Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division (RND) Transporter AcrD Confers Resistance to Egg White in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Caco-2 Cell Culture Preparation
2.3. Egg White and Its Filtrate Preparation
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Construction of acrD Deletion Mutant Strain
2.6. Measurement of Bacterial Growth
2.7. Survival Ability of S. Enteritidis Strains in Egg White and Its Filtrate
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.9. Adhesion and Invasion Assays
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
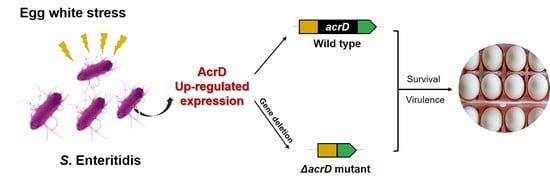
3.1. Expression of acrD in S. Enteritidis in Response to Whole Egg White and Construction of acrD Mutant
3.2. Survival Study of S. Enteritidis ΔacrD Mutant in Egg White and Its Filtrate
3.3. Cellular Morphology of S. Enteritidis in Egg White under SEM
3.4. The Adhesion and Invasion Ability of S. Enteritidis to Caco-2 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.R.; Zhang, H.N.; Jia, H.Y.; Liu, X.G.; Yu, B.; Zeng, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, X.Y.; Yang, D.J. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella in the commercial eggs in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 325, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Loui, C.; Clavijo, R.I.; Riley, L.W.; Lu, S. Survival characteristics of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis in chicken egg albumen. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Bonnassie, S.; Gautier, M.; Andrews, S.C.; Jan, S. Egg white versus Salmonella Enteritidis! A harsh medium meets a resilient pathogen. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavijo, R.I.; Loui, C.; Andersen, G.L.; Riley, L.W.; Lu, S. Identification of genes associated with survival of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis in chicken egg albumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Vylder, J.; Raspoet, R.; Dewulf, J.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Van Immerseel, F. Salmonella Enteritidis is superior in egg white survival compared with other Salmonella serotypes. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Z.; Zhou, X.J.; Jia, B.; Li, N.; Jia, J.Y.; He, M.; He, Y.C.; Qin, X.J.; Shi, C.L.; Shi, X.M. Transcriptional sequencing uncovers survival mechanisms of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis in antibacterial egg white. mSphere 2019, 4, e00700-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.W.; Killoran, P.B.; Riley, L.W. Association of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis YafD with resistance to chicken egg albumen. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6734–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gantois, I.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F. Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis genes induced during oviduct colonization and egg contamination in laying hens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6616–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, F.; Bonnassie, S.; Alabdeh, M.; Cochet, M.; Nau, F.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Gautier, M.; Andrews, S.C.; Jan, S. Global gene-expression analysis of the response of Salmonella Enteritidis to egg white exposure reveals multiple egg white-imposed stress responses. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspoet, R.; Eeckhaut, V.; Vermeulen, K.; De Smet, L.; Wen, Y.; Nishino, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Devreese, B.; Van Immerseel, F. The Salmonella Enteritidis TolC outer membrane channel is essential for egg white survival. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspoet, R.; Gantois, I.; Devloo, R.; Martel, A.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Van Immerseel, F. Salmonella Enteritidis universal stress protein (usp) gene expression is stimulated by egg white and supports oviduct colonization and egg contamination in laying hens. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.J.; He, S.K.; Zhou, X.J.; Cheng, X.; Huang, X.Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.L.; Shi, X.M. Quantitative proteomics reveals the crucial role of YbgC for Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis survival in egg white. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 289, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Richmond, G.E.; Piddock, L.J.V. Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, M.M.C.; Blair, J.M.A.; Ragione, R.M.L.; Newcombe, J.; Dwyer, D.J.; Lvens, A.; Piddock, L.J.V. Beyond antimicrobial resistance: Evidence for a distinct role of the AcrD efflux pump in Salmonella biology. mBio 2016, 7, e01916-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stephanie, B.; Ekanayaka, A.S.; Piddock, L.J.; Webber, M.A. Loss of or inhibition of all multidrug resistance efflux pumps of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium results in impaired ability to form a biofilm. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eaves, D.J.; Ricci, V.; Piddock, L.J.V. Expression of acrB, acrF, acrD, marA, and soxS in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium: Role in multiple antibiotic resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishino, K.; Latifi, T.; Groisman, E.A. Virulence and drug resistance roles of multidrug efflux systems of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, K.; Nikaido, E.; Yamaguchi, A. Regulation of multidrug efflux systems involved in multidrug and metal resistance of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 9066–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Begley, M.; Prieto, M.; Messens, W.; López, M.; Bernardo, A.; Hill, C. Salmonella spp. survival strategies within the host gastrointestinal tract. Microbiology 2011, 157, 3268–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budak, G.; Ozsoy, O.E.; Son, Y.A.; Can, T.; Tuncbag, N. Reconstruction of the temporal signaling network in Salmonella-infected human cells. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.J.; Dong, R.; He, S.K.; Zhou, X.J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Shi, X.M. Characterization of the role of ybgC in lysozyme resistance of Salmonella Enteritidis. Food Control 2020, 109, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Liu, B.; Shi, C.L.; Shi, X.M. Mutation of a Salmonella serogroup-C1-specific gene abrogates O7-antigen biosynthesis and triggers NaCl-dependent motility deficiency. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubirés, X.; Saigi, F.; Piqué, N.; Climent, N.; Merino, S.; Alberti, S.; Tomas, J.M.; Regué, M. A gene (wbbL) from Serratia marcescens N28b (O4) complements the rfb-50 mutation of Escherichia coli K-12 derivatives. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 7581–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edward, R.A.; Keller, L.H.; Schifferli, D.M. Improved allelic exchange vectors and their use to analyze 987P fimbria gene expression. Gene 1998, 207, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, I.; Cordero, H.; Mahdhi, A.; Morcillo, P.; Fedhila, K.; Cuesta, A.; Bakhrouf, A.; Mahdouani, K.; Esteban, M.Á. Adhesion, invasion, cytotoxic effect and cytokine production in response to atypical Salmonella Typhimurium infection. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hou, W.W.; Li, K.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Yue, T.L. Specific gene SEN 1393 contributes to higher survivability of Salmonella Enteritidis in egg white by regulating sulfate assimilation pathway. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 337, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabdeh, M.; Lechevalier, V.; Nau, F.; Gautier, M.; Cochet, M.; Gonnet, F.; Jan, S.; Baron, F. Role of incubation conditions and protein fraction on the antimicrobial activity of egg white against Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli. J. Food Protect. 2011, 74, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Chen, P.X.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Chang, M.X.; Jiang, H.X. Coordinated expression of acrAB-tolC and eight other functional efflux pumps through activating ramA and marA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiyama, T.; Nishino, K. AcrB, AcrD, and MdtABC multidrug efflux systems are involved in enterobactin export in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McWhorter, A.R.; Chousalkar, K.K. Comparative phenotypic and genotypic virulence of Salmonella strains isolated from Australian layer farms. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mine, Y.; Ma, F.; Lauriau, S. Antimicrobial peptides released by enzymatic hydrolysis of hen egg white lysozyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, E.R.; Billings, G.; Odermatt, P.D.; Auer, G.K.; Zhu, L.; Miguel, A.; Chang, F.; Weibel, D.B.; Theriot, J.A.; Huang, K.C. The outer membrane is an essential load-bearing element in Gram-negative bacteria. Nature 2018, 559, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervé-Grépinet, V.; Réhault-Godbert, S.; Labas, L.; Magallon, T.; Derache, C.; Lavergne, M.; Gautron, J.; Lalmanach, A.C.; Nys, Y. Purification and characterization of avian β-defensin 11, an antimicrobial peptide of the hen egg. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4401–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.H.; Yoo, B.B.; Hwang, C.; Suo, Y.J.; Sheen, S.; Khosravi, P.; Huang, L.H. LMOf2365_0442 encoding for a fructose specific PTS permease IIA may be required for virulence in L. monocytogenes strain F2365. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Negi, V.D. Stress-induced adaptations in Salmonella: A ground for shaping its pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 229, 126311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Smith, H.E.; Vito, R.; Lawler, A.J.; Thompson, L.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Expression of homologous RND efflux pump genes is dependent upon AcrB expression: Implications for efflux and virulence inhibitor design. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| acrD-F1 | GCTCTAGACTCTACGCCGCTGCTGA (Xba I) |
| acrD-R1 | GGCCGGGAGCTAAAGGGGAACCTCGTGTTT |
| acrD-F2 | TTCCCCTTTAGCTCCCGGCCAGCCTGATAC |
| acrD-R2 | CGAGCTCGGCGACGAATAAGTTGCTGTG (Sac I) |
| Strains or Plasmids | Relevant Characteristics | Reference or Source |
|---|---|---|
| S. Enteritidis SJTUF10978 | Wild-type strain | Lab stock |
| ΔacrD | acrD deletion mutant of S. Enteritidis SJTUF10978 | This study |
| E. coli DH5α | Host for cloning | Lab stock |
| E. coli SM10 (λpir) | thi thr-1 leu6 proA2 his-4 arg E2 lacY1 galK2, ara14xyl5 supE44, λpir | [24] |
| pMD19-T | Cloning vector, Ampr | TaKaRa, China |
| pMD19-ΔacrD | pMD19-T containing a 3113 bp acrD deletion PCR product | This study |
| pRE112 | pGP704 suicide plasmid, pir dependent, oriT oriV sacB, Cmr | [25] |
| pRE112-ΔacrD | pRE112 containing a 3113 bp acrD deletion PCR product | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division (RND) Transporter AcrD Confers Resistance to Egg White in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Foods 2022, 11, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010090
Qin X, Liu Y, Shi X. Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division (RND) Transporter AcrD Confers Resistance to Egg White in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Foods. 2022; 11(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Xiaojie, Yanhong Liu, and Xianming Shi. 2022. "Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division (RND) Transporter AcrD Confers Resistance to Egg White in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis" Foods 11, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010090
APA StyleQin, X., Liu, Y., & Shi, X. (2022). Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division (RND) Transporter AcrD Confers Resistance to Egg White in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Foods, 11(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010090