heat-injured Listeria innocua. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Mendis, N.; Trigui, H.; Oliver, J.D.; Faucher, S.P. The importance of the viable but non-culturable state in human bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto, D.; Santos, M.A.; Chabel, L. Thirty years of viable but nonculturable state research: Unsolved molecular mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 41, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angarano, V.; Smet, C.; Akkermans, S.; Watt, C.; Chieffi, A.; Van Impe, J.F. Visible Light as an Antimicrobial Strategy for Inactivation of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Govaert, M.; Smet, C.; Baka, M.; Ećimović, B.; Walsh, J.L.; Van Impe, J. Resistance of L. monocytogenes and S. Typhimurium towards Cold Atmospheric Plasma as Function of Biofilm Age. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Govaert, M.; Smet, C.; Vergauwen, L.; Ećimović, B.; Walsh, J.L.; Baka, M.; Van Impe, J. Influence of plasma characteristics on the efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) for inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium biofilms. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaert, M.; Smet, C.; Graeffe, A.; Walsh, J.L.; Van Impe, J.F.M. Inactivation of L. monocytogenes and S. typhimurium Biofilms by Means of an Air-Based Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) System. Foods 2020, 9, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Smet, C.; Noriega, E.; Rosier, F.; Walsh, J.L.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Van Impe, J.F. Influence of food intrinsic factors on the inactivation efficacy of cold atmospheric plasma: Impact of osmotic stress, suboptimal pH and food structure. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Smet, C.; Noriega, E.; Rosier, F.; Walsh, J.L.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Van Impe, J.F. Impact of food model (micro)structure on the microbial inactivation efficacy of cold atmospheric plasma. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 240, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, C.; Baka, M.; Steen, L.; Fraeye, I.; Walsh, J.L.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Van Impe, J.F. Combined effect of cold atmospheric plasma, intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the microbial behavior in/on (food) model systems during storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 53, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyen, D.; Baka, M.; Van Impe, J.F.M. Sublethal Injury Caused to Listeria monocytogenes by Natural Plant Extracts: Case Study on Grape Seed Extract and Garlic Extract. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2731. [Google Scholar]
- Verheyen, D.; Baka, M.; Akkermans, S.; Skåra, T.; Van Impe, J.F. Effect of microstructure and initial cell conditions on thermal inactivation kinetics and sublethal injury of Listeria monocytogenes in fish-based food model systems. Food Microbiol. 2019, 84, 103267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verheyen, D.; Govaert, M.; Seow, T.K.; Ruvina, J.; Mukherjee, V.; Baka, M.; Skåra, T.; Van Impe, J.F. The Complex Effect of Food Matrix Fat Contect on Thermal Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes: Case Study in Emulsion and Gelled Emulsion Model Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Impe, J.F.; Bernaerts, K.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Poschet, F.; Versyck, K.J. Modelling and prediction in an uncertain environment. In Food Process Modelling; Tijskens, L.M.M., Hertog, M.L.A.T.M., Nicolaï, B.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: England, UK, 2001; pp. 156–179. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, E.; Pronzato, L. Identification of Parameteric Models from Experimental Data; Springer: Paris, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Perni, S.; Chalise, P.R.; Shama, G.; Kong, M.G. Bacterial cells exposed to nanosecond pulsed electric fields show lethal and sublethal effects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 120, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bigelow, W.D.; Esty, J.R. The thermal death point in relation to time of typical thermophilic organisms. J. Infect. Dis. 1920, 27, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerf, O. Tailing of survival curves of bacterial spores. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1977, 42, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Akkermans, S.; Smet, C.; Valdramidis, V.; Van Impe, J. Microbial Inactivation Models for Thermal Processing. In Food Safety Engineering; Demirci, A., Feng, H., Krishnamurthy, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 399–420. [Google Scholar]
- Geeraerd, A.H.; Herremans, C.H.; Van Impe, J.F. Structural model requirements to describe microbial inactivation during a mild heat treatment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 59, 185–209. [Google Scholar]





| Model Parameter | Parameter Estimate | 95% Confidence Bounds |
|---|---|---|
| Independent models | ||
| MSE | ||
| Sublethal injury model | ||
| MSE | ||
| Model Parameter | Parameter Estimate | 95% Confidence Bounds |
|---|---|---|
| Independent models | ||
| MSE | ||
| Sublethal injury model | ||
| MSE | ||
| Model Parameter | Parameter Estimate | 95% Confidence Bounds |
|---|---|---|
| Independent models | ||
| MSE | ||
| Sublethal injury model | ||
| MSE | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akkermans, S.; Verheyen, D.; Smet, C.; Van Impe, J.F.M. A Population Balance Model to Describe the Evolution of Sublethal Injury. Foods 2021, 10, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071674
Akkermans S, Verheyen D, Smet C, Van Impe JFM. A Population Balance Model to Describe the Evolution of Sublethal Injury. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071674
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkkermans, Simen, Davy Verheyen, Cindy Smet, and Jan F. M. Van Impe. 2021. "A Population Balance Model to Describe the Evolution of Sublethal Injury" Foods 10, no. 7: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071674
APA StyleAkkermans, S., Verheyen, D., Smet, C., & Van Impe, J. F. M. (2021). A Population Balance Model to Describe the Evolution of Sublethal Injury. Foods, 10(7), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071674