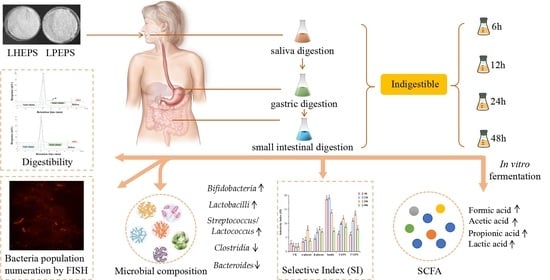
Prebiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5 and L. pentosus LZ-R-17 Evaluated by In Vitro Simulated Digestion and Fermentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Isolation and Purification of LHEPS and LPEPS
2.3. In Vitro Simulated Saliva and GSI Digestion of LHEPS and LPEPS
2.4. Mw Determination and Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
2.5. Origin of Human Fecal Samples and Fecal Suspension Preparation
2.6. In Vitro Fermentation
2.7. Determination of Bacterial Populations by FISH
2.8. Selectivity Index (SI) Scores
2.9. SCFAs Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Digestibility of LHEPS and LPEPS
3.2. Effects of LHEPS and LPEPS on Probiotic and Enteric Bacteria Population
3.3. Selectivity Index (SI)
3.4. SCFAs Production during Fermentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quigley, E.M.M. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Digestive Health. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.C.; Carmo, M.R.S.; Balthazar, C.F.; Guimarães, J.T.; Esmerino, E.A.; Freitas, M.Q.; Silva, M.C.; Pimentel, T.C.; Cruz, A.G. Dairy products with prebiotics: An overview of the health benefits, technological and sensory properties. Int. Dairy. J. 2021, 117, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheraji, S.H.; Ismail, A.; Manap, M.Y.; Mustafa, S.; Yusof, R.M.; Hassan, F.A. Prebiotics as functional foods: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1542–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.U.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Hassan, F.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Khafaga, A.F.; Batiha, G.E.; Yehia, N.; Elnesr, S.S.; Alagawany, M.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; et al. The potential mechanistic insights and future implications for the effect of prebiotics on poultry performance, gut microbiome, and intestinal morphology. Poult Sci. 2021, 100, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, T.; Yang, L.; Peng, T.; Wu, M. Structures of fructan and galactan from Polygonatum cyrtonema and their utilization by probiotic bacteria. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daba, G.M.; Elnahas, M.O.; Elkhateeb, W.A. Contributions of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria as biotechnological tools in food, pharmaceutical, and medical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dertli, E.; Mercan, E.; Arıcı, M.; Yılmaz, M.T.; Sağdıç, O. Characterisation of lactic acid bacteria from Turkish sourdough and determination of their exopolysaccharide (EPS) production characteristics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerning, J. Exocellular polysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 7, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, W.; Rui, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. Characterization of a novel exopolysaccharide with antitumor activity from Lactobacillus plantarum 70810. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 63, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Rui, X.; Dong, M. Structural elucidation and antioxidant activities of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xia, X.; Tang, W.; Ji, J.; Rui, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, M. Structural characterization and anticancer activity of cell-bound exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3454–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, C. The anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides in vitro: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbini, S.R.; Kolida, S.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. In vitro fermentation of commercial α-gluco-oligosaccharide by faecal microbiota from lean and obese human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, P.; Feng, R.; Li, X. Effect of in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion on structural characteristics and anti-proliferative activities of the polysaccharides from the shells of Juglans regia L. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yue, F.; Liu, L.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacteria: Structures, physiochemical functions and applications in the food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.-M.; Liu, W.; Pi, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Zhou, T.; Gu, Q. Effects of exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus rhamnosus on human gut microbiota in in vitro fermentation model. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 139, 110524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Yuan, Q.; Guo, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, S.P.; Gan, R.Y. Dynamic changes of structural characteristics of snow chrysanthemum polysaccharides during in vitro digestion and fecal fermentation and related impacts on gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 109888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelders, J.; Olaerts, H.; Dornez, E.; Van de Wiele, T.; Aura, A.-M.; Vanhaecke, L.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Structural features and feruloylation modulate the fermentability and evolution of antioxidant properties of arabinoxylanoligosaccharides during in vitro fermentation by human gut derived microbiota. J. Funct. Foods. 2014, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Dong, M.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Dong, M.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Isolation, purification, characterization and immunostimulatory activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus pentosus LZ-R-17 isolated from Tibetan kefir. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.H.; Wu, J.; Weng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, A. An improved phenol-sulfuric acid method for the determination of carbohydrates in the presence of persulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensadoun, A.; Weinstein, D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 70, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, L.J.; Hurst, R.E.; Simpson, L.; Settine, J.M. Analysis of sulfate in complex carbohydrates. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 123, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Dong, M.; Wang, W.; Han, S.; Rui, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, W. Structural characterization and antioxidant property of released exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus SRFM-1. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Q.; Dong, M.; Fan, X.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Wu, J.; et al. In vitro digestion and fermentation of released exopolysaccharides (r-EPS) from Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus SRFM-1. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X. Influences of structures of galactooligosaccharides and fructooligosaccharides on the fermentation in vitro by human intestinal microbiota. J. Funct. Foods. 2015, 13, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X. Lactosucrose and its analogues derived from lactose and sucrose: Influence of structure on human intestinal microbiota in vitro. J. Funct. Foods. 2015, 17, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Su, D.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X. Purification and fermentation in vitro of sesaminol triglucoside from sesame cake by human intestinal microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.L.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Influence of Disaccharide Structure on Prebiotic Selectivity in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5192–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Municio, M.; Kolida, S.; Herrero, M.; Rastall, R.A.; Moreno, F.J. In vitro faecal fermentation of novel oligosaccharides enzymatically synthesized using microbial transglycosidases acting on sucrose. J. Funct. Foods. 2016, 20, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-H.; Song, A.-X.; Li, L.-Q.; Siu, K.-C.; Yao, Z.-P.; Wu, J.-Y. Effects of exopolysaccharide fractions with different molecular weights and compositions on fecal microflora during in vitro fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peredo-Lovillo, A.; Romero-Luna, H.E.; Jiménez-Fernández, M. Health promoting microbial metabolites produced by gut microbiota after prebiotics metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.B.; Kavitake, D.; Jayamanohar, J.; Shetty, P.H. Preferential growth stimulation of probiotic bacteria by galactan exopolysaccharide from Weissella confusa KR780676. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ke, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, A.; Luo, Q.; Wu, W. In vitro saliva-gastrointestinal digestion and fecal fermentation of Oudemansiella radicata polysaccharides reveal its digestion profile and effect on the modulation of the gut microbiota. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Exopolysaccharides of lactic acid bacteria: Structure, bioactivity and associations: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint of FAO/WHO Working Group. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Joint of FAO/WHO Working Group: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, F.; Chen, S.; Marcotte, H. Engineer probiotic bifidobacteria for food and biomedical applications—Current status and future prospective. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 45, 107654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Ventura, M.; Buttó, L.F.; Duranti, S.; O’Toole, P.W.; Motherway, M.O.C.; van Sinderen, D. Molecular dialogue between the human gut microbiota and the host: A Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolida, S.; Gibson, G.R. Prebiotic capacity of inulin-type fructans. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2503S–2506S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Petito, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Commensal Clostridia: Leading players in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secher, T.; Brehin, C.; Oswald, E. Early settlers: Which E. coli strains do you not want at birth? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G123–G129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandalari, G.; Nueno-Palop, C.; Bisignano, G.; Wickham, M.S.; Narbad, A. Potential prebiotic properties of almond (Amygdalus communis L.) seeds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4264–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D.; Bauer, L.L.; Gourineni, V.; Pelkman, C.L.; Fahey, G.C., Jr.; Swanson, K.S. Agave inulin supplementation affects the fecal microbiota of healthy adults participating in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayol-Messaoudi, D.; Berger Cédric, N.; Coconnier-Polter, M.-H.; Liévin-Le Moal, V.; Servin Alain, L. pH-, lactic acid-, and non-lactic acid-dependent activities of probiotic Lactobacilli against salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6008–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Gut microbiota fermentation of marine polysaccharides and its effects on intestinal ecology: An overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.-T.; Fu, Y.; Guo, H.; Yuan, Q.; Nie, X.-R.; Wang, S.-P.; Gan, R.-Y. In vitro simulated digestion and fecal fermentation of polysaccharides from loquat leaves: Dynamic changes in physicochemical properties and impacts on human gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, D.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y. In vitro digestion under simulated saliva, gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation by human gut microbiota of polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Forano, E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Probe | Carbon Sources | Fermentation Time (h) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 | ||
| DAPI (Total bacteria) | CK | 9.04 (0.12) C | 9.07 (0.06) c,C | 9.30 (0.13) c,B | 9.49 (0.13) b,A | 9.28 (0.13) d,B |
| LHEPS | 9.21 (0.15) ab,C | 9.38 (0.12) b,B | 9.43 (0.04) bc,B | 9.79 (0.13) c,A | ||
| LPEPS | 9.23 (0.13) ab,D | 9.39 (0.11) b,C | 9.44 (0.05) bc,B | 9.48 (0.12) b,A | ||
| α-glucan | 9.13 (0.12) b,C | 9.71 (0.12) a,B | 9.72 (0.11) a,B | 9.66 (0.11) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 9.25 (0.13) a,C | 9.37 (0.12) b,B | 9.43 (0.13) bc,AB | 9.51 (0.10) c,A | ||
| Inulin | 9.18 (0.08) ab,C | 9.39 (0.12) b,B | 9.42 (0.13) c,B | 9.62 (0.11) b,A | ||
| Bif164 (Bifidobacteria) | CK | 7.11 (0.10) C | 7.50 (0.17) e,B | 7.52 (0.13) c,B | 7.74 (0.13) d,A | 7.53 (0.14) c,B |
| LHEPS | 7.91 (0.15) d,C | 8.39 (0.21) ab,AB | 8.49 (0.11) c,A | 8.39 (0.04) b,B | ||
| LPEPS | 7.95 (0.14) d,C | 8.41 (0.15) a,B | 8.54 (0.10) b,A | 8.48 (0.13) a,AB | ||
| α-glucan | 8.14 (0.12) b,B | 8.43 (0.12) a,A | 8.48 (0.12) c,A | 8.48 (0.12) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 8.02 (0.15) c,C | 8.36 (0.12) b,B | 8.51 (0.11) c,A | 8.48 (0.12) a,A | ||
| Inulin | 8.31 (0.13) a,C | 8.43 (0.13) a,B | 8.58 (0.11) a,A | 8.35 (0.11) b,A | ||
| Lab158 (Lactobacilli) | CK | 7.22 (0.08) E | 7.49 (0.14) b,D | 7.67 (0.22) d,C | 7.80 (0.13) d,B | 7.91 (0.12) d,A |
| LHEPS | 7.77 (0.12) a,D | 7.87 (0.11) c,C | 7.92 (0.11) c,B | 8.00 (0.11) c,A | ||
| LPEPS | 7.80 (0.13) a,D | 7.91 (0.10) b,C | 7.95 (0.12) bc,B | 8.05 (0.11) b,A | ||
| α-glucan | 7.77 (0.10) a,D | 7.97 (0.12) a,C | 8.03 (0.11) a,B | 8.11 (0.14) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 7.77 (0.09) a,C | 7.87 (0.11) c,B | 7.93 (0.12) bc,AB | 8.01 (0.12) c,A | ||
| Inulin | 7.82 (0.11) a,C | 7.87 (0.10) c,C | 7.95 (0.11) b,B | 8.05 (0.12) bc,A | ||
| Str493 (Streptococcus/Lactococcus) | CK | 7.45 (0.09) C | 7.54 (0.10) c,B | 7.77 (0.13) d,A | 7.62 (0.08) c,AB | 7.56 (0.08) c,B |
| LHEPS | 7.72 (0.14) ab,B | 8.01 (0.12) bc,A | 7.97 (0.12) b,A | 7.96 (0.13) b,A | ||
| LPEPS | 7.78 (0.11) ab,C | 8.05 (0.13) ab,B | 8.17 (0.15) a,A | 8.10 (0.11) a,AB | ||
| α-glucan | 7.81 (0.13) a,C | 8.09 (0.13) a,B | 8.18 (0.13) a,A | 8.11 (0.12) a,AB | ||
| β-glucan | 7.78 (0.16) ab,C | 8.09 (0.13) a,A | 7.94 (0.13) b,B | 7.95 (0.13) b,B | ||
| Inulin | 7.67 (0.13) b,C | 7.97 (0.15) c,A | 8.23 (0.14) a,B | 8.16 (0.14) a,B | ||
| Bac303 (Bacteroides) | CK | 8.20 (0.11) E | 8.21 (0.11) b,D | 8.29 (0.13) b,C | 8.33 (0.11) d,B | 8.37 (0.11) c,A |
| LHEPS | 8.24 (0.11) a,B | 8.51 (0.09) a,A | 8.50 (0.10) b,A | 8.45 (0.12) b,A | ||
| LPEPS | 8.21 (0.11) b,B | 8.47 (0.17) a,A | 8.48 (0.10) c,A | 8.42 (0.11) b,A | ||
| α-glucan | 8.19 (0.11) c,B | 8.53 (0.20) a,A | 8.55 (0.11) a,A | 8.48 (0.11) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 8.25 (0.11) a,B | 8.47 (0.17) a,A | 8.49 (0.10) bc,A | 8.44 (0.12) b,A | ||
| Inulin | 8.22 (0.10) b,C | 8.50 (0.18) a,A | 8.48 (0.11) c,AB | 8.42 (0.11) b,B | ||
| His150 (Clostridia) | CK | 7.59 (0.14) E | 7.67 (0.02) c,D | 7.75 (0.11) d,C | 7.79 (0.12) d,A | 7.93 (0.12) a,B |
| LHEPS | 7.83 (0.12) a,C | 7.95 (0.13) ab,A | 7.92 (0.12) b,AB | 7.90 (0.12) ab,B | ||
| LPEPS | 7.80 (0.11) b,B | 7.91 (0.12) abc,A | 7.89 (0.11) b,A | 7.88 (0.12) b,A | ||
| α-glucan | 7.79 (0.11) b,C | 7.90 (0.14) c,A | 7.83 (0.1) c,B | 7.81 (0.12) c,BC | ||
| β-glucan | 7.83 (0.11) a,C | 7.95 (0.12) a,A | 7.91 (0.12) b,B | 7.90 (0.13) ab,B | ||
| Inulin | 7.79 (0.11) b,C | 7.91 (0.12) bc,B | 7.96 (0.12) a,A | 7.88 (0.13) b,B | ||
| EC1531 (Escherichia coil) | CK | 7.56 (0.12) D | 7.85 (0.08) c,C | 8.02 (0.12) c,B | 8.13 (0.11) c,A | 8.05 (0.11) d,B |
| LHEPS | 8.04 (0.14) ab,D | 8.43 (0.13) a,C | 8.56 (0.12) a,A | 8.50 (0.11) a,B | ||
| LPEPS | 8.02 (0.13) b,D | 8.38 (0.10) b,C | 8.52 (0.12) b,A | 8.43 (0.12) b,B | ||
| α-glucan | 7.97 (0.11) b,C | 8.43 (0.12) a,B | 8.50 (0.12) a,A | 8.45 (0.11) b,B | ||
| β-glucan | 8.02 (0.14) b,C | 8.36 (0.12) b,B | 8.51 (0.10) b,A | 8.51 (0.11) a,A | ||
| Inulin | 8.10 (0.14) a,D | 8.43 (0.13) a,B | 8.58 (0.12) a,A | 8.35 (0.13) c,C | ||
| SCFA and Lactic Acid | Carbon Sources | Fermentation Time (h) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 | ||
| Formic acid | CK | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.97 (0.15) c,C | 1.54 (0.18) d,B | 2.15 (0.44) c,A | 2.41 (0.31) e,A |
| LHEPS | 1.89 (0.09) b,D | 3.68 (0.31) c,C | 6.45 (0.55) b,B | 9.16 (0.41) d,A | ||
| LPEPS | 2.13 (0.22) ab,D | 3.77 (0.29) c,C | 6.72 (0.61) b,B | 9.29 (0.08) cd,A | ||
| α-glucan | 2.42 (0.20) a,D | 4.40 (0.25) a,C | 7.90 (0.47) a,B | 11.31 (0.53) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 2.22 (0.24) ab,D | 3.86 (0.13) bc,C | 6.79 (0.26) b,B | 9.87 (0.16) bc,A | ||
| Inulin | 2.36 (0.22) a,D | 4.36 (0.43) ab,C | 7.88 (0.68) a,B | 10.43 (0.51) b,A | ||
| Lactic acid | CK | 0.00 (0.00) | 2.03 (0.11) c,D | 3.41 (0.32) c,C | 4.56 (0.21) c,B | 5.42 (0.15) d,A |
| LHEPS | 7.54 (0.21) b,D | 15.15 (0.59) b,C | 25.73 (1.13) b,B | 35.20 (2.20) c,A | ||
| LPEPS | 7.53 (0.29) b,D | 15.55 (0.66) b,C | 26.20 (1.56) b,B | 35.74 (1.50) bc,A | ||
| α-glucan | 7.95 (0.23) a,D | 17.09 (0.10) a,C | 30.14 (0.90) a,B | 39.93 (1.08) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 7.58 (0.20) ab,D | 15.62 (0.60) b,C | 28.49 (0.68) a,B | 37.69 (1.08) ab,A | ||
| Inulin | 7.79 (0.17) ab,D | 16.85 (0.58) a,C | 29.52 (1.04) a,B | 38.60 (0.76) a,A | ||
| Acetic acid | CK | 0.00 (0.00) | 2.17 (0.18) b,D | 3.97 (0.14) d,C | 5.74 (0.57) d,B | 6.66 (0.29) d,A |
| LHEPS | 11.22 (0.36) a,D | 16.27 (0.65) c,C | 33.11 (1.56) c,B | 44.65 (2.25) c,A | ||
| LPEPS | 11.33 (0.39) a,D | 16.89 (0.77) c,C | 33.93 (1.32) bc,B | 45.91 (2.17) bc,A | ||
| α-glucan | 12.47 (1.27) a,D | 20.18 (1.39) a,C | 37.80 (0.94) a,B | 50.23 (2.24) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 11.53 (0.38) a,D | 17.79 (0.65) bc,C | 34.62 (0.42) bc,B | 47.03 (1.66) abc,A | ||
| Inulin | 12.01 (0.80) a | 19.23 (1.30) ab | 35.87 (1.19) b | 49.14 (2.65) ab | ||
| Propionic acid | CK | 0.00 (0.00) | 1.66 (0.59) b,B | 1.80 (0.17) b,B | 2.15 (0.21) d,B | 2.95 (0.49) c,A |
| LHEPS | 2.67 (0.31) a,D | 6.61 (0.41) a,C | 11.61 (0.38) c,B | 14.84 (0.87) b,A | ||
| LPEPS | 2.70 (0.21) a,D | 6.81 (0.49) a,C | 11.93 (0.47) bc,B | 15.04 (0.85) b,A | ||
| α-glucan | 3.05 (0.28) a,D | 7.26 (0.24) a,C | 12.96 (0.44) a,B | 18.20 (0.93) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 2.82 (0.24) a,D | 6.81 (0.30) a,C | 12.03 (0.26) bc,B | 16.89 (0.87) a,A | ||
| Inulin | 2.93 (0.27) a | 7.12 (0.35) a | 12.63 (0.66) ab | 17.34 (1.47) a | ||
| Butyric acid | CK | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.38 (0.28) b,BC | 0.49 (0.28) b,B | 0.78 (0.20) b,B | 1.30 (0.36) b,A |
| LHEPS | 1.28 (0.49) a,B | 1.83 (0.43) a,B | 3.69 (0.63) a,A | 4.29 (0.92) a,A | ||
| LPEPS | 1.30 (0.49) a,BC | 1.93 (0.44) a,B | 3.83 (0.66) a,A | 4.88 (1.50) a,A | ||
| α-glucan | 1.39 (0.41) a,B | 2.17 (0.54) a,B | 4.38 (0.64) a,A | 5.38 (1.25) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 1.25 (0.40) a,B | 2.02 (0.54) a,B | 4.23 (0.72) a,A | 4.90 (1.04) a,A | ||
| Inulin | 1.29 (0.45) a,BC | 2.11 (0.43) a,B | 4.76 (1.06) a,A | 5.14 (1.20) a,A | ||
| Total acids | CK | 0.00 (0.00) | 7.19 (1.29) b,D | 11.21 (1.07) d,C | 15.38 (1.60) d,B | 18.73 (1.54) d,A |
| LHEPS | 24.60 (1.42) a,D | 43.54 (2.34) c,C | 80.60 (4.17) c,B | 108.13 (6.28) c,A | ||
| LPEPS | 24.97 (1.53) a,D | 44.95 (2.59) c,C | 82.61 (4.40) c,B | 110.86 (5.88) c,A | ||
| α-glucan | 27.28 (2.37)a,D | 51.10 (2.46) a,C | 93.18 (3.27) a,B | 125.06 (6.00) a,A | ||
| β-glucan | 25.40 (1.42) a,D | 46.10 (2.06) bc,C | 86.17 (2.27) bc,B | 115.76 (5.55) abc,A | ||
| Inulin | 26.38 (1.87) a,D | 49.63 (2.88) ab,C | 90.66 (4.47) ab,B | 120.66 (6.44) ab,A | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, W. Prebiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5 and L. pentosus LZ-R-17 Evaluated by In Vitro Simulated Digestion and Fermentation. Foods 2022, 11, 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162501
Xu M, Li Z, Zhao X, Li W. Prebiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5 and L. pentosus LZ-R-17 Evaluated by In Vitro Simulated Digestion and Fermentation. Foods. 2022; 11(16):2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162501
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Mengjia, Zhi Li, Xiaogan Zhao, and Wei Li. 2022. "Prebiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5 and L. pentosus LZ-R-17 Evaluated by In Vitro Simulated Digestion and Fermentation" Foods 11, no. 16: 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162501
APA StyleXu, M., Li, Z., Zhao, X., & Li, W. (2022). Prebiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5 and L. pentosus LZ-R-17 Evaluated by In Vitro Simulated Digestion and Fermentation. Foods, 11(16), 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162501