Effects of Hydroxy-Alpha-Sanshool on Intestinal Metabolism in Insulin-Resistant Mice
Abstract
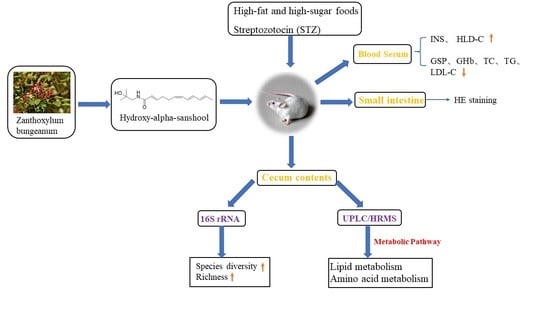
:1. Introductions
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Insulin Resistance Model
2.4. Mice Diets
2.5. Sample Collection
2.6. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.6.1. DNA Extraction
2.6.2. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing and Analysis
2.7. Metabonomics Analysis
2.7.1. Metabolite Extraction and Mix Standard Curve Preparation
2.7.2. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Serum Parameters and Cecal Tissue Parameters
3.2. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
3.2.1. Diversity Analysis
3.2.2. Relative Abundance of Gut Microbiota
3.3. Metabonomics Analysis
3.3.1. PCA and OPLS-DA Analysis
3.3.2. Differential Metabolite Analysis
3.4. HE Staining
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- James, D.E.; Stöckli, J.; Birnbaum, M.J. The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catherine, M.E.; Kenneth, C. Prediabetes A Worldwide Epidemic. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbert, S.; Andreas, F.; Fritz, S.; Hans-Ulrich, H. Phenotypes of prediabetes and stratification of cardiometabolic risk. Lancet 2016, 4, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sir Muir, G. Diabetes: Do you mean type 2 or type 1? Lancet 2015, 386, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronica, M.T.; Cosimo, G.; Francesco, C. Insulin Resistance in Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katherine, G.; Iris, G.; Montserrat, P.; Anna, A.; Mayte, B.; Ximena, T. Effects of flavonoids on intestinal inflammation, barrier integrity and changes in gut microbiota during diet-induced obesity. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsten, P.M.S.; Geesje, M.D.; Willem, M.D.V.; Max, N.; Daniël, H.V.R. Causality of small and large intestinal microbiota in weight regulation and insulin resistance. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, T.B.; Austin, G.D.; Adriana, G.; Kelsey, A.G.; David, B.C.; Nabanita, M.; George, C.; Jennifer, C.D.; Jorma, I.; Mikael, K.; et al. Gut microbiome metagenomics analysis suggests a functional model for the development of autoimmunity for type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2017, 6, e25792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Everard, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B. Gut microorganisms as promising targets for the management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perichet, C.; Philippe, F.; Dupouyet, A.; Marteaux, B.; Schnaebele, N.; Dubrulle, N.; Lavoine-Hanneguelle, S.; Giraud, N. Study of Some Zanthoxylum Species by Chemical and DNA Analysis Approaches. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengmeng, Z.; Jiaolong, W.; Lei, Z.; Tao, L.; Weidong, J.; Juan, Z.; Wei, P.; Chunjie, W. Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. (Rutaceae): A Systematic Review of Its Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Toxicology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Zhu, Y.; Kan, J. Zanthoxylum alkylamides activate phosphorylated AMPK and ameliorate glycolipid metabolism in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2017, 39, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohei, T.; Hirotada, A.; Kazuhiko, N.; Eikichi, I.; Masahiro, Y. Contraction of gut smooth muscle cells assessed by fluorescence imaging. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 127, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, K.; Ohtake, N.; Ohbuchi, K.; Mase, A.; Imamura, S.; Sudo, Y.; Miyano, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kono, T.; Uezono, Y. Hydroxy-α sanshool induces colonic motor activity in rat proximal colon: A possible involvement of KCNK9. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G579–G590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X. Effects of Zanthoxylum alkylamides on Intestinal Microecology in Diabetic Rats. J. Nutr. 2017, 39, 170–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhang, S.; Shirima, G.G.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X. Hypoglycemic effects of Zanthoxylum alkylamides by enhancing glucose metabolism and ameliorating pancreatic dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, X.; Ding, Y.; Guo, J.; Kan, J. Zanthoxylum alkylamides ameliorate protein metabolism disorder in STZ-induced diabetic rats. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 58, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begorre, M.; Dib, A.; Habchi, K.; Guihot, A.; Bourreau, J.; Vessieres, E.; Blondeau, B.; Loufrani, L.; Chabbert, M.; Henrion, D.; et al. Microvascular vasodilator properties of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Fan, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wei, D.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Antiobesity, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism, and Attenuation of Liver Oxidative Stress Effects of Hydroxy-alpha-sanshool Isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5852494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Wen, L.; Kan, J. Zanthoxylum alkylamides ameliorate protein metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats by regulating multiple signaling pathways. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3740–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Caporaso, J.G. QIIME 2: Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. PeerJ Prepr. 2018, 6, e27295v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huson, D.H.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.; Weber, N.; Schuster, S.C. Integrative analysis of environmental sequences using MEGAN4. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asnicar, F.; Weingart, G.; Tickle, T.L.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnerat, G.; Seara, F.; Evaristo, J.; Carneiro, G.; Carvalho, A. Aging-related compensated hypogonadism: Role of metabolomic analysis in physiopathological and therapeutic evaluation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 183, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, O.H.; Othman, E.M.; Fahim, J.R.; Desoukey, S.Y.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Metabolomics analysis and biological investigation of three malvaceae plants. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeldon, A.M.; Morizot, A.; Douglas, T.; Santoro, N.; Kursawe, R.; Kozlitina, J.; Caprio, S.; Mehal, W.Z.; Saleh, M. Caspase-12, but Not Caspase-11, Inhibits Obesity and Insulin Resistance. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaelides, A.; Raby, C.; Wood, M.; Farr, K.; Toro-Ramos, T. Weight loss efficacy of a novel mobile Diabetes Prevention Program delivery platform with human coaching. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2016, 4, e000264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Yao, W.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Chi, X.; et al. Hyperglycemia Aggravates Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Chronic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3919627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanz, Y.; Olivares, M.; Moya-Pérez, Á.; Agostoni, C. Understanding the role of gut microbiome in metabolic disease risk. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, L.; Nemeş, S.A.; Szabo, K.; Teleky, B.E.; Vodnar, D.C. Guts Imbalance Imbalances the Brain: A Review of Gut Microbiota Association with Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Med. 2022, 31, 813204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer-Englar, T.; Barlow, G.; Mathur, R. Obesity, diabetes, and the gut microbiome: An updated review. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, R.; Fayyaz, S.; Zhang, S.; Qin, Y. Integrated 16S rRNA Sequencing, Metagenomics, and Metabolomics to Characterize Gut Microbial Composition, Function, and Fecal Metabolic Phenotype in Non-obese Type 2 Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokhee, P.J.; Hojeong, K. Assessment of microbial diversity bias associated with soil heterogeneity and sequencing resolution in pyrosequencing analyses. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 574–580, Erratum in J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Backhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Cui, C.; Wei, H.; Zheng, R.; Peng, J. Combined Soluble Fiber-Mediated Intestinal Microbiota Improve Insulin Sensitivity of Obese Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. The Relationship between Branched-Chain Amino Acid Related Metabolomic Signature and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2794591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, H.; Li, Q.; Gu, P. Metabolic engineering for the production of l-phenylalanine in Escherichia coli. Biotech 2019, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, N.D.; Stevens, R.D.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Anderson, A.; Bergman, R.N.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Newgard, C.B.; Bowden, D.W. Metabolomic Profile Associated with Insulin Resistance and Conversion to Diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E463–E468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangipurapu, J.; Stancakova, A.; Smith, U.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. Nine Amino Acids Are Associated with Decreased Insulin Secretion and Elevated Glucose Levels in a 7.4-Year Follow-up Study of 5,181 Finnish Men. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Iino, C.; Endo, T.; Mikami, K.; Kimura, M.; Sawada, N.; Nakaji, S.; Fukuda, S. Changed Amino Acids in NAFLD and Liver Fibrosis: A Large Cross-Sectional Study without Influence of Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, G. Effects of free fatty acids (FFA) on glucose metabolism: Significance for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2003, 111, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, G.M. The Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes: An Overview. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reaven, G.M. Banting lecture 1988: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| INS (mU/L) | GSP (mmol/L) | GHb (ng/mL) | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 60.69 ± 5.86 | 3.21 ± 0.10 | 8.66 ± 1.08 | 3.08 ± 0.48 | 1.18 ± 0.33 | 3.43 ± 0.19 | 0.22 ± 0.03 |
| MG | 32.24 ± 4.42 *a | 6.45 ± 0.42 *a | 13.66 ± 1.05 *a | 7.06 ± 0.75 *a | 2.53 ± 0.18 *a | 0.87 ± 0.24 *a | 0.58 ± 0.06 *a |
| DG | 52.35 ± 4.22 b | 4.09 ± 0.17 b | 5.04 ± 1.05 b | 5.57 ± 0.38 a | 1.75 ± 0.24 b | 2.87 ± 0.49 b | 0.46 ± 0.10 a |
| Total Cecal Mass (g) | Cecal Wall Mass (g) | Cecal Surface Area (cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 0.44 ± 0.17 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.51 ± 0.01 |
| MG | 0.57 ± 0.04 *a | 0.19 ± 0.04 a | 0.74 ± 0.11 *a |
| DG | 0.50 ± 0.09 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.57 ± 0.04 b |
| Name | Formula | m/z | Rt (s) | Exact Mass | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol sulfate | C27H46O4S | 467.32 | 716.49 | 466.31 | Lipid |
| Campesterol | C28H48O | 383.37 | 805.14 | 400.37 | Lipid |
| Bovinic acid | C18H32O2 | 279.23 | 788.14 | 280.24 | Lipid |
| L-Phenylalanine | C9H11NO2 | 164.07 | 322.73 | 165.08 | Amino acid |
| L-Tryptophan | C11H12N2O2 | 203.08 | 371.93 | 204.09 | Amino acid |
| 11-Dehydrocorticosterone | C21H28O4 | 325.18 | 810.04 | 344.20 | Lipid |
| Phenylpyruvic acid | C9H8O3 | 163.04 | 398.84 | 164.05 | Amino acid |
| Tyramine | C8H11NO | 136.08 | 442.01 | 137.08 | Amino acid |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, M.; Qin, L.; Zhao, D.; Ren, T. Effects of Hydroxy-Alpha-Sanshool on Intestinal Metabolism in Insulin-Resistant Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142040
Xu F, Zhu Y, Lu M, Qin L, Zhao D, Ren T. Effects of Hydroxy-Alpha-Sanshool on Intestinal Metabolism in Insulin-Resistant Mice. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142040
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fangyan, Yuping Zhu, Mintao Lu, Likang Qin, Degang Zhao, and Tingyuan Ren. 2022. "Effects of Hydroxy-Alpha-Sanshool on Intestinal Metabolism in Insulin-Resistant Mice" Foods 11, no. 14: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142040
APA StyleXu, F., Zhu, Y., Lu, M., Qin, L., Zhao, D., & Ren, T. (2022). Effects of Hydroxy-Alpha-Sanshool on Intestinal Metabolism in Insulin-Resistant Mice. Foods, 11(14), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142040