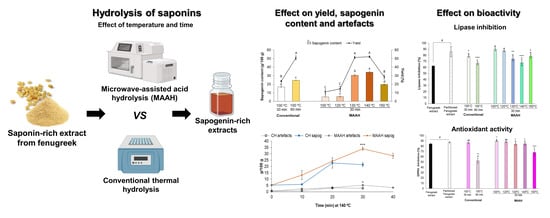
Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis vs. Conventional Hydrolysis to Produce Sapogenin-Rich Products from Fenugreek Extracts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Production of Sapogenin-Rich Extracts by Conventional Thermal Acid Hydrolysis
2.3. Production of Sapogenin-Rich Extracts by Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis (MAAH)
2.4. Analysis of the Sapogenin-Rich Extracts by GC-MS
2.5. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Assay
2.6. Antioxidant Activity Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrolysis Extraction Yield and Sapogenin Content of Hydrolyzed Extracts
3.1.1. Effect of MAAH Temperature
3.1.2. Effect of MAAH Time
3.2. Effect of Acid Hydrolysis Conditions on the Bioactivity of Sapogenin-Rich Extracts
3.2.1. Effect on Inhibitory Activity against Pancreatic Lipase
3.2.2. Effect on the Antioxidant Activity by the DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; van Staden, J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güçlü-Üstündağ, Ö.; Mazza, G. Saponins: Properties, applications and processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. The biological action of saponins in animal systems: A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Saponins in pulses and their health promoting activities: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez de Cedrón, M.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Reguero, M.; Wagner, S.; Bouzas, A.; Quijada-Freire, A.; Reglero, G.; Martín, D.; Ramírez de Molina, A. Saponin-Rich Extracts and Their Acid Hydrolysates Differentially Target Colorectal Cancer Metabolism in the Frame of Precision Nutrition. Cancers 2020, 12, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrelli, M.; Conforti, F.; Araniti, F.; Statti, G. Effects of Saponins on Lipid Metabolism: A Review of Potential Health Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Herrera, T.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The gastrointestinal behavior of saponins and its significance for their bioavailability and bioactivities. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.C.; Doss, R.B.; Garg, R.C.; Srivastava, A.; Lall, R.; Sinha, A. Fenugreek: Multiple health benefits. Nutraceuticals 2021, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, P.; Kumar, P. Diosgenin a steroidal compound: An emerging way to cancer management. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e14005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, F.R.S.; Araújo-Filho, H.G.; Monteiro, B.S.; Shanmugam, S.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; da Silva Almeida, J.R.G.; Thangaraj, P.; Júnior, L.J.Q.; de Souza Siqueira Quintans, J. Anti-inflammatory and modulatory effects of steroidal saponins and sapogenins on cytokines: A review of pre-clinical research. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Yang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, S.; Yu, L.; Lu, H.; Yin, G.; Liang, P.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, F. The Effects of Diosgenin on Hypolipidemia and Its Underlying Mechanism: A Review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, P.S.; Singh, P.P.; Padwad, Y.S.; Sharma, U. Steroidal saponins from Trillium govanianum as α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory agents. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustini, K.; Firdayani, F.; Churiyah, C. Cytotoxic Activity on MCF-7 Cells and in Silico Study of Sapogenin Steroids from Trigonella foenum-graecum L. Indones. J. Cancer Chemoprevention 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.D.; Mishra, S.; Verma, S.S.; Shekher, A.; Rai, V.; Awasthee, N.; Das, T.J.; Paul, D.; Das, S.K.; Tag, H.; et al. Evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of diosgenin enriched Paris polyphylla rhizome extract of Indian Himalayan landraces. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts from fenugreek and quinoa improves their pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity and hypocholesterolemic effect. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Ji, G.-E. Transformation of Ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by Food Microorganisms. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, P.A.; Dziedzic, S.Z. Effect of hydrolysis on sapogenin release in soy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1986, 34, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Teng, S.P.; Popovich, D.G. Generation of Group B Soyasaponins I and III by Hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, T.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Acid hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts of quinoa, lentil, fenugreek and soybean to yield sapogenin-rich extracts and other bioactive compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tava, A.; Biazzi, E.; Mella, M.; Quadrelli, P.; Avato, P. Artefact formation during acid hydrolysis of saponins from Medicago spp. Phytochemistry 2017, 138, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Meza, I.G.; Aluwi, N.A.; Saunders, S.R.; Ganjyal, G.M. GC–MS Profiling of Triterpenoid Saponins from 28 Quinoa Varieties (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Grown in Washington State. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8583–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.-F.; Gao, J.-Y.; Wang, J.; Geng, Y.-M.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.-X.; Li, F.; Feng, L.; Yu, M.-J.; Wang, G.-S. New Triterpenoid Saponins from the Herb Hylomecon japonica. Molecules 2017, 22, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiełbasa, A.; Krakowska, A.; Rafińska, K.; Buszewski, B. Isolation and determination of saponin hydrolysis products from Medicago sativa using supercritical fluid extraction, solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tava, A.; Mella, M.; Bialy, Z.; Jurzysta, M. Stability of Saponins in Alcoholic Solutions: Ester Formation as Artifacts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbecq, F.; Len, C. Recent Advances in the Microwave-Assisted Production of Hydroxymethylfurfural by Hydrolysis of Cellulose Derivatives—A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Li, P. Salt-assisted acid hydrolysis of chitosan to oligomers under microwave irradiation. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2150–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartella, L.; Mazzotti, F.; Napoli, A.; Sindona, G.; Di Donna, L. A comprehensive evaluation of tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol derivatives in extra virgin olive oil by microwave-assisted hydrolysis and HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Sethi, R.; Tewari, A.; Srivastava, V.; Sanghi, R. Hydrolysis of plant seed gums by microwave irradiation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 54, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Calinescu, I. Ultrasonically assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave assisted extraction (MAE) of functional compounds from plant materials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, P.; Kulawik, P.; Zając, M.; Migdał, W. Microwave applications in the food industry: An overview of recent developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, C.; Chen, S.; Zhu, S.; Lou, Z.; Wang, H. Conversion of steroid saponins into diosgenin by catalytic hydrolysis using acid-functionalized ionic liquid under microwave irradiation. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 79, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, E.; Savarino, P.; Claereboudt, E.J.S.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Deleu, M.; Lins, L.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Enhancing the Membranolytic Activity of Chenopodium quinoa Saponins by Fast Microwave Hydrolysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Chemical Characterization and Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Saponin-Rich Extracts and Their Acid-Hydrolysates Obtained from Fenugreek and Quinoa. Foods 2020, 9, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzi, C.A.; Barin, J.S.; Hermes, A.L.; Mortari, S.R.; Flores, É.M.M. A fast microwave-assisted procedure for loss on drying determination in saccharides. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, T.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Inhibitory effect of quinoa and fenugreek extracts on pancreatic lipase and α-amylase under in vitro traditional conditions or intestinal simulated conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blois, M. Antioxidant Determinations by the Use of a Stable Free Radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, P.; Huisingh, D. Removal of naphthenic acid by microwave. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Singco, B.; Liu, W.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Huang, H.Y. A rapid synthetic method for organic polymer-based monoliths in a room temperature ionic liquid medium via microwave-assisted vinylization and polymerization. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bao, J.; Hong, Y. Pathways for the steroidal saponins conversion to diosgenin during acid hydrolysis of Dioscorea zingiberensis C. H. Wright. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 2620–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.G.; Elder, J.L.; Chang, P.R.; Richards, K.W. Microdetermination of Diosgenin from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) Seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5206–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.G.; Zaman, M.S.; Mir, Z.; Mir, P.S.; Acharya, S.N.; Mears, G.J.; Elder, J.L. Analysis of Steroidal Sapogenins from Amber Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) by Capillary Gas Chromatography and Combined Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunagariya, N.A.; Patel, N.K.; Jagtap, S.C.; Bhutani, K.K. Inhibitors of pancreatic lipase: State of the art and clinical perspectives. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamden, K.; Keskes, H.; Elgomdi, O.; Feki, A.; Alouche, N. Modulatory Effect of an Isolated Triglyceride from Fenugreek Seed Oil on of α-Amylase, Lipase and ACE Activities, Liver-Kidney Functions and Metabolic Disorders of Diabetic Rats. J. Oleo Sci. 2017, 66, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Bhandari, U.; Jamadagni, S. Fenugreek seed extract inhibit fat accumulation and ameliorates dyslipidemia in high fat diet-induced obese rats. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hozzein, W.N.; Saleh, A.M.; Habeeb, T.H.; Wadaan, M.A.M.; AbdElgawad, H. CO2 treatment improves the hypocholesterolemic and antioxidant properties of fenugreek seeds. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamden, K.; Jaouadi, B.; Carreau, S.; Bejar, S.; Elfeki, A. Inhibitory effect of fenugreek galactomannan on digestive enzymes related to diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and liver-kidney dysfunctions. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2010, 15, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, P.S.; Somani, G.; Kanchan, D.; Sathaye, S.; Varakumar, S.; Singhal, R.S. Evaluation of debittered and germinated fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.) seed flour on the chemical characteristics, biological activities, and sensory profile of fortified bread. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, N.; Najafpour-Darzi, G. Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant activity, and pancreatic lipase inhibitory effect of ethanolic extract of Trigonella foenumgraceum L. leaves. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, P.; Colson, E.; Caulier, G.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Microwave-Assisted Desulfation of the Hemolytic Saponins Extracted from Holothuria scabra Viscera. Molecules 2022, 27, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro del Hierro, J.; Cantero-Bahillo, E.; Fernández-Felipe, M.T.; Martin, D. Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis vs. Conventional Hydrolysis to Produce Sapogenin-Rich Products from Fenugreek Extracts. Foods 2022, 11, 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131934
Navarro del Hierro J, Cantero-Bahillo E, Fernández-Felipe MT, Martin D. Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis vs. Conventional Hydrolysis to Produce Sapogenin-Rich Products from Fenugreek Extracts. Foods. 2022; 11(13):1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131934
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro del Hierro, Joaquin, Emma Cantero-Bahillo, M. Teresa Fernández-Felipe, and Diana Martin. 2022. "Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis vs. Conventional Hydrolysis to Produce Sapogenin-Rich Products from Fenugreek Extracts" Foods 11, no. 13: 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131934
APA StyleNavarro del Hierro, J., Cantero-Bahillo, E., Fernández-Felipe, M. T., & Martin, D. (2022). Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis vs. Conventional Hydrolysis to Produce Sapogenin-Rich Products from Fenugreek Extracts. Foods, 11(13), 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131934